3.2、Factorization Machine实践
1、在上一篇博客中我们构建度为二的因子分解机模型,这篇博客对这个模型进行实践
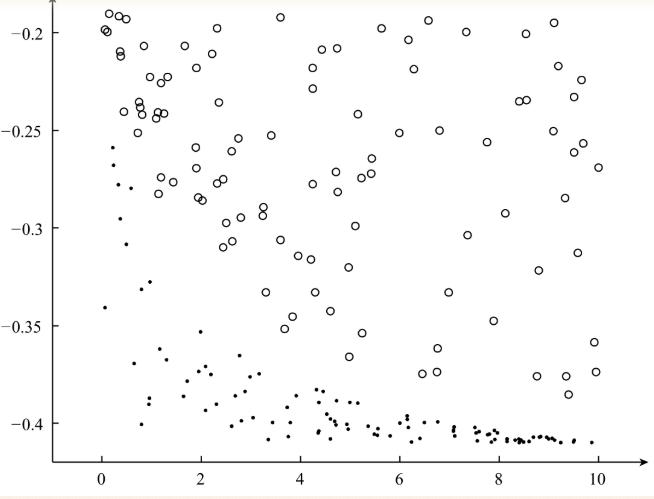
下图为准备的数据集:
完整代码为:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# date:2018/6/6
# User:WangHong
import numpy as np
from random import normalvariate # 正态分布 def loadDataSet(data):
'''导入训练数据
input: data(string)训练数据
output: dataMat(list)特征
labelMat(list)标签
'''
dataMat = []
labelMat = []
fr = open(data) # 打开文件
for line in fr.readlines():
lines = line.strip().split("\t")
lineArr = [] for i in range(len(lines) - 1):
lineArr.append(float(lines[i]))
dataMat.append(lineArr) labelMat.append(float(lines[-1]) * 2 - 1) # 转换成{-1,1}
fr.close()
return dataMat, labelMat def sigmoid(inx):
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inx)) def initialize_v(n, k):
'''初始化交叉项
input: n(int)特征的个数
k(int)FM模型的超参数
output: v(mat):交叉项的系数权重
'''
v = np.mat(np.zeros((n, k))) for i in range(n):
for j in range(k):
# 利用正态分布生成每一个权重
v[i, j] = normalvariate(0, 0.2)
return v def stocGradAscent(dataMatrix, classLabels, k, max_iter, alpha):
'''利用随机梯度下降法训练FM模型
input: dataMatrix(mat)特征
classLabels(mat)标签
k(int)v的维数
max_iter(int)最大迭代次数
alpha(float)学习率
output: w0(float),w(mat),v(mat):权重
'''
m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix)
# 1、初始化参数
w = np.zeros((n, 1)) # 其中n是特征的个数
w0 = 0 # 偏置项
v = initialize_v(n, k) # 初始化V # 2、训练
for it in range(max_iter):
for x in range(m): # 随机优化,对每一个样本而言的
inter_1 = dataMatrix[x] * v
inter_2 = np.multiply(dataMatrix[x], dataMatrix[x]) * \
np.multiply(v, v) # multiply对应元素相乘
# 完成交叉项
interaction = np.sum(np.multiply(inter_1, inter_1) - inter_2) / 2.
p = w0 + dataMatrix[x] * w + interaction # 计算预测的输出
loss = sigmoid(classLabels[x] * p[0, 0]) - 1 w0 = w0 - alpha * loss * classLabels[x]
for i in range(n):
if dataMatrix[x, i] != 0:
w[i, 0] = w[i, 0] - alpha * loss * classLabels[x] * dataMatrix[x, i] for j in range(k):
v[i, j] = v[i, j] - alpha * loss * classLabels[x] * \
(dataMatrix[x, i] * inter_1[0, j] -\
v[i, j] * dataMatrix[x, i] * dataMatrix[x, i]) # 计算损失函数的值
if it % 1000 == 0:
print ("\t------- iter: ", it, " , cost: ", \
getCost(getPrediction(np.mat(dataMatrix), w0, w, v), classLabels)) # 3、返回最终的FM模型的参数
return w0, w, v def getCost(predict, classLabels):
'''计算预测准确性
input: predict(list)预测值
classLabels(list)标签
output: error(float)计算损失函数的值
'''
m = len(predict)
error = 0.0
for i in range(m):
error -= np.log(sigmoid(predict[i] * classLabels[i] ))
return error def getPrediction(dataMatrix, w0, w, v):
'''得到预测值
input: dataMatrix(mat)特征
w(int)常数项权重
w0(int)一次项权重
v(float)交叉项权重
output: result(list)预测的结果
'''
m = np.shape(dataMatrix)[0]
result = []
for x in range(m): inter_1 = dataMatrix[x] * v
inter_2 = np.multiply(dataMatrix[x], dataMatrix[x]) * \
np.multiply(v, v) # multiply对应元素相乘
# 完成交叉项
interaction = np.sum(np.multiply(inter_1, inter_1) - inter_2) / 2.
p = w0 + dataMatrix[x] * w + interaction # 计算预测的输出
pre = sigmoid(p[0, 0])
result.append(pre)
return result def getAccuracy(predict, classLabels):
'''计算预测准确性
input: predict(list)预测值
classLabels(list)标签
output: float(error) / allItem(float)错误率
'''
m = len(predict)
allItem = 0
error = 0
for i in range(m):
allItem += 1
if float(predict[i]) < 0.5 and classLabels[i] == 1.0:
error += 1
elif float(predict[i]) >= 0.5 and classLabels[i] == -1.0:
error += 1
else:
continue
return float(error) / allItem def save_model(file_name, w0, w, v):
'''保存训练好的FM模型
input: file_name(string):保存的文件名
w0(float):偏置项
w(mat):一次项的权重
v(mat):交叉项的权重
'''
f = open(file_name, "w")
# 1、保存w0
f.write(str(w0) + "\n")
# 2、保存一次项的权重
w_array = []
m = np.shape(w)[0]
for i in range(m):
w_array.append(str(w[i, 0]))
f.write("\t".join(w_array) + "\n")
# 3、保存交叉项的权重
m1 , n1 = np.shape(v)
for i in range(m1):
v_tmp = []
for j in range(n1):
v_tmp.append(str(v[i, j]))
f.write("\t".join(v_tmp) + "\n")
f.close() if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1、导入训练数据
print ("---------- 1.load data ---------")
dataTrain, labelTrain = loadDataSet("data_1.txt")
print( "---------- 2.learning ---------")
# 2、利用随机梯度训练FM模型
w0, w, v = stocGradAscent(np.mat(dataTrain), labelTrain, 3, 10000, 0.01)
predict_result = getPrediction(np.mat(dataTrain), w0, w, v) # 得到训练的准确性
print( "----------training accuracy: %f" % (1 - getAccuracy(predict_result, labelTrain)))
print ("---------- 3.save result ---------")
# 3、保存训练好的FM模型
save_model("weights", w0, w, v)
最终训练过程为:
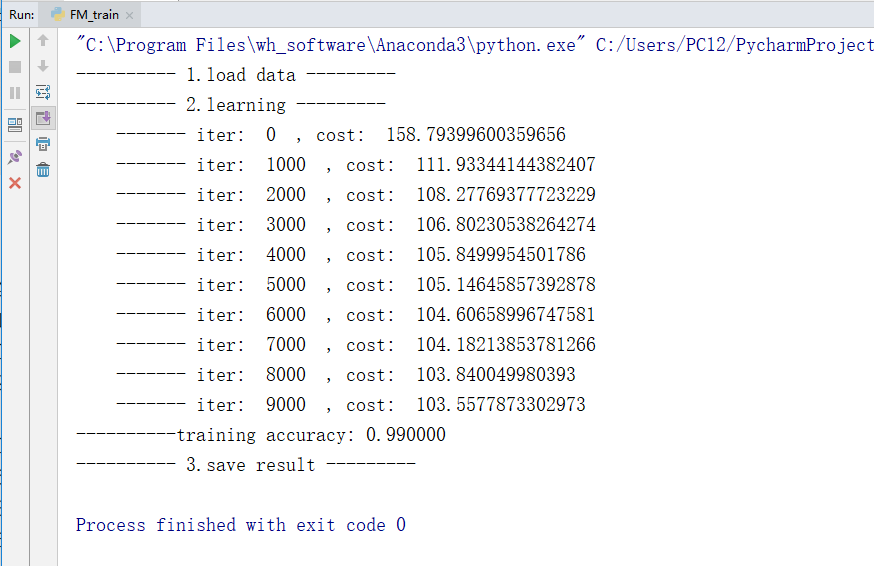
训练的过程比较慢,我用来将近有一分半
得到的权值文件为:
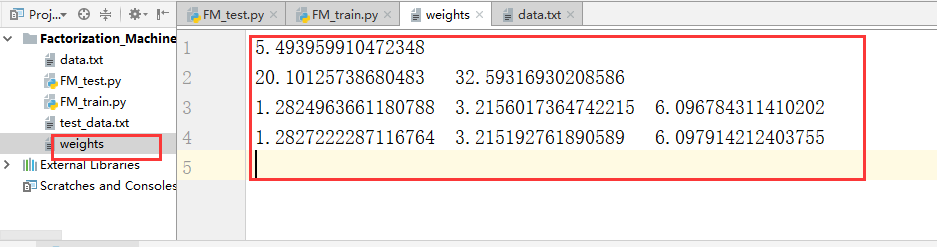
最终分隔得到的超平面为:
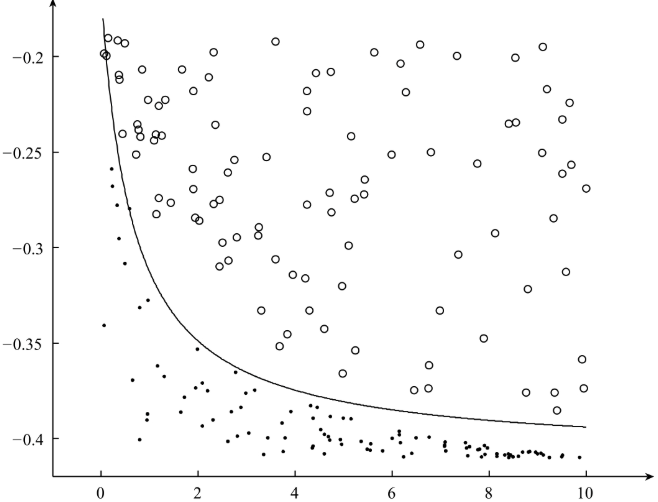
2、对新的数据进行预测:
预测的全部代码为:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# date:2018/6/6
# User:WangHong import numpy as np from FM_train import getPrediction def loadDataSet(data):
'''导入测试数据集
input: data(string)测试数据
output: dataMat(list)特征
'''
dataMat = []
fr = open(data) # 打开文件
for line in fr.readlines():
lines = line.strip().split("\t")
lineArr = [] for i in range(len(lines)):
lineArr.append(float(lines[i]))
dataMat.append(lineArr) fr.close()
return dataMat def loadModel(model_file):
'''导入FM模型
input: model_file(string)FM模型
output: w0, np.mat(w).T, np.mat(v)FM模型的参数
'''
f = open(model_file)
line_index = 0
w0 = 0.0
w = []
v = []
for line in f.readlines():
lines = line.strip().split("\t")
if line_index == 0: # w0
w0 = float(lines[0].strip())
elif line_index == 1: # w
for x in lines:
w.append(float(x.strip()))
else:
v_tmp = []
for x in lines:
v_tmp.append(float(x.strip()))
v.append(v_tmp)
line_index += 1
f.close()
return w0, np.mat(w).T, np.mat(v) def save_result(file_name, result):
'''保存最终的预测结果
input: file_name(string)需要保存的文件名
result(mat):对测试数据的预测结果
'''
f = open(file_name, "w")
f.write("\n".join(str(x) for x in result))
f.close() if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1、导入测试数据
dataTest = loadDataSet("test_data.txt")
# 2、导入FM模型
w0, w , v = loadModel("weights")
# 3、预测
result = getPrediction(dataTest, w0, w, v)
# 4、保存最终的预测结果
save_result("predict_result", result)
最终测试结果得到一个predict_result.txt文件
3.2、Factorization Machine实践的更多相关文章
- Factorization Machine因子分解机
隐因子分解机Factorization Machine[http://www. w2bc. com/article/113916] https://my.oschina.net/keyven/blog ...
- Factorization Machine
Factorization Machine Model 如果仅考虑两个样本间的交互, 则factorization machine的公式为: $\hat{y}(\mathbf{x}):=w_0 + \ ...
- 3.1、Factorization Machine模型
Factorization Machine模型 在Logistics Regression算法的模型中使用的是特征的线性组合,最终得到的分隔超平面属于线性模型,其只能处理线性可分的二分类问题,现实生活 ...
- Factorization Machine算法
参考: http://stackbox.cn/2018-12-factorization-machine/ https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1641085157432 ...
- AI Factorization Machine(FM)算法
FM算法 参考链接: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~b97053/paper/Rendle2010FM.pdf
- CTR预估算法之FM, FFM, DeepFM及实践
https://blog.csdn.net/john_xyz/article/details/78933253 目录目录CTR预估综述Factorization Machines(FM)算法原理代码实 ...
- 深入理解FFM原理与实践
原文:http://tech.meituan.com/deep-understanding-of-ffm-principles-and-practices.html 深入理解FFM原理与实践 del2 ...
- zz深度学习在美团配送 ETA 预估中的探索与实践
深度学习在美团配送 ETA 预估中的探索与实践 比前一版本有改进: 基泽 周越 显杰 阅读数:32952019 年 4 月 20 日 1. 背景 ETA(Estimated Time of A ...
- 个性化排序算法实践(二)——FFM算法
场感知分解机(Field-aware Factorization Machine ,简称FFM)在FM的基础上进一步改进,在模型中引入类别的概念,即field.将同一个field的特征单独进行one- ...
随机推荐
- 各种异常 及异常类和Object类 Math类
Day05 异常 Object类 equals方法,用于比较两个对象是否相同,它其实就是使用两个对象的内存地址在比较.Object类中的equals方法内部使用的就是==比较运算符. 2. 描述人这个 ...
- Redis只作为缓存,不做持久化的配置
#1.配置缓存内存限制和清理策略 #作为缓存服务器,如果不加以限制内存的话,就很有可能出现将整台服务器内存都耗光的情况,可以在redis的配置文件里面设置: #example: # 限定最多使用1.5 ...
- sql2008 安装提示重启失败
[转] https://www.cnblogs.com/chenshaogang/p/4313022.html
- CNN和GAN 比较nice的介绍
CNN是个什么鬼:https://www.zhihu.com/question/52668301 就是这样GAN : https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27199954
- NHibernate获取实体配置信息(表名,列名等等)
// 注意这里有个&符号,并不是写错了,而是约定 就是这样写的ctx.GetObject("&SessionFactory") 这是官网地址http://nhfor ...
- 重定向和请求转发后面加“return;”语句
请求转发 RequestDispatcher 重定向 Redirect 代码的执行: 无论是 request.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(reque ...
- Perl 学习笔记-文件测试
1.文件测试操作符 针对文件和目录的测试操作符: -r/-w/-x/-o: 文件或目录, 对有效的(负责运行这个程序的)用户或组来说是可读/写/执行/拥有 的; 这些测试位会查看文件的权限位, 以此判 ...
- 关于利用word发布文章到博客
目前大部分的博客作者在写博客这件事情上都会遇到以下3个痛点:1.所有博客平台关闭了文档发布接口,用户无法使用Word,Windows Live Writer等工具来发布博客.2.发布到博客或公众号平台 ...
- 编写高质量代码改善C#程序的157个建议——建议106:为静态类添加静态构造函数
建议106:为静态类添加静态构造函数 静态类可以拥有构造方法,这就是静态构造方法.静态构造方法与实例构造方法比较有几个自己的特点: 只被执行一次,且在第一次调用类成员之前被运行时执行. 代码无法调用它 ...
- makeword()
MAKEWORD(学习之用,转载) MAKEWORD 宏 平台:SDK 这个宏创建一个被指定变量连接而成的WORD变量.返回一个WORD变量. (注:typedef unsigned short WO ...
