Spring源码加载过程图解(一)
最近看了一下Spring源码加载的简装版本,为了更好的理解,所以在绘图的基础上,进行了一些总结。(图画是为了理解和便于记忆Spring架构)
Spring的核心是IOC(控制反转)和AOP(面向切面编程),首先我们先一步一步的来了解IOC的实现:
一:首先是第一个模型:Model1:
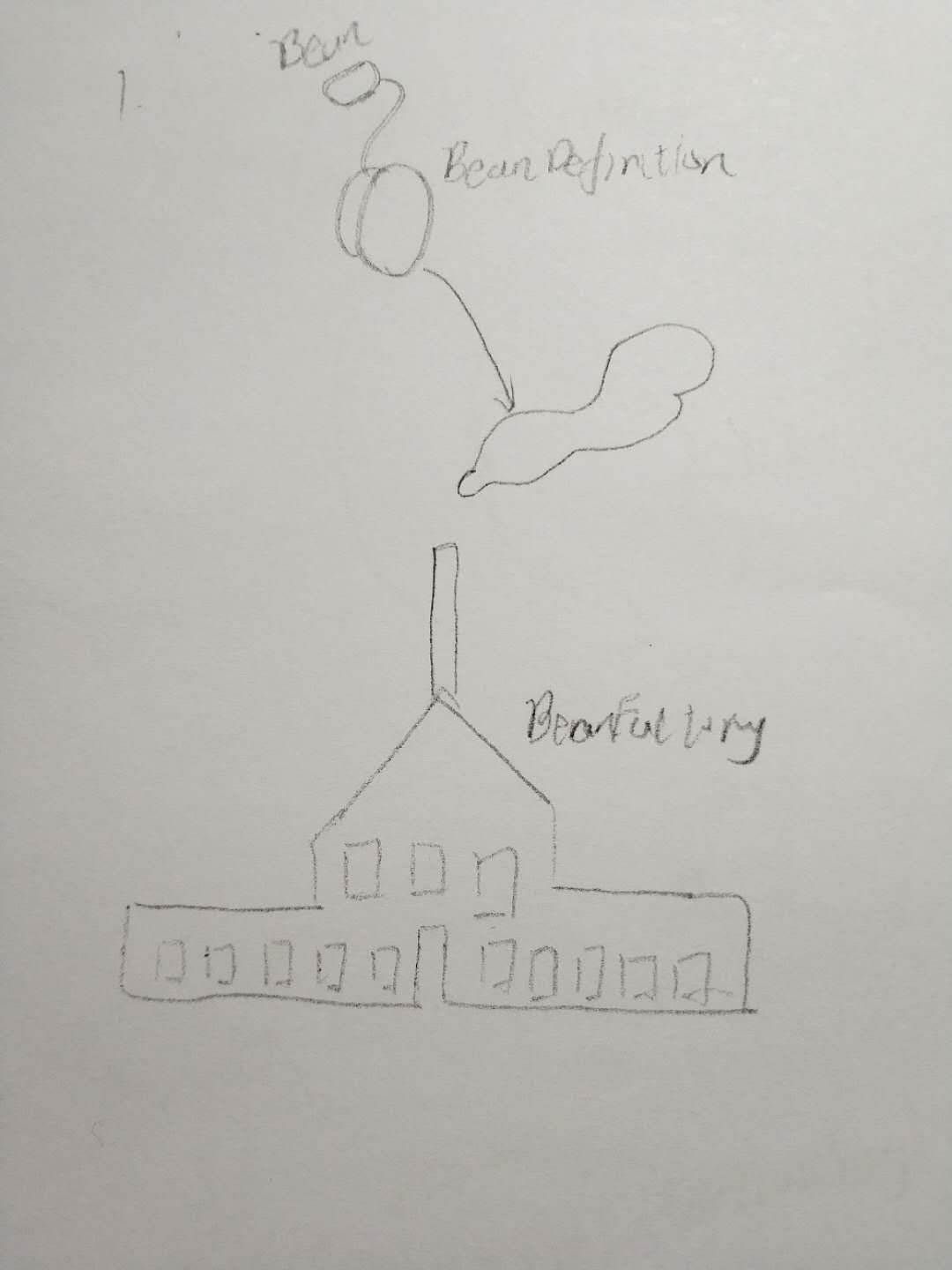 种子 = BeanDefinition 工厂=BeanFactory
种子 = BeanDefinition 工厂=BeanFactory
1、此处我们可以看见两个对象 BeanDefinition和BeanFactory,此处把创建对象的权限交给了BeanFactory,现在我们可以看到IOC的雏形,即把创建对象的权利交给了工厂。
public class BeanDefinition {
private Object bean;
public BeanDefinition(Object bean) {
this.bean = bean;
}
public Object getBean() {
return bean;
}
}
public class BeanFactory {
private Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
public Object getBean(String name) {
return beanDefinitionMap.get(name).getBean();
}
public void registerBeanDefinition(String name, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
beanDefinitionMap.put(name, beanDefinition);
}
}
二:接下來我們看第二个模型,对BeanFactory进行扩展
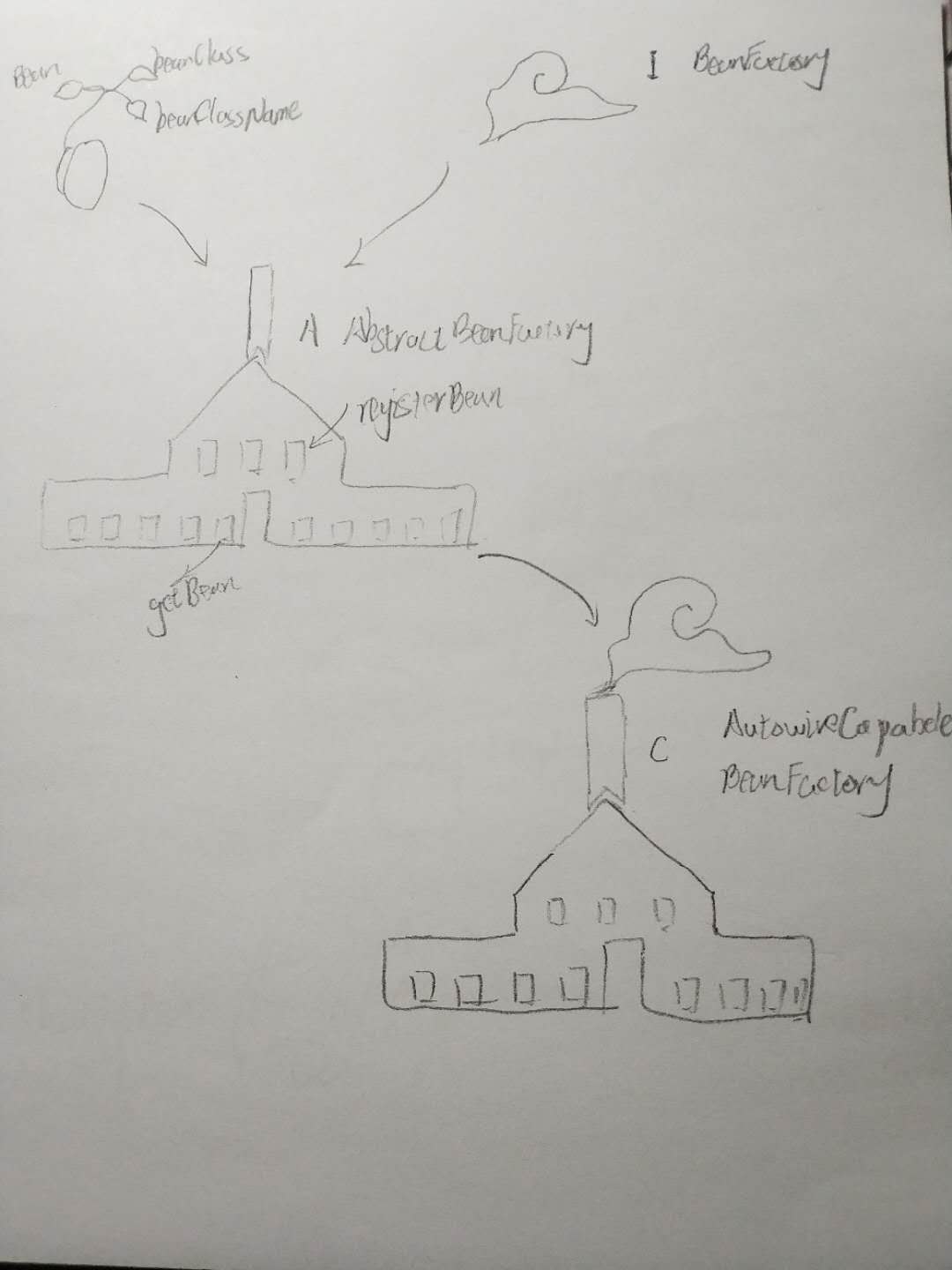 1、此处的BeanDefinition 进行了扩展字段,可以看做是种子有了 3 片叶子,便于记忆,分别是 :
1、此处的BeanDefinition 进行了扩展字段,可以看做是种子有了 3 片叶子,便于记忆,分别是 :
Object -> bean Class ->beanClass String ->beanClassName
2、此处的BeanFactory有了解耦的思想,使用了接口和抽象类
public class BeanDefinition {
private Object bean;
private Class beanClass;
private String beanClassName;
public BeanDefinition() {
}
public void setBean(Object bean) {
this.bean = bean;
}
public Class getBeanClass() {
return beanClass;
}
public void setBeanClass(Class beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
}
public String getBeanClassName() {
return beanClassName;
}
public void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName) {
this.beanClassName = beanClassName;
try {
this.beanClass = Class.forName(beanClassName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getBean() {
return bean;
}
}
public interface BeanFactory {
Object getBean(String name);
void registerBeanDefinition(String name, BeanDefinition beanDefinition);
}
此处 BeanFactory定义了获取Bean 和注册Bean的方法
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory implements BeanFactory {
private Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) {
return beanDefinitionMap.get(name).getBean();
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String name, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Object bean = doCreateBean(beanDefinition);
beanDefinition.setBean(bean);
beanDefinitionMap.put(name, beanDefinition);
}
/**
* 初始化bean
* @param beanDefinition
* @return
*/
protected abstract Object doCreateBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition);
}
此处实现了getBean 和registerBean的方法;另外声明了 doCreateBean的抽象方法;
public class AutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory {
@Override
protected Object doCreateBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
try {
Object bean = beanDefinition.getBeanClass().newInstance();
return bean;
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
最后实现类通过反射的方式,创建bean;并注册到工厂里,以便调用。
三:接下来继续完善,查看第三个模型:
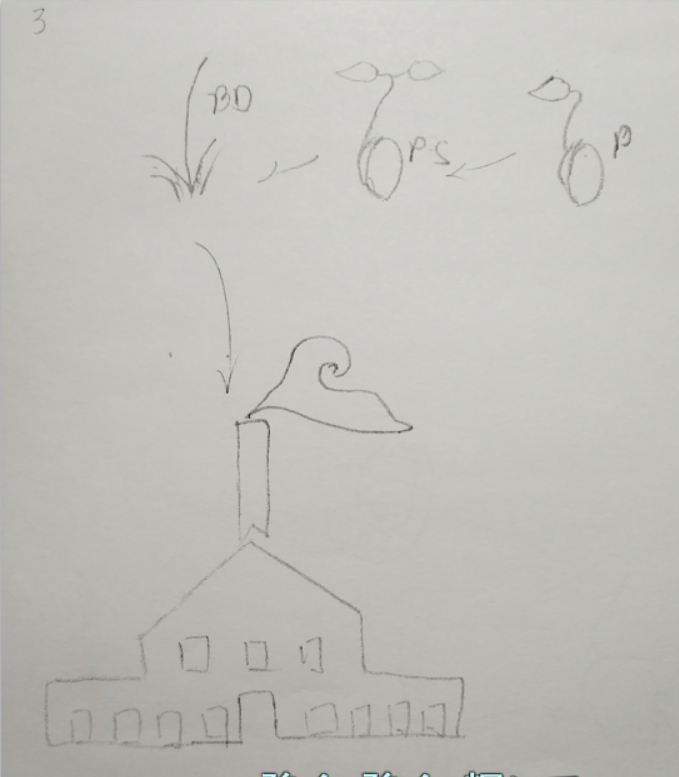 1、此处 BeanDefiniton多了一个自定义的属性 propertyValues,便于属性的注入,BeanFactory方法也有所改变
1、此处 BeanDefiniton多了一个自定义的属性 propertyValues,便于属性的注入,BeanFactory方法也有所改变
1、BeanDefinition类的定义
public class BeanDefinition {
private Object bean;
private Class beanClass;
private String beanClassName;
private PropertyValues propertyValues;
public BeanDefinition() {
}
public void setBean(Object bean) {
this.bean = bean;
}
public Class getBeanClass() {
return beanClass;
}
public void setBeanClass(Class beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
}
public String getBeanClassName() {
return beanClassName;
}
public void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName) {
this.beanClassName = beanClassName;
try {
this.beanClass = Class.forName(beanClassName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getBean() {
return bean;
}
public PropertyValues getPropertyValues() {
return propertyValues;
}
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.propertyValues = propertyValues;
}
}
/**
* 用于bean的属性注入
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class PropertyValue { private final String name; private final Object value; public PropertyValue(String name, Object value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; /**
* 包装一个对象所有的PropertyValue。<br/>
* 为什么封装而不是直接用List?因为可以封装一些操作。
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class PropertyValues { private final List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList = new ArrayList<PropertyValue>(); public PropertyValues() {
} public void addPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) {
//TODO:这里可以对于重复propertyName进行判断,直接用list没法做到
this.propertyValueList.add(pv);
} public List<PropertyValue> getPropertyValues() {
return this.propertyValueList;
} }
2、BeanFactory的定义
/**
* bean的容器
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public interface BeanFactory { Object getBean(String name); void registerBeanDefinition(String name, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception;
}
/**
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory implements BeanFactory { private Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>(); @Override
public Object getBean(String name) {
return beanDefinitionMap.get(name).getBean();
} @Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String name, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception {
Object bean = doCreateBean(beanDefinition);
beanDefinition.setBean(bean);
beanDefinitionMap.put(name, beanDefinition);
} /**
* 初始化bean
* @param beanDefinition
* @return
*/
protected abstract Object doCreateBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception; }
/**
* 可自动装配内容的BeanFactory
*
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class AutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory { @Override
protected Object doCreateBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception {
Object bean = createBeanInstance(beanDefinition);
applyPropertyValues(bean, beanDefinition);
return bean;
} protected Object createBeanInstance(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception {
return beanDefinition.getBeanClass().newInstance();
} protected void applyPropertyValues(Object bean, BeanDefinition mbd) throws Exception {
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : mbd.getPropertyValues().getPropertyValues()) {
Field declaredField = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField(propertyValue.getName());
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(bean, propertyValue.getValue());
}
}
}
此处增加了添加 属性的方法 applyPropertyValues;
此模型可概括为:
#1.step1-最基本的容器
*step-1-container-register-and-get*
单纯的map,有get和put bean的功能
# 2.step2-将bean创建放入工厂
*step-2-abstract-beanfactory-and-do-bean-initilizing-in-it*
1. 抽象beanfactory
2. 将bean初始化放入beanfactory
# 2.step3-为bean注入属性
*step-3-inject-bean-with-property*
4、接下来我们来看第四个模型,Spring是如何实现读取配置文件的bean属性的,Model4:
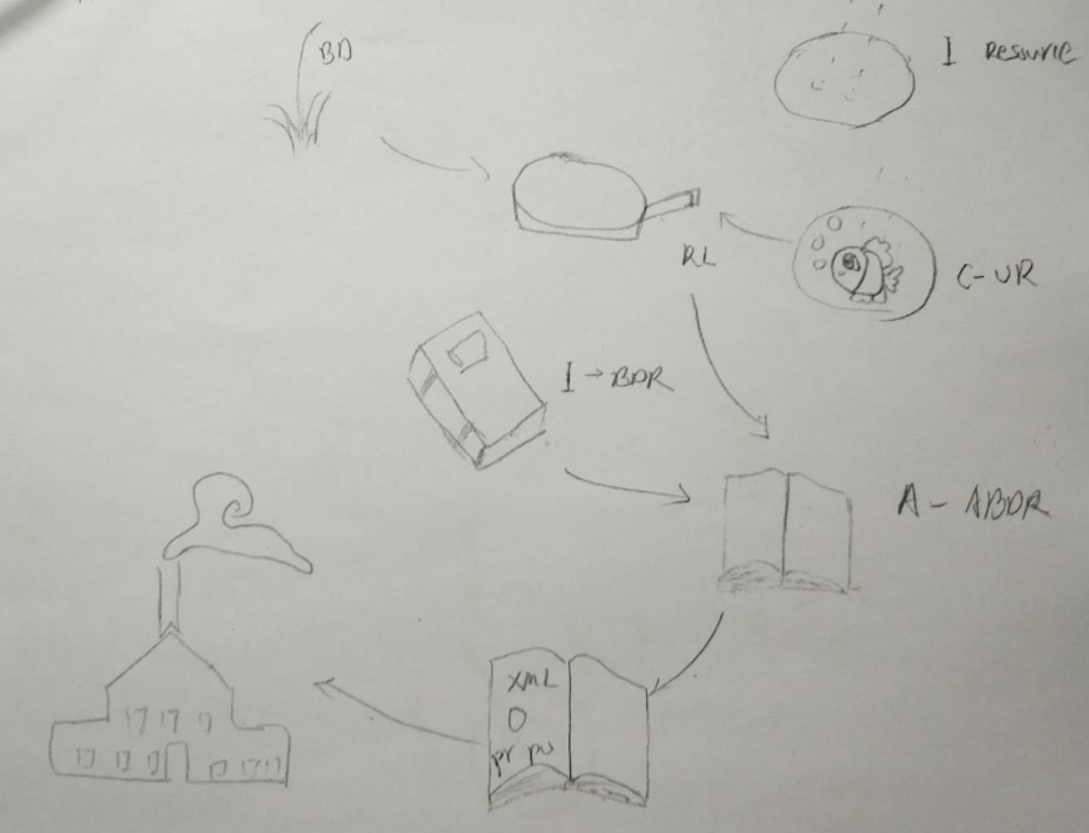
从图中可以看出多了几个模块,现在分别来介绍一下:
1、BD 是简化绘制版的 BeanDefiniton
2、UR 对应下面 IO类,用于读取xml文件
RL 是ResourceLoader,用于配置文件路径
3、BDR 是用来解析XML文件的模块类
4、最后交由BeanFactory创造bean,并提供bean.
1、BeanDefinition
BeanDefiniton
/**
* bean的内容及元数据,保存在BeanFactory中,包装bean的实体
*
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class BeanDefinition { private Object bean; private Class beanClass; private String beanClassName; private PropertyValues propertyValues = new PropertyValues(); public BeanDefinition() {
} public void setBean(Object bean) {
this.bean = bean;
} public Class getBeanClass() {
return beanClass;
} public void setBeanClass(Class beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
} public String getBeanClassName() {
return beanClassName;
} public void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName) {
this.beanClassName = beanClassName;
try {
this.beanClass = Class.forName(beanClassName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} public Object getBean() {
return bean;
} public PropertyValues getPropertyValues() {
return propertyValues;
} public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.propertyValues = propertyValues;
}
PropertyValue
/**
* 用于bean的属性注入
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class PropertyValue { private final String name; private final Object value; public PropertyValue(String name, Object value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
}
PropertyValues
/**
* 包装一个对象所有的PropertyValue。<br/>
* 为什么封装而不是直接用List?因为可以封装一些操作。
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class PropertyValues { private final List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList = new ArrayList<PropertyValue>(); public PropertyValues() {
} public void addPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) {
//TODO:这里可以对于重复propertyName进行判断,直接用list没法做到
this.propertyValueList.add(pv);
} public List<PropertyValue> getPropertyValues() {
return this.propertyValueList;
} }
2、IO类
Resource
/**
* Resource是spring内部定位资源的接口。
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public interface Resource { InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
/**
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class UrlResource implements Resource { private final URL url; public UrlResource(URL url) {
this.url = url;
} @Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException{
URLConnection urlConnection = url.openConnection();
urlConnection.connect();
return urlConnection.getInputStream();
}
}
ResourceLoader
/**
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class ResourceLoader { public Resource getResource(String location){
URL resource = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(location);
return new UrlResource(resource);
}
}
3、BeanDefinitionReader
/**
* 从配置中读取BeanDefinitionReader
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionReader { void loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws Exception;
}
/**
* 从配置中读取BeanDefinitionReader
*
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements BeanDefinitionReader { private Map<String,BeanDefinition> registry; private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.registry = new HashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
} public Map<String, BeanDefinition> getRegistry() {
return registry;
} public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return resourceLoader;
}
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
/**
* @author yihua.huang@dianping.com
*/
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader { public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
super(resourceLoader);
} @Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws Exception {
InputStream inputStream = getResourceLoader().getResource(location).getInputStream();
doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputStream);
} protected void doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputStream inputStream) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder docBuilder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = docBuilder.parse(inputStream);
// 解析bean
registerBeanDefinitions(doc);
inputStream.close();
} public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc) {
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); parseBeanDefinitions(root);
} protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
processBeanDefinition(ele);
}
}
} protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele) {
String name = ele.getAttribute("name");
String className = ele.getAttribute("class");
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
processProperty(ele,beanDefinition);
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName(className);
getRegistry().put(name, beanDefinition);
} private void processProperty(Element ele,BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
NodeList propertyNode = ele.getElementsByTagName("property");
for (int i = 0; i < propertyNode.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = propertyNode.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element propertyEle = (Element) node;
String name = propertyEle.getAttribute("name");
String value = propertyEle.getAttribute("value");
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(name,value));
}
}
}
}
此文件用来定义文名,并解析xml文件
未完,待续 。。。。。。
Spring源码加载过程图解(一)的更多相关文章
- Spring源码加载BeanDefinition过程
本文主要讲解Spring加载xml配置文件的方式,跟踪加载BeanDefinition的全过程. 源码分析 源码的入口 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数 new C ...
- Spring源码-加载和IOC部分
源代码和注释放在了github上,包括加载过程的注释和getBean部分的 地址: https://github.com/lvxingzhi/spring-framework-4.3.9-note.g ...
- 工厂模式模拟Spring的bean加载过程
一.前言 在日常的开发过程,经常使用或碰到的设计模式有代理.工厂.单例.反射模式等等.下面就对工厂模式模拟spring的bean加载过程进行解析,如果对工厂模式不熟悉的,具体可以先去学习一下工厂 ...
- Spring Bean 的加载过程
Spring Bean 的加载过程 一个是populateBean,一个是initializeBean,这两个方法完成了bean的赋值与初始化. 这里有一个BeanDefinitionValueRes ...
- Spring源码:Spring IoC容器加载过程(1)
Spring源码版本:4.3.23.RELEASE 一.加载过程概览 Spring容器加载过程可以在org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplic ...
- Spring源码:Spring IoC容器加载过程(2)
Spring源码版本:4.3.23.RELEASE 一.加载XML配置 通过XML配置创建Spring,创建入口是使用org.springframework.context.support.Class ...
- Spring IOC bean加载过程
首先我们不要在学习Spring的开始产生畏难情绪.Spring没有臆想的那么高深,相反,它帮我们再项目开发中制定项目框架,简化项目开发.它的主要功能是将项目开发中繁琐的过程流程化,模式化,使用户仅在固 ...
- 【学习底层原理系列】重读spring源码3-加载beanDefinition的方法obtainFreshBeanFactory
obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法概述 定义BeanFactory,并加载以下两种bean的定义,装配到BeanFactory: 1.配置文件中定义的bean 2.通过<con ...
- spring的BeanFactory加载过程
ApplicationContext spring = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:spring/applicationCo ...
随机推荐
- [置顶]
kubernetes1.7新特性:日志审计变化
背景概念 出于安全方面的考虑,Kubernetes提供了日志审计记录,用来记录不同普通用户.管理员和系统中各个组件的日志信息. Kubernetes日志审计是Kube-apiserver组件的一部分功 ...
- Ubuntu循环登录libGL error: fbConfigs swrast等
Ubuntu16.04更新NVIDIA驱动后,无法进入桌面,使用vim .xsession-errors 查看错误信息,如下: libGL error: No matching fbConfigs o ...
- [Linux] Boot分区满了的处理方法 The volume "boot" has only 0 bytes disk space remaining
1.查看系统目前正在用的内核 abby@abby:~$ uname -r ..--generic 2.查看/boot保存的所有内核 abby@abby:~$ ls -lah /boot total 3 ...
- .net collection tips
1.数组对象都是Array的子类,Array是一个抽象类,不能显示实例化,Array提供了大量操作数组的静态方法 2.ArrayList其实是内部封装了一个array,实现了IList的接口.add ...
- BZOJ2152 聪聪可可 【点分治】
BZOJ2152 聪聪可可 Description 聪聪和可可是兄弟俩,他们俩经常为了一些琐事打起来,例如家中只剩下最后一根冰棍而两人都想吃.两个人都想玩儿电脑(可是他们家只有一台电脑)--遇到这种问 ...
- 如何向整个 Git 仓库补提交一个文件
微软在 Reference Source 里开放了 .Net Framework 多个版本的源码.为了更方便地阅读这些源码,我们把每一个版本都下载下来后按顺序提交到 git 仓库中. 但是!!!居然忘 ...
- python环境搭建-Linux系统下python2.7升级python3.5.2步骤
首先Python 查看版本 , 在Linux下特别注意权限问题,创建目录时候切记给予权限 如果是 ubnutu 请使用首先切换到 sudo su , 否则 make install 会出现问题.. 升 ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example6.2
2017年了,阳历新年都11号了,已从外地回到家乡,依然苦逼的生活…… 接着写读书(Digital Signal Processing using MATLAB)笔记吧 代码: b = [1 -3 1 ...
- Git与github常用命令
Git项目与github建立联系 首先,需要在github上建立一个repository mkdir github-project cd github-project git init 此时githu ...
- python 读取 xlsx
>>> xl = pd.ExcelFile("dummydata.xlsx") >>> xl.sheet_names [u'Sheet1', u ...
