为什么KVM计算机点无故重启?
一.故障1:机器hangs
本地一台cloudstack计算节点无故连不上了,cloudstack也坏了,后查看有一台系统虚拟机在这台计算节点上,导致cs挂了。去找到这台机器后,发现这台机器卡住了,重启后卡在starting udev,等好久也不行,即使进入单用户也是一样,重启很多次也是卡在这。最后查到一篇文章,原话:
Remove quiet from the kernel command line and you should get enough output to see the cause of the hang.
然后进入系统菜单,在编辑kernel行,quiet静默模式。相当于设置"loglevel=4"(WARNING)。将quiet删除后,等待进入系统。大概一个小时后,进去系统了,能ssh了,问题解决了一个,得查一下机器为什么重启。
二.故障2:kvm计算机点为什么无故重启
通过查看cloudstack-agent的日志。
[root@kvm204 ~]# tail -1000f /var/log/cloudstack/agent/cloudstack-agent.out

看到了这里有报警,并且执行了reboot命令。继续往上面翻,又看到一条信息,如下:
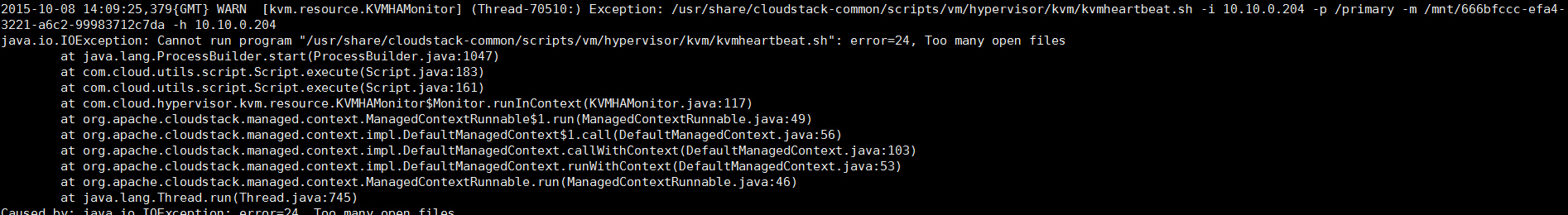
看到很多这样的报错,但最后一次报错是下面这个,可能是它导致了kvm检测脚本执行了reboot命令,然后就出现了本文第一张图片日志里reboot the host。

现在知道了是谁重启了电脑,但kvm为什么会重启这台计算节点呢?带着疑问,我去查看了一下那个脚本,也就是kvmheartbeat.sh脚本。内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
# distributed with this work for additional information
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
# under the License. help() {
printf "Usage: $0
-i nfs server ip
-p nfs server path
-m mount point
-h host
-r write/read hb log
-c cleanup
-t interval between read hb log\n"
exit
}
#set -x
NfsSvrIP=
NfsSvrPath=
MountPoint=
HostIP=
interval=
rflag=
cflag= while getopts 'i:p:m:h:t:rc' OPTION
do
case $OPTION in
i)
NfsSvrIP="$OPTARG"
;;
p)
NfsSvrPath="$OPTARG"
;;
m)
MountPoint="$OPTARG"
;;
h)
HostIP="$OPTARG"
;;
r)
rflag=
;;
t)
interval="$OPTARG"
;;
c)
cflag=
;;
*)
help
;;
esac
done if [ -z "$NfsSvrIP" ]
then
exit
fi #delete VMs on this mountpoint
deleteVMs() {
local mountPoint=$
vmPids=$(ps aux| grep qemu | grep "$mountPoint" | awk '{print $2}' > /dev/null)
if [ $? -gt ]
then
return
fi if [ -z "$vmPids" ]
then
return
fi for pid in $vmPids
do
kill - $pid &> /dev/null
done
} #checking is there the same nfs server mounted under $MountPoint?
mounts=$(cat /proc/mounts |grep nfs|grep $MountPoint)
if [ $? -gt ]
then
# remount it
mount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath $MountPoint -o sync,soft,proto=tcp,acregmin=,acregmax=,acdirmin=,acdirmax=,noac,timeo=,retrans= &> /dev/null
if [ $? -gt ]
then
printf "Failed to remount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath under $MountPoint"
exit
fi
if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
then
deleteVMs $MountPoint
fi
fi hbFolder=$MountPoint/KVMHA/
hbFile=$hbFolder/hb-$HostIP write_hbLog() {
#write the heart beat log
stat $hbFile &> /dev/null
if [ $? -gt ]
then
# create a new one
mkdir -p $hbFolder &> /dev/null
touch $hbFile &> /dev/null
if [ $? -gt ]
then
printf "Failed to create $hbFile"
return
fi
fi timestamp=$(date +%s)
echo $timestamp > $hbFile
return $?
} check_hbLog() {
now=$(date +%s)
hb=$(cat $hbFile)
diff=`expr $now - $hb`
if [ $diff -gt $interval ]
then
return
fi
return
} if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
then
check_hbLog
if [ $? == ]
then
echo "=====> ALIVE <====="
else
echo "=====> DEAD <======"
fi
exit
elif [ "$cflag" == "" ]
then
reboot
exit $?
else
write_hbLog
exit $?
fi
上面这个脚本是我们现在的计算节点上的版本。从上面可以看出,有判断reboot命令,也就是知道了为什么会重启。但这很坑爹呀,你检测检测,你还重启。。。。
下面这个脚本是我在github上看到的。而且版本已经更新。距离现在8月。应该是最新的,从下面看出,这个坑爹的reboot命令已经被修改了。
#!/bin/bash
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
# distributed with this work for additional information
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
# under the License. help() {
printf "Usage: $0
-i nfs server ip
-p nfs server path
-m mount point
-h host
-r write/read hb log
-c cleanup
-t interval between read hb log\n"
exit
}
#set -x
NfsSvrIP=
NfsSvrPath=
MountPoint=
HostIP=
interval=
rflag=
cflag= while getopts 'i:p:m:h:t:rc' OPTION
do
case $OPTION in
i)
NfsSvrIP="$OPTARG"
;;
p)
NfsSvrPath="$OPTARG"
;;
m)
MountPoint="$OPTARG"
;;
h)
HostIP="$OPTARG"
;;
r)
rflag=
;;
t)
interval="$OPTARG"
;;
c)
cflag=
;;
*)
help
;;
esac
done if [ -z "$NfsSvrIP" ]
then
exit
fi #delete VMs on this mountpoint
deleteVMs() {
local mountPoint=$
vmPids=$(ps aux| grep qemu | grep "$mountPoint" | awk '{print $2}' > /dev/null)
if [ $? -gt ]
then
return
fi if [ -z "$vmPids" ]
then
return
fi for pid in $vmPids
do
kill - $pid &> /dev/null
done
} #checking is there the same nfs server mounted under $MountPoint?
mounts=$(cat /proc/mounts |grep nfs|grep $MountPoint)
if [ $? -gt ]
then
# remount it
mount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath $MountPoint -o sync,soft,proto=tcp,acregmin=,acregmax=,acdirmin=,acdirmax=,noac,timeo=,retrans= &> /dev/null
if [ $? -gt ]
then
printf "Failed to remount $NfsSvrIP:$NfsSvrPath under $MountPoint"
exit
fi
if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
then
deleteVMs $MountPoint
fi
fi hbFolder=$MountPoint/KVMHA/
hbFile=$hbFolder/hb-$HostIP write_hbLog() {
#write the heart beat log
stat $hbFile &> /dev/null
if [ $? -gt ]
then
# create a new one
mkdir -p $hbFolder &> /dev/null
touch $hbFile &> /dev/null
if [ $? -gt ]
then
printf "Failed to create $hbFile"
return
fi
fi timestamp=$(date +%s)
echo $timestamp > $hbFile
return $?
} check_hbLog() {
now=$(date +%s)
hb=$(cat $hbFile)
diff=`expr $now - $hb`
if [ $diff -gt $interval ]
then
return
fi
return
} if [ "$rflag" == "" ]
then
check_hbLog
if [ $? == ]
then
echo "=====> ALIVE <====="
else
echo "=====> DEAD <======"
fi
exit
elif [ "$cflag" == "" ]
then
/usr/bin/logger -t heartbeat "kvmheartbeat.sh rebooted system because it was unable to write the heartbeat to the storage."
sync &
sleep
echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger
exit $?
else
write_hbLog
exit $?
fi
为什么KVM计算机点无故重启?的更多相关文章
- ACPI引起linux系统无故重启
新装机器无故重启多次. centos6 64bit uname -a Linux Eos 2.6.32-71.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri May 20 03:51:51 BST 201 ...
- centos7无故重启-内核升级
最近有一台物理服务器,centos7操作系统,无故重启,每天都会发生这种情况: 解决: 升级内核 CentOS 允许使用 ELRepo,这是一个第三方仓库,可以将内核升级到最新版本,使用ELRepo升 ...
- PowerShell工作流学习-4-工作流中重启计算机
关键点: a)工作流中重新启动计算机,请使用Restart-Computer的Wait参数,Wait参数不仅适用于本地计算机,也适用于远程计算机. b)重启运行工作流的计算机,手工恢复请使用Resum ...
- Win10自动重启原因怎么查Windows10无故自动重启
电脑偶尔自动重启,可能很少用户会在意,若电脑经常无故重启,那么应该怎么办,怎么查找电脑无故自动重启原因呢?下面就以Windows10系统自动重启为例,来查查WIN10无故重启是什么原因导致.百度经验: ...
- kvm 使用入门详解
kvm 是虚拟化技术的一个典型实现,功能非常强大,使用很方便.kvm 本身主要实现对 CPU 的虚拟化,内存和IO的虚拟化使用了开源软件 qemu,qemu 是纯软件层面的虚拟化,其实就是个模拟器.k ...
- Linux 修改计算机名
查看计算机名:在终端输入hostname 修改的话 hostname +计算机名(重启后失效) 要永久修改的话要修改配置文件/etc/sysconfig/network 修改hostname=你要改的 ...
- centos linux中怎么查看和修改计算机名/etc/sysconfig/network
centos linux中怎么查看和修改计算机名 查看计算机名:在终端输入hostname 修改的话 hostname +计算机名(重启后失效)要永久修改的话要修改配置文件/etc/sysconfig ...
- cmd 更改计算机名
bat 更改计算机名 不用重启电脑就生效^_^ @Echo off Color 0A title --更改计算机名 :A cls echo. echo. [0]退出 echo. echo. 不用重启 ...
- KVM之五:KVM日常管理常用命令
1.查看.编辑及备份KVM 虚拟机配置文件 以及查看KVM 状态: 1.1.KVM 虚拟机默认的配置文件在 /etc/libvirt/qemu 目录下,默认是以虚拟机名称命名的.xml 文件,如下,: ...
随机推荐
- Okhttp之连接池ConnectionPool简单分析(一)
开篇声明:由于本篇博文用到的一些观点或者结论在之前的博文中都已经分析过,所以本篇博文直接拿来用,建议读此博文的Monkey们按照下面的顺序读一下博主以下博文,以便于对此篇博文的理解: <Okht ...
- U盘传送容量与格式问题
问题 今天想将7.6G的文件拷到U盘里,提示u盘内存不足,其实内存为14+G. 解答 U盘格式对于U盘的传送大小有限制 下面为U盘三种不同格式的应用及优缺点 FAT32格式:为系统默认格式,具有极佳的 ...
- 【剑指offer-21】调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面,C++实现(冒泡排序)
1.题目 输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于位于数组的后半部分. 2.思路 本题有两种解法,一种是不保证数组稳定性的解法,一种是保 ...
- 分布式版本控制系统Git——图形化Git客户端工具TortoiseGit
本篇导读: 上篇介绍了一款Windows环境下的Git服务器工具GitStack ,搭建了最简单的Windows下的Git服务器,需要再次提醒的是GitStack是打包了相对较稳定的Git原生版本的, ...
- 自定义requestAnimationFrame帧频
requestAnimationFrame(callback)触发的callback方法会接受一个时间戳参数,所以如果不想直接跟随浏览器系统帧频的话, 就可以利用这个时间戳参数来做到自定义帧频,做法就 ...
- 每天一个linux命令(性能、优化):【转载】top命令
top命令是Linux下常用的性能分析工具,能够实时显示系统中各个进程的资源占用状况,类似于Windows的任务管理器.下面详细介绍它的使用方法.top是一个动态显示过程,即可以通过用户按键来不断刷新 ...
- BZOJ3747 POI2015 Kinoman 【线段树】*
BZOJ3747 POI2015 Kinoman Description 共有m部电影,编号为1~m,第i部电影的好看值为w[i]. 在n天之中(从1~n编号)每天会放映一部电影,第i天放映的是第f[ ...
- python笔记-7(shutil/json/pickle/shelve/xml/configparser/hashlib模块)
一.shutil模块--高级的文件.文件夹.压缩包处理模块 1.通过句柄复制内容 shutil.copyfileobj(f1,f2)对文件的复制(通过句柄fdst/fsrc复制文件内容) 源码: Le ...
- 【C#】datetimepicker初始为空值的方法
方法一: 在窗口初始化函数中添加: dateTimePickerEnd.Format = DateTimePickerFormat.Custom; dateTimePickerEnd.CustomFo ...
- bat命令1
echo 命令 打开回显或关闭请求回显功能,或显示消息.如果没有任何参数,echo命令将显示当前回显设置. 语法 echo [{on|off}] [message] Sample:@echo off ...
