《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.13


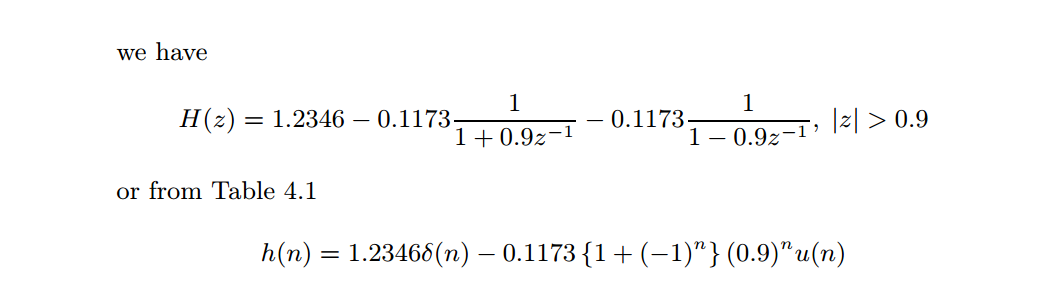


代码:
b = [1, 0, -1]; a = [1, 0, -0.81]; % [R, p, C] = residuez(b,a); Mp = (abs(p))'
Ap = (angle(p))'/pi %% ----------------------------------------------
%% START a determine H(z) and sketch
%% ----------------------------------------------
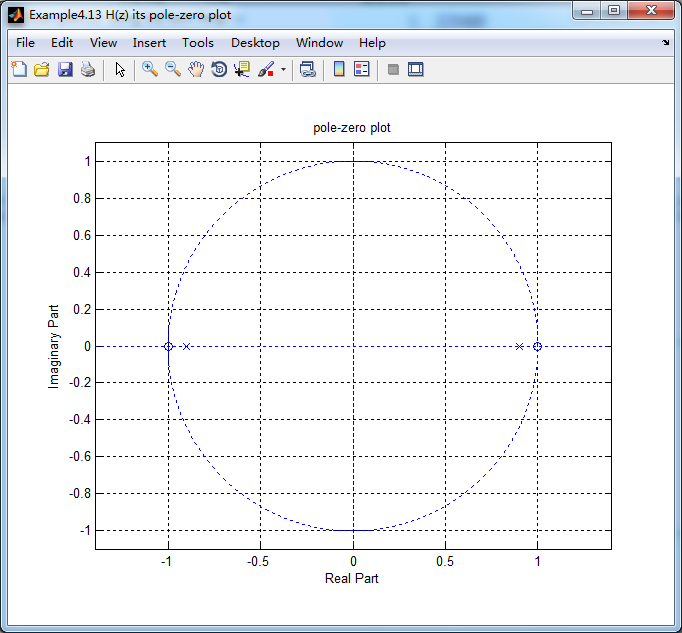
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.13 H(z) its pole-zero plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title('pole-zero plot'); grid on; %% ----------------------------------------------
%% END
%% ---------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 1st form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
[H,w] = freqz(b,a,500); % 1st form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.13 H its mag ang real imag');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% --------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 3rd form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; H = freqz(b,a,w);
%[H,w] = freqz(b,a,200,'whole'); % 3rd form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.13 using 3rd form freqz ');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% ---------------------------------------------------------------
结果:



《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.13的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
随机推荐
- JS 异步加载的方法
(1) defer,只支持IE : <script type="text/javascript" defer="defer"> </scrip ...
- jquery中使用event.target的几点
jquery中使用event.target的几点 1.this和event.target的区别: js中事件是会冒泡的,所以this是可以变化的,但event.target不会变化,它永远是直接接受事 ...
- java中方法参数的一些总结(1)
1.问题说明 在C++中,函数调用时有传值调用和传址调用两种方式,但在Java中只有传值调用一种方式.Java中的方法参数为那几种基本数据类型的情况跟C++中一样,传入的只是变量的拷贝. ...
- .net如何实现时间相减得到天数
第一种方法: 为了得到时间的天数,代码如下:(计算整天,不含半天) DateTime start = DateTime.Parse(txt_start.Value.Trim());//开始时间 Dat ...
- Android开发环境搭建:离线安装ADT插件和安装SDK
一.准备 在线安装SDK较慢,在此我选择了离线安装,所需要的工具下载:http://yun.baidu.com/share/link?shareid=2286446004&uk=2000812 ...
- 使用dynatrace+showslow进行前端性能测试
1.背景 应用的性能测试与优化目前主要停留在服务器端的反馈,而对于前端性能标准的研究与测试相对比较空白,缺乏统一的标准与工具.众所周知,浏览器html组件的下载及渲染性能直接影响最终的用户体验,目前应 ...
- Android Programming: Pushing the Limits -- Chapter 7:Android IPC -- AIDL
服务端: 最终项目结构: 这个项目中,我们将用到自定义类CustomData作为服务端与客户端传递的数据. Step 1:创建CustomData类 package com.ldb.android.e ...
- elk安装(这个是初级的可以把这个套件安上)
http://udn.yyuap.com/doc/logstash-best-practice-cn/index.html ELK其实并不是一款软件,而是一整套解决方案,是三个开源软件Elastics ...
- EF – 问题集锦
1.对一个或多个实体的验证失败.有关详细信息,请参见“EntityValidationErrors”属性 在EF5.0修改实体的时候,出现“对一个或多个实体的验证失败.有关详细信息,请参见“Entit ...
- 【数据库】 Sqlserver 2008 error 40出现连接错误的解决方法
经常要连接到远程数据库上,因此常常碰到这个错误,然后又屡次忘记解决方法,所以今天坐下笔迹,好下次能快速回忆起来. 一.首先检查数据库的TCP/TP是否启动 1.启动Sql server配置管理器 2. ...
