DBus通讯
linux下进程间通信的方式主要有Pipe(管道),FIFO(命名管道),信号,共享内存,消息队列,信号灯等,这些方式各有 各得特点,如管道是linux下命令行中常用的,用于父子进程的通信。但是这些通信方式都比较原始,要属功能最强大的IPC应该是dbus,故查看了一下 dbus的资料,但是资料相对较少,特别是有关python的部分。 1.dbus概念
网上有一篇叫“D-Bus Tutorial”的文章,流传较广。
D-Bus是针对桌面环境优化的IPC(interprocess communication )机制,用于进程间的通信或进程与内核的通信。最基本的D-Bus协议是一对一的通信协议。但在很多情况下,通信的一方是消息总线。消息总线是一个特殊的 应用,它同时与多个应用通信,并在应用之间传递消息。下面我们会在实例中观察消息总线的作用。消息总线的角色有点类似与X系统中的窗口管理器,窗口管理器 既是X客户,又负责管理窗口。
支持dbus的系统都有两个标准的消息总线:系统总线和会话总线。系统总线用于系统与应用的通信。会话总线用于应用之间的通信。网上有一个叫d-feet的python程序,我们可以用它来观察系统中的dbus世界。
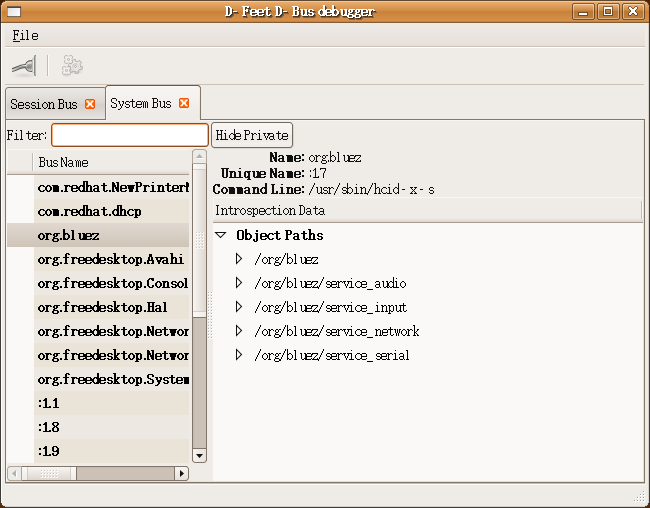
图1、由d-feet观察到的D-Bus世界
dbus还提供了两个命令行工具用于dbus测试,dbus-send和dbus-monitor,前一个命令用于测试信号的发送,后一个命令用于监控dbus的数据流。
2.dbus概念
有关dbus的基础知识不在本文的范围内,具体的参见dbus的文档。下面给出dbus常用的流程。
2.1建立服务的流程
dbus_bus_get(),建立一个dbus连接;
dbus_bus_request_name(),为这个dbus连接(DbusConnection)起名,这个名字将会成为我们在后续进行远程调用的时候的服务名;
然后我们进入监听循环 -- dbus_connection_read_write();
从总线上取出消息 -- dbus_connection_pop_message();
并通过比对消息中的方法接口名和方法名 -- dbus_message_is_method_call();
如果一致,那么我们跳转到相应的处理中去;
在相应的处理中,我们会从消息中取出远程调用的参数。并且建立起回传结果的通路 -- reply_to_method_call()。回传动作本身等同于一次不需要等待结果的远程调用。
2.2建立服务的流程
建立好dbus连接之后,为这dbus连接命名,申请一个远程调用通道 -- dbus_message_new_method_call(),注意,在申请远程调用通道的时候,需要填写服务器名,本次调用的接口名,和本次调用名 (方法名)。压入本次调用的参数 -- dbus_message_iter_init_append(); dbus_message_iter_append_basic(),实际上是申请了一个首地址,我们就是把我们真正要传的参数,往这个首地址里面送(送 完之后一般都会判断是否内存越界了)。然后就是启动发送调用并释放发送相关的消息结构 -- dbus_connection_send_with_reply()。这个启动函数中带有一个句柄。我们马上会阻塞等待这个句柄给我们带回总线上回传的 消息。当这个句柄回传消息之后,我们从消息结构中分离出参数。用dbus提供的函数提取参数的类型和参数 -- dbus_message_iter_init(); dbus_message_iter_next(); dbus_message_iter_get_arg_type(); dbus_message_iter_get_basic()。也就达成了我们进行本次远程调用的目的了。
2.3发送信号的流程
建立一个dbus连接之后,为这个dbus连接起名,建立一个发送信号的通道,注意,在建立通道的函数中,需要我们填写该信号的接口名和信号名 --
dbus_message_new_signal()。然后我们把信号对应的相关参数压进去 --
dbus_message_iter_init_append();
dbus_message_iter_append_basic()。然后就可以启动发送了 -- dbus_connection_send();
dbus_connection_flush。
2.4信号接收流程
建立一个dbus连接之后,为这个dbus连接起名,为我们将要进行的消息循环添加匹配条件(就是通过信号名和信号接口名来进行匹配控制的) --
dbus_bus_add_match()。我们进入等待循环后,只需要对信号名,信号接口名进行判断就可以分别处理各种信号了。在各个处理分支上。我们
可以分离出消息中的参数。对参数类型进行判断和其他的处理。
3. 一个C语言的示例代码
网上大部分代码都是基于dbus的一个封装库libdbus做的,以及使用glib,gtk的事件循环;为了减少库的依赖,直接使用C语言调用dbus的底层函数编写一个远程调用的示例代码,代码很简单,没使用GObject等一些复杂的库。
远程调用的服务器代码,用于监控,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
|
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void reply_to_method_call(DBusMessage* msg, DBusConnection* conn)
{
DBusMessage* reply;
DBusMessageIter args;
bool stat = true;
dbus_uint32_t level = 21614;
dbus_uint32_t serial = 0;
char* param = "";
// read the arguments
if (!dbus_message_iter_init(msg, &args))
fprintf(stderr, "Message has no arguments!\n");
else if (DBUS_TYPE_STRING != dbus_message_iter_get_arg_type(&args))
fprintf(stderr, "Argument is not string!\n");
else
dbus_message_iter_get_basic(&args, ¶m);
printf("Method called with %s\n", param);
// create a reply from the message
reply = dbus_message_new_method_return(msg);
// add the arguments to the reply
dbus_message_iter_init_append(reply, &args);
if (!dbus_message_iter_append_basic(&args, DBUS_TYPE_BOOLEAN, &stat)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out Of Memory!\n");
exit(1);
}
if (!dbus_message_iter_append_basic(&args, DBUS_TYPE_UINT32, &level)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out Of Memory!\n");
exit(1);
}
// send the reply && flush the connection
if (!dbus_connection_send(conn, reply, &serial)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out Of Memory!\n");
exit(1);
}
dbus_connection_flush(conn);
// free the reply
dbus_message_unref(reply);
}
static void
reply_to_Introspect(DBusMessage* msg, DBusConnection* conn)
{
/*反馈的消息*/
char *xml = "http://www.freedesktop.org/standards/dbus/1.0/introspect.dtd\">\n"
"\n"
" \n"
" \n"
" \n"
" \n \n"
" \n"
" \n"
" \n"
" \n"
" \n"
" \n"
"\n";
DBusMessage* reply;
DBusMessageIter args;
bool stat = true;
// create a reply from the message
reply = dbus_message_new_method_return(msg);
// add the arguments to the reply
dbus_message_iter_init_append(reply, &args);
if (!dbus_message_iter_append_basic(&args, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &xml)) {
printf ("Dbus Error: append args error\n");
dbus_message_unref(reply);
return;
}
// send the reply && flush the connection
if (!dbus_connection_send(conn, reply, NULL)) {
printf ("Dbus Error: send error\n");
dbus_message_unref(reply);
return;
}
dbus_connection_flush(conn);
// free the reply
dbus_message_unref(reply);
}
/**
* Server that exposes a method call and waits for it to be called
*/
void listen()
{
DBusMessage* msg;
DBusMessage* reply;
DBusMessageIter args;
DBusConnection* conn;
DBusError err;
int ret;
char* param;
printf("Listening for method calls\n");
// initialise the error
dbus_error_init(&err);
// connect to the bus and check for errors
conn = dbus_bus_get(DBUS_BUS_SESSION, &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Connection Error (%s)\n", err.message);
dbus_error_free(&err);
}
if (NULL == conn) {
fprintf(stderr, "Connection Null\n");
exit(1);
}
// request our name on the bus and check for errors
ret = dbus_bus_request_name(conn, "test.method.server",
DBUS_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING , &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Name Error (%s)\n", err.message);
dbus_error_free(&err);
}
if (DBUS_REQUEST_NAME_REPLY_PRIMARY_OWNER != ret) {
fprintf(stderr, "Not Primary Owner (%d)\n", ret);
exit(1);
}
// loop, testing for new messages
while (true) {
// non blocking read of the next available message
dbus_connection_read_write(conn, 0);
msg = dbus_connection_pop_message(conn);
// loop again if we haven't got a message
if (NULL == msg) {
sleep(1);
continue;
}
// check this is a method call for the right interface & method
if (dbus_message_is_method_call(msg, "test.method.Type", "Method"))
reply_to_method_call(msg, conn);
/*实现反射接口*/
if (dbus_message_is_method_call(msg, "org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable", "Introspect"))
reply_to_Introspect(msg, conn);
// free the message
dbus_message_unref(msg);
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
listen();
return 0;
}
|
代码中很关键的一个地方是一个标准接口的实现,该接口虽说无实际意义,仅仅是反射出该session的接口信息,包含各个接口信息和信号信息,但是该信息在python版的dbus中调用很重要,否则python的调用会失败。
编译命令如下
|
1
|
gcc -o main main.c `pkg-config --cflags --libs dbus-1`
|
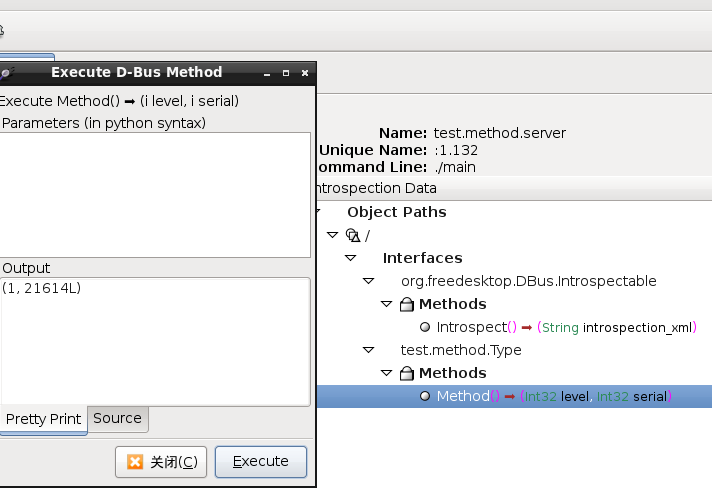
可以用d-feet测试一下:
用dbus-send测试命令如下:
|
1
|
dbus-send --session --type=method_call --print-reply --dest=test.method.server / test.method.Type.Method
|
客户端代码(及远程调用的代码):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/**
* Call a method on a remote object
*/
void query(char* param)
{
DBusMessage* msg;
DBusMessageIter args;
DBusConnection* conn;
DBusError err;
DBusPendingCall* pending;
int ret;
bool stat;
dbus_uint32_t level;
printf("Calling remote method with %s\n", param);
// initialiset the errors
dbus_error_init(&err);
// connect to the system bus and check for errors
conn = dbus_bus_get(DBUS_BUS_SESSION, &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Connection Error (%s)\n", err.message);
dbus_error_free(&err);
}
if (NULL == conn) {
exit(1);
}
// request our name on the bus
ret = dbus_bus_request_name(conn, "test.method.caller", DBUS_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING , &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Name Error (%s)\n", err.message);
dbus_error_free(&err);
}
if (DBUS_REQUEST_NAME_REPLY_PRIMARY_OWNER != ret) {
exit(1);
}
// create a new method call and check for errors
msg = dbus_message_new_method_call("test.method.server", // target for the method call
"/test/method/Object", // object to call on
"test.method.Type", // interface to call on
"Method"); // method name
if (NULL == msg) {
fprintf(stderr, "Message Null\n");
exit(1);
}
// append arguments
dbus_message_iter_init_append(msg, &args);
if (!dbus_message_iter_append_basic(&args, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, ¶m)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out Of Memory!\n");
exit(1);
}
// send message and get a handle for a reply
if (!dbus_connection_send_with_reply (conn, msg, &pending, -1)) { // -1 is default timeout
fprintf(stderr, "Out Of Memory!\n");
exit(1);
}
if (NULL == pending) {
fprintf(stderr, "Pending Call Null\n");
exit(1);
}
dbus_connection_flush(conn);
printf("Request Sent\n");
// free message
dbus_message_unref(msg);
// block until we recieve a reply
dbus_pending_call_block(pending);
// get the reply message
msg = dbus_pending_call_steal_reply(pending);
if (NULL == msg) {
fprintf(stderr, "Reply Null\n");
exit(1);
}
// free the pending message handle
dbus_pending_call_unref(pending);
// read the parameters
if (!dbus_message_iter_init(msg, &args))
fprintf(stderr, "Message has no arguments!\n");
else if (DBUS_TYPE_BOOLEAN != dbus_message_iter_get_arg_type(&args))
fprintf(stderr, "Argument is not boolean!\n");
else
dbus_message_iter_get_basic(&args, &stat);
if (!dbus_message_iter_next(&args))
fprintf(stderr, "Message has too few arguments!\n");
else if (DBUS_TYPE_UINT32 != dbus_message_iter_get_arg_type(&args))
fprintf(stderr, "Argument is not int!\n");
else
dbus_message_iter_get_basic(&args, &level);
printf("Got Reply: %d, %d\n", stat, level);
// free reply
dbus_message_unref(msg);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
char* param = "no param";
query(param);
return 0;
}
|
执行结果:
Calling remote method with no param
Request Sent
Got Reply: 1, 21614
4.Pthon调用dbus
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import dbus
bus = dbus.SessionBus()
bus_obj = bus.get_object('test.method.server', '/')
interface = dbus.Interface(bus_obj, 'test.method.Type')
info = interface.Method()
print info
|
DBus通讯的更多相关文章
- Linux 下搭建流媒体服务器
http://blog.csdn.net/huangtaishuai/article/details/9836581 ----------------------------------------- ...
- Qt4 和 Qt5 模块的分类
Qt5 与 Qt4 其中的一个区别是底层架构进行了改变,Qt5 引入了更加详细的模块化的概念,将众多功能细分到几个模块之中,Qt4 则是一种粗略的划分.本文主要对 Qt5 和 Qt4的模块进行一个简单 ...
- DBus学习笔记
摘要:DBus作为一个轻量级的IPC被越来越多的平台接受,在MeeGo中DBus也是主要的进程间通信方式,这个笔记将从基本概念开始记录笔者学习DBus的过程 [1] DBus学习笔记一:DBus学习的 ...
- D-BUS详细分析
转:http://blog.csdn.net/yclzh0522/article/details/7090599 一.概述 官方网站:http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/S ...
- dbus通信与接口介绍
DBUS是一种高级的进程间通信机制.DBUS支持进程间一对一和多对多的对等通信,在多对多的通讯时,需要后台进程的角色去分转消息,当一个进程发消息给另外一个进程时,先发消息到后台进程,再通过后台进程将信 ...
- Dbus组成和原理
DBUS是实质上一个适用于桌面应用的进程间的通讯机制,即所谓的IPC机制.适合在同一台机器,不适合于INTERNET的IPC机制.DBUS不是一个为所有可能的应用的通用的IPC机制,不支持其他IPC机 ...
- DBUS及常用接口介绍
[原文] 1. 概述 1.1 DBUS概述 DBUS是一种高级的进程间通信机制.DBUS支持进程间一对一和多对多的对等通信,在多对多的通讯时,需要后台进程的角色去分转消息,当一个进程发消息 ...
- DBus介绍
1. 介绍 DBus是一种桌面环境的进程间通讯(IPC)机制,有低时延.低消耗等优点 基于socket,提供了一对一的对等通讯:使用dbus-daemon作为后台进程时,可实现多对多通讯 由如下三个层 ...
- HTML5笔记:跨域通讯、多线程、本地存储和多图片上传技术
最近做项目在前端我使用了很多新技术,这些技术有bootstrap.angularjs,不过最让我兴奋的还是使用了HTML5的技术,今天我想总结一些HTML5的技术,好记性不如烂笔头,写写文章可以很好的 ...
随机推荐
- ASP三种常用传值方式:
ASP 页面(两个aspx页面)传值方式:背景: 两个aspx 页面valuepage.aspx tbusername tbpwdobtainvalue.aspx tbusername tbpwd 1 ...
- Oracle数据库作业-6 29、查询选修编号为“3-105“课程且成绩至少高于选修编号为“3-245”的同学的Cno、Sno和Degree,并按Degree从高到低次序排序。 select tname,prof from teacher where depart = '计算机系' and prof not in ( select prof from teacher where depart 。
29.查询选修编号为"3-105"课程且成绩至少高于选修编号为"3-245"的同学的Cno.Sno和Degree,并按Degree从高到低次序排序. selec ...
- android四种更新UI的方法
笔记: // 使用handler.post(Runnable)更新UI public void updateUI_Fun1() { new Thread() { public void run() { ...
- 路由器之VPN应用与配置指南
应用背景 近日,公司需要在外人员通过直接访问连接到公司内网,实现办公等一系列操作,这个时候就需要通过配置路由器VPN实现该需求了. 无线企业路由器可以帮助中小型企业搭建高性价比.稳定的企业办公网络,灵 ...
- 实例:使用纹理对象创建Sprite对象
精灵类是Sprite,它的类图如下图所示: Sprite类直接继承了Node类,具有Node基本特征.此外,我们还可以看到Sprite类的派生类有:PhysicsSprite和Skin.Physics ...
- C#代码配置IIS 操纵IIS
前言: IIS到目前经历了四个版本分别为 IIS4.0 IIS5.0 IIS6.0 IIS7.0,其中IIS6.0 IIS7.0是在5.0的安全问题的基础上获得的发展,目前为止.6.0版本以后的都是 ...
- jQuery checkBox 全选的例子
表单处理时经常会有全选的功能,但是这个功能往往会被忽视一个细节,就是逐个选中 checkBox 直至全选时,经常会忘记修改全选 checkBox 的状态,某知名互联网公司的网盘就会出现这样的问题,问题 ...
- Codevs 2627 村村通
时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 32000 KB 题目等级 : 黄金 Gold 题目描述 Description 农民约翰被选为他们镇的镇长!他其中一个竞选承诺就是在镇上建立起互联网,并连接到 ...
- Linux驱动编程--基于I2C子系统的I2C驱动的Makefile
ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/buildPWD := $(shell pwd) TEST = ...
- 使用DriverManager获取数据库连接的一个小改进
由于使用DriverManager获取数据库连接时,由于DriverManager实现类中有一段静态代码块,可以直接注册驱动,且可以同时管理多个驱动程序 所以当换数据库连接时需要指定不同的数据库,那么 ...