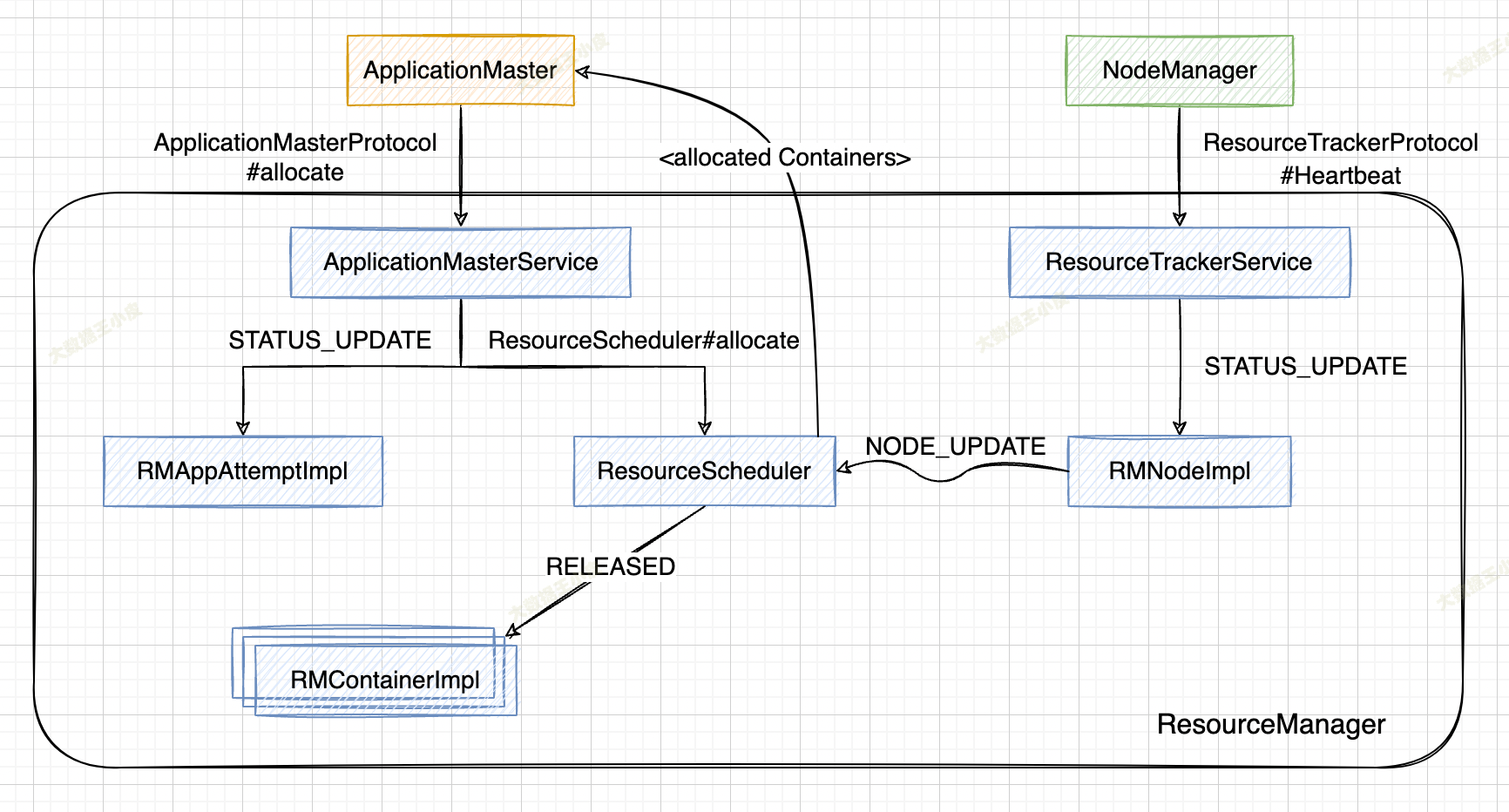
【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】4-6 RM 行为探究 - 申请与分配 Container
本小节介绍应用程序的 ApplicationMaster 在 NodeManager 成功启动并向 ResourceManager 注册后,向 ResourceManager 请求资源(Container)到获取到资源的整个过程,以及 ResourceManager 内部涉及的主要工作流程。
一、整体流程
整个过程可看做以下两个阶段的送代循环:
- 阶段1 ApplicationMaster 汇报资源需求并领取已经分配到的资源;
- 阶段2 NodeManager 向 ResourceManager 汇报各个 Container 运行状态,如果 ResourceManager 发现它上面有空闲的资源,则进行一次资源分配,并将分配的资源保存到对应的 应用程序数据结构中,等待下次 ApplicationMaster 发送心跳信息时获取(即阶段1)。
一)AM 汇报心跳
1、ApplicationMaster 通过 RPC 函数 ApplicationMasterProtocol#allocate 向 ResourceManager 汇报资源需求(由于该函数被周期性调用,我们通常也称之为“心跳”),包括新的资源需求描述、待释放的 Container 列表、请求加入黑名单的节点列表、请求移除黑名单的节点列表等。
public AllocateResponse allocate(AllocateRequest request) {
// Send the status update to the appAttempt.
// 发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.STATUS_UPDATE 事件
this.rmContext.getDispatcher().getEventHandler().handle(
new RMAppAttemptStatusupdateEvent(appAttemptId, request.getProgress()));
// 从 am 心跳 AllocateRequest 中取出新的资源需求描述、待释放的 Container 列表、黑名单列表
List<ResourceRequest> ask = request.getAskList();
List<ContainerId> release = request.getReleaseList();
ResourceBlacklistRequest blacklistRequest = request.getResourceBlacklistRequest();
// 接下来会做一些检查(资源申请量、label、blacklist 等)
// 将资源申请分割(动态调整 container 资源量)
// Split Update Resource Requests into increase and decrease.
// No Exceptions are thrown here. All update errors are aggregated
// and returned to the AM.
List<UpdateContainerRequest> increaseResourceReqs = new ArrayList<>();
List<UpdateContainerRequest> decreaseResourceReqs = new ArrayList<>();
List<UpdateContainerError> updateContainerErrors =
RMServerUtils.validateAndSplitUpdateResourceRequests(rmContext,
request, maximumCapacity, increaseResourceReqs,
decreaseResourceReqs);
// 调用 ResourceScheduler#allocate 函数,将该 AM 资源需求汇报给 ResourceScheduler
// (实际是 Capacity、Fair、Fifo 等实际指定的 Scheduler 处理)
allocation =
this.rScheduler.allocate(appAttemptId, ask, release,
blacklistAdditions, blacklistRemovals,
increaseResourceReqs, decreaseResourceReqs);
}
2、ResourceManager 中的 ApplicationMasterService#allocate 负责处理来自 AM 的心跳请求,收到该请求后,会发送一个 RMAppAttemptEventType.STATUS_UPDATE 事件,RMAppAttemptImpl 收到该事件后,将更新应用程序执行进度和 AMLivenessMonitor 中记录的应用程序最近更新时间。
3、调用 ResourceScheduler#allocate 函数,将该 AM 资源需求汇报给 ResourceScheduler,实际是 Capacity、Fair、Fifo 等实际指定的 Scheduler 处理。
以 CapacityScheduler#allocate 实现为例:
// CapacityScheduler#allocate
public Allocation allocate(ApplicationAttemptId applicationAttemptId,
List<ResourceRequest> ask, List<ContainerId> release,
List<String> blacklistAdditions, List<String> blacklistRemovals,
List<UpdateContainerRequest> increaseRequests,
List<UpdateContainerRequest> decreaseRequests) {
// Release containers
// 发送 RMContainerEventType.RELEASED
releaseContainers(release, application);
// update increase requests
LeafQueue updateDemandForQueue =
updateIncreaseRequests(increaseRequests, application);
// Decrease containers
decreaseContainers(decreaseRequests, application);
// Sanity check for new allocation requests
// 会将资源请求进行规范化,限制到最小和最大区间内,并且规范到最小增长量上
SchedulerUtils.normalizeRequests(
ask, getResourceCalculator(), getClusterResource(),
getMinimumResourceCapability(), getMaximumResourceCapability());
// Update application requests
// 将新的资源需求更新到对应的数据结构中
if (application.updateResourceRequests(ask)
&& (updateDemandForQueue == null)) {
updateDemandForQueue = (LeafQueue) application.getQueue();
}
// 获取已经为该应用程序分配的资源
allocation = application.getAllocation(getResourceCalculator(),
clusterResource, getMinimumResourceCapability());
return allocation;
}
4、ResourceScheduler 首先读取待释放 Container 列表,向对应的 RMContainerImpl 发送 RMContainerEventType.RELEASED 类型事件,杀死正在运行的 Container;然后将新的资源需求更新到对应的数据结构中,之后获取已经为该应用程序分配的资源,并返回给 ApplicationMasterService。
二)NM 汇报心跳
1、NodeManager 将当前节点各种信息(container 状况、节点利用率、健康情况等)封装到 nodeStatus 中,再将标识节点的信息一起封装到 request 中,之后通过RPC 函数 ResourceTracker#nodeHeartbeat 向 ResourceManager 汇报这些状态。
// NodeStatusUpdaterImpl#startStatusUpdater
protected void startStatusUpdater() {
statusUpdaterRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void run() {
// ...
Set<NodeLabel> nodeLabelsForHeartbeat =
nodeLabelsHandler.getNodeLabelsForHeartbeat();
NodeStatus nodeStatus = getNodeStatus(lastHeartbeatID);
NodeHeartbeatRequest request =
NodeHeartbeatRequest.newInstance(nodeStatus,
NodeStatusUpdaterImpl.this.context
.getContainerTokenSecretManager().getCurrentKey(),
NodeStatusUpdaterImpl.this.context
.getNMTokenSecretManager().getCurrentKey(),
nodeLabelsForHeartbeat);
// 发送 nm 的心跳
response = resourceTracker.nodeHeartbeat(request);
2、ResourceManager 中的 ResourceTrackerService 负责处理来自 NodeManager 的请 求,一旦收到该请求,会向 RMNodeImpl 发送一个 RMNodeEventType.STATUS_UPDATE 类型事件,而 RMNodelmpl 收到该事件后,将更新各个 Container 的运行状态,并进一步向 ResoutceScheduler 发送一个 SchedulerEventType.NODE_UPDATE 类型事件。
// ResourceTrackerService#nodeHeartbeat
public NodeHeartbeatResponse nodeHeartbeat(NodeHeartbeatRequest request)
throws YarnException, IOException {
NodeStatus remoteNodeStatus = request.getNodeStatus();
/**
* Here is the node heartbeat sequence...
* 1. Check if it's a valid (i.e. not excluded) node
* 2. Check if it's a registered node
* 3. Check if it's a 'fresh' heartbeat i.e. not duplicate heartbeat
* 4. Send healthStatus to RMNode
* 5. Update node's labels if distributed Node Labels configuration is enabled
*/
// 前 3 步都是各种检查,后面才是重点的逻辑
// Heartbeat response
NodeHeartbeatResponse nodeHeartBeatResponse =
YarnServerBuilderUtils.newNodeHeartbeatResponse(
getNextResponseId(lastNodeHeartbeatResponse.getResponseId()),
NodeAction.NORMAL, null, null, null, null, nextHeartBeatInterval);
// 这里会 set 待释放的 container、application 列表
// 思考:为何只有待释放的列表呢?分配的资源不返回么? - 分配的资源是和 AM 进行交互的
rmNode.setAndUpdateNodeHeartbeatResponse(nodeHeartBeatResponse);
populateKeys(request, nodeHeartBeatResponse);
ConcurrentMap<ApplicationId, ByteBuffer> systemCredentials =
rmContext.getSystemCredentialsForApps();
if (!systemCredentials.isEmpty()) {
nodeHeartBeatResponse.setSystemCredentialsForApps(systemCredentials);
}
// 4. Send status to RMNode, saving the latest response.
// 发送 RMNodeEventType.STATUS_UPDATE 事件
RMNodeStatusEvent nodeStatusEvent =
new RMNodeStatusEvent(nodeId, remoteNodeStatus);
if (request.getLogAggregationReportsForApps() != null
&& !request.getLogAggregationReportsForApps().isEmpty()) {
nodeStatusEvent.setLogAggregationReportsForApps(request
.getLogAggregationReportsForApps());
}
this.rmContext.getDispatcher().getEventHandler().handle(nodeStatusEvent);
3、ResourceScheduler 收到事件后,如果该节点上有可分配的空闲资源,则会将这些资源分配给各个应用程序,而分配后的资源仅是记录到对应的数据结构中,等待 ApplicationMaster 下次通过心跳机制来领取。(资源分配的具体逻辑,将在后面介绍 Scheduler 的文章中详细讲解)。
三、总结
本篇分析了申请与分配 Container 的流程,主要分为两个阶段。
第一阶段由 AM 发起,通过心跳向 RM 发起资源请求。
第二阶段由 NM 发起,通过心跳向 RM 汇报资源使用情况。
之后就是,RM 根据 AM 资源请求以及 NM 剩余资源进行一次资源分配(具体分配逻辑将在后续文章中介绍),并将分配的资源通过下一次 AM 心跳返回给 AM。
【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】4-6 RM 行为探究 - 申请与分配 Container的更多相关文章
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】4-2 RM 管理 Application Master
上一篇文章对 ResourceManager 整体架构和功能进行了讲述.本篇将对 RM 中管理 Application Master 的部分进行深入的讲解. 下面将会介绍 RM 与 AM 整体通信执行 ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】4-3 RM 管理 NodeManager
本篇继续对 RM 中管理 NodeManager 的部分进行深入的讲解.主要有三个部分:检查 NM 是否存活:管理 NM 的黑白名单:响应 NM RPC 请求. 一.简介 在 RM 的主从结构中,最主 ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】4-4 RM 管理 Application
在 YARN 中,Application 是指应用程序,它可能启动多个运行实例,每个运行实例由 -个 ApplicationMaster 与一组该 ApplicationMaster 启动的任务组成, ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】1-1 设计理念与基本架构
一.Yarn 产生的背景 Hadoop2 之前是由 HDFS 和 MR 组成的,HDFS 负责存储,MR 负责计算. 一)MRv1 的问题 耦合度高:MR 中的 jobTracker 同时负责资源管理 ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】4-1 ResourceManager 功能概述
前面几篇文章对 Yarn 基本架构.程序基础库.应用设计方法等进行了介绍.之后几篇将开始对 Yarn 核心组件进行剖析. ResourceManager(RM)是 Yarn 的核心管理服务,负责集群管 ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】3-1 Yarn Application 流程与编写方法
本篇学习 Yarn Application 编写方法,将带你更清楚的了解一个任务是如何提交到 Yarn ,在运行中的交互和任务停止的过程.通过了解整个任务的运行流程,帮你更好的理解 Yarn 运作方式 ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】3-2 Yarn Client 编写
上篇文章介绍了编写 Yarn Application 的整体框架流程,本篇文章将详细介绍其中 Client 部分的编写方式. 一.Yarn Client 编写方法 本篇代码已上传 Github: Gi ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】1-2 搭建 Hadoop 源码阅读环境
本文将介绍如何使用 idea 搭建 Hadoop 源码阅读环境.(默认已安装好 Java.Maven 环境) 一.搭建源码阅读环境 一)idea 导入 hadoop 工程 从 github 上拉取代码 ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】2-2 Yarn 基础库 - 底层通信库 RPC
RPC(Remote Procedure Call) 是 Hadoop 服务通信的关键库,支撑上层分布式环境下复杂的进程间(Inter-Process Communication, IPC)通信逻辑, ...
- 【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】3-3 Yarn Application Master 编写
本篇文章继续介绍 Yarn Application 中 ApplicationMaster 部分的编写方法. 一.Application Master 编写方法 上一节讲了 Client 提交任务给 ...
随机推荐
- Logseq001笔记类--视频悬浮插件--Helium
这是我准备新开的学习记录系列之一 今天写一个插件的介绍吧-- Helium -- 视频悬浮插件 youtube/b站/本地视频都可以导入 主要功能就是你在看视频时,要记一些学习笔记,随着不断往下写,视 ...
- python 之集合(set)
集合是一个无序的,不允许重复的元素列表,根据这个特性,可以利用集合对列表进行去重操作 集合创建 # 集合中不能含list.dict set2 = {"rice", 1, (True ...
- 百倍加速IO读写!快使用Parquet和Feather格式!⛵
作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI 数据分析实战系列:https://www.showmeai.tech/tutorials/40 本文地址:https://www.showmeai.tech/artic ...
- vue下载与安装
首先安装node.js环境: node.js 安装推荐文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouyu2017/p/6485265.html 基于node.js安装淘宝镜像npm i ...
- 2022NewStarCTF新生赛一些比较有意思的题目wp
Misc_蚁剑流量分析 Pcap的文件可以直接使用工具 编辑器打开目录,一个一个看,可以找到eval危险函数 看到n3wst4r,直接使用linux正则匹配,找出相关内容 Url解码,了解一下蚁剑流量 ...
- 前端工程化筑基-Node/npm/babel/polyfill/webpack
00.前端搬砖框架 开发 ⇨ 构建 ⇨ 部署上线 ⇨ 摸鱼: 01.Node.js/npm Node.JS 是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎 的 JavaScript 运行时环境,不是JS库(是C ...
- 【博学谷学习记录】超强总结,用心分享|前端CSS总结(一)
CSS总结(一) shift+alt,选中多行 外链式 <link rel="stylesheet" href="./my.css"> 1 选择器 ...
- 迁移学习(DANN)《Domain-Adversarial Training of Neural Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:Domain-Adversarial Training of Neural Networks论文作者:Yaroslav Ganin, Evgeniya Ustinova, Hana ...
- NW js 打包入门教程
NW js 打包入门教程 NW.JS的安装与打包_u013288292的博客-CSDN博客_nwjs打包
- Linux 驱动像单片机一样读取一帧dmx512串口数据
硬件全志R528 目标:实现Linux 读取一帧dmx512串口数据. 问题分析:因为串口数据量太大,帧与帧之间的间隔太小.通过Linux自带的读取函数方法无法获取到 帧头和帧尾,读取到的数据都是缓存 ...