spring启动流程 (3) BeanDefinition详解
BeanDefinition在Spring初始化阶段保存Bean的元数据信息,包括Class名称、Scope、构造方法参数、属性值等信息,本文将介绍一下BeanDefinition接口、重要的实现类,以及在Spring中的使用示例。
BeanDefinition接口
用于描述了一个Bean实例,该Bean实例具有属性、构造方法参数以及由具体实现提供的其他信息。
这是一个基础接口:主要目的是允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor获取和修改Bean实例属性和其他元数据。
封装以下信息:
- ParentName - The name of the parent definition of this bean definition.
- BeanClassName - The bean class name of this bean definition. The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing, typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
- Scope - Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
- isLazyInit - Whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
- DependsOn - The names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized. The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
- AutowireCandidate - Whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
- Primary - Whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
- FactoryBeanName - The factory bean to use. This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
- FactoryMethodName - Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified. The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any, or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
- ConstructorArgumentValues - Constructor argument values for this bean.
- PropertyValues - The property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
- InitMethodName - The name of the initializer method.
- DestroyMethodName - The name of the destroy method.
- Role - The role hint for this BeanDefinition. The role hint provides the frameworks as well as tools an indication of the role and importance of a particular BeanDefinition.
- ResolvableType - A resolvable type for this bean definition, based on the bean class or other specific metadata.
- isSingleton - Whether this a Singleton, with a single, shared instance returned on all calls.
- isPrototype - Whether this a Prototype, with an independent instance returned for each call.
- isAbstract - Whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
- OriginatingBeanDefinition - The originating BeanDefinition.
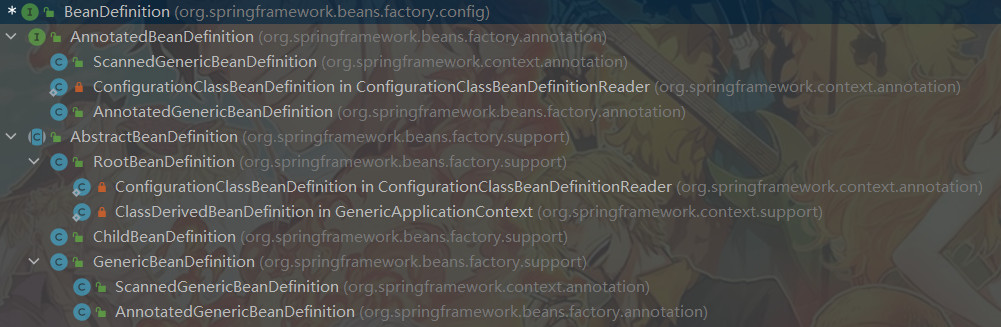
AbstractBeanDefinition类
实现了BeanDefinition接口,具体的、完整的BeanDefinition基类,抽取出GenericBeanDefinition、RootBeanDefinition和ChildBeanDefinition的公共属性。
扩展的属性:
- AutowireMode - The autowire mode. This determines whether any automagical detection and setting of bean references will happen. Default is AUTOWIRE_NO which means there won't be convention-based autowiring by name or type (however, there may still be explicit annotation-driven autowiring).
- AUTOWIRE_NO
- AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME
- AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE
- AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR
- AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT
RootBeanDefinition类
继承AbstractBeanDefinition类。
RootBeanDefinition表示在运行时支持BeanFactory中指定Bean的合并BeanDefinition。它可能是由多个相互继承的原始BeanDefinition创建的,通常注册为GenericBeanDefinitions。RootBeanDefinition本质上是运行时的"统一"RootBeanDefinition视图。
RootBeanDefinition也可以用于在配置阶段注册各个BeanDefinition。然而,自Spring2.5以来,以编程方式注册BeanDefinition的首选方式是GenericBeanDefinition类。GenericBeanDefinition的优势是允许动态定义父依赖项,而不是将角色硬编码为RootBeanDefinition。
扩展的属性:
- DecoratedDefinition - Target definition that is being decorated by this bean definition.
- QualifiedElement - Specify the AnnotatedElement defining qualifiers, to be used instead of the target class or factory method.
- TargetType - Specify a generics-containing target type of this bean definition, if known in advance.
- stale - Determines if the definition needs to be re-merged.
- allowCaching
- isFactoryBean
GenericBeanDefinition类
继承AbstractBeanDefinition类。
GenericBeanDefinition是用于构建标准BeanDefinition的一站式组件。与其他BeanDefinition一样,它允许指定一个类以及可选的构造方法参数和属性。另外,从父BeanDefinition派生可以通过parentName属性灵活配置。
通常,使用GenericBeanDefinition类来注册用户可见的BeanDefinition,后置处理器可能会对其进行操作,甚至可能重新配置parentName属性。如果父子关系恰好是预先确定的,请使用RootBeanDefinition和ChildBeanDefinition。
AnnotatedBeanDefinition接口
继承BeanDefinition接口。
扩展BeanDefinition接口,提供Bean的AnnotationMetadata,而不需要加载该类。
public interface AnnotatedBeanDefinition extends BeanDefinition {
/**
* Obtain the annotation metadata (as well as basic class metadata)
* for this bean definition's bean class.
*/
AnnotationMetadata getMetadata();
/**
* Obtain metadata for this bean definition's factory method, if any.
*/
MethodMetadata getFactoryMethodMetadata();
}
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition类
GenericBeanDefinition类的扩展,基于ASM ClassReader,实现了AnnotatedBeanDefinition接口,可以获取注解元数据。
这个类不会提前加载Bean Class。它从.class文件检索所有相关的元数据,并使用ASM ClassReader进行解析。
public class ScannedGenericBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition implements AnnotatedBeanDefinition {
private final AnnotationMetadata metadata;
/**
* Create a new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition for the class that the
* given MetadataReader describes.
* @param metadataReader the MetadataReader for the scanned target class
*/
public ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
this.metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
setBeanClassName(this.metadata.getClassName());
setResource(metadataReader.getResource());
}
@Override
public final AnnotationMetadata getMetadata() {
return this.metadata;
}
@Override
public MethodMetadata getFactoryMethodMetadata() {
return null;
}
}
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition类
GenericBeanDefinition类的扩展,实现了AnnotatedBeanDefinition接口,可以获取注解元数据。
public class AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
extends GenericBeanDefinition implements AnnotatedBeanDefinition {
private final AnnotationMetadata metadata;
private MethodMetadata factoryMethodMetadata;
public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(Class<?> beanClass) {
setBeanClass(beanClass);
this.metadata = AnnotationMetadata.introspect(beanClass);
}
public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
if (metadata instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {
setBeanClass(((StandardAnnotationMetadata) metadata).getIntrospectedClass());
} else {
setBeanClassName(metadata.getClassName());
}
this.metadata = metadata;
}
public AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(
AnnotationMetadata metadata,
MethodMetadata factoryMethodMetadata) {
this(metadata);
setFactoryMethodName(factoryMethodMetadata.getMethodName());
this.factoryMethodMetadata = factoryMethodMetadata;
}
@Override
public final AnnotationMetadata getMetadata() {
return this.metadata;
}
@Override
public final MethodMetadata getFactoryMethodMetadata() {
return this.factoryMethodMetadata;
}
}
Spring中使用BeanDefinition示例
注册componentClasses
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext启动代码:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
applicationContext.register(ServiceConfig.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext在启动时可以使用register方法注册@Configuration类,本小节将从这个方法入手看一个BeanDefinition的使用示例:
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(componentClasses, "At least one component class must be specified");
this.reader.register(componentClasses);
}
// reader.register(...)
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
for (Class<?> componentClass : componentClasses) {
registerBean(componentClass);
}
}
private <T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> beanClass, String name,
Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, Supplier<T> supplier,
BeanDefinitionCustomizer[] customizers) {
// 构造方法中会解析AnnotationMetadata元数据
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(beanClass);
// 判断是否允许装配
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(supplier);
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
// 解析Lazy,Primary,DependsOn,Role等属性
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
} else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
} else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
if (customizers != null) {
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
// 处理Scope的proxyMode
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils
.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
// 注册到容器
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
// BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(...)
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
// 将Bean注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
此处的registry是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象,registerBeanDefinition方法的实现在GenericApplicationContext类:
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
// beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(...)
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
} catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
} else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
} else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
} else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}
@Bean注解
@Bean注解注入的Bean最终在ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod方法注册BeanDefinition:
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(BeanMethod beanMethod) {
ConfigurationClass configClass = beanMethod.getConfigurationClass();
MethodMetadata metadata = beanMethod.getMetadata();
String methodName = metadata.getMethodName();
// Do we need to mark the bean as skipped by its condition?
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
configClass.skippedBeanMethods.add(methodName);
return;
}
if (configClass.skippedBeanMethods.contains(methodName)) {
return;
}
AnnotationAttributes bean = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Bean.class);
// Consider name and any aliases
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(bean.getStringArray("name")));
String beanName = (!names.isEmpty() ? names.remove(0) : methodName);
// Register aliases even when overridden
for (String alias : names) {
this.registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
// Has this effectively been overridden before (e.g. via XML)?
if (isOverriddenByExistingDefinition(beanMethod, beanName)) {
return;
}
// 创建ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition
// 是RootBeanDefinition的子类
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition beanDef =
new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(configClass, metadata, beanName);
beanDef.setSource(this.sourceExtractor.extractSource(metadata, configClass.getResource()));
if (metadata.isStatic()) {
// static @Bean method
if (configClass.getMetadata() instanceof StandardAnnotationMetadata) {
beanDef.setBeanClass(
((StandardAnnotationMetadata) configClass.getMetadata()).getIntrospectedClass());
} else {
beanDef.setBeanClassName(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);
} else {
// instance @Bean method
beanDef.setFactoryBeanName(configClass.getBeanName());
beanDef.setUniqueFactoryMethodName(methodName);
}
if (metadata instanceof StandardMethodMetadata) {
beanDef.setResolvedFactoryMethod(((StandardMethodMetadata) metadata).getIntrospectedMethod());
}
beanDef.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
beanDef.setAttribute(org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(beanDef, metadata);
Autowire autowire = bean.getEnum("autowire");
if (autowire.isAutowire()) {
beanDef.setAutowireMode(autowire.value());
}
boolean autowireCandidate = bean.getBoolean("autowireCandidate");
if (!autowireCandidate) {
beanDef.setAutowireCandidate(false);
}
String initMethodName = bean.getString("initMethod");
if (StringUtils.hasText(initMethodName)) {
beanDef.setInitMethodName(initMethodName);
}
String destroyMethodName = bean.getString("destroyMethod");
beanDef.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
// Consider scoping
ScopedProxyMode proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Scope.class);
if (attributes != null) {
beanDef.setScope(attributes.getString("value"));
proxyMode = attributes.getEnum("proxyMode");
if (proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;
}
}
// Replace the original bean definition with the target one, if necessary
BeanDefinition beanDefToRegister = beanDef;
if (proxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.NO) {
BeanDefinitionHolder proxyDef = ScopedProxyCreator.createScopedProxy(
new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName), this.registry,
proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS);
beanDefToRegister = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(
(RootBeanDefinition) proxyDef.getBeanDefinition(), configClass, metadata, beanName);
}
this.registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefToRegister);
}
@ComponentScan注解
支持@ComponentScan注解的最终逻辑在ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider类的scanCandidateComponents方法中:
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
// 此处获取到的是SimpleMetadataReader对象,
// 内部使用ASM解析.class文件封装AnnotationMetadata对象
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
// 判断是一个Component
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
// 创建ScannedGenericBeanDefinition对象
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
candidates.add(sbd);
}
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
spring启动流程 (3) BeanDefinition详解的更多相关文章
- Linux的启动流程以及GRUB详解
一.Linux引导和启动流程 概述,计算机电源接通后通过BISO之后,没有问题,就会去硬盘上找到MBR(Main Boot Record 主引导记录区)位于整个硬盘的0磁道0柱面1扇区, ...
- Tomcat5启动流程与配置详解
标签:配置 tomcat 休闲 职场 原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任.http://zhangjunhd.blog.51cto. ...
- 2017.3.31 spring mvc教程(二)核心流程及配置详解
学习的博客:http://elf8848.iteye.com/blog/875830/ 我项目中所用的版本:4.2.0.博客的时间比较早,11年的,学习的是Spring3 MVC.不知道版本上有没有变 ...
- Spring学习 6- Spring MVC (Spring MVC原理及配置详解)
百度的面试官问:Web容器,Servlet容器,SpringMVC容器的区别: 我还写了个文章,说明web容器与servlet容器的联系,参考:servlet单实例多线程模式 这个文章有web容器与s ...
- [PXE] Linux(centos6)中PXE 服务器搭建,PXE安装、启动及PXE理论详解
[PXE] Linux(centos6)中PXE 服务器搭建,PXE安装.启动及PXE理论详解 本篇blog主要讲述了[PXE] linux(centos)PXE无盘服务器搭建,安装,启动及pxe协议 ...
- Spring Boot Actuator监控使用详解
在企业级应用中,学习了如何进行SpringBoot应用的功能开发,以及如何写单元测试.集成测试等还是不够的.在实际的软件开发中还需要:应用程序的监控和管理.SpringBoot的Actuator模块实 ...
- DBA_Oracle Startup / Shutdown启动和关闭过程详解(概念)
2014-08-07 Created By BaoXinjian
- [置顶] 深入浅出Spring(三) AOP详解
上次的博文深入浅出Spring(二) IoC详解中,我为大家简单介绍了一下Spring框架核心内容中的IoC,接下来我们继续讲解另一个核心AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming ...
- Spring Boot的启动器Starter详解
Spring Boot的启动器Starter详解 作者:chszs,未经博主允许不得转载.经许可的转载需注明作者和博客主页:http://blog.csdn.net/chszs Spring Boot ...
- 服务启动项 Start类型详解
注册表的服务启动项 Start类型详解 HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\ 下的服务项.不论有没有在services.msc服务管理控制台中显示,在注册表中 ...
随机推荐
- 2024年 为什么不建议新人学习ABAP
引言 每个应届生都希望自己有良好的职业发展,当他们发现前路难通时,便会寻找更好的出路. "转码"曾经是个很火热的话题.在互联网行业高速发展的年代,转行学代码,入职大厂,升职加薪,是 ...
- LeetCode132:分割回文串(DP、回文)
解题思路:有两个问点:1.如何快速当前字符串哪些的字串是回文:2.如何组合这些字串达到分割次数最少 针对问点1,可以开辟一个二维布尔数组 a[][],a[i][j]表示以索引i为起点,j为结束位置的字 ...
- Roaring bitmaps
Roaring bitmaps 最近看一篇文章,里面涉及到使用roaring bitmaps来推送用户广告并通过计算交集来降低用户广告推送次数.本文给出roaring bitmaps的原理和基本用法, ...
- Python——第五章:处理异常try、except、else、finally
处理异常try 和 except 在 Python 中,try 和 except 语句用于处理异常(错误).通过使用这两个关键字,你可以编写代码来捕获和处理可能发生的异常,以保持程序的稳定性. try ...
- 善用 vscode 的批量和模板技巧来提效
vs code 其实有很多实用的技巧可以在日常工作中带来很大的提效,但可能是开发中没有相应的痛点场景,因此有些技巧接触的人不多 本篇就来介绍下多光标的批量操作和模板代码两种技巧在日常工作中的提效 涉及 ...
- Kafka 具体分析
前面的相关文件简要地介绍了 Kafka 的基本使用,本文将将要介绍一下关于 Kafka 的集群关系.存储结构以及架构方面的内容进行简要的解析 组件之间的关系 Kafka 中,各个组件之间的关系如下图所 ...
- 文心一言 VS 讯飞星火 VS chatgpt (44)-- 算法导论6.1 1题
一.在高度为h的堆中,元素个数最多和最少分别是多少? 文心一言: 在高度为 h 的二叉搜索树(BST)中,元素个数最多和最少的情况分别如下: 1.最多情况:当每个节点都包含两个子节点时,BST 中的元 ...
- 文心一言 VS 讯飞星火 VS chatgpt (36)-- 算法导论5.3 6题
六.请解释如何实现算法 PERMUTE-BY-SORTING,以处理两个或更多优先级相同的情形.也就是说,即使有两个或更多优先级相同,你的算法也应该产生一个均匀随机排列. 文心一言: 算法 PERMU ...
- FlinkSQL实战开发
FlinkSQL实战开发 1.基础知识 FlinkSQL分为Table API和SQL API,是架构于Flink Core之上用SQL予以方便快捷地进行结构化数据处理的上层库. 工作流程 SQL和T ...
- Prometheus 快速入门
Prometheus&Grafana快速入门 一.prometheus简介 prometheus是监控多个大数据组件的监控系统.Prometheus是由SoundCloud开发的开源监控报警系 ...
