ThreadPoolExecutor使用方法
构造方法
ThreadPoolExecutor共4个构造方法:

直接看参数最多的7个参数分别代表:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize: 线程池核心线程数
- maximumPoolSize:线程池最大数
- keepAliveTime: 空闲线程存活时间
- unit: 时间单位
- workQueue: 线程池所使用的缓冲队列
- threadFactory:线程池创建线程使用的工厂
- handler: 线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略
- CallerRunsPolicy:由调用execute方法提交任务的线程来执行这个任务
- AbortPolicy:抛出异常RejectedExecutionException拒绝提交任务
- DiscardPolicy:直接抛弃任务,不做任何处理
- DiscardOldestPolicy:去除任务队列中的第一个任务,重新提交
RejectedExecutionHandler来处理;ThreadPoolExecutor内部有实现4个拒绝策略,默认为AbortPolicy策略:
1.当池中正在运行的线程数(包括空闲线程数)小于corePoolSize时,新建线程执行任务
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1));
// 任务1
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3 * 1000);
System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
//任务2
pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
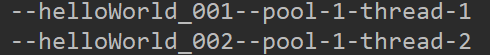
结论:线程1 结束后 没有继续线程1 而是启动线程2
2.当池中正在运行的线程数(包括空闲线程数)大于等于corePoolSize时,新插入的任务进入workQueue排队(如果workQueue长度允许),等待空闲线程来执行。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1));
// 任务1
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3 * 1000);
System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 任务2
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 任务3
pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_003--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
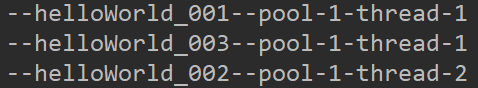
结论:任务2在运行过程中,任务3启动不会新建线程,因为有一个队列是空的,maximumPoolSize=3这个参数不起作用。
3.当队列里的任务达到上限,并且池中正在进行的线程小于maxinumPoolSize,对于新加入的任务,新建线程。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1));
// 任务1
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3 * 1000);
System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 任务2
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 任务3
pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_003--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
// 任务4
pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_004--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
结果:任务1,2启动后 任务3在队列 ,队列就满了,由于正在进行的线程数是2<maximumPoolSize,只能新建一个线程了 然后任务4就进了新线程-3,任务4结束,队列里的任务3在线程3 进行。
4.队列里的任务达到上限,并且池中正在运行的线程等于maximumPoolSize,对于新加入的任务,执行拒绝策略(线程池默认的策略是抛异常)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1));
// 任务1
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3 * 1000);
System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 任务2
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 任务3
pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_003--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
// 任务4
pool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("--helloWorld_004--" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
// 任务5
pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_005--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
运行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task ExecutorDemo$$Lambda$5/999966131@7699a589 rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@58372a00[Running, pool size = 3, active threads = 3, queued tasks = 1, completed tasks = 0]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2063)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:830)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1379)
at ExecutorDemo.main(ExecutorDemo.java:40)
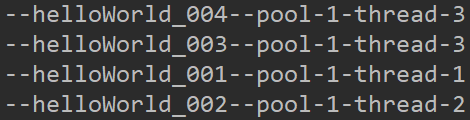
--helloWorld_004----pool-1-thread-3
--helloWorld_003--pool-1-thread-3
--helloWorld_001--pool-1-thread-1
--helloWorld_002--pool-1-thread-2
结论:队列达到上限,线程池达到最大值,故抛出异常。
关闭线程
分为两种方式:
pool.shutdown();//平缓关闭,不允许新的线程加入,正在运行的都跑完即可关闭。
pool.shutdownNow();//暴力关闭。不允许新的线程加入,且直接停到正在进行的线程。
ThreadPoolExecutor使用方法的更多相关文章
- 12.ThreadPoolExecutor线程池原理及其execute方法
jdk1.7.0_79 对于线程池大部分人可能会用,也知道为什么用.无非就是任务需要异步执行,再者就是线程需要统一管理起来.对于从线程池中获取线程,大部分人可能只知道,我现在需要一个线程来执行一个任 ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor机制探索-我们到底能走多远系列(41)
我们到底能走多远系列(41) 扯淡: 这一年过的不匆忙,也颇多感受,成长的路上难免弯路,这个世界上没人关心你有没有变强,只有自己时刻提醒自己,不要忘记最初出发的原因. 其实这个世界上比我们聪明的人无数 ...
- java线程API学习 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor(转)
线程池ThreadPoolExecutor继承自ExecutorService.是jdk1.5加入的新特性,将提交执行的任务在内部线程池中的可用线程中执行. 构造函数 ThreadPoolExecut ...
- 《java.util.concurrent 包源码阅读》12 线程池系列之ThreadPoolExecutor 第二部分
接着说worker线程是如何工作的.ThreadPoolExecutor有一个成员类叫Worker,所起到的作用就是线程池worker线程的作用. private final class Worker ...
- JAVA线程池学习,ThreadPoolTaskExecutor和ThreadPoolExecutor有何区别?
初学者很容易看错,如果没有看到spring或者JUC源码的人肯定是不太了解的. ThreadPoolTaskExecutor是spring core包中的,而ThreadPoolExecutor是JD ...
- 自定义 ThreadPoolExecutor 处理线程运行时异常
自定义 ThreadPoolExecutor 处理线程运行时异常 最近看完了ElasticSearch线程池模块的源码,感触颇深,然后也自不量力地借鉴ES的 EsThreadPoolExecutor ...
- java内置线程池ThreadPoolExecutor源码学习记录
背景 公司业务性能优化,使用java自带的Executors.newFixedThreadPool()方法生成线程池.但是其内部定义的LinkedBlockingQueue容量是Integer.MAX ...
- Java线程池ThreadPoolExecutor使用和分析(二) - execute()原理
相关文章目录: Java线程池ThreadPoolExecutor使用和分析(一) Java线程池ThreadPoolExecutor使用和分析(二) - execute()原理 Java线程池Thr ...
- 多线程相关-ThreadPoolExecutor
应用层面: ThreadPoolExecutor: 创建多线程池执行器:new ThreadPoolExecutor(),创建方法最终都是走的以下这个构造方法: /** * Creates a new ...
随机推荐
- 年年有余之java求余的技巧集合
背景 传说里玉皇大帝派龙王马上降雨到共光一带,龙王接到玉皇大帝命令,立马从海上调水,跑去共光施云布雨,但粗心又着急的龙王不小心把海里的鲸鱼随着雨水一起降落在了共光,龙王怕玉皇大帝责怪,灵机一动便声称他 ...
- loadrunner12下载、安装、认证、汉化
友情提示 推荐工具pandownload下载 本文尽可能地写得详细一些,有不懂的请先自行百度 安装过程中会有大量英文,可以用有道词典截图翻译 若你的电脑只有一个分区,则建议所有位置选择默认,或者根据个 ...
- linux初学者小记(二)
文件管理 1.文件系统结构元素 文件和目录被组织成一个单根倒置树结构文件系统从根目录下开始,用"/"表示. 1.1文件系统 # 根文件系统(rootfs):root filesys ...
- Redis 5.0 redis-cli --cluster help说明
背景: Redis Cluster 在5.0之后取消了ruby脚本 redis-trib.rb的支持(手动命令行添加集群的方式不变),集合到redis-cli里,避免了再安装ruby的相关环境.直接使 ...
- .net 更新access数据库 影响的行数为0
在更新Access数据库的时候,明明传入的数据及参数类型都正确,但是一直更新不了,查看影响的行数一直为0 此原因为 C#操作Access数据库的时候更新的参数和条件参数要按照更新语句中的顺序进行设置, ...
- ORM增删改查
目录 orm django 连接mysql顺序 1 settings配置文件中 2 项目文件夹下的init文件中写上下面内容, 补充 3 models文件中创建一个类(类名就是表名) 4.执行数据库同 ...
- Hbase入门(四)——表结构设计-RowKey
Hbase的表结构设计与关系型数据库有很多不同,主要是Hbase有Rowkey和列族.timestamp这几个全新的概念,如何设计表结构就非常的重要. 创建 Hbase就是通过 表 Rowkey 列族 ...
- Webstorm轻松部署项目至服务器
wo大前端在开发环境下,需要将项目部署到测试环境,webstorm进行基础配置操作就可实现. 一.在Deployment选项下配置远程服务器地址 点击加号,选择type类型,Name自己填,帮你找到这 ...
- 对BUG的分析与理解
对BUG的分析与理解 bug的分类 bug,其实就是软件期望的行为与实际行为的差异.从程序的角度来看,在软件整个生命周期中都会有bug的出现.需求分析过程中,需求理解的不足,导致的理解错位 ,遗漏甚至 ...
- A-08 拉格朗日对偶性
目录 拉格朗日对偶性 一.原始问题 1.1 约束最优化问题 1.2 广义拉格朗日函数 1.3 约束条件的考虑 二.对偶问题 三.原始问题和对偶问题的关系 3.1 定理1 3.2 推论1 3.3 定理2 ...
