Codeforces 768 E. Game of Stones 博弈DP
Sam has been teaching Jon the Game of Stones to sharpen his mind and help him devise a strategy to fight the white walkers. The rules of this game are quite simple:
- The game starts with n piles of stones indexed from 1 to n. The i-th pile contains si stones.
- The players make their moves alternatively. A move is considered as removal of some number of stones from a pile. Removal of 0stones does not count as a move.
- The player who is unable to make a move loses.
Now Jon believes that he is ready for battle, but Sam does not think so. To prove his argument, Sam suggested that they play a modified version of the game.
In this modified version, no move can be made more than once on a pile. For example, if 4 stones are removed from a pile, 4 stones cannot be removed from that pile again.
Sam sets up the game and makes the first move. Jon believes that Sam is just trying to prevent him from going to battle. Jon wants to know if he can win if both play optimally.
First line consists of a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106) — the number of piles.
Each of next n lines contains an integer si (1 ≤ si ≤ 60) — the number of stones in i-th pile.
Print a single line containing "YES" (without quotes) if Jon wins, otherwise print "NO" (without quotes)
1
5
NO
In the first case, Sam removes all the stones and Jon loses.
In second case, the following moves are possible by Sam: 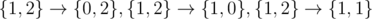
In each of these cases, last move can be made by Jon to win the game as follows: 
题意:
一堆石子,一开始你可以拿走任意个,假设拿走k(k>=1)个,那么另外一个人就不能再拿k个了
现在有n堆石子,两人轮流拿,不能拿的时候那个人就输了
问后手是否能赢
题解:
石子最多60颗,1<<60,状态压缩跑sg函数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#define ls i<<1
#define rs ls | 1
#define mid ((ll+rr)>>1)
#define pii pair<LL,int>
#define MP make_pair
typedef long long LL;
const long long INF = 1e18;
const double Pi = acos(-1.0);
const int N = 1e6+, maxn = 1e3+, mod = 1e9+, inf = 2e9; map<LL,int > dp[N];
int sg[N],n;
int dfs(int x,LL dep) {
if(dp[x].count(dep)) return dp[x][dep];
LL ret = ;
for(int i = ; i < x; ++i) {
if(((dep>>i)&) == ) {
ret |= <<(dfs(x-i-,dep|(<<i)));
}
}
for(int i = ; i < ; ++i) {
if((ret>>i&) == ) {
dp[x][dep] = i;
break;
}
}
return dp[x][dep];
}
int main() {
for(int i = ; i <= ; ++i) sg[i] = dfs(i,);
scanf("%d",&n);
int ans = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
ans ^= sg[x];
}
if(!ans) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
return ;
}
Codeforces 768 E. Game of Stones 博弈DP的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 538E Demiurges Play Again(博弈DP)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/538/E 题目大意: 给出一棵树,叶子节点上都有一个值,从1-m.有两个人交替从根选择道路,先手希望到达的叶子节点尽 ...
- Codeforces 219D. Choosing Capital for Treeland (树dp)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/219/problem/D 树dp //#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:10240000 ...
- HDU 5623 KK's Number (博弈DP)
KK's Number 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/121332#problem/K Description Our lovely KK h ...
- 博弈dp 以I Love this Game! POJ - 1678 为例
写在前面的话 知识基础:一些基础的博弈论的方法,动态规划的一些知识 前言:博弈论就是一些关于策略或者游戏之间的最优解,动态规划就是对于一些状态之间转移的一些递推式(or 递归),dp分为很多很多种,比 ...
- [CodeForces - 1272D] Remove One Element 【线性dp】
[CodeForces - 1272D] Remove One Element [线性dp] 标签:题解 codeforces题解 dp 线性dp 题目描述 Time limit 2000 ms Me ...
- 博弈dp入门 POJ - 1678 HDU - 4597
本来博弈还没怎么搞懂,又和dp搞上了,哇,这真是冰火两重天,爽哉妙哉. 我自己的理解就是,博弈dp有点像对抗搜索的意思,但并不是对抗搜索,因为它是像博弈一样,大多数以当前的操作者来dp,光想是想不通的 ...
- codeforces 768 D. Jon and Orbs(概率dp)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/768/problem/D 题意:一共有k种球,要得到k种不同的球至少一个,q个提问每次提问给出一个数pi,问概率大小大于等于pi ...
- Codeforces Round #222 (Div. 1) 博弈 + dp
一般这种要倒着来. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long #define fi first #define se second #def ...
- Codeforces 455B A Lot of Games:博弈dp【多局游戏】
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/455/B 题意: 给你n个字符串,然后进行k局游戏. 每局游戏开始有一个空串,然后双方轮流给这个串的末尾添 ...
随机推荐
- vue 运行时 + 编译器 vs. 只包含运行时
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/installation.html#运行时-编译器-vs-只包含运行时 文档中的这个地方,说的不清楚 If you need to comp ...
- bootstrap3之栅格系统
原理 栅格系统的核心就是媒体查询.指定的尺寸都是百分比,也就是流式布局. 查看bootstrap中的源码可以发现,对样式的定义次序全都是依次 xs.sm.md.lg,如: // grid-framew ...
- 条款14:在资源管理类中心copying行为(Think carefully about copying behavior in resource-manage classes)
NOTE: 1.复制RAII 对象必须一并赋值它所管理的资源,所以资源的copying行为决定RAII对象的copying行为. 2.普遍而常见的RAII class copying 行为是: 抑制c ...
- POJ 1383 Labyrinth (树的直径求两点间最大距离)
Description The northern part of the Pyramid contains a very large and complicated labyrinth. The la ...
- [luoguP2420] 让我们异或吧(dfs + 异或的性质)
传送门 因为异或满足结合律和交换律. a^b^b=a 所以这个题直接求根节点到每个点路径上的异或值. 对于每组询问直接输出根到两个点的异或值的异或的值. ——代码 #include <cstdi ...
- NodeJS仿WebApi路由
用过WebApi或Asp.net MVC的都知道微软的路由设计得非常好,十分方便,也十分灵活.虽然个人看来是有的太灵活了,team内的不同开发很容易使用不同的路由方式而显得有点混乱. 不过这不是重点, ...
- 【HDOJ6300】Triangle Partition(极角排序)
题意:给定3n个点,保证没有三点共线,要求找到一组点的分组方案使得它们组成的三角形之间互不相交. n<=1e3 思路:以y为第一关键字,x为第二关键字,按x递减,y递增排序 #include&l ...
- delete NULL
面试某公司的时候,某技术主管说你这delete前没有判断指针是否为NULL,当时我就…… 看来这是个传说中的好习惯,每当delete一个指针的时候,要先判断是不是NULL.比如: if ( p != ...
- [bzoj2595][WC2008]游览计划/[bzoj5180][Baltic2016]Cities_斯坦纳树
游览计划 bzoj-2595 wc-2008 题目大意:题目链接.题目连接. 注释:略. 想法:裸题求斯坦纳树. 斯坦纳树有两种转移方式,设$f[s][i]$表示联通状态为$s$,以$i$为根的最小代 ...
- uva 1364
刘书上例题 #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <set> # ...
