TF之BN:BN算法对多层中的每层神经网络加快学习QuadraticFunction_InputData+Histogram+BN的Error_curve
# 23 Batch Normalization import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ACTIVATION = tf.nn.tanh
N_LAYERS = 7
N_HIDDEN_UNITS = 30 def fix_seed(seed=1):
# reproducible
np.random.seed(seed)
tf.set_random_seed(seed) def plot_his(inputs, inputs_norm):
# plot histogram for the inputs of every layer for j, all_inputs in enumerate([inputs, inputs_norm]):
for i, input in enumerate(all_inputs):
plt.subplot(2, len(all_inputs), j*len(all_inputs)+(i+1))
plt.cla()
if i == 0:
the_range = (-7, 10)
else:
the_range = (-1, 1)
plt.hist(input.ravel(), bins=15, range=the_range, color='#0000FF')
plt.yticks(())
if j == 1:
plt.xticks(the_range)
else:
plt.xticks(())
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
plt.title("%s normalizing" % ("Without" if j == 0 else "With"))
plt.title('Matplotlib,BN,histogram--Jason Niu')
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.001) def built_net(xs, ys, norm):
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None, norm=False):
# weights and biases (bad initialization for this case)
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size], mean=0., stddev=1.))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1) # fully connected product
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases # normalize fully connected product
if norm:
# Batch Normalize
fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments(
Wx_plus_b,
axes=[0], )
scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([out_size]))
shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_size]))
epsilon = 0.001 # apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5)
def mean_var_with_update():
ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var])
with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]):
return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var)
mean, var = mean_var_with_update() Wx_plus_b = tf.nn.batch_normalization(Wx_plus_b, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon) # Wx_plus_b = (Wx_plus_b - fc_mean) / tf.sqrt(fc_var + 0.001) #进行BN一下
# Wx_plus_b = Wx_plus_b * scale + shift # activation
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs #输出激活结果 fix_seed(1) if norm:
# BN for the first input
fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments(
xs,
axes=[0],
)
scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([1]))
shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
epsilon = 0.001
# apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5)
def mean_var_with_update():
ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var])
with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]):
return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var)
mean, var = mean_var_with_update()
xs = tf.nn.batch_normalization(xs, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon) # record inputs for every layer
layers_inputs = [xs] # build hidden layers
for l_n in range(N_LAYERS):
layer_input = layers_inputs[l_n]
in_size = layers_inputs[l_n].get_shape()[1].value output = add_layer(
layer_input, # input
in_size, # input size
N_HIDDEN_UNITS, # output size
ACTIVATION, # activation function
norm, # normalize before activation
)
layers_inputs.append(output) # build output layer
prediction = add_layer(layers_inputs[-1], 30, 1, activation_function=None) cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)
return [train_op, cost, layers_inputs] fix_seed(1)
x_data = np.linspace(-7, 10, 2500)[:, np.newaxis] #水平轴-7~10
np.random.shuffle(x_data)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 8, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 5 + noise xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) # [num_samples, num_features]
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) #建立两个神经网络作对比
train_op, cost, layers_inputs = built_net(xs, ys, norm=False)
train_op_norm, cost_norm, layers_inputs_norm = built_net(xs, ys, norm=True) sess = tf.Session()
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init) # record cost
cost_his = []
cost_his_norm = []
record_step = 5 plt.ion()
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 3))
for i in range(250):
if i % 50 == 0:
# plot histogram
all_inputs, all_inputs_norm = sess.run([layers_inputs, layers_inputs_norm], feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
plot_his(all_inputs, all_inputs_norm) # train on batch每一步都run一下
sess.run([train_op, train_op_norm], feed_dict={xs: x_data[i*10:i*10+10], ys: y_data[i*10:i*10+10]}) if i % record_step == 0:
# record cost
cost_his.append(sess.run(cost, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))
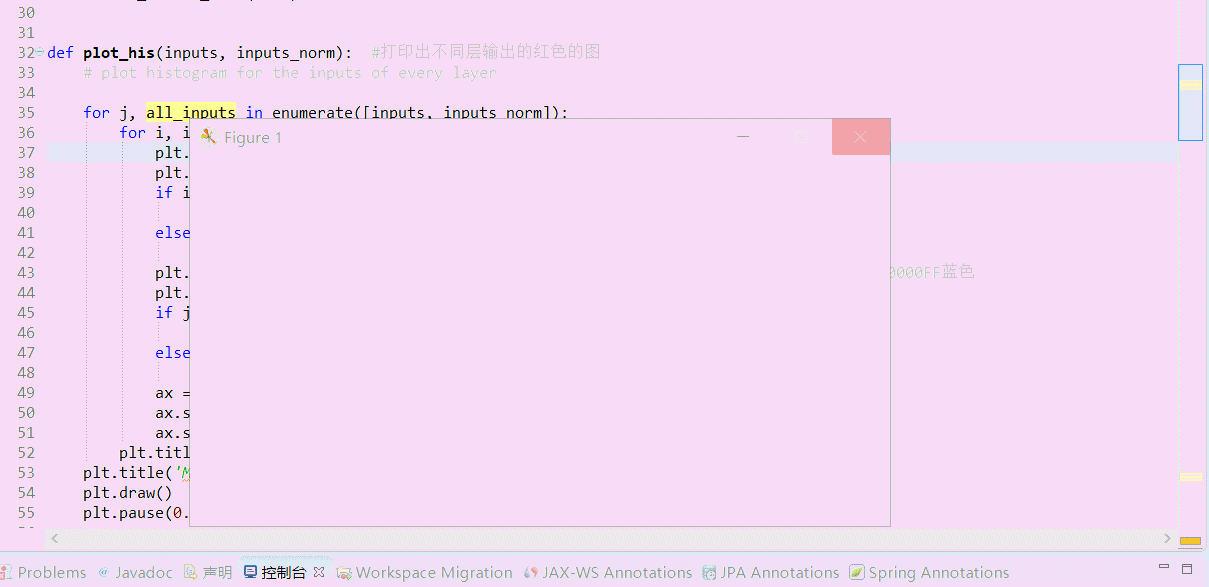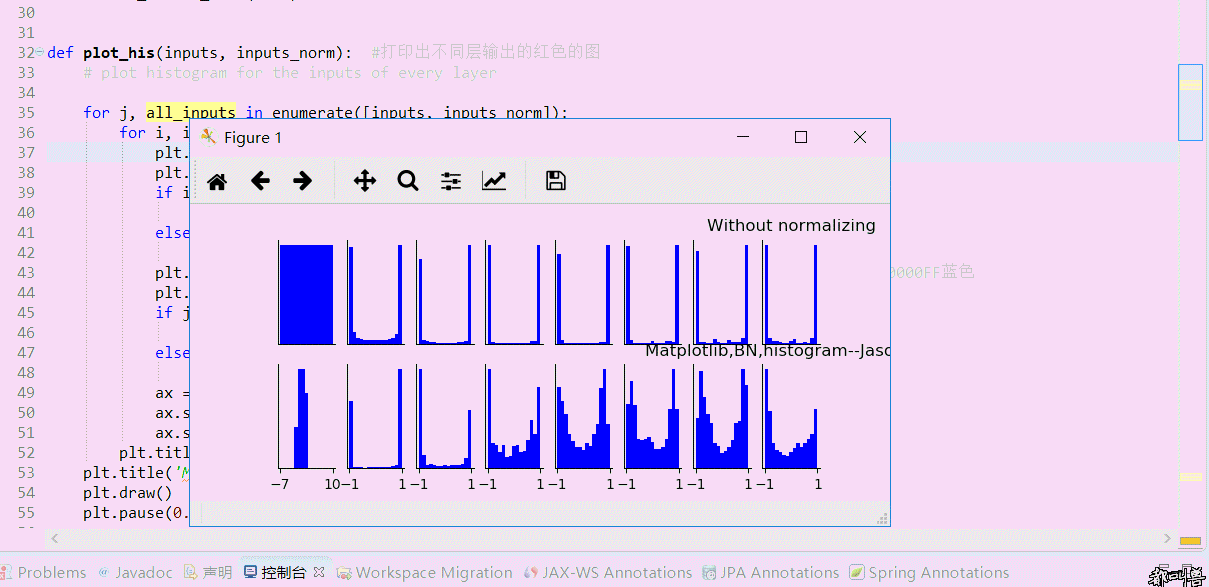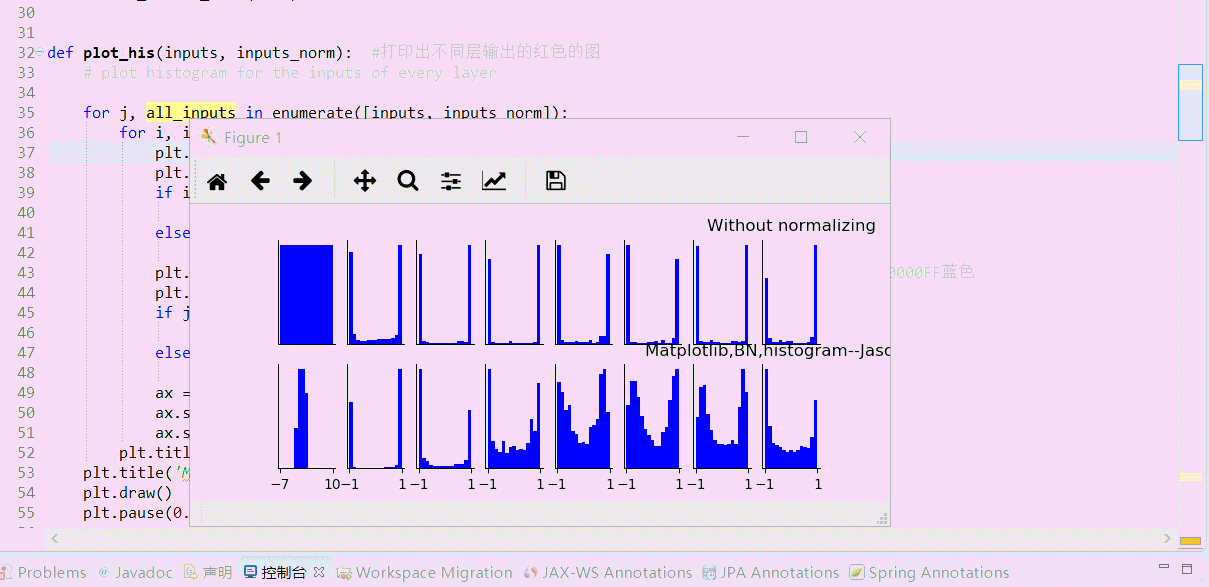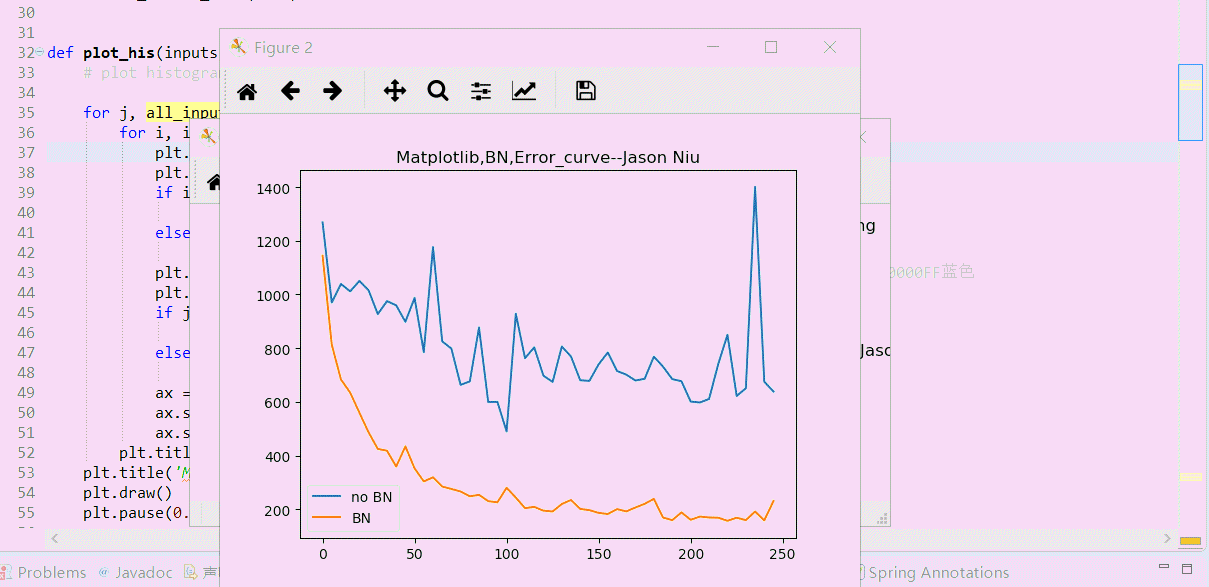
cost_his_norm.append(sess.run(cost_norm, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})) #以下是绘制误差值Cost误差曲线的方法
plt.ioff()
plt.figure()
plt.title('Matplotlib,BN,Error_curve--Jason Niu')
plt.plot(np.arange(len(cost_his))*record_step, np.array(cost_his), label='no BN') # no norm
plt.plot(np.arange(len(cost_his))*record_step, np.array(cost_his_norm), label='BN') # norm
plt.legend()
plt.show()
TF之BN:BN算法对多层中的每层神经网络加快学习QuadraticFunction_InputData+Histogram+BN的Error_curve的更多相关文章
- Batch Normalization的算法本质是在网络每一层的输入前增加一层BN层(也即归一化层),对数据进行归一化处理,然后再进入网络下一层,但是BN并不是简单的对数据进行求归一化,而是引入了两个参数λ和β去进行数据重构
Batch Normalization Batch Normalization是深度学习领域在2015年非常热门的一个算法,许多网络应用该方法进行训练,并且取得了非常好的效果. 众所周知,深度学习是应 ...
- 信息检索中的TF/IDF概念与算法的解释
https://blog.csdn.net/class_brick/article/details/79135909 概念 TF-IDF(term frequency–inverse document ...
- 深度学习归一化:BN、GN与FRN
在深度学习中,使用归一化层成为了很多网络的标配.最近,研究了不同的归一化层,如BN,GN和FRN.接下来,介绍一下这三种归一化算法. BN层 BN层是由谷歌提出的,其相关论文为<Batch No ...
- 任意半径局部直方图类算法在PC中快速实现的框架。
在图像处理中,局部算法一般来说,在很大程度上会获得比全局算法更为好的效果,因为他考虑到了图像领域像素的信息,而很多局部算法可以借助于直方图获得加速.同时,一些常规的算法,比如中值滤波.最大值滤波.最小 ...
- 06 - 从Algorithm 算法派生类中删除ExecuteInformation() 和ExecuteData() VTK 6.0 迁移
在先前的vtk中,如vtkPointSetAlgorithm 等算法派生类中定义了虚方法:ExecuteInformation() 和 ExecuteData().这些方法的定义是为了平稳的从VTK4 ...
- 1145: 零起点学算法52——数组中删数II
1145: 零起点学算法52--数组中删数II Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MB 64bit IO Format: %lldSubmitted: 293 ...
- KMP算法 --- 在文本中寻找目标字符串
KMP算法 --- 在文本中寻找目标字符串 很多时候,为了在大文本中寻找到自己需要的内容,往往需要搜索关键字.这其中就牵涉到字符串匹配的算法,通过接受文本和关键词参数来返回关键词在文本出现的位置.一般 ...
- 剑指Offer——算法复杂度中的O(logN)底数是多少
剑指Offer--算法复杂度中的O(logN)底数是多少 前言 无论是计算机算法概论.还是数据结构书中,关于算法的时间复杂度很多都用包含O(logN)这样的描述,但是却没有明确说logN的底数究竟是多 ...
- 机器学习算法中如何选取超参数:学习速率、正则项系数、minibatch size
机器学习算法中如何选取超参数:学习速率.正则项系数.minibatch size 本文是<Neural networks and deep learning>概览 中第三章的一部分,讲机器 ...
随机推荐
- iOS 高德地图轨迹回放的 思路, 及方法
// 开始,公司要求制作一段跑步轨迹 在地图上的 动画回放, 传入一段经纬度, 开始一想,这不是很简单吗, 高德地图有可以把经纬度转换成坐标点的方法 /** * @brief 将经纬度转换为指定vie ...
- Confluence 6 设置 Oracle 数据库准备
请查看 Supported Platforms 页面来获得 Confluence 系统支持的 Oracle 数据库版本.你需要在安装 Confluence 之前升级你的 Oracle 数据库. 如果你 ...
- 【数据库】MySQL的左连接、右连接和全连接的实现
表student:+----+-----------+------+| id | name | age |+----+-----------+------+| 1 | Jim | 18 || 2 | ...
- SpringMVC文件下载与JSON格式
点击查看上一章 现在JSON这种数据格式是被使用的非常的广泛的,SpringMVC作为目前最受欢迎的框架,它对JSON这种数据格式提供了非常友好的支持,可以说是简单到爆. 在我们SpringMVC中只 ...
- JAVA 编程思想第一章习题
//: ch1.01/IntChar.java package object; import java.util.*; public class IntChar { int x; char y; pu ...
- lightoj1214 大数取模模板
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define maxn 300 #define ll long long ll a,b; ]; ...
- sass基础—具体编译步骤及对应命令:详细
/*基础语法*/h1{ color: red;} /*变量定义*/ $color: red; /*嵌套*/body{ header{ } footer{ }} /*mixin函数*/@mixin al ...
- appium 手势
1.2 appium玩转安卓手机 智能手机发展到今天,形成了一整套有关手势操作的操作习惯,如手指左右上下滑动,及双指缩放,还有手指的滑动解锁,摇晃手机等动作.那么我们怎么在python中利用appiu ...
- AI学习吧-结算中心
结算中心流程 在结算中心中,主要是对用户添加到购物车商品的结算,由于用户可能添加了多个课程,但是,结算时会选择性的进行支付.在结算时会选中课程id,和对应的价格策略.在后台,首先会对用户进行校验,验证 ...
- Android播放图片动画
1.布局文件中添加ImageView <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_fan" android:layout_width="wrap_ ...
