vmware vSphere 5.5的14个新功能
1.Flash Read Cache

This completely new feature in vSphere 5.5 provides a mechanism for utilizing fast SSD as a Linux host swap cache or to provide improved read speed for a host virtual disk. To make use of this feature, you first have to create a new resource, as shown in the screenshot. Then you must connect to that resource from each VM needing access. For a Linux guest, this would consist of configuring a swap disk to use part of the read cache. Another option would be to enable caching for a VM.
2.Application HA

Also new in vSphere 5.5 is policy-based application monitoring and automatic remediation. Based on vFabric Hyperic, Application HA supports a short list of off-the-shelf applications, including Microsoft SQL Server, SharePoint, IIS, and the Apache Web Server, and makes it possible to attempt a restart when a failure is detected. If the application restart is unsuccessful, the feature will leverage vSphere HA to restart the VM on the same host after a predetermined amount of time. If that process fails, the VM will be restarted on another host.
3.Low latency improvements

VMware has added a number of improvements at both the VM and hypervisor level to help improve overall latency. At the VM level, this consists of a single setting to indicate to vSphere the sensitivity to latency. For high sensitivity applications, the underlying hypervisor can do things like bypass the CPU scheduling algorithms and dedicate one or more CPU sockets exclusively to a single VM. Additional actions include reserving memory for a latency sensitive VMs and disabling networking features, such as coalescing and LRO vNIC support for predictable network response.
4.62TB virtual machine disks

The 2TB limit on VM disks is starting to pinch. With vSphere 5.5, the maximum size for VMDK files increases all the way up to 62TB. Why that particular number you might ask? VMware settled on something smaller than 64TB to allow room for snapshots and any other required services while staying under a 64TB volume size. Existing VMDK files will have to be offline in order to be expanded. The new huge VMDK file size will not be supported in the initial release of the VSAN product, however -- expect that to come at a later date.
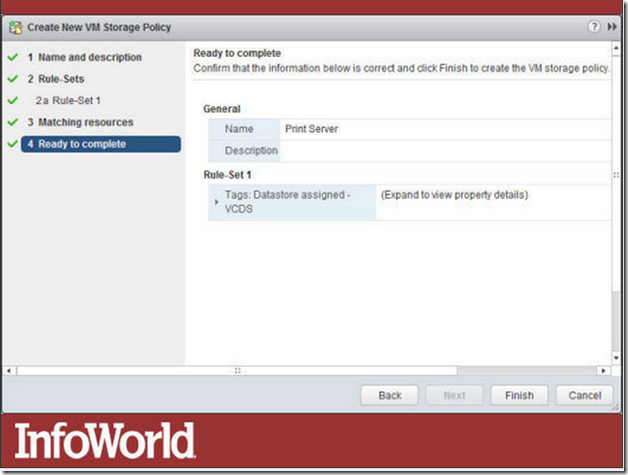
5.Storage tagging
In really large data centers, it can be a challenge to identify the appropriate class of storage for a specific purpose. In this screenshot, you can see the name Print Server being assigned to a new VM Storage Policy. This creates a new policy that can be applied to all new virtual machines needing storage for a print server, making storage provisioning much simpler.
6.Improved LACP support

LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) allows you to aggregate the bandwidth of multiple physical NICs. Whereas vSphere 5.1 supported only one LACP group per distributed switch, severely limiting your aggregation options, vSphere 5.5 supports up to 64. Plus, you can now save LACP configurations as templates to use on other hosts, and you can draw on 22 different hashing algorithms (versus just IP hash in 5.5) to distribute load across links.
7.Port mirroring

Sometimes it becomes necessary to capture the packets going across the network to track down a problem. The latest version of vSphere includes a an enhanced version of the open source packet analyzer tcpdump and a number of options for mirroring ports to capture traffic in a variety of places. You can capture packets from virtual NICs, virtual switches, and uplinks at the host level as well.
8.Traffic filtering

Moving network traffic from host A to host B in a virtual network now resembles what you would expect to see on a physical network with sophisticated switches. The vSphere 5.5 distributed switch now includes the ability to shape and direct Layer 3 network traffic using the Differentiated Services Code Point field in the IP packet header. It's also known as DiffServ and acts like the access control list feature found on many high-end physical switches. Individual rules can be configured on a distributed switch to handle specific types of traffic in order to provide a higher quality of service when necessary.
9.vCenter Server improvements

The vSphere Web Client has seen a number of enhancements in this release. Many reflect user feedback, such as the “10 most recent objects” list shown in the screenshot. Other improvements to the user experience include the new drag and drop support and the ability to filter search results for large installations.
The vCenter Server Appliance, meanwhile, gets a scalability boost. Previous versions supported a limited number of hosts and VMs, but these limits have been increased to 500 hosts and up to 5,000 VMs.
VMware has also poured a good deal of effort into making vCenter Single Sign-On simpler to install and easier to scale across multiple vCenter Server instances. Version 5.5 will even include a suite of diagnostic tools.
10.Multiple point-in-time replicas

Previous versions of vSphere Replication kept only the most recent copy of a virtual machine. Version 5.5 can keep up to 24 historical snapshots. You could retain one replica per day for 24 days, or one per hour for 24 hours -- however you want to slice it. Recovery always draws on the most recent copy, but from there, you can use the snapshot manager to revert to any other point in time.
11.ACPI support

One of the limitations of previous versions of VMware virtual machines was the small number of virtual devices supported. The vSphere 5.5 release introduces Virtual Hardware 10, which adds SATA-based virtual device nodes via AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) support. AHCI support is required for OS X guests going forward due to Apple’s elimination of support for IDE devices. It also makes it possible to connect up to 120 devices per VM.
12.Support for new graphics devices

Virtual Hardware 10 also adds support for a number of new graphic capabilities. First up is support for both AMD and Intel GPUs. Included in this update is the ability to vMotion a VM between disparate hardware platforms including disparate GPU support. This previously required similar hardware for the vMotion to work. Also included in this release is support for OpenGL version 2.1, which is the default graphics API used in popular Linux distributions including Fedora 17 and Ubuntu 12.
vmware vSphere 5.5的14个新功能的更多相关文章
- VMware vsphere Hypervisor、VMware vsphere和VMware Workstation小记
VMware Workstation软件需要依赖于宿主操作系统之上. VMware vSphere是VMware公司推出一套服务器虚拟化解决方案,它是可以直接独立安装和运行在祼机上的系统. VMwar ...
- 超详细 Java 15 新功能介绍
点赞再看,动力无限.微信搜「程序猿阿朗 」,认认真真写文章. 本文 Github.com/niumoo/JavaNotes 和 未读代码博客 已经收录,有很多知识点和系列文章. Java 15 在 2 ...
- Java 17 新功能介绍(LTS)
点赞再看,动力无限.Hello world : ) 微信搜「程序猿阿朗 」. 本文 Github.com/niumoo/JavaNotes 和 未读代码博客 已经收录,有很多知识点和系列文章. Jav ...
- VMware vSphere 5.1 简介与安装
虚拟化系列-VMware vSphere 5.1 简介与安装 标签: 虚拟化 esxi5.1 VMware vSphere 5.1 原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 . ...
- [转载]【虚拟化系列】VMware vSphere 5.1 网络管理
转载自:http://mabofeng.blog.51cto.com/2661587/1020375 网络是VMware vSphere 5.1的基础,所有虚拟机都需要网络来进行通信.如果将所有的虚拟 ...
- [转载]【虚拟化系列】VMware vSphere 5.1 虚拟机管理
转载自:http://mabofeng.blog.51cto.com/2661587/1019497 在上一博文中我们安装了强大的VMware vCenter管理中心,通过VMware vSphere ...
- [转载]【虚拟化系列】VMware vSphere 5.1 简介与安装
转载自:http://mabofeng.blog.51cto.com/2661587/1017680 一. VMware vSphere 5.1简介 vSphere是VMware推 ...
- VMware vSphere学习整理
知识点整理 内存选择 一般来说,每个虚拟机需要的内存在1~4GB甚至更多,还要为VMware ESXi预留一部分内存 2个6核的2U服务器配置64GB内存,4个6核或8核心的4U服务器配置128GB或 ...
- 【虚拟化系列】VMware vSphere 5.1 网络管理
网络是VMware vSphere 5.1的基础,所有虚拟机都需要网络来进行通信.如果将所有的虚拟机都看成是物理机,则在网络拓扑上,需要网卡和交换机等不同的网络连接设备和方式.而在虚拟化中,这些 ...
随机推荐
- Zookeeper单机安装部署与配置(二)
在上篇博客中简单介绍了Zookeeper的特点和应用场景,详情可参考:<Zookeeper简介(一)>,那么这篇博客我们介绍一下关于Zookeeper的单机模式安装步骤与配置. 环境准备 ...
- Android SDK安装及配置模拟器
环境搭建 1.安装JDK 2.下载Android sdk exe格式和zip格式都可以 3.安装installer_r24.4.1-windows.exe文件,里面有两个应用程序: "SDK ...
- hdu 2197 求长度为n的本原串 (快速幂+map)
Problem Description由0和1组成的串中,不能表示为由几个相同的较小的串连接成的串,称为本原串,有多少个长为n(n<=100000000)的本原串?答案mod2008.例如,10 ...
- 自动化部署之gitlab权限管理--issue管理
一.删除测试项目 先进入项目,选择编辑项目 二.拉取到最下方,移除项目 三 输入你要删除的项目名称 二 创建Group,User,Project 2.1 创建一个组,组名为java Group pat ...
- MSF《构建之法》阅读笔记5
第七章 MSF MSF是一种软件开发方法,MSF原则包括1推动信息共享和沟通,2为共同的远景而工作,3充分授权和信任,4各司其职,对项目共同负责,5交付增量的价值,6保持敏捷,预期和适应变化,7投资质 ...
- MySQL 8.0 Docker使用注解
PUBLIC | AUTOMATED BUILD cytopia/mysql-8.0 Last pushed: 8 months ago Repo Info Tags Dockerfile Build ...
- HDU 1503【LCS】(字符串合并输出)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1503 题目大意: 给两个字符串,组成一个长度尽可能小的字符串,它包含上述两个字符串,且原字符串中的字符 ...
- P2789 直线交点数
P2789 直线交点数分成两种情况,一种是平行直线,一种是自由直线,在自由直线中可以存在平行直线,但是不能和第一组的直线平行.自由直线和平行直线的交点是i*(n-i). #include<ios ...
- Python 函数装饰器
首次接触到装饰器的概念,太菜啦! Python 装饰器可以大大节省代码的编写量,提升代码的重复使用率.函数装饰器其本质也是一个函数,我们可以把它理解为函数中定义了一个子函数. 例如我们有这么一个需求, ...
- python数据分析之pandas数据选取:df[] df.loc[] df.iloc[] df.ix[] df.at[] df.iat[]
1 引言 Pandas是作为Python数据分析著名的工具包,提供了多种数据选取的方法,方便实用.本文主要介绍Pandas的几种数据选取的方法. Pandas中,数据主要保存为Dataframe和Se ...