建立链表的虚拟头结点 203 Remove Linked List Element,82,147,148,237
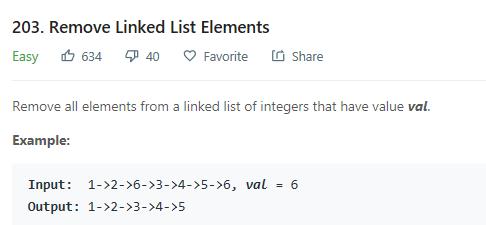


该逻辑对于删除第一个元素不适用。
这样的代码不优美
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { while(head!=NULL && head->val == val){
ListNode* delNode = head;
head = delNode ->next;
delete delNode;
} if(head == NULL)
return NULL; ListNode* cur = head; while(cur->next != NULL){
if(cur->next->val == val){
//删除
ListNode* delNode = cur->next;
cur->next = delNode->next;
delete delNode;
}
else
cur = cur->next;
} return head;
}
};
可以设置一个虚拟的头结点:

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead->next = head; ListNode* cur = dummyHead; while(cur->next != NULL){
if(cur->next->val == val){
//删除
ListNode* delNode = cur->next;
cur->next = delNode->next;
delete delNode;
}
else
cur = cur->next;
} ListNode* retNode = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return retNode;
}
};


这道题想了好久,原因是要把重复的所有元素都删除,这里设立一个duplicate标志位来记录当前cur是否与下一个结点重复。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* h = new ListNode(-);
h->next = head;
ListNode* pre = h;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur!=NULL){
bool duplicate = false;
while(cur->next!=NULL && cur->val==cur->next->val){
ListNode* delNode = cur;
cur = cur->next;
delete delNode;
duplicate = true;
}
if(duplicate == false){
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
else{
pre->next = cur->next;
ListNode* delNode = cur;
cur = cur->next;
delete delNode;
}
}
return h->next;
}
};
又重新做了一遍这道题,思路和前面设置标志位记录重复的不太一样。重点在于在两个结点不相同时,需要判断在它们前面是否存在重复的元素,若存在,pre需要跳过这些结点;若不存在,pre直接指向pre->next即cur即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode dummy();
dummy.next = head;
ListNode* pre = &dummy, *cur = head;
while(cur){
ListNode* next = cur->next;
while(next && next->val == cur->val){
cur = cur->next;
next = next->next;
}
if(cur != pre->next){
cur = next; //将最后一个重复的跳过
pre->next = cur;
}
else{ //pre和cur之间没有重复的
pre = cur;
cur = next;
} }
return dummy.next;
}
};
归并两个有序的链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* h = new ListNode(-);
ListNode* cur = h;
ListNode* cur1 = l1;
ListNode* cur2 = l2;
while(cur1 != NULL && cur2 != NULL){
if(cur1->val <= cur2->val){
cur->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else{
cur->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(cur1 != NULL){
cur->next = cur1; }
if(cur2 != NULL){
cur->next = cur2; }
ListNode* ret = h->next;
delete h;
return ret;
}
};

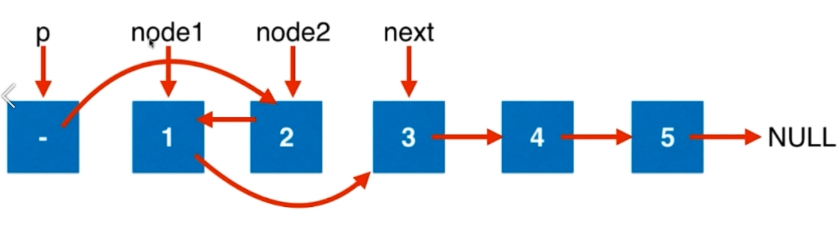

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* p = dummyHead;
while(p->next && p->next->next){
ListNode* node1 = p->next;
ListNode* node2 = node1->next;
ListNode* next = node2->next; node2->next = node1;
node1->next = next;
p->next = node2; p = node1;
}
ListNode* ret = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return ret;
}
};


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head || k==) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-);
ListNode* pre = dummy, *cur = head;
dummy->next = head;
int i = ;
while(cur){
i++;
if(i%k == ){
pre = reverseOneGroup(pre, cur->next);
cur = pre->next;
}
else{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
} ListNode* reverseOneGroup(ListNode* pre, ListNode* next){
ListNode* last = pre->next;
ListNode* cur = last->next;
while(cur!=next)
{
last->next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre->next; //注意这里是指向pre->next
pre->next = cur;
cur = last->next;
}
return last; //返回需要翻转的最后一个元素
}
};

用链表来实现插入排序。
思路:创建一个辅助的新链表,并且使用一个指针遍历原链表,每次将原链表中的一个节点插入到新链表的合适位置(即该节点的值大于新链表上的节点的值,又小于后一节点的值)。最后将新链表的头部返回即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) { if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head; ListNode* pre = new ListNode(-), *ans = pre; //创建一个新链表的头结点,并用一个临时变量来保存
ListNode* cur = head; //cur是原链表的指针
while(cur != NULL){
//每次循环前重置pre为头结点,保证每次都从头到尾遍历
pre = ans;
while(pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val < cur->val){
pre = pre->next;
} //此时,pre->next->val大于cur->val,应把cur插入到pre后
//保存原链表当前节点的下一个节点
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
//插入cur到pre后
cur->next = pre->next;
pre->next = cur; cur = tmp; //cur在原链表中后移一位
}
return ans->next;
}
};
一样的思路,又写了一遍,创建一个新链表,dummy指向新链表的头结点。扫描原链表,对于每个结点v,从前往后扫描已排序好的结果链表,找到第一个比v大的u结点,将v插入到u之前。
时间复杂度:共遍历n个结点,为每个结点找到合适的位置,最多再遍历n次,所以总的时间复杂度是O(n^2)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-); //dummy指向已排序链表的头结点 while(head){
ListNode* next = head->next;
ListNode *p = dummy;
while(p->next && p->next->val <= head->val)
p = p -> next; //p->next指向比head大的第一个结点,则p指向比head小的最后一个结点
//将head插入到p和p->next之间
head->next = p->next;
p->next = head; head = next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
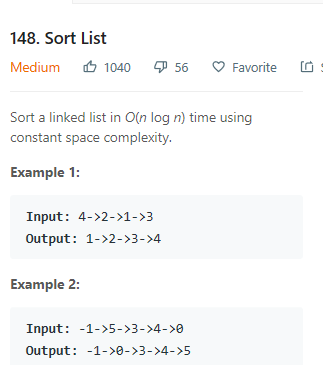
本题适用于归并排序,难点是:怎么样找到分治时的middle指针,采用快慢指针的思想。快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针走到头时,慢指针刚好走到中间位置,此位置即为middle的位置。
快慢指针思想:
快慢指针是指指针移动的步长,快指针移动的快,慢指针移动的慢,例如可以让快指针一次移动两个步长,让慢指针一次移动一个步长。
快慢指针有两个比较重要的应用:
1、判断链表是否为单链表
2、在有序链表中寻找中位数
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
//将一个链表平分为两个链表
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head, *pre = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
pre->next = NULL;
return merge(sortList(head), sortList(slow));
} ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-);
ListNode* cur = dummy;
while(l1 && l2){
if(l1->val < l2->val){
cur->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
cur->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(l1) cur->next = l1;
if(l2) cur->next = l2;
return dummy->next;
}
};


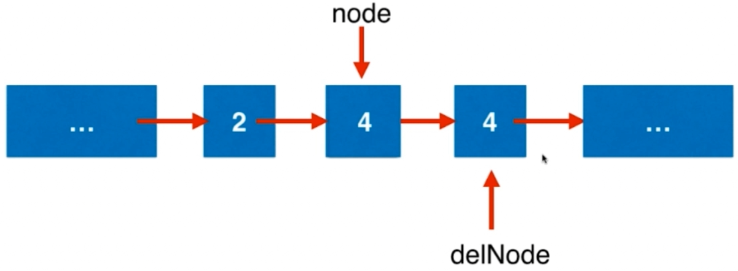
改变节点的值来解决问题。

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
if(node == NULL)
return;
if(node->next == NULL){
delete node;
node = NULL;
return;
}
node->val = node->next->val;
ListNode* delNode = node->next;
node->next = delNode->next;
delete delNode;
return;
}
};
建立链表的虚拟头结点 203 Remove Linked List Element,82,147,148,237的更多相关文章
- leetcode 203. Remove Linked List Elements 、83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List 、82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II(剑指offer57 删除链表中重复的结点)
203题是在链表中删除一个固定的值,83题是在链表中删除重复的数值,但要保留一个:82也是删除重复的数值,但重复的都删除,不保留. 比如[1.2.2.3],83题要求的结果是[1.2.3],82题要求 ...
- 单链表在不知头结点的情况下对第i个元素的删除
一.首先,看看单链表中第i个元素的删除: Status ListDelete_L (LinkList &L,int i,ElemType &e){ //在带头结点的单链表L中,删除第i ...
- 203. Remove Linked List Elements - LeetCode
Question 203. Remove Linked List Elements Solution 题目大意:从链表中删除给定的数 思路:遍历链表,如果该节点的值等于给的数就删除该节点,注意首节点 ...
- 203. Remove Linked List Elements【easy】
203. Remove Linked List Elements[easy] Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have ...
- LeetCode 203. Remove Linked List Elements 移除链表元素 C++/Java
Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have value val. Example: Input: ->->-& ...
- [刷题] 203 Remove Linked List Elements
要求 在链表中删除值为val的所有节点 示例 如 1->2->3->4->5->6->NULL,要求删除值为6的节点 返回1->2->3->4-& ...
- 【LeetCode】203. Remove Linked List Elements
Remove Linked List Elements Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have value val. ...
- 【刷题-LeetCode】203. Remove Linked List Elements
Remove Linked List Elements Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have value *val* ...
- LeetCode 203. Remove Linked List Elements (移除链表中的项)
Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have value val. ExampleGiven: 1 --> 2 --& ...
随机推荐
- HTML5样式、链接和表格
-------------------siwuxie095 HTML5 样式 1.标签 <style> 标签:样式定义 <link> 标签:资源引用 2.属性 rel:用于指定 ...
- 使用FileReader与FileWriter读写数据
-------------siwuxie095 工程名:TestFileRW 包名:com.siwuxie095.filerw 类名:FileReade ...
- ubuntu16.04 Mask_RCNN AlphaPose OpenPose Librealsense
#############MaskRCNNcource activate flappbirdcd /home/luo/Desktop/MyFile/MaskRCNN/MyOwnMaskRCNN1/sa ...
- 16-math_M_PI
头文件math.h中宏定义的是M_PI#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846所以不需要记忆PI的值了可以直接用
- C/C++ 经典面试题汇总
面试题1:变量的声明和定义有什么区别 ? 为变量分配地址和存储空间的称为定义,不分配地址的称为声明.一个变量可以在多个地方声明,但是只在一个地方定义.加入extern修饰的是变量的声明,说明此变量将在 ...
- 【Head First Java 读书笔记】(三)primitive主数据类型和引用
认识变量 变量有两种:primitive数数据类型和引用. 声明变量 Java注重变量.它不会让你将浮点数类型变量放进整数类型的变量中,除非你先跟编译器确认过数字可以损失掉精确度. 为了要让类型安全能 ...
- POJ2513 Colored Sticks(Trie+欧拉回路)
Description You are given a bunch of wooden sticks. Each endpoint of each stick is colored with some ...
- Codeforces 12D Ball(线段树)
N ladies attend the ball in the King's palace. Every lady can be described with three values: beauty ...
- MongoDB整理笔记のSharding分片
这是一种将海量的数据水平扩展的数据库集群系统,数据分表存储在sharding 的各个节点上,使用者通过简单的配置就可以很方便地构建一个分布式MongoDB 集群.MongoDB 的数据分块称为 chu ...
- Ubuntu的Unable to locate package无法更新源问题解决方案
https://blog.csdn.net/long19910605/article/details/47017889/ 问题: 更新源时提示不能联网(does the network require ...
