Modern Operating System
No one can do all things, learn to be good at use what others already did.
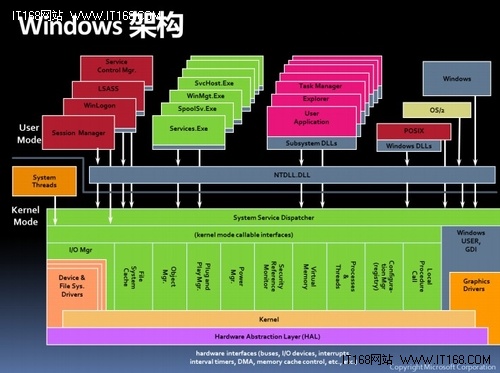
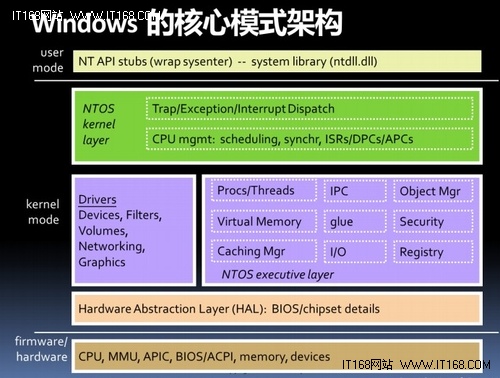
- Most computers have two modes of operation: kernel mode and user mode. The OS is the most fundamental piece of software and runs in kermel mode(also called usperivosr mode). In this mode, OS has complete access to all the hardware and can execute any instruction th machine is capable of exectuing.
- The rest of the software runs in user mode, in which only a subset of machine instructions are available. In particular, those instructions that affect control of machine or do I/O are forbidden to user-mode program.
- The user interface program, shell or GUI(Launcher or home screen or destop), is the lowest level of user-mode program, and is used to allow uer to start other programs which make heavy use of the OS.
- OS perform two basically unrelated functions:providing application programmer a clean abstract set of resources instead of the messy hardware ones and managing and managing these hardware resource.
- Every hardware device has its controler chip, which has some command registers and data registers and status registers. What we shall do is to use machine instructions to operate these device registers with defined-well address(MMP) for reading and writing.
- Abstraction is the key to managing complexity and one of the keys to understanding OS.
- The job of the OS is to create/define good abstractions and then implement and manage the abstract objects thus created.
- One of the major tasks of the OS is to hide the hardware and present programs with nice,clean, elegant, consistent, abstractions wo work with instead.
- Top-down view, Bottom-Up view.
- The CPU and memory are not the only resource that the OS must manage. I/O devices also interact heavily with the OS.
- I/O devices generally consist of two parts: a controller and the device itself. The controller is a chip or a set of chips that physically controls the device.It accepts commands from the the OS, intialize the control regitser to set working way and read data from data register or write data to data registers.
- The softeware that talks to a controller, giving it commands and accepting responses, is called a device driver.
- Every device controller has a small number of registers that are used to communicate with it.
- The collection of all the device registers forms the I/O port space, mapping to the specific memory via MMU
- The device registers are mapped into the OS's address space, so they can be read and written like ordinary memory words, another way to interact with device registers is using special CPU instructions for I/O operation with defined port address.
- OS normally use interrupt mechanism to interact with device driver via special interrupter controller connected to CPU.
- The CPU talks to the PCI bridge chip over the local bus, and the PCI bridge chip talks to the memor over a dedicated memory bus.
- Before plug and play, each I/O card had a fixed interrupt request level and fixed address for its I/O registers.
- What plug and play does is have the system automatcially collect information about the I/O devices, centrally assign interrupt levels and I/O address, and then tell each card what its numbers are.
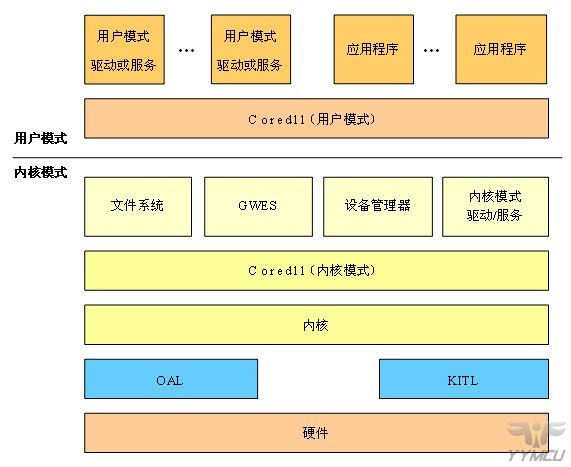
- Window CE Driver Model:
- Device Name: XXX_Init(), XXX_DeInit(), XXX_PowerDown(), XXX_PowerUp(),XXX_IOControl, XXX_Open(),XXX_Close(),XXX_Seek(),XXX_Read(), XXX_Write()
- Use a class to define the detailed implementation
- Create a class object (pointer) which is returned as Handle
- Convert Handle into pointer to object, then call method of class
- Create thread and event to handle interrupt, in thread there is a for(;;) loop with WaitForSingleObject() to wait for interrupt event, after done call InterruptDone()
- Register Interrupt handler which just signal a event.
- Initialization method within class to access device's control registers, do some configuration, including interrupt handler
- In thread, when interrupt event is coming, it will read data from or write data into device's data registers.
- Write Driver Information to registry and project.blb
- Process And Thread
- The most central concept in any OS is the process: an abstraction of a running program.
- There are four principal events that cause processes to be created.
- When an OS is booted, typically serveral processes are created.Some of these are foreground processes, interacting with users and perform work for them. Others are background processes with some specific function(such as Web Server).
- The fork system call creats an exact clone of the calling process.After the fork, the two processes, the parent and child, have the same memory image, the same environment strings, and the same open files.
- Some of the process run programs that carry out commands typed in by a user; other processes are part of the system and handle tasks such as carrying out requests for file services or managing the details of running a disk or a tape drive.
- When a disk interrupt occurs, the system makes a decision to stop running the current process and run the disk process which was blocked waiting for that interrupt.
- Instead of thinking about interrupts, we can think about user processes, disk processes, termianl processes, and so on, which block when they are waiting for something to happen.
- Here the lowest level of the operating system is the scheduler, with a variety of processes on top of it.All the interrupt handling and details of actually starting and stopping processes are hidden away in what here called the scheduler, which is actually not much code.
- The rest of the OS is nicely structured in process form.
- To implement the process model, the OS maintains a table(an array of structures or a list of structures),called the process table, with one entry per process. Or it can be called process control block.
- Process Table includes: process state, PC, SP, Memory allocation, the status of its open files, its accounting and scheduling information, and everything else about the process that must be saved when the process is switched from running to ready or blocked state so that it can ben restarted later as if it had never been stopped.
- Associated with each I/O class is a location (typically at a fixed location near the bottom of memory) called the interrupt vector. It contains the address of the interrupt service procedure.
- When interrupt come in, the interrupt service handler will run, and at the same time, before running the interrupt hardware will push current process's information into stack.
- Skeleton designed when an interrupt occurs:
- Hardware stacks program counter(PC), etc;
- Hardware loads new program ounter(PC) from interrupt vector;
- Assembly language procedure saves registers;
- Assembly language procedure sets up new stack;
- C interrupt service runs(typically reads and buffers input);
- Scheduler decides which process is to run next;
- C procedure retursn to the assemly code;
- Assemly language procedure starts up new current process
- ddd
- dd

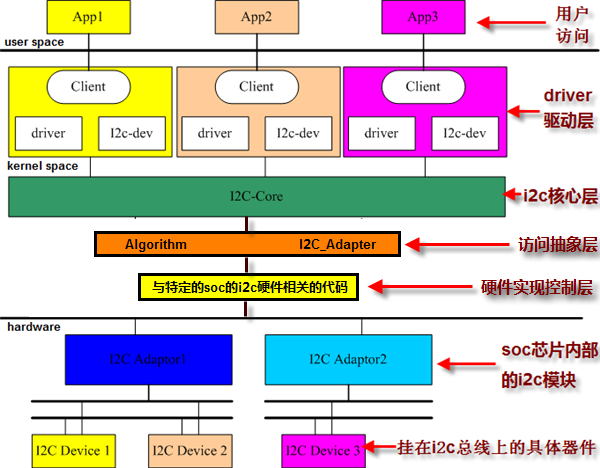
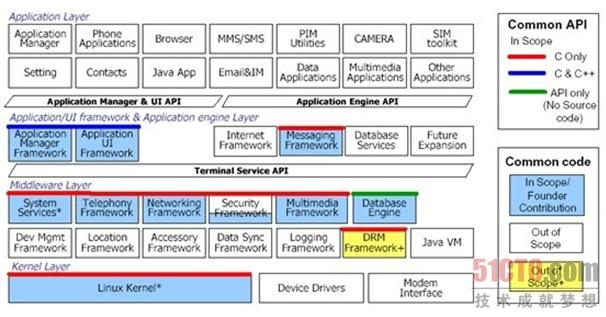
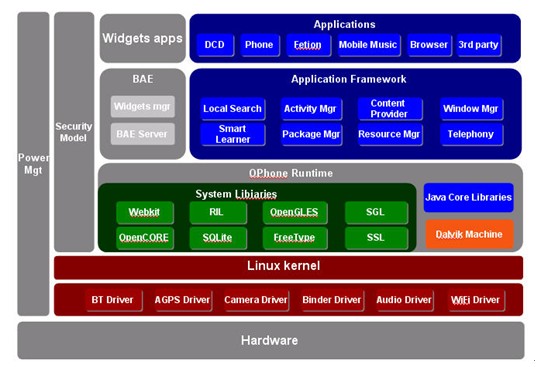
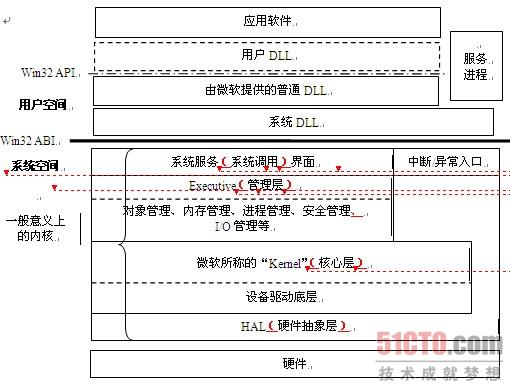


Modern Operating System的更多相关文章
- 《modern operating system》 chapter 5 Input and output 注意事项
Input / Output It should also provide an interface between the devices and the rest of the system th ...
- 《modern operating system》 chapter 6 DEADLOCKS 笔记
DEADLOCKS Both processes are blocked and will remain so forever. This situation is called a deadlock ...
- Portable Operating System Interface for uni-X
https://kb.iu.edu/d/agjv Short for "Portable Operating System Interface for uni-X", POSIX ...
- General-Purpose Operating System Protection Profile
1 Protection Profile Introduction This document defines the security functionality expected to be ...
- book-rev8 Chapter 0 Operating system interfaces
Chapter 0 第0章 Operating system interfaces 操作系统接口 The job of an operating system is to share a comput ...
- DBCC CHECKDB 遭遇Operating system error 112(failed to retrieve text for this error. Reason: 15105) encountered
我们一个SQL Server服务器在执行YourSQLDBa的作业YourSQLDba_FullBackups_And_Maintenance时遇到了错误: Exec YourSQLDba.Maint ...
- The World's Only Advanced Operating System
The World's Only Advanced Operating System
- Unable to open the physical file xxxx. Operating system error 2
在新UAT服务器上,需要将tempdb放置在SSD(固态硬盘)上.由于SSD(固态硬盘)特性,所以tempdb的文件只能放置在D盘下面,而不能是D盘下的某一个目录下面. ALTER DATABASE ...
- CREATE FILE encountered operating system error 5(Access is denied.)
这篇博文主要演示"CREATE FILE encountered operating system error 5(Access is denied.)"错误如出现的原因(当然只是 ...
随机推荐
- Python全栈开发:list、元祖常用方法操作
列表[] 索引与切片#例题#li = ['yijiajun',[1,3,5,7,9],'zhangliang','zhaoritian','sunwukong'] # #例子1 找出列表中索引为0的元 ...
- jmeter之beanshell断言---数据处理
在做接口测试时,对响应数据的校验是非常重要的部分:在使用Jmeter进行接口测试时,有多种respone校验方式,比如响应断言.BeanShell断言等等,BeanShell断言可以自定义断言,自由灵 ...
- CF1007D. Ants(树链剖分+线段树+2-SAT及前缀优化建图)
题目链接 https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1007/D 题解 其实这道题本身还是挺简单的,这里只是记录一下 2-SAT 的前缀优化建图的相关内容. ...
- Q147 对链表进行插入排序
插入排序的动画演示如上.从第一个元素开始,该链表可以被认为已经部分排序(用黑色表示). 每次迭代时,从输入数据中移除一个元素(用红色表示),并原地将其插入到已排好序的链表中. 插入排序算法: 插入排序 ...
- MIME类型是什么?包含哪些类型?
摘自:http://www.tuidc.com/idczixun/newsx/newsidc/3479.html 问:MIME类型是什么? 答:MIME(Multipurpose Interne ...
- javascript中的抽象相等==与严格相等===
1.数据类型:String,Number,Boolean,Object,Null,Undefined 2.抽象相等:x==y A.两者数据类型相同:typeof x == typeof y a.Str ...
- jQuery事件之传递参数
一.jQuery绑定事件的三种方法 我们这里首先复习一下jQuery绑定事件的三种方法: target.click(function(){}); target.on("click" ...
- 由UI刷新谈到线程安全和Android单线程模型
1.为什么说invalidate()不能直接在线程中调用? Android提供了Invalidate方法实现界面刷新,但是Invalidate不能直接在非UI主线程中调用,因为他是违背了单线程模型:A ...
- 《LeetBook》leetcode题解(12):Integer to Roman[M]
我现在在做一个叫<leetbook>的免费开源书项目,力求提供最易懂的中文思路,目前把解题思路都同步更新到gitbook上了,需要的同学可以去看看 书的地址:https://hk029.g ...
- nginx图片处理笔记(http-image-filter-module、lua)
实验环境:CentOS 6.10 目标:1.使用http-image-filter-module进行图片变换:2.使用lua进行格式转换: 安装EPEL https://fedoraproject.o ...
