Codeforces 866C Gotta Go Fast - 动态规划 - 概率与期望 - 二分答案
You're trying to set the record on your favorite video game. The game consists of N levels, which must be completed sequentially in order to beat the game. You usually complete each level as fast as possible, but sometimes finish a level slower. Specifically, you will complete the i-th level in either Fi seconds or Si seconds, where Fi < Si, and there's a Pi percent chance of completing it in Fi seconds. After completing a level, you may decide to either continue the game and play the next level, or reset the game and start again from the first level. Both the decision and the action are instant.
Your goal is to complete all the levels sequentially in at most R total seconds. You want to minimize the expected amount of time playing before achieving that goal. If you continue and reset optimally, how much total time can you expect to spend playing?
The first line of input contains integers N and R 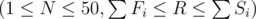 , the number of levels and number of seconds you want to complete the game in, respectively. N lines follow. The ith such line contains integers Fi, Si, Pi (1 ≤ Fi < Si ≤ 100, 80 ≤ Pi ≤ 99), the fast time for level i, the slow time for level i, and the probability (as a percentage) of completing level i with the fast time.
, the number of levels and number of seconds you want to complete the game in, respectively. N lines follow. The ith such line contains integers Fi, Si, Pi (1 ≤ Fi < Si ≤ 100, 80 ≤ Pi ≤ 99), the fast time for level i, the slow time for level i, and the probability (as a percentage) of completing level i with the fast time.
Print the total expected time. Your answer must be correct within an absolute or relative error of 10 - 9.
Formally, let your answer be a, and the jury's answer be b. Your answer will be considered correct, if 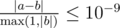 .
.
1 82 8 81
3.14
2 3020 30 803 9 85
31.4
4 31963 79 8979 97 9175 87 8875 90 83
314.159265358
In the first example, you never need to reset. There's an 81% chance of completing the level in 2 seconds and a 19% chance of needing 8 seconds, both of which are within the goal time. The expected time is 0.81·2 + 0.19·8 = 3.14.
In the second example, you should reset after the first level if you complete it slowly. On average it will take 0.25 slow attempts before your first fast attempt. Then it doesn't matter whether you complete the second level fast or slow. The expected time is 0.25·30 + 20 + 0.85·3 + 0.15·9 = 31.4.
题目大意 一个人打游戏,需要不超过$R$秒通过$n$关,第$i$关有$P_{i}$的概率用$F_{i}$秒通过,$\left(1 - P_{i}\right)$的概率用$S_{i}$通过($F_{i} < S_{i}$),通过每一关可以选择重置游戏,然后从头开始,或者去打下一关。问不超过$R$秒通过所有关卡的期望耗时。
转移是显然的。(如果这个都不会,请自定百度“概率dp入门题”)
然后发现转移有环,还要做决策?
然后列方程吧。。开心地发现不会解。
可惜这里是信息学竞赛,不是数学竞赛。由于转移都需要 dp[][] 但是开始不知道它,所以考虑二分它,然后和推出来的 dp[][] 作比较。
经过各种瞎猜和乱搞,可以发现一个神奇的事情
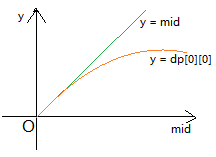
然后就可根据它来确定一次check后,二分的范围。
另外,由于坑人的精度问题,所以最好不要写while (l + eps < r) ,总之我这么写各种因为精度问题的TLE来了。
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#866C
* Accepted
* Time: 62ms
* Memory: 4316k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
;
;
int n, R;
int *fs, *ss;
double *ps;
inline void init() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &R);
fs = )];
ss = )];
ps = )];
; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", fs + i, ss + i);
cin >> ps[i];
ps[i] *= 0.01;
}
}
boolean vis[][];
][];
double dfs(int d, int t, double &mid) {
);
if(vis[d][t]) return f[d][t];
vis[d][t] = true;
f[d][t] = (dfs(d + , t + fs[d + ], mid) + fs[d + ]) * ps[d + ] + (dfs(d + , t + ss[d + ], mid) + ss[d + ]) * ( - ps[d + ]);
if(mid < f[d][t]) f[d][t] = mid;
return f[d][t];
}
double dp(double mid) {
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
, , mid);
}
inline void solve() {
, r = 1e9;
; i < binary_lim; i++) {
;
if(dp(mid) < mid) r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
printf("%.9lf", l);
}
int main() {
init();
solve();
;
}
Codeforces 866C Gotta Go Fast - 动态规划 - 概率与期望 - 二分答案的更多相关文章
- [Codeforces 865C]Gotta Go Fast(期望dp+二分答案)
[Codeforces 865C]Gotta Go Fast(期望dp+二分答案) 题面 一个游戏一共有n个关卡,对于第i关,用a[i]时间通过的概率为p[i],用b[i]通过的时间为1-p[i],每 ...
- Codeforces 865C Gotta Go Fast 二分 + 期望dp (看题解)
第一次看到这种骚东西, 期望还能二分的啊??? 因为存在重置的操作, 所以我们再dp的过程中有环存在. 为了消除环的影响, 我们二分dp[ 0 ][ 0 ]的值, 与通过dp得出的dp[ 0 ][ 0 ...
- bzoj 4318 OSU! - 动态规划 - 概率与期望
Description osu 是一款群众喜闻乐见的休闲软件. 我们可以把osu的规则简化与改编成以下的样子: 一共有n次操作,每次操作只有成功与失败之分,成功对应1,失败对应0,n次操作对应为1 ...
- bzoj 4008 亚瑟王 - 动态规划 - 概率与期望
Description 小 K 不慎被 LL 邪教洗脑了,洗脑程度深到他甚至想要从亚瑟王邪教中脱坑. 他决定,在脱坑之前,最后再来打一盘亚瑟王.既然是最后一战,就一定要打得漂 亮.众所周知,亚瑟王是一 ...
- bzoj 1419 Red is good - 动态规划 - 概率与期望
Description 桌面上有R张红牌和B张黑牌,随机打乱顺序后放在桌面上,开始一张一张地翻牌,翻到红牌得到1美元,黑牌则付出1美元.可以随时停止翻牌,在最优策略下平均能得到多少钱. Input 一 ...
- Codeforces Round #202 (Div. 1) A. Mafia 推公式 + 二分答案
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/348/A A. Mafia time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit p ...
- Codeforces Round #402 (Div. 2) D. String Game(二分答案水题)
D. String Game time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input standard inpu ...
- Codeforces Round #402 (Div. 2) D题 【字符串二分答案+暴力】
D. String Game Little Nastya has a hobby, she likes to remove some letters from word, to obtain anot ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 80 (Rated for Div. 2)D(二分答案,状压检验)
这题1<<M为255,可以logN二分答案后,N*M扫一遍表把N行数据转化为一个小于等于255的数字,再255^2检验答案(比扫一遍表复杂度低),复杂度约为N*M*logN #define ...
随机推荐
- cocos2dx JS 清除缓存重新编译打包安卓apk
复制他人工程时打包出错,无法进行.或者是资源缓存问题需要重新编译删除 proj.android 工程下的三个文件夹 frameworks -> runtime-src -> proj.an ...
- ASP.Net Core 2.2 MVC入门到基本使用系列 (一)(转)
本教程会对基本的.Net Core 进行一个大概的且不会太深入的讲解, 在您看完本系列之后, 能基本甚至熟练的使用.Net Core进行Web开发, 感受到.Net Core的魅力. 本教程知识点大体 ...
- 读书笔记_Effective_C++_条款二:尽量以const, enum, inline替换#define
其实这个条款分成两部分介绍会比较好,第一部分是用const和enum替换不带参的宏,第二部分是用inline替换带参的宏. 第一部分:用const和enum替换不带参宏 宏定义#define发生在预编 ...
- 24.form表单提交的六种方式
form表单提交方式 1.无刷新页面提交表单 表单可实现无刷新页面提交,无需页面跳转,如下,通过一个隐藏的iframe实现,form表单的target设置为iframe的name名称,form提交目标 ...
- PHP 中最全的设计模式(23种)
https://my.oschina.net/botkenni/blog/1603660 PHP 中最全的设计模式(23种) 原 botkenni 发布于 01/07 21:22 字数 8726 阅读 ...
- <8>Lua继承
模拟继承方式 代码: --继承 -- 基类:Person local Person = {} --基类的表 -- 方法 function Person:test() print("Perso ...
- lua学习之循环打印九九乘法表
--第4题 输出99乘法表 function PrintMulitiplyTable() , do local res = {} local str = "" , i do res ...
- python2.7之乱码问题
python 3之后当然不存在乱码问题了.python 2的乱码问题有时就有点头疼了.(代码均为在windows下测试) 示例:保存为test1.py 报错信息如下: 解决办法: 我将代码保存为tes ...
- html5-output的用法
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8&qu ...
- sitecore系统教程之媒体库
您可以管理媒体库中的所有媒体项目,例如要嵌入网页的图像或供访问者下载的图像.媒体库包含所有媒体项目,例如图像,文档,视频和音频文件. 在媒体库中,您可以: 将所有媒体文件保存在一个位置,并将其组织在与 ...
