Tensorflow Probability Distributions 简介
摘要:Tensorflow Distributions提供了两类抽象:distributions和bijectors。distributions提供了一系列具备快速、数值稳定的采样、对数概率计算以及其他统计特征计算方法的概率分布。bijectors提供了一系列针对distribution的可组合的确定性变换。
1、Distributions
1.1 methods
一个distribution至少实现以下方法:sample、log_prob、batch_shape_tensor、event_shape_tensor;同时也实现了一些其他方法,例如:cdf、survival_function、quantile、mean、variance、entropy等;Distribution基类实现了给定log_prob计算prob、给定log_cdf计算log_survival_fn的方法。
1.2 shape semantics
将一个tensor的形状分为三个部分:sample shape、batch shape、event shape。
sample shape:描述从给定概率分布上独立同分布的采样形状;
batch shape:描述从概率分布上独立、非同分布的采样形状,也即,我们可以指定一组参数不同的相同分布,batch shape通常用来为机器学习中一个batch的样本每个样本指定一个分布;
event shape:描述从概率分布上单次采样的形状;
1.3 sampling
reparameterization:distributions拥有一个reparameterization属性,这个属性表明了自动化微分和采样之间的关系。目前包括两种:“fully reparameterized” 和 “not reparameterized”。
fully reparameterized:例如,对于分布dist = Normal(loc, scale),采样y = dist.sample()的内部过程为x = tf.random_normal([]); y = scale * x + loc. 样本y是reparameterized的,因为它是参数loc、scale及无参数样本x的光滑函数。
not reparameterized:例如,gamma分布使用接收-拒绝的方式进行采样,是参数的非光滑函数。
end to end automatic differentiation:通过与tensorflow结合,一个fully reparameterized的分布可以进行端到端的自动微分。例如,要最小化分布Y的期望损失E [φ(Y)],可以使用蒙特卡洛近似的方法最小化
 这使得我们可以使用SN作为期望损失的估计,还可以使用ΔλSN作为梯度ΔλE [φ(Y)]的估计,其中λ是分布Y的参数。
这使得我们可以使用SN作为期望损失的估计,还可以使用ΔλSN作为梯度ΔλE [φ(Y)]的估计,其中λ是分布Y的参数。
1.4 high order distributions
TransformedDistribution:对一个基分布执行一个可逆可微分转换即可得到一个TransformedDistribution。例如,可以从一个Exponential分布得到一个标准Gumbel分布:
standard_gumbel = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Exponential(rate=1.),
bijector=tfb.Chain([
tfb.Affine(
scale_identity_multiplier=-1.,
event_ndims=0),
tfb.Invert(tfb.Exp()),
]))
standard_gumbel.batch_shape # ==> []
standard_gumbel.event_shape # ==> []
基于gumbel分布,可以构建一个Gumbel-Softmax(Concrete)分布:
alpha = tf.stack([
tf.fill([28 * 28], 2.),
tf.ones(28 * 28)]) concrete_pixel = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=standard_gumbel,
bijector=tfb.Chain([
tfb.Sigmoid(),
tfb.Affine(shift=tf.log(alpha)),
]),
batch_shape=[2, 28 * 28])
concrete_pixel.batch_shape # ==> [2, 784]
concrete_pixel.event_shape # ==> []
Independent:对batch shape和event shape进行转换。例如:
image_dist = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Independent(concrete_pixel),
bijector=tfb.Reshape(
event_shape_out=[28, 28, 1],
event_shape_in=[28 * 28]))
image_dist.batch_shape # ==> [2]
image_dist.event_shape # ==> [28, 28, 1]
Mixture:定义了由若干分布组合成的新的分布,例如:
image_mixture = tfd.MixtureSameFamily(
mixture_distribution=tfd.Categorical(
probs=[0.2, 0.8]),
components_distribution=image_dist)
image_mixture.batch_shape # ==> []
image_mixture.event_shape # ==> [28, 28, 1]
1.5 distribution functionals
functional以一个分布作为输入,输出一个标量,例如:entropy、cross entropy、mutual information、kl距离等。
p = tfd.Normal(loc=0., scale=1.)
q = tfd.Normal(loc=-1., scale=2.)
xent = p.cross_entropy(q)
kl = p.kl_divergence(q)
# ==> xent - p.entropy()
2、Bijectors
2.1 definition
Bijector API提供了针对distribution的可微分双向映射(differentialble, bijective map, diffeomorphism)转换接口。给定随机变量X和一个diffeomorphism F,可以定义一个新的随机变量Y,Y的密度可由下式计算:
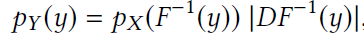
其中DF-1是F的Jacobian的逆。(参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100287713)
每个bijector子类都对应一个F,TransformedDistribution自动计算Y=F(X)的密度。bijector使得我们可以利用已有的分布构建许多其他分布。
bijector主要包含以下三个函数:
forward:实现x → F (x),TransformedDistribution.sample函数使用该函数将一个tensor转换为另一个tensor;
inverse:forward的逆变换,实现y → F-1(y),TransformedDistribution.log_prob使用该函数计算对数概率(上式);
inverse_log_det_jacobian:计算log |DF−1(y)|,TransformedDistribution.log_prob使用该函数计算对数概率(上式);
通过使用bijectors,TransformedDistribution可以自动高效地实现sample、log_prob、prob,对于具有恒定Jacobian的bijector,TransformedDistribution自动实现一些基础统计量,如mean、variance、entropy等。
以下实现了对Laplace的放射变换:
vector_laplace = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Laplace(loc=0., scale=1.),
bijector=tfb.Affine(
shift=tf.Variable(tf.zeros(d)),
scale_tril=tfd.fill_triangular(
tf.Variable(tf.ones(d * (d + 1) / 2)))),
event_shape=[d])
由于tf.Variables,该分布是可学习的。
2.2 composability
bijectors可以构成高阶bijectors,例如Chain、Invert。
chain bijector可以构建一系列丰富的分布,例如创建一个多变量logit-Normal分布:
matrix_logit_mvn =
tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Normal(0., 1.),
bijector=tfb.Chain([
tfb.Reshape([d, d]),
tfb.SoftmaxCentered(),
tfb.Affine(scale_diag=diag),
]),
event_shape=[d * d])
Invert可以通过交换inverse和forward函数,高效地将bijectors数量翻倍,例如:
softminus_gamma = tfd.TransformedDistribution(
distribution=tfd.Gamma(
concentration=alpha,
rate=beta),
bijector=tfb.Invert(tfb.Softplus()))
2.3 caching
bijector自动缓存操作的输入输出对,包括log det jacobian。caching的意义时,当inverse计算很慢或数值不稳定或难以实现时,可以高效的执行inverse操作。当计算采样结果的概率是,缓存被触发。如果q(x)是x=f(ε)的密度,且ε~r,那么caching可以降低计算q(xi)的计算成本:
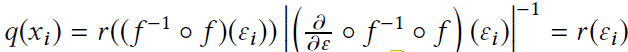
caching机制也可用来进行高效地重要性采样(importance sampling):

3、 应用
3.1 核密度估计(KDE)
例如,可以通过以下代码构建一个由n个mvn_diag分布作为kernel的混合高斯模型,其中每个kernel的权重为1/n。注意,此时Independent会对分布的shape进行重定义(reinterpret),tfd.Normal(loc=x, scale=1.)创建了一个batch_shape = n*d, event_shape = []的分布,对其Independent之后,变为batch_shape = n, event_shape = d的分布。
Independent文档:https://www.tensorflow.org/probability/api_docs/python/tfp/distributions/Independent?hl=zh-cn
f = lambda x: tfd.Independent(tfd.Normal(
loc=x, scale=1.))
n = x.shape[0].value
kde = tfd.MixtureSameFamily(
mixture_distribution=tfd.Categorical(
probs=[1 / n] * n),
components_distribution=f(x))
3.2 变分自编码器(VAE)
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1312.6114.pdf
博客:https://spaces.ac.cn/archives/5253
def make_encoder(x, z_size=8):
net = make_nn(x, z_size * 2) return tfd.MultivariateNormalDiag(
loc=net[..., :z_size],
scale=tf.nn.softplus(net[..., z_size:]))) def make_decoder(z, x_shape=(28, 28, 1)):
net = make_nn(z, tf.reduce_prod(x_shape)) logits = tf.reshape(
net, tf.concat([[-1], x_shape], axis=0))
return tfd.Independent(tfd.Bernoulli(logits)) def make_prior(z_size=8, dtype=tf.float32):
return tfd.MultivariateNormalDiag(
loc=tf.zeros(z_size, dtype))) def make_nn(x, out_size, hidden_size=(128, 64)):
net = tf.flatten(x) for h in hidden_size:
net = tf.layers.dense(
net, h, activation=tf.nn.relu)
return tf.layers.dense(net, out_size)
3.3 Edward概率编程
tfd是Edward的后端。以下代码实现一个随机循环神经网络(stochastic rnn),其隐藏状态是随机的。
stochastic rnn论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.7610.pdf
from edward.models import Normal z = x = []
z[0] = Normal(loc=tf.zeros(K), scale=tf.ones(K))
h = tf.layers.dense(
z[0], 512, activation=tf.nn.relu)
loc = tf.layers.dense(h, D, activation=None)
x[0] = Normal(loc=loc, scale=0.5)
for t in range(1, T):
inputs = tf.concat([z[t - 1], x[t - 1]], 0)
loc = tf.layers.dense(
inputs, K, activation=tf.tanh)
z[t] = Normal(loc=loc, scale=0.1)
h = tf.layers.dense(
z[t], 512, activation=tf.nn.relu)
loc = tf.layers.dense(h, D, activation=None)
x[t] = Normal(loc=loc, scale=0.5)
Tensorflow Probability Distributions 简介的更多相关文章
- PRML读书笔记——2 Probability Distributions
2.1. Binary Variables 1. Bernoulli distribution, p(x = 1|µ) = µ 2.Binomial distribution + 3.beta dis ...
- PRML读书会第二章 Probability Distributions(贝塔-二项式、狄利克雷-多项式共轭、高斯分布、指数族等)
主讲人 网络上的尼采 (新浪微博: @Nietzsche_复杂网络机器学习) 网络上的尼采(813394698) 9:11:56 开始吧,先不要发言了,先讲PRML第二章Probability Dis ...
- PRML Chapter 2. Probability Distributions
PRML Chapter 2. Probability Distributions P68 conjugate priors In Bayesian probability theory, if th ...
- Common Probability Distributions
Common Probability Distributions Probability Distribution A probability distribution describes the p ...
- Study note for Continuous Probability Distributions
Basics of Probability Probability density function (pdf). Let X be a continuous random variable. The ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 8: Normal Distribution
PDF version PDF & CDF The probability density function is $$f(x; \mu, \sigma) = {1\over\sqrt{2\p ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 7: Uniform Distribution
PDF version PDF & CDF The probability density function of the uniform distribution is $$f(x; \al ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 6: Exponential Distribution
PDF version PDF & CDF The exponential probability density function (PDF) is $$f(x; \lambda) = \b ...
- 基本概率分布Basic Concept of Probability Distributions 5: Hypergemometric Distribution
PDF version PMF Suppose that a sample of size $n$ is to be chosen randomly (without replacement) fro ...
随机推荐
- 简单ping确定网络故障
1.ping localhost (127.0.0.1) 目的:确定TCP/IP有无问题 2.ping本机地址 用来检测网卡驱动有无问题 如何获取本机地址? win+r cmd 输入ipconfig/ ...
- PTA 统计二叉树度为2的结点个数
6-4 统计二叉树度为2的结点个数 (11 分) 本题要求实现一个函数,可统计二叉树中度为2的结点个数. 函数接口定义: int NodeCount ( BiTree T); T是二叉树树根指针, ...
- java例题_14 该日期一年中的第几天问题
1 /*14 [程序 14 求日期] 2 题目:输入某年某月某日,判断这一天是这一年的第几天? 3 程序分析:以 3 月 5 日为例,应该先把前两个月的加起来,然后再加上 5 天即本年的第几天,特殊情 ...
- 接口自动化——读取Excle中遇到的问题
一.module 'openpyxl' has no attribute 'load_workbook'问题 原因:在pycharm中py文件名字为openpyxl导致 修改方法:重新对py名字进行命 ...
- 前端 | JS Promise:axios 请求结果后面的 .then() 是什么意思?
Promise 是JS中一种处理异步操作的机制,在现在的前端代码中使用频率很高.Promise 这个词可能有点眼生,但你肯定见过 axios.get(...).then(res => {...} ...
- dll远线程注入
原理 核心函数 CreateRemoteThread:让在其他进程中创建一个线程变成可能 核心思想 HANDLE WINAPI CreateRemoteThread( __in HANDLE hPro ...
- 计划任务统一集中管理系统cronsun(替代crontab)
一.背景 crontab 是 Linux 系统里面最简单易用的定时任务管理工具,相信绝大多数开发和运维都用到过,很多业务系统的定时任务都是通过 crontab 来定义的,时间长了后会发现存在很多问题: ...
- Flex属性你真的搞清楚了吗?我深表怀疑
背景 在使用弹性布局实现两侧宽度固定,中间宽度自适应的效果时,发现自己理解的和实际效果不一致,所以亲自实践验证了一个flex属性的诸多场景的表现,不仅解开了我之前使用过程遇到的疑惑,而且发现了许多自己 ...
- Shell prompt(PS1) 与 Carriage Return(CR) 的关系?-- Shell十三问<第二问>
Shell prompt(PS1) 与 Carriage Return(CR) 的关系?-- Shell十三问<第二问> 当你成功登录进一个文字界面之后,大部份情形下,你会在荧幕上看到一个 ...
- 201871030106-陈鑫莲 实验二 个人项目-《D{0-1} KP 问题》项目报告
项目 内容 课程班级博客链接 班级博客 这个作业要求链接 作业要求 我的课程学习目标 1.掌握软件项目个人开发流程2.掌握Github发布软件项目的操作方法 这个作业在哪些方面帮助我实现学习目标 1. ...
