from组件
目录
- 一.生成页面可用的 HTML标签
- 二.对用户提交的数据进行校验
- 三. form 综合示例:
- 四. modelform(自动根据字段生成表单)
- 五.modelformset
1.form 所有内置字段

Field
required=True, 是否允许为空
widget=None, HTML插件
label=None, 用于生成Label标签或显示内容
initial=None, 初始值
help_text='', 帮助信息(在标签旁边显示)
error_messages=None, 错误信息 {'required': '不能为空', 'invalid': '格式错误'}
validators=[], 自定义验证规则
localize=False, 是否支持本地化
disabled=False, 是否可以编辑
label_suffix=None Label内容后缀
CharField(Field)
max_length=None, 最大长度
min_length=None, 最小长度
strip=True 是否移除用户输入空白
IntegerField(Field)
max_value=None, 最大值
min_value=None, 最小值
FloatField(IntegerField)
...
DecimalField(IntegerField)
max_value=None, 最大值
min_value=None, 最小值
max_digits=None, 总长度
decimal_places=None, 小数位长度
BaseTemporalField(Field)
input_formats=None 时间格式化
DateField(BaseTemporalField) 格式:2015-09-01
TimeField(BaseTemporalField) 格式:11:12
DateTimeField(BaseTemporalField)格式:2015-09-01 11:12
DurationField(Field) 时间间隔:%d %H:%M:%S.%f
...
RegexField(CharField)
regex, 自定制正则表达式
max_length=None, 最大长度
min_length=None, 最小长度
error_message=None, 忽略,错误信息使用 error_messages={'invalid': '...'}
EmailField(CharField)
...
FileField(Field)
allow_empty_file=False 是否允许空文件
ImageField(FileField)
...
注:需要PIL模块,pip3 install Pillow
以上两个字典使用时,需要注意两点:
- form表单中 enctype="multipart/form-data"
- view函数中 obj = MyForm(request.POST, request.FILES)
URLField(Field)
...
BooleanField(Field)
...
NullBooleanField(BooleanField)
...
ChoiceField(Field)
...
choices=(), 选项,如:choices = ((0,'上海'),(1,'北京'),)
required=True, 是否必填
widget=None, 插件,默认select插件
label=None, Label内容
initial=None, 初始值
help_text='', 帮助提示
ModelChoiceField(ChoiceField)
... django.forms.models.ModelChoiceField
queryset, # 查询数据库中的数据
empty_label="---------", # 默认空显示内容
to_field_name=None, # HTML中value的值对应的字段
limit_choices_to=None # ModelForm中对queryset二次筛选
ModelMultipleChoiceField(ModelChoiceField)
... django.forms.models.ModelMultipleChoiceField
TypedChoiceField(ChoiceField)
coerce = lambda val: val 对选中的值进行一次转换
empty_value= '' 空值的默认值
MultipleChoiceField(ChoiceField)
...
TypedMultipleChoiceField(MultipleChoiceField)
coerce = lambda val: val 对选中的每一个值进行一次转换
empty_value= '' 空值的默认值
ComboField(Field)
fields=() 使用多个验证,如下:即验证最大长度20,又验证邮箱格式
fields.ComboField(fields=[fields.CharField(max_length=20), fields.EmailField(),])
MultiValueField(Field)
PS: 抽象类,子类中可以实现聚合多个字典去匹配一个值,要配合MultiWidget使用
SplitDateTimeField(MultiValueField)
input_date_formats=None, 格式列表:['%Y--%m--%d', '%m%d/%Y', '%m/%d/%y']
input_time_formats=None 格式列表:['%H:%M:%S', '%H:%M:%S.%f', '%H:%M']
FilePathField(ChoiceField) 文件选项,目录下文件显示在页面中
path, 文件夹路径
match=None, 正则匹配
recursive=False, 递归下面的文件夹
allow_files=True, 允许文件
allow_folders=False, 允许文件夹
required=True,
widget=None,
label=None,
initial=None,
help_text=''
GenericIPAddressField
protocol='both', both,ipv4,ipv6支持的IP格式
unpack_ipv4=False 解析ipv4地址,如果是::ffff:192.0.2.1时候,可解析为192.0.2.1, PS:protocol必须为both才能启用
SlugField(CharField) 数字,字母,下划线,减号(连字符)
...
UUIDField(CharField) uuid类型
复制代码
内置字段

2.form常用字段和插件
① initial (初始值 input框里面的初始值)

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
username = forms.CharField(
min_length=8,
label="用户名",
initial="张三" # 设置默认值
)
pwd = forms.CharField(min_length=6, label="密码")

②error_messages (重写错误信息)

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
username = forms.CharField(
min_length=8,
label="用户名",
initial="张三",
error_messages={
"required": "不能为空",
"invalid": "格式错误",
"min_length": "用户名最短8位"
}
)
pwd = forms.CharField(min_length=6, label="密码")

③ password

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
...
pwd = forms.CharField(
min_length=6,
label="密码",
widget=forms.widgets.PasswordInput(attrs={'class': 'c1'}, render_value=True)
)

④ radioselect (单radio值为字符串)

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
username = forms.CharField( #其他选择框或者输入框,基本都是在这个CharField的基础上通过插件来搞的
min_length=8,
label="用户名",
initial="张三",
error_messages={
"required": "不能为空",
"invalid": "格式错误",
"min_length": "用户名最短8位"
}
)
pwd = forms.CharField(min_length=6, label="密码")
gender = forms.fields.ChoiceField(
choices=((1, "男"), (2, "女"), (3, "保密")),
label="性别",
initial=3,
widget=forms.widgets.RadioSelect()
)

⑤ 单选 select

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
...
hobby = forms.fields.ChoiceField(
choices=((1, "篮球"), (2, "足球"), (3, "双色球"), ),
label="爱好",
initial=3,
widget=forms.widgets.Select()
)

⑥多选select

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
...
hobby = forms.fields.MultipleChoiceField(
choices=((1, "篮球"), (2, "足球"), (3, "双色球"), ),
label="爱好",
initial=[1, 3],
widget=forms.widgets.SelectMultiple()
)

⑦ 单选 checkbox

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
...
keep = forms.fields.ChoiceField(
label="是否记住密码",
initial="checked",
widget=forms.widgets.CheckboxInput()
)

⑧ 多选 checkbox

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
...
hobby = forms.fields.MultipleChoiceField(
choices=((1, "篮球"), (2, "足球"), (3, "双色球"),),
label="爱好",
initial=[1, 3],
widget=forms.widgets.CheckboxSelectMultiple()
)

⑨choice (字段注意事项)
方式一:

from django.forms import Form
from django.forms import widgets
from django.forms import fields
class MyForm(Form):
user = fields.ChoiceField(
# choices=((1, '上海'), (2, '北京'),),
initial=2,
widget=widgets.Select
)
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(MyForm,self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# self.fields['user'].choices = ((1, '上海'), (2, '北京'),)
# 或
self.fields['user'].choices = models.Classes.objects.all().values_list('id','caption')

方式二:

from django import forms
from django.forms import fields
from django.forms import models as form_model
class FInfo(forms.Form):
authors = form_model.ModelMultipleChoiceField(queryset=models.NNewType.objects.all()) # 多选
# authors = form_model.ModelChoiceField(queryset=models.NNewType.objects.all()) # 单选

二.对用户提交的数据进行校验
1.RegexValidator 验证器

from django.forms import Form
from django.forms import widgets
from django.forms import fields
from django.core.validators import RegexValidator
class MyForm(Form):
user = fields.CharField(
validators=[RegexValidator(r'^[0-9]+$', '请输入数字'), RegexValidator(r'^159[0-9]+$', '数字必须以159开头')],
)

2.自定义验证函数

import re
from django.forms import Form
from django.forms import widgets
from django.forms import fields
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
# 自定义验证规则
def mobile_validate(value):
mobile_re = re.compile(r'^(13[0-9]|15[012356789]|17[678]|18[0-9]|14[57])[0-9]{8}$')
if not mobile_re.match(value):
raise ValidationError('手机号码格式错误') #自定义验证规则的时候,如果不符合你的规则,需要自己发起错误
class PublishForm(Form):
title = fields.CharField(max_length=20,
min_length=5,
error_messages={'required': '标题不能为空',
'min_length': '标题最少为5个字符',
'max_length': '标题最多为20个字符'},
widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={'class': "form-control",
'placeholder': '标题5-20个字符'}))
# 使用自定义验证规则
phone = fields.CharField(validators=[mobile_validate, ],
error_messages={'required': '手机不能为空'},
widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={'class': "form-control",
'placeholder': u'手机号码'}))
email = fields.EmailField(required=False,
error_messages={'required': u'邮箱不能为空','invalid': u'邮箱格式错误'},
widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={'class': "form-control", 'placeholder': u'邮箱'}))

3.钩子方法
① 局部钩子
我们在Fom类中定义 clean_字段名() 方法,就能够实现对特定字段进行校验。

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
username = forms.CharField(
min_length=8,
label="用户名",
initial="张三",
error_messages={
"required": "不能为空",
"invalid": "格式错误",
"min_length": "用户名最短8位"
},
widget=forms.widgets.TextInput(attrs={"class": "form-control"})
)
...
# 定义局部钩子,用来校验username字段,之前的校验股则还在,给你提供了一个添加一些校验功能的钩子
def clean_username(self):
value = self.cleaned_data.get("username")
if "666" in value:
raise ValidationError("光喊666是不行的")
else:
return value

②全局钩子 (如在 '确认密码' 中用到)
我们在Fom类中定义 clean() 方法,就能够实现对字段进行全局校验,字段全部验证完,
局部钩子也全部执行完之后,执行这个全局钩子校验。

class LoginForm(forms.Form):
...
password = forms.CharField(
min_length=6,
label="密码",
widget=forms.widgets.PasswordInput(attrs={'class': 'form-control'}, render_value=True)
)
re_password = forms.CharField(
min_length=6,
label="确认密码",
widget=forms.widgets.PasswordInput(attrs={'class': 'form-control'}, render_value=True)
)
...
# 定义全局的钩子,用来校验密码和确认密码字段是否相同,执行全局钩子的时候,cleaned_data里面肯定是有了通过前面验证的所有数据
def clean(self):
password_value = self.cleaned_data.get('password')
re_password_value = self.cleaned_data.get('re_password')
if password_value == re_password_value:
return self.cleaned_data #全局钩子要返回所有的数据
else:
self.add_error('re_password', '两次密码不一致') #在re_password这个字段的错误列表中加上一个错误,并且clean_data里面会自动清除这个re_password的值,所以打印clean_data的时候会看不到它
raise ValidationError('两次密码不一致')

三. form 综合示例:
1. 使用form组件建立HTML标签,可在views.py文件中
也可在appo1 下建立一个.py文件(更整洁)

2.在views.py 文件中

from django.shortcuts import render
from app01 import models
# Create your views here.
from app01 import form_test #引入form 表单建立验证的文件
def register(request):
form_obj = form_test.MyForm() #引入建立form表单的对象
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request,'register_page.html',{'form_obj':form_obj})
else:
#用户提交过来的数据
# print(request.POST)
form_obj = form_test.MyForm(request.POST)
# print(form_obj.is_valid())
# print(form_obj.cleaned_data)
print('>>>>',form_obj.fields)
if form_obj.is_valid():
print(form_obj.cleaned_data) #获取验证通过的数据
# else:
# print(form_obj.errors.as_data()) #拿错误信息
# print(form_obj.errors.as_data())
# print(form_obj)
# username = request.POST.get('username')
# password = request.POST.get('password')
# print(username,password)
# if username == ''
# print(form_obj.cleaned_data)
return render(request,'register_page.html',{'form_obj':form_obj})

3.在form_test.py 文件中

from django import forms
from django.forms import ValidationError
from django.core.validators import RegexValidator
from app01 import models
import re
def mobile_validate(value):
mobile_re = re.compile(r'^1[0-9]*$')
if not mobile_re.match(value):
raise ValidationError('手机号码格式错误')
#自定义验证规则的时候,如果不符合你的规则,需要自己发起错误
class MyForm(forms.Form):
uname = forms.CharField(
required=True,
label='用户名:',
# initial='张三', #输入框中的默认值
min_length=6, #最小长度
strip=True, #去掉两侧空白
max_length=8, #最大长度
# validators=[mobile_validate,],
validators=[RegexValidator(r'^[0-9]+$', '请输入数字'), RegexValidator(r'^159[0-9]+$', '数字必须以159开头')],
# disabled=True,
error_messages={
'required':'用户名不能为空',
'min_length':'你太短了,',
'max_length':'太长了',
},
# widget=forms.TextInput(attrs={'class':'form-control'}),
help_text='请输入用户名,不能短于6个字符,不能超过8个字符!'
)
pword = forms.CharField(
label='密码:',
# required=False,
# widget=forms.PasswordInput(attrs={'class':'form-control'}),
widget=forms.PasswordInput(),
)
re_pword = forms.CharField(
label='确认密码:',
# required=False,
# widget=forms.PasswordInput(attrs={'class':'form-control'}),
widget=forms.PasswordInput(),
)
#局部钩子,在自定义的form类里面针对每个字段都可以写一些定制的规则,def clean_字段名(self):
def clean_pword(self):
data1 = self.cleaned_data.get('pword')
if '666' in data1:
raise ValidationError('你还不够6,包含敏感词汇')
else:
return data1
# def clean_uname(self):
#
# data1 = self.cleaned_data.get('uname')
# if '666' in data1:
# raise ValidationError('你还不够6,包含敏感词汇')
# else:
# return data1
# data1 = self.cleaned_data.get('pword')
# data2 = self.cleaned_data.get('re_pword')
# if data1 == data2:
#全局钩子
def clean(self):
p1 = self.cleaned_data.get('pword')
p2 = self.cleaned_data.get('re_pword')
if p1 == p2:
return self.cleaned_data
else:
self.add_error('re_pword','和你上面输入的密码不同@@@')
# raise ValidationError('两次输入的密码不同!!!')
# sex = forms.CharField(
# label='请选择性别:',
# widget=forms.RadioSelect(
# choices=((1,'男'),(2,'女'),('3','二椅子')),
# )
# )
# sex = forms.ChoiceField(
#
# choices=(('1', '男'), ('2', '女'), ('3', '二椅子')),
# # widget=forms.RadioSelect,
# # widget=forms.CheckboxSelectMultiple,
# # widget=forms.CheckboxSelectMultiple,
# widget=forms.SelectMultiple,
#
# )
userinfo = forms.ModelMultipleChoiceField(
label='请选择作者:',
queryset=models.Author.objects.all(),
)
email = forms.EmailField()

4.在 .html 文件中

{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Bootstrap 101 Template</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css' %}">
</head>
<body>
<form action="{% url 'register' %}" method="post" novalidate> # novalidate : 自定义错误提示
{% csrf_token %}
{# {{ form_obj.as_p }}#}
{# <p>#}
{# 所有字段错误汇总#}
{# {{ form_obj.errors }}#}
{# </p>#}
<div>
<div>
{{ form_obj.uname.label }} #引入 '用户民'
{{ form_obj.uname }} #引入输入框
<span style="color: red;font-size: 12px;">
{{ form_obj.uname.errors.0 }} #错误提示
</span>
</div>
<div>
{{ form_obj.uname.help_text }} #输入提示
</div>
</div>
<p>
{{ form_obj.pword.label }}
{{ form_obj.pword }}
<span style="color: red;font-size: 12px;">
{{ form_obj.pword.errors.0 }}
</span>
</p>
<p>
{{ form_obj.re_pword.label }} #确认密码
{{ form_obj.re_pword }}
<span style="color: red;font-size: 12px;">
{{ form_obj.re_pword.errors.0 }}
</span>
</p>
<p>
------ {{ form_obj.errors }}
</p>
{# <p>#}
{# {{ form_obj.sex.label }}#}
{# {{ form_obj.sex }}#}
{# <span style="color: red;font-size: 12px;">#}
{# {{ form_obj.sex.errors.0 }}#}
{# </span>#}
{# </p>#}
<p>
{{ form_obj.userinfo.label }}
{{ form_obj.userinfo }}
{{ form_obj.userinfo.errors.0 }}
</p>
<p>
{{ form_obj.email.label }}
{{ form_obj.email }}
{{ form_obj.email.errors.0 }}
</p>
<p>
<button>提交</button>
</p>
</form>
</body>
</html>

四. modelform(自动根据字段生成表单)
1.常用属性

class XXXModelForm(ModelForm)
a. class Meta:
model, # 对应Model的
fields=None, # 字段
exclude=None, # 排除字段
labels=None, # 提示信息
help_texts=None, # 帮助提示信息
widgets=None, # 自定义插件
error_messages=None, # 自定义错误信息(整体错误信息from django.core.exceptions import NON_FIELD_ERRORS)
field_classes=None # 自定义字段类 (也可以自定义字段)
localized_fields=('birth_date',) # 本地化,如:根据不同时区显示数据
如:
数据库中
2016-12-27 04:10:57
setting中的配置
TIME_ZONE = 'Asia/Shanghai'
USE_TZ = True
则显示:
2016-12-27 12:10:57
b. 验证执行过程
is_valid -> full_clean -> 钩子 -> 整体错误
c. 字典字段验证
def clean_字段名(self): # 可以抛出异常 # from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError return "新值" d. 用于验证 model_form_obj = XXOOModelForm() model_form_obj.is_valid() model_form_obj.errors.as_json() model_form_obj.clean() model_form_obj.cleaned_data e. 用于创建 model_form_obj = XXOOModelForm(request.POST) #### 页面显示,并提交 ##### # 默认保存多对多 obj = form.save(commit=True) # 不做任何操作,内部定义 save_m2m(用于保存多对多) obj = form.save(commit=False) obj.save() # 保存单表信息 obj.save_m2m() # 保存关联多对多信息 f. 用于更新和初始化 obj = model.tb.objects.get(id=1) model_form_obj = XXOOModelForm(request.POST,instance=obj) ...
2.示例
在项目中新建立forms.py 文件

from django import forms
# 注册的form
class RegForm(forms.ModelForm):
password = forms.CharField(widget=forms.PasswordInput, label='密码', min_length=6) # 重写默认字段
re_password = forms.CharField(widget=forms.PasswordInput, label='确认密码', min_length=6) # 新增字段
class Meta:
model = models.UserProfile # 指定model
fields = '__all__' #所有字段 ['username','password'] # 指定字段
exclude = ['is_active']
labels = {
'username': '用户名' # 两种设置label方式,另一种是设置 verbose_name=' '
widgets = { 'username': forms.TextInput(attrs={'class': 'form-control', 'placeholder': '用户名'}), # 'password': forms.PasswordInput(attrs={'class': 'form-control'})
} error_messages = {
'min_length': '不能少于6位' }
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) # 自定义操作 for field in self.fields.values(): field.widget.attrs.update({'class': 'form-control'})
def clean(self): # 全局钩子 pwd = self.cleaned_data.get('password', '') re_pwd = self.cleaned_data.get('re_password', '')
if pwd == re_pwd: # 密码加密 md5 = hashlib.md5() md5.update(pwd.encode('utf-8')) pwd = md5.hexdigest()
self.cleaned_data['password'] = pwd return self.cleaned_data # 两次密码不一致 self.add_error('re_password', '两次密码不一致!!') raise ValidationError('两次密码不一致')

在view.py中进行实例化(操作更简单)

from crm.froms import RegForm #引入文件
# 注册
def reg(request):
# 判断请求方式
if request.method == 'POST':
form_obj = RegForm(request.POST)
# 对数据进行校验
if form_obj.is_valid():
form_obj.save()
return redirect(reverse('login'))
else:
form_obj = RegForm() #实例化
return render(request, 'reg.html', {'form_obj': form_obj})

1.对多个对象直接进行编辑和保存
2.示例:
①在forms.py 文件中(与modelform相同)

from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
# BootstropFormclass BSForm(forms.ModelForm): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) # 自定义操作 for field in self.fields.values(): if not isinstance(field, forms.BooleanField): # field.widget.attrs['class'] = 'form-control' field.widget.attrs.update({'class': 'form-control'})
# 学习记录的formclass StudyRecordForm(BSForm): class Meta: model = models.StudyRecord fields = "__all__"
def clean_note(self): #局部钩子 note = self.cleaned_data.get('note', '') if not note: note = '' if '666' in note: raise ValidationError('不能太6')
return note

②在view.py 文件中

from crm.froms import StudyRecordForm
from django.forms import modelformset_factory
# 展示学习记录
def study_record_list(request, course_record_id):
FormSet = modelformset_factory(models.StudyRecord, StudyRecordForm, extra=0)
#注意格式
formset = FormSet(queryset=models.StudyRecord.objects.filter(course_record_id=course_record_id))
#注意格式
if request.method == 'POST':
formset = FormSet(request.POST)
if formset.is_valid():
formset.save()
return redirect(reverse('study_record_list', args=(course_record_id,)))
return render(request, 'teacher/study_record_list.html', {'formset': formset})

③.在 . html 文件中

{% extends 'layout.html' %}
{% block content %}
{% load my_tags %}
<div>
</div>
<form action="" method="get" class="form-inline pull-right">
<input type="text" name="query" class="form-control">
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-primary">搜索</button>
</form>
<form action="" method="post" class="form-inline">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ formset.management_form }} #必带
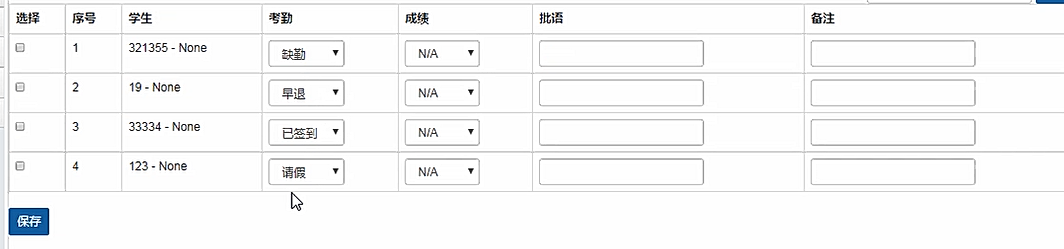
<table class="table table-bordered table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>选择</th>
<th>序号</th>
<th>学生</th>
<th>考勤</th>
<th>成绩</th>
<th>批语</th>
<th>备注</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for form in formset %}
<tr>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="{{ course_record.pk }}">
</td>
{{ form.id }} #必带
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ form.instance.student }}</td>
<td>{{ form.attendance }}</td>
<td>{{ form.score }}</td>
<td>{{ form.homework_note }}</td>
<td>{{ form.note }}</td>
<span style="display: none"> {{ form.student }} {{ form.course_record }} </span>
#必带
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-primary">保存</button>
</form>
{% endblock %}

from组件的更多相关文章
- ExtJS 4.2 评分组件
上一文章是扩展ExtJS自带的Date组件.在这里将创建一个评分组件. 目录 1. 介绍 2. 示例 3. 资源下载 1. 介绍 代码参考的是 Sencha Touch 2上的一个RatingStar ...
- react组件的生命周期
写在前面: 阅读了多遍文章之后,自己总结了一个.一遍加强记忆,和日后回顾. 一.实例化(初始化) var Button = React.createClass({ getInitialState: f ...
- react-router 组件式配置与对象式配置小区别
1. react-router 对象式配置 和 组件式配置 组件式配置(Redirect) ----对应---- 对象式配置(onEnter钩子) IndexRedirect -----对应-- ...
- Angular2入门系列教程3-多个组件,主从关系
上一篇 Angular2项目初体验-编写自己的第一个组件 好了,前面简单介绍了Angular2的基本开发,并且写了一个非常简单的组件,这篇文章我们将要学会编写多个组件并且有主从关系 现在,假设我们要做 ...
- Angular2入门系列教程2-项目初体验-编写自己的第一个组件
上一篇 使用Angular-cli搭建Angular2开发环境 Angular2采用组件的编写模式,或者说,Angular2必须使用组件编写,没有组件,你甚至不能将Angular2项目启动起来 紧接着 ...
- .NET Core 首例 Office 开源跨平台组件(NPOI Core)
前言 最近项目中,需要使用到 Excel 导出,找了一圈发现没有适用于 .NET Core的,不依赖Office和操作系统限制的 Office 组件,于是萌生了把 NPOI 适配并移植到 .NET C ...
- .NetCore中的日志(1)日志组件解析
.NetCore中的日志(1)日志组件解析 0x00 问题的产生 日志记录功能在开发中很常用,可以记录程序运行的细节,也可以记录用户的行为.在之前开发时我一般都是用自己写的小工具来记录日志,输出目标包 ...
- BootStrap_02之全局样式及组件
1.BootStrap指定的四种屏幕尺寸: ①超大PC屏幕--lg(large):w>=1200px: ②中等PC屏幕--md(medium):1200px>w>=992px: ③P ...
- ExtJS 4.2 组件介绍
目录 1. 介绍 1.1 说明 1.2 组件分类 1.3 组件名称 1.4 组件结构 2. 组件的创建方式 2.1 Ext.create()创建 2.2 xtype创建 1. 介绍 1.1 说明 Ex ...
- ExtJS 4.2 组件的查找方式
组件创建了,就有方法找到这些组件.在DOM.Jquery都有各自的方法查找元素/组件,ExtJS也有自己独特的方式查找组件.元素.本次从全局查找.容器内查找.form表单查找.通用组件等4个方面介绍组 ...
随机推荐
- springboot 热部署
1 pom文件添加 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId& ...
- servlet操作本地文件汇总: 判断文件是否存在;文件重命名;文件复制; 获取文件属性信息,转成Json对象; 获取指定类型的文件; 查找替换.txt中的文本
package servlet; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; ...
- 初读"Thinking in Java"读书笔记之第三章 --- 操作符
更简单的打印语句 导入自己编写的静态类库,即可使用print();打印 使用Java操作符 操作符:+,-,*,/,=,==,!=,+=,?:,%等 几乎所有操作符都只能操作"基本类型&qu ...
- enquire.js-响应css媒体查询的轻量级javascript库
轻量,没有依赖. 安装: npm install enquire.js API: enquire.register(mediaQuery, handler). mediaQuery: 字符串,需要响应 ...
- Burpsuite安全测试测试指导
1 Burpsuite简介 Burpsuite是一款安全领域非常重要的Web扫描工具(或者说是平台),它用于攻击Web应用程序.在Burp Suite上集成了各种扫描工具插件,各个集成插件可以组 ...
- RPC 知识科普一下
RPC概念及分类 RPC全称为Remote Procedure Call,翻译过来为“远程过程调用”.目前,主流的平台中都支持各种远程调用技术,以满足分布式系统架构中不同的系统之间的远程通信和相互调用 ...
- clickhouse在Linux上的安装部署
$ sudo apt-get install clustershell #输入你的管理员密码 $ cd /etc/clustershell $ sudo gedit groups #在文件中添加如下内 ...
- SpringBoot项目如何打War包
首先,需要添加Tomcat启动依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <art ...
- ARM内核单片机Bootloader中断向量重定位问题
Bootloader中断向量重定位问题 1.Bootloader程序在内核Cortex-M0+内核中运行时需要进行地址跳转执行应用程序主程序,此时就涉及到了中断向量重定位问题,以下截图为单片机启动文件 ...
- WebService中用CXF框架的wsdl部署生成客户端代码时,使用cmd命令口出现wsimport不是内部或外部命令的问题
网上有很多,都不好用,这个立竿见影的 set JAVA_HOME = *:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_181(此处为自己jdk的安装路径) set CLASSPATH = ...
