转:locality sensitive hashing

Motivation
The task of finding nearest neighbours is very common. You can think of applications like finding duplicate or similar documents, audio/video search. Although using brute force to check for all possible combinations will give you the exact nearest neighbour but it’s not scalable at all. Approximate algorithms to accomplish this task has been an area of active research. Although these algorithms don’t guarantee to give you the exact answer, more often than not they’ll be provide a good approximation. These algorithms are faster and scalable.
Locality sensitive hashing (LSH) is one such algorithm. LSH has many applications, including:
- Near-duplicate detection: LSH is commonly used to deduplicate large quantities of documents, webpages, and other files.
- Genome-wide association study: Biologists often use LSH to identify similar gene expressions in genome databases.
- Large-scale image search: Google used LSH along with PageRank to build their image search technology VisualRank.
- Audio/video fingerprinting: In multimedia technologies, LSH is widely used as a fingerprinting technique A/V data.
In this blog, we’ll try to understand the workings of this algorithm.
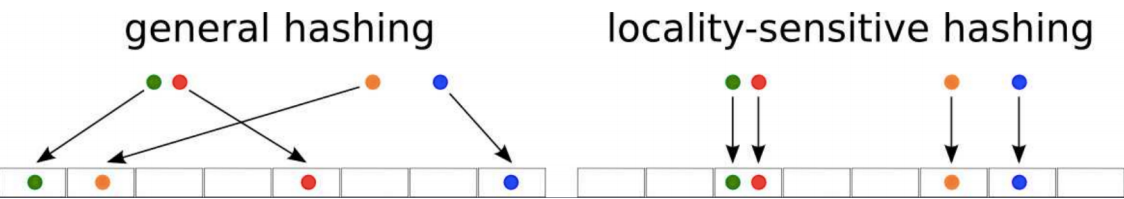
General Idea
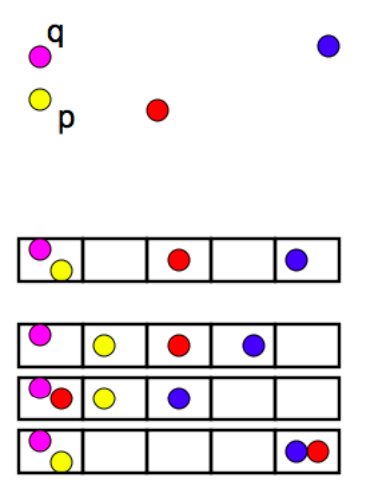
LSH refers to a family of functions (known as LSH families) to hash data points into buckets so that data points near each other are located in the same buckets with high probability, while data points far from each other are likely to be in different buckets. This makes it easier to identify observations with various degrees of similarity.
Finding similar documents
Let’s try to understand how we can leverage LSH in solving an actual problem. The problem that we’re trying to solve:
Goal: You have been given a large collections of documents. You want to find “near duplicate” pairs.
In the context of this problem//////再次问题的背景下, we can break down the LSH algorithm into 3 broad steps:
- Shingling
- Min hashing
- Locality-sensitive hashing
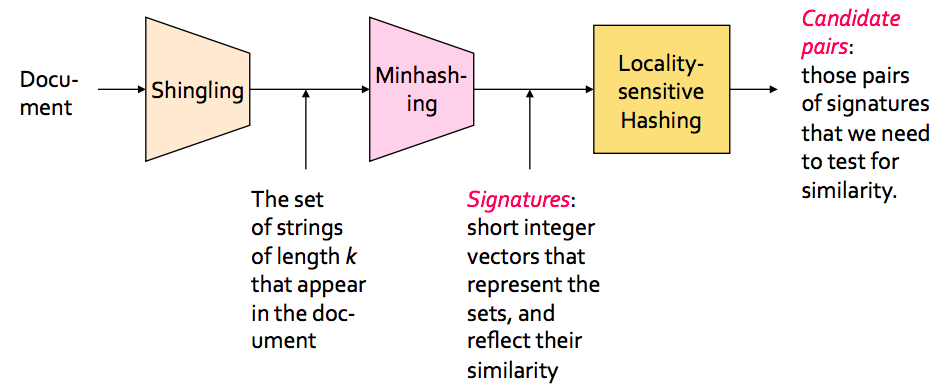
Shingling
In this step, we convert each document into a set of characters of length k (also known as k-shingles or k-grams). The key idea is to represent each document in our collection as a set of k-shingles.
For ex: One of your document (D): “Nadal”. Now if we’re interested in 2-shingles, then our set: {Na, ad, da, al}. Similarly set of 3-shingles: {Nad, ada, dal}.
- Similar documents are more likely to share more shingles
- Reordering paragraphs in a document of changing words doesn’t have much affect on shingles
- k value of 8–10 is generally used in practice. A small value will result in many shingles which are present in most of the documents (bad for differentiating documents)
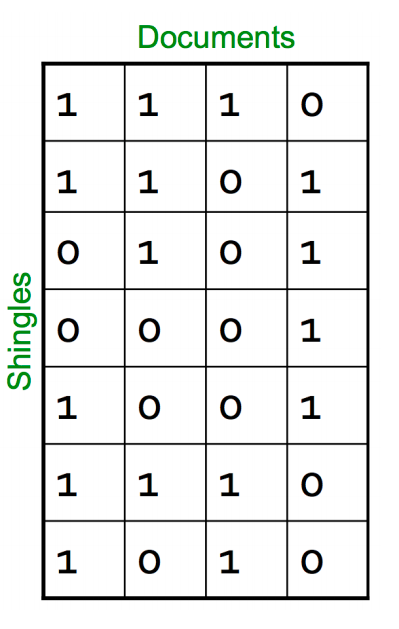
Jaccard Index
We’ve a representation of each document in the form of shingles. Now, we need a metric to measure similarity between documents. Jaccard Index is a good choice for this. Jaccard Index between document A & B can be defined as:
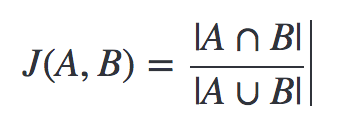
It’s also known as intersection over union (IOU).
A: {Na, ad, da, al} and B: {Na, ad, di, ia}.
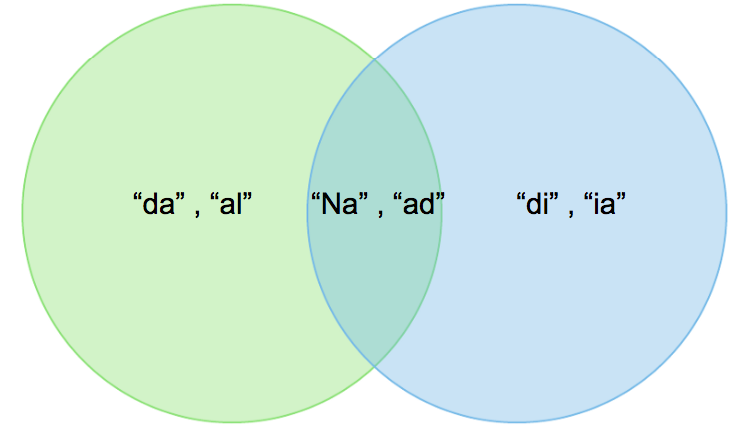
Jaccard Index = 2/6
Let’s discuss 2 big issues that we need to tackle:
Time complexity
Now you may be thinking that we can stop here. But if you think about the scalability, doing just this won’t work. For a collection of n documents, you need to do n*(n-1)/2 comparison, basically O(n²). Imagine you have 1 million documents, then the number of comparison will be 5*10¹¹ (not scalable at all!).
Space complexity
The document matrix is a sparse matrix and storing it as it is will be a big memory overhead. One way to solve this is hashing.
Hashing
The idea of hashing is to convert each document to a small signature using a hashing function H*.* Suppose a document in our corpus is denoted by d. Then:
- H(d) is the signature and it’s small enough to fit in memory
- If similarity(d1,d2) is high then *Probability(H(d1)==H(d2))* is high
- If similarity(d1,d2) is low then *Probability(H(d1)==H(d2))* is low
Choice of hashing function is tightly linked to the similarity metric we’re using. For Jaccard similarity the appropriate hashing function is min-hashing.
Min hashing
This is the critical and the most magical aspect of this algorithm so pay attention:
Step 1: Random permutation (π) of row index of document shingle matrix.

////////对行进行随机排列
Step 2: Hash function is the index of the first (in the permuted order) row in which column C has value 1. Do this several time (use different permutations) to create signature of a column.
第2步:哈希函数是列C值为1的第一行(按顺序排列)的索引。这样做几次(使用不同的排列)来创建一个列的签名。
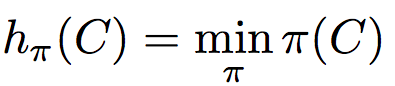
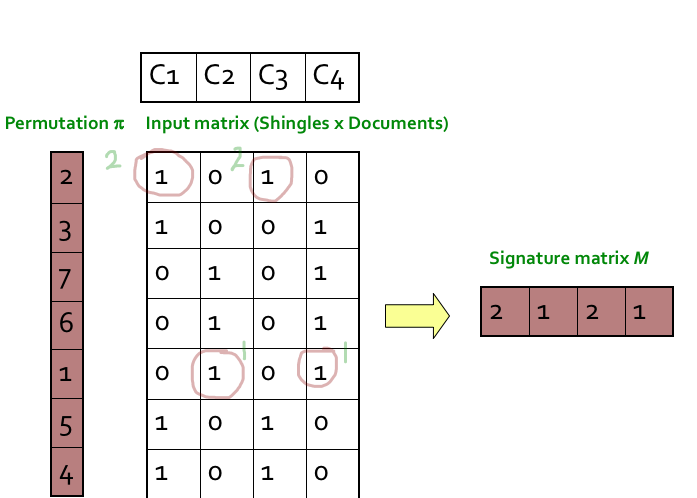
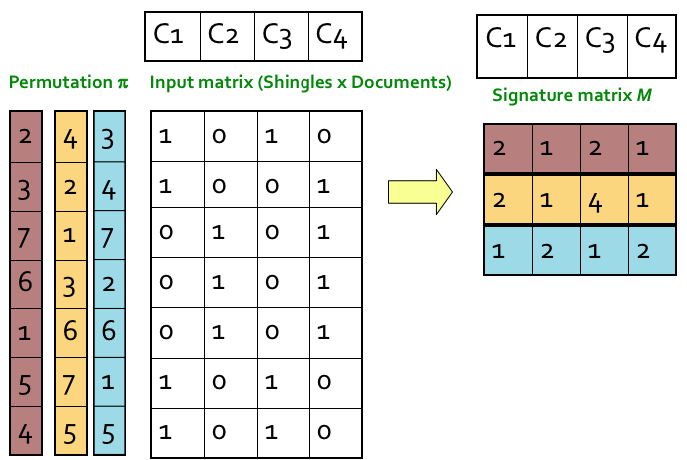
////这个图根本看不懂
转:locality sensitive hashing的更多相关文章
- [Algorithm] 局部敏感哈希算法(Locality Sensitive Hashing)
局部敏感哈希(Locality Sensitive Hashing,LSH)算法是我在前一段时间找工作时接触到的一种衡量文本相似度的算法.局部敏感哈希是近似最近邻搜索算法中最流行的一种,它有坚实的理论 ...
- 局部敏感哈希-Locality Sensitive Hashing
局部敏感哈希 转载请注明http://blog.csdn.net/stdcoutzyx/article/details/44456679 在检索技术中,索引一直须要研究的核心技术.当下,索引技术主要分 ...
- LSH(Locality Sensitive Hashing)原理与实现
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/guoziqing506/article/details/53019049 LSH(Locality Sensitive Hashing)翻译成中 ...
- Locality Sensitive Hashing,LSH
1. 基本思想 局部敏感(Locality Senstitive):即空间中距离较近的点映射后发生冲突的概率高,空间中距离较远的点映射后发生冲突的概率低. 局部敏感哈希的基本思想类似于一种空间域转换思 ...
- 局部敏感哈希算法(Locality Sensitive Hashing)
from:https://www.cnblogs.com/maybe2030/p/4953039.html 阅读目录 1. 基本思想 2. 局部敏感哈希LSH 3. 文档相似度计算 局部敏感哈希(Lo ...
- 局部敏感哈希Locality Sensitive Hashing(LSH)之随机投影法
1. 概述 LSH是由文献[1]提出的一种用于高效求解最近邻搜索问题的Hash算法.LSH算法的基本思想是利用一个hash函数把集合中的元素映射成hash值,使得相似度越高的元素hash值相等的概率也 ...
- 局部敏感哈希-Locality Sensitivity Hashing
一. 近邻搜索 从这里开始我将会对LSH进行一番长篇大论.因为这只是一篇博文,并不是论文.我觉得一篇好的博文是尽可能让人看懂,它对语言的要求并没有像论文那么严格,因此它可以有更强的表现力. 局部敏感哈 ...
- 从NLP任务中文本向量的降维问题,引出LSH(Locality Sensitive Hash 局部敏感哈希)算法及其思想的讨论
1. 引言 - 近似近邻搜索被提出所在的时代背景和挑战 0x1:从NN(Neighbor Search)说起 ANN的前身技术是NN(Neighbor Search),简单地说,最近邻检索就是根据数据 ...
- Locality Sensitive Hash 局部敏感哈希
Locality Sensitive Hash是一种常见的用于处理高维向量的索引办法.与其它基于Tree的数据结构,诸如KD-Tree.SR-Tree相比,它较好地克服了Curse of Dimens ...
随机推荐
- 用GitHub Pages搭建博客(五)
本篇介绍GitHub Pages自定义域名 在用GitHub Pages搭建博客(二)中介绍到,默认的GitHub Pages域名就是仓库地址,即: 账号名.github.io 如果我们要使用自定义域 ...
- 使用Ganglia监控系统监控集群(debian)
ganglia是一个集群监控软件,底层使用RRDTool获得数据. Ganglia分为ganglia-monitor和gmetad两部分,前者运行在集群每个节点上(被监控机器)收集RRDTool产生的 ...
- MOOC JAVA笔记
MOOC JAVA笔记 1.基础了解 JDK是开发人员安装的,它提供了开发java程序的必须工具 JRE是普通用户安装的,它提供了java的运行环境 JVM是java虚拟机运行程序的核心 2.程序的移 ...
- Docker 初始
1. Docker 是什么? 官网的介绍是"Docker is the world's leading software container platform." 官方给Docke ...
- rsync未授权访问漏洞复现
rsync未授权访问漏洞简介 rsync是Linux/Unix下的一个远程数据同步工具,可通过LAN/WAN快速同步多台主机间的文件和目录,默认运行在873端口.由于配置不当,导致任何人可未授权访问r ...
- php 判断网站是http还是https
//判断是http还是https $http_type = ((isset($_SERVER['HTTPS']) && $_SERVER['HTTPS'] == 'on') || (i ...
- 精尽MyBatis源码分析 - MyBatis初始化(四)之 SQL 初始化(下)
该系列文档是本人在学习 Mybatis 的源码过程中总结下来的,可能对读者不太友好,请结合我的源码注释(Mybatis源码分析 GitHub 地址.Mybatis-Spring 源码分析 GitHub ...
- 深度分析:Java 静态方法/变量,非静态方法/变量的区别,今天一并帮你解决!
静态/非静态 方法/变量的写法 大家应该都明白静态方法/字段比普通方法/字段的写法要多一个static关键字,简单写下他们的写法吧,了解的可以直接略过 class Test{ // 静态变量 publ ...
- 修改pycharm中的flask项目名遇到的坑
曾修改过自己的项目名,并在settings中的解释器也更正过来了.然后执行pip list 报错: failed to create process. 解决方法如下: 到你的项目的venv目录下的Sc ...
- CorelDRAW复制及镜面反转对象
复制的设计都是由简单的图案和基础的操作堆砌而成的,如何恰当地使用这些基础操作,就是各位新学者要格外注意的地方. 这次我们介绍CorelDRAW中的复制和镜面操作. 一.复制 1.复制单个对象 使用Co ...
