Gitlab添加K8S集群
介绍如何在Gitlab项目中添加K8S集群,以便使用K8S集群部署gitlab-runner帮我们运行gitlab的CI/CD。
参考官方文档:https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/clusters/add_remove_clusters.html#add-existing-cluster
1.登入gitlab后,进入自己的项目主页,菜单栏 Operations => Kubernetes => Add Kubernetes cluster,选择页签 Add existing cluster。
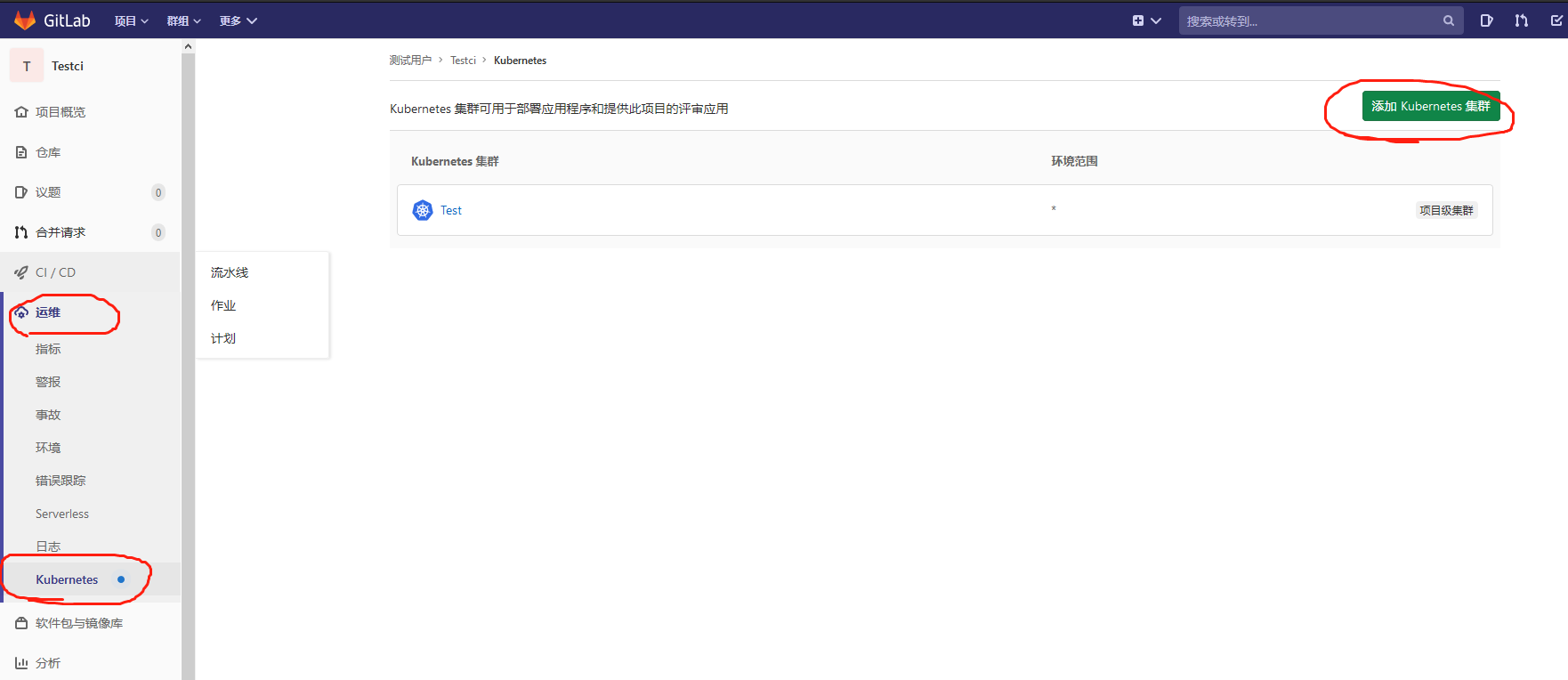

2.只需要获取响应的值填录到该表单即可。Kubernetes cluster name集群名称随意填,Project namespace可不填。

2.1 获取API URL
运行以下命令得到输出值:
kubectl cluster-info | grep 'Kubernetes master' | awk '/http/ {print $NF}'
2.2 获取CA Certificate
运行以下命令得到输出值:
kubectl get secrets # 获取一个类似default-token-xxxxx的名称,填写在下面这个命令<secret name>
kubectl get secret <secret name> -o jsonpath="{['data']['ca\.crt']}" | base64 --decode
2.3 获取Token
创建文件gitlab-admin-service-account.yaml:
vim gitlab-admin-service-account.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: gitlab
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: gitlab-admin
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: gitlab
namespace: kube-system
kubectl apply -f gitlab-admin-service-account.yaml
kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep gitlab | awk '{print $1}')
添加完成之后,可以在集群中安装你想用的插件了,例如gitlab-runner。
官方操作步骤:
Add existing cluster
If you have an existing Kubernetes cluster, you can add it to a project, group, or instance.
NOTE: Note: Kubernetes integration is not supported for arm64 clusters. See the issue Helm Tiller fails to install on arm64 cluster for details.
Existing Kubernetes cluster
To add a Kubernetes cluster to your project, group, or instance:
Navigate to your:
- Project's {cloud-gear} Operations > Kubernetes page, for a project-level cluster.
- Group's {cloud-gear} Kubernetes page, for a group-level cluster.
- Admin Area > {cloud-gear} Kubernetes page, for an instance-level cluster.
Click Add Kubernetes cluster.
Click the Add existing cluster tab and fill in the details:
Kubernetes cluster name (required) - The name you wish to give the cluster.
Environment scope (required) - The associated environment to this cluster.
API URL (required) - It's the URL that GitLab uses to access the Kubernetes API. Kubernetes exposes several APIs, we want the "base" URL that is common to all of them. For example,
https://kubernetes.example.comrather thanhttps://kubernetes.example.com/api/v1.Get the API URL by running this command:
kubectl cluster-info | grep 'Kubernetes master' | awk '/http/ {print $NF}'
CA certificate (required) - A valid Kubernetes certificate is needed to authenticate to the cluster. We will use the certificate created by default.
List the secrets with
kubectl get secrets, and one should be named similar todefault-token-xxxxx. Copy that token name for use below.Get the certificate by running this command:
kubectl get secret <secret name> -o jsonpath="{['data']['ca\.crt']}" | base64 --decode
NOTE: Note: If the command returns the entire certificate chain, you need copy the root ca certificate at the bottom of the chain.
Token - GitLab authenticates against Kubernetes using service tokens, which are scoped to a particular
namespace. The token used should belong to a service account with cluster-admin privileges. To create this service account:Create a file called
gitlab-admin-service-account.yamlwith contents:apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: gitlab
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: gitlab-admin
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: gitlab
namespace: kube-system
Apply the service account and cluster role binding to your cluster:
kubectl apply -f gitlab-admin-service-account.yaml
You will need the
container.clusterRoleBindings.createpermission to create cluster-level roles. If you do not have this permission, you can alternatively enable Basic Authentication and then run thekubectl applycommand as an admin:kubectl apply -f gitlab-admin-service-account.yaml --username=admin --password=<password>
NOTE: Note: Basic Authentication can be turned on and the password credentials can be obtained using the Google Cloud Console.
Output:
serviceaccount "gitlab" created
clusterrolebinding "gitlab-admin" created
Retrieve the token for the
gitlabservice account:kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep gitlab | awk '{print $1}')
Copy the
<authentication_token>value from the output:Name: gitlab-token-b5zv4
Namespace: kube-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name=gitlab
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid=bcfe66ac-39be-11e8-97e8-026dce96b6e8 Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token Data
====
ca.crt: 1025 bytes
namespace: 11 bytes
token: <authentication_token>
NOTE: Note: For GKE clusters, you will need the
container.clusterRoleBindings.createpermission to create a cluster role binding. You can follow the Google Cloud documentation to grant access.GitLab-managed cluster - Leave this checked if you want GitLab to manage namespaces and service accounts for this cluster. See the Managed clusters section for more information.
Project namespace (optional) - You don't have to fill it in; by leaving it blank, GitLab will create one for you. Also:
- Each project should have a unique namespace.
- The project namespace is not necessarily the namespace of the secret, if you're using a secret with broader permissions, like the secret from
default. - You should not use
defaultas the project namespace. - If you or someone created a secret specifically for the project, usually with limited permissions, the secret's namespace and project namespace may be the same.
Finally, click the Create Kubernetes cluster button.
After a couple of minutes, your cluster will be ready to go. You can now proceed to install some pre-defined applications.
Gitlab添加K8S集群的更多相关文章
- 使用RKE快速部署k8s集群
一.环境准备 1.1环境信息 IP地址 角色 部署软件 10.10.100.5 K8s Master Etcd.Control 10.10.100.17 K8s Worker1 Worker 10.1 ...
- rancher导入k8s集群后添加监控无数据
1.日志报错 rancher导入k8s集群后添加监控无数据,rancher日志报错: k8s.io/kube-state-metrics/pkg/collectors/builder.go:: Fai ...
- k8s集群节点更换ip 或者 k8s集群添加新节点
1.需求情景:机房网络调整,突然要回收我k8s集群上一台node节点机器的ip,并调予新的ip到这台机器上,所以有了k8s集群节点更换ip一说:同时,k8s集群节点更换ip也相当于k8s集群添加新节点 ...
- kubernetes系列03—kubeadm安装部署K8S集群
本文收录在容器技术学习系列文章总目录 1.kubernetes安装介绍 1.1 K8S架构图 1.2 K8S搭建安装示意图 1.3 安装kubernetes方法 1.3.1 方法1:使用kubeadm ...
- rancher2.X搭建k8s集群平台
一, 新版特性 Rancher 1.6支持多种容器编排框架,包括Kubernetes.Mesos.Docker Swarm,默认的基础编排引擎是Cattle,Cattle极简的操作体验受到了大量开源社 ...
- 关于使用rancher部署k8s集群的一些小问题的解决
问题一: 在rancher的ui上,不能创建k8s的master节点的高可用集群.创建k8s集群,添加节点的时候,可以添加多个master,但是多个master又没有高可用,只要其中一个出问题了,那么 ...
- jenkins流水线部署springboot应用到k8s集群(k3s+jenkins+gitee+maven+docker)(2)
前言:上篇已介绍了jenkins在k3s环境部署,本篇继续上篇讲述流水线构建部署流程 1.从gitlab上拉取代码步骤 在jenkins中,新建一个凭证:Manage Jenkins -> Ma ...
- China Azure中部署Kubernetes(K8S)集群
目前China Azure还不支持容器服务(ACS),使用名称"az acs create --orchestrator-type Kubernetes -g zymtest -n kube ...
- k8s重要概念及部署k8s集群(一)--技术流ken
重要概念 1. cluster cluster是 计算.存储和网络资源的集合,k8s利用这些资源运行各种基于容器的应用. 2.master master是cluster的大脑,他的主要职责是调度,即决 ...
随机推荐
- logback-spring 集成 ELK、kafka的配置
pom.xml <dependency> <groupId>com.github.danielwegener</groupId> <artifactId> ...
- CF1702B Polycarp Writes a Srting from Memory 题解
给定一个字符串,每天可以记忆三个字符,求书写出整个字符串的天数. 每次确定要记忆的三个字母,并向后寻找,若有非三个字母其中一个,则重新开启一天记忆三个字母. #include<cstdio> ...
- 聊聊 C++ 中的几种智能指针 (下)
一:背景 上一篇我们聊到了C++ 的 auto_ptr ,有朋友说已经在 C++ 17 中被弃用了,感谢朋友提醒,今天我们来聊一下 C++ 11 中引入的几个智能指针. unique_ptr shar ...
- 9.2 DAG上的动态规划
在有向无环图上的动态规划是学习动态规划的基础,很多问题都可以转化为DAG上的最长路,最短路或路径计数问题 9.2.1 DAG模型 嵌套矩形问题: 矩形之间的可嵌套关系是一种典型的二元关系,二元关系可以 ...
- 封装Fraction-分数类(C++)
Fraction 分数类 默认假分数,可自行修改 由于concept的原因 template <typename T> concept is_float_v = std::is_float ...
- 前端须知的 Cookie 知识
文章已收录到我的 GitHub 中,欢迎 star cookie 是什么和使用场景 cookie 是服务器端保存在浏览器的一小段文本信息,浏览器每次向服务器端发出请求,都会附带上这段信息(不是所有都带 ...
- C++ 漫谈哈夫曼树
1. 前言 什么是哈夫曼树? 把权值不同的n个结点构造成一棵二叉树,如果此树满足以下几个条件: 此 n 个结点为二叉树的叶结点 . 权值较大的结点离根结点较近,权值较小的结点离根结点较远. 该树的带权 ...
- HCIA-Datacom 2.2 实验:OSPF路由协议基础实验
前言:才发现IA也要学OSPF,忍不住吐槽一句,现在太卷了! OSPF简介: 开放式最短路径优先OSPF(Open Shortest Path First)是IETF组织开发的一个基于链路状态的内部网 ...
- Excelize 发布 2.6.0 版本,功能强大的 Excel 文档基础库
Excelize 是 Go 语言编写的用于操作 Office Excel 文档基础库,基于 ECMA-376,ISO/IEC 29500 国际标准.可以使用它来读取.写入由 Microsoft Exc ...
- JavaScript基础回顾知识点记录3
js 中 垃圾回收 //将不在使用的对象设置为null , js就会自动进行垃圾回收机制 var obj = {}; obj = null; js 中 数组基本介绍 数组也是一个对象 与普通对象功能类 ...
