再看SpringMVC通过一个DispatcherServlet处理Servlet
初始入口:
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader
类的继承关系图如下:
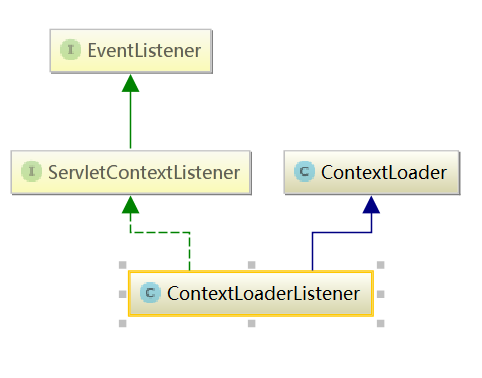
可以看到这个Listener实现了Servlet标准提供的接口,这个listener只有两个方法是 用来监听web容器启动和关闭动作的:
/**
* Receives notification that the web application initialization
* process is starting.
*
* <p>All ServletContextListeners are notified of context // 这里已经说了,使用的观察者模式,容器启动会调用
* initialization before any filters or servlets in the web
* application are initialized.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext
* that is being initialized
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce); /**
* Receives notification that the ServletContext is about to be
* shut down.
*
* <p>All servlets and filters will have been destroyed before any
* ServletContextListeners are notified of context
* destruction.
*
* @param sce the ServletContextEvent containing the ServletContext //这里也说了,容器关闭会调用
* that is being destroyed
*/
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce);
当然ContextLoaderListener实现了这两个方法:
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); //这个方法在父类ContextLoader中实现 ,这里只是把ServletContext当参数传过去了,因为在执行逻辑中需要用到很多与web容器相关的参数
} /**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext()); //同上
}
切换到父类ContextLoader 中initWebApplicationContext方法中:
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
} Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); //这里先创建Web环境的 ApplicationContext ,这个Context的地位就类似于ServletContext,是获取Bean的入口
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext); //这才是最核心的方法,看名字就知道 配置并刷新 ApplicationContext,这个动作完成了类示例的创建,初始化和 注册事件的发布,各种监听的执行, 为
} //DispatcherServlet这个核心类执行Handler的注册做好了万全准备
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); //这里可以看到把当前Context绑定到当前线程,是为了做隔离使用,保证线程安全,稍后再说这个问题
} if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
} return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
先来看看ApplicationContext的创建,进入createWebApplicationContext,毕竟它是获取Bean的入口。
/**
* Instantiate the root WebApplicationContext for this loader, either the
* default context class or a custom context class if specified.
* <p>This implementation expects custom contexts to implement the
* {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} interface.
* Can be overridden in subclasses.
* <p>In addition, {@link #customizeContext} gets called prior to refreshing the
* context, allowing subclasses to perform custom modifications to the context.
* @param sc current servlet context
* @return the root WebApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
} /**
* Return the WebApplicationContext implementation class to use, either the
* default XmlWebApplicationContext or a custom context class if specified.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the WebApplicationContext implementation class to use
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
这里先从ServletContext中获取参数是contextClass的值,也就是从web.xml读取contextParam或者硬编码的方式(servlet3.0以上的版本)中获取配置指定的ApplicationContext。如果没有,使用默认的策略 XmlWebApplicationContext,这个默认的策略 defaultStrategies是在ContextLoader开头的静态代码块中初始的:
/**
* Name of the class path resource (relative to the ContextLoader class)
* that defines ContextLoader's default strategy names.
*/
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties"; private static final Properties defaultStrategies; static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class); //这里从ContextLoader所在的包下加载一个叫ContextLoader.properties的文件,
//这个文件在spring-web包的context子包中,内容只有一行,配置了默认的WebApplicationContext
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
有了ApplicationContext了,再回到上面initWebApplicationContext方法,下面就开始判断这个context是不是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext实例,如果是,并且没有执行过刷新,就执行配置刷新的方法,也就是上面提到的最核心的方法,用于bean的初始化,
这里在判断后,还获取了parent context并将它设置成当前context的parent.
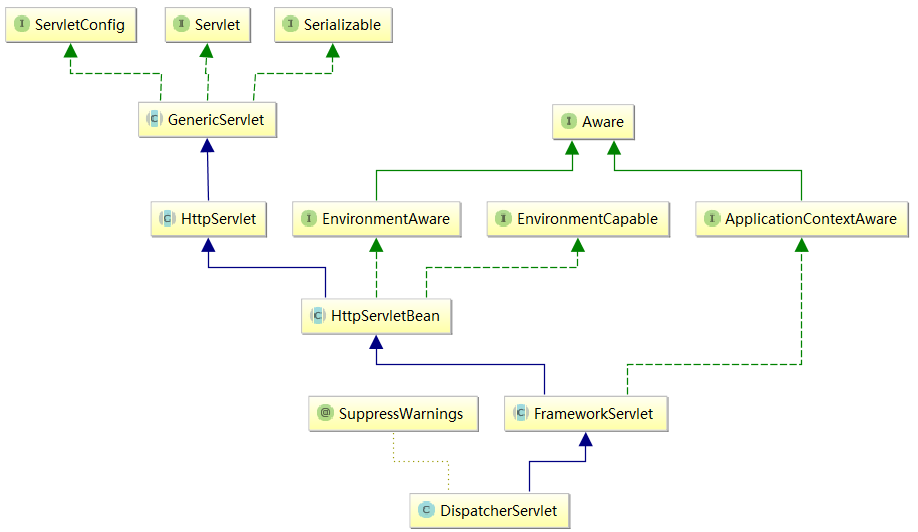
当然最核心的入口,一切源头:
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
该类的继承关系(使用Idea分析工具)如下:
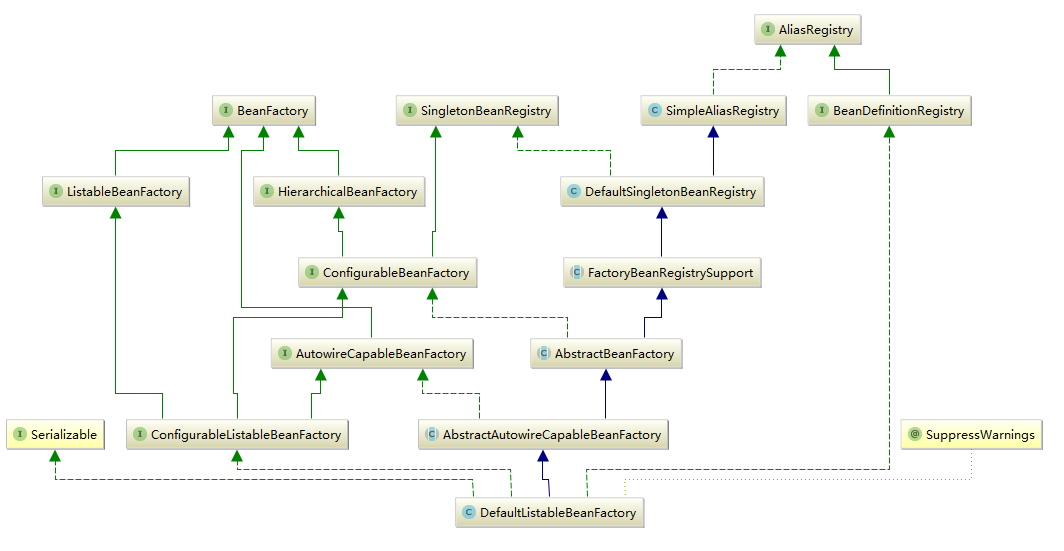
DefaultListableBeanFactory类的继承关系:
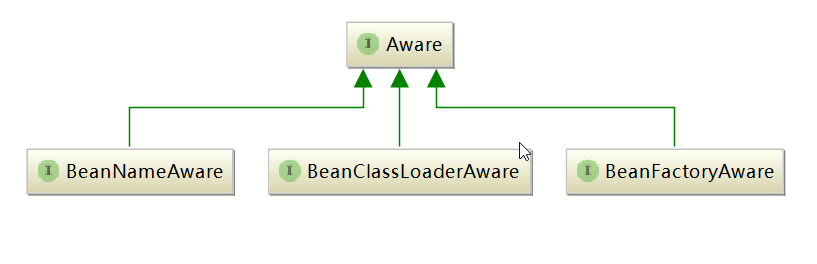
与Bean创建时相关的Aware接口的三个直接子接口:
再看SpringMVC通过一个DispatcherServlet处理Servlet的更多相关文章
- 1.SpringMVC设计理念与DispatcherServlet
SpringMVC作为Struts2之后异军突起的一个表现层框架,正越来越流行,相信javaee的开发者们就算没使用过SpringMVC,也应该对其略有耳闻.我试图通过对SpringMVC的设计思想和 ...
- springmvc源码分析----入门看springmvc的加载过程
接上一篇我们写的入门---http://www.cnblogs.com/duanxiaojun/p/6591448.html 今天从这个门里进去我们看springmvc是如何在容器启动的时候将各个模块 ...
- SpringMVC源码分析2:SpringMVC设计理念与DispatcherServlet
转自:https://my.oschina.net/lichhao/blog SpringMVC简介 SpringMVC作为Struts2之后异军突起的一个表现层框架,正越来越流行,相信javaee的 ...
- SpringMVC 01: SpringMVC + 第一个SpringMVC项目
SpringMVC SpringMVC概述: 是基于MVC开发模式的框架,用来优化控制器 是Spring家族的一员,也具备IOC和AOP 什么是MVC: 它是一种开发模式,是模型视图控制器的简称,所有 ...
- Spring Mvc中DispatcherServlet和Servlet的区别小结
在web开发过程中开始接触的是servlet,用来处理用户请求.这几年随着spring 框架越来越成熟,几乎成了java web开发界的主流框架.既然这么受欢迎肯定有它的优点,spring框架在原来的 ...
- 探秘Tomcat——一个简易的Servlet容器
即便再简陋的服务器也是服务器,今天就来循着书本的第二章来看看如何实现一个servlet容器. 背景知识 既然说到servlet容器这个名词,我们首先要了解它到底是什么. servlet 相比你或多或少 ...
- SpringMVC基础——一个简单的例子
一.导入 jar 包 二.配置 web.xml 文件 <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name> ...
- how tomcat works 札记(两)----------一个简单的servlet集装箱
app1 (看着眼前这章建议读者,看how tomcat works 札记(一个)----------一个简单的webserver http://blog.csdn.net/dlf123321/art ...
- 再看Ajax
再回顾Ajax相关的内容,再次梳理学习还是很有必要的,尤其是实际的开发中,ajax更是必不可少,仔细学习以便避免不必要的错误. 文章导读: --1.使用XMLHttpRequest---------- ...
随机推荐
- Session移除
Session.Clear()就是把Session对象中的所有项目都删除了,Session对象里面啥都没有.但是Session对象还保留. Session.Abandon()就是把当前Session对 ...
- 简单数位DP
https://cn.vjudge.net/problem/HDU-4722 懒得写看,代码注释吧;主要存板子 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring ...
- 使用openssl的aes各种加密算法
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/sta ...
- node之get与post
Get获取内容: var http=require('http'), util=require('util'),//util 提供常用函数集合 url=require('url'); http.cre ...
- 如何在Flask的构架中传递logger给子模块
Logger的传递 作为一个新手,如何将主函数的logger传入子模块是一件棘手的事情.某些情况下可以直接将logger作为参数传入子模块的构造函数中,但倘若子模块与主模块存在相互依赖的关系则容易出现 ...
- Ubuntu install JDK
1.#下载JDK,记住保存的目录 2. sudo mkdir /usr/java 3. sudo tar zxvf jdk-7u75-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/java 4. ...
- java web 工程找不到tomcat类 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
ava.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driverat org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappClassLoade ...
- yzm10铺瓷砖 一只小蜜蜂 ycb与取款机
yzm10铺瓷砖 一天yzm10接到任务,要求用2×1大小的瓷砖,来铺2×4的地面,地面需要恰好被铺满.这对yzm10来说太容易了,于是他马上设计出了5种不同的铺法(旋转情况算不同种,如图示2.4). ...
- 洛谷 - P4449 - 于神之怒加强版 - 莫比乌斯反演
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P4449 \(F(n)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m} gcd(i, ...
- Event事件的三个阶段
转自www.w3school.com.cn/htmldom/event_bubbles.asp 在 2 级 DOM标准中,事件传播分为三个阶段: 第一,捕获阶段.事件从 Document 对象沿着文档 ...
