探秘Tomcat——启动篇
tomcat作为一款web服务器本身很复杂,代码量也很大,但是模块化很强,最核心的模块还是连接器Connector和容器Container。具体请看下图:
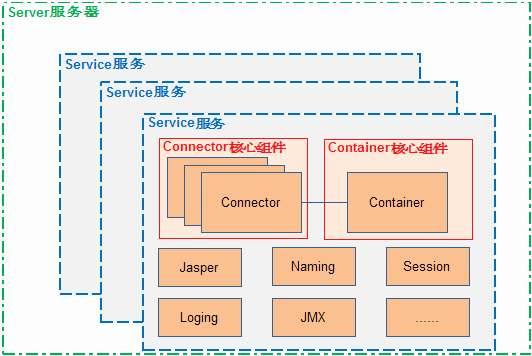
从图中可以看出
a. 高亮的两块是Connector和Container,为什么说他们两最核心,其中Connector是负责接收http请求,当你在浏览器中输入URL为http://www.demon.com,这样的http请求就会被Connector接收并转发给容器Container。
到了Container后,会经过不同的容器层有:
Engine:表示整个Catalina servlet引擎;
Host: 表示包含有一个或多个Context容器的虚拟主机;
Context: 表示一个Web应用程序,一个Context可以有多个Wrapper;
Wrapper: 表示一个独立的servlet
一层层的处理后最终到达的是Wrapper即特定的serlvet处理器,具体用于处理http的请求响应。
b. 图中除了Connector和Container以外还有一些Naming、Session等一些服务,统统封装在了一个service里面,可以用于对外提供各种服务,比如我们不仅希望 tomcat可以提供一个web请求响应的服务,还希望知道其中的详细处理细节,我们可以使用service中的日志服务,用于打印一些请求处理过程中的细节信息。
c. 有了这些service模块,我们还需要有一个落脚点,这个落脚点用于控制service的生杀大全,负责service的整个生命周期,包括service的初始化、启动、结束等等。
d. 综上举一个例子,现在有A软件公司,共有三个部门——研发部门、财务部门、技术支持部门
其中每个部门相当于一个service,在每个service中可以提供不同的服务,比如研发部门可以提供功能开发服务、功能测试服务、持续集成部署服务、美工服务等。
而封装在server中的各个服务由server来统一管理,好比A公司可以实现研发部门的组建(或重组)——开工——裁撤等一系列的生命周期功能,如果A公司逢上国家法定节假日需要放假休息,那么相关的service部门也都会执行放假模式,同理,如果A公司正常运营上班,那么各个service也都会切换到上班模式。有了server的存在,从而方便对于service的管理。
大致了解了tomcat的架构和工作原理,我们来看看平时我们通过点击startup.bat来启动tomcat是如何从代码层面实现的,在启动过程中又做了哪些事情(基于tomcat6版本的源码)。
1.启动入口
在代码中,tomcat的启动是通过运行org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap类的main方法来启动服务的
public static void main(String args[]) {
if (daemon == null) {
daemon = new Bootstrap();
try {
daemon.init();
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
return;
}
}
try {
String command = "start";
if (args.length > 0) {
command = args[args.length - 1];
}
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stopd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "stop";
daemon.stop();
} else if (command.equals("start")) {
daemon.setAwait(true);
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stop")) {
daemon.stopServer(args);
} else {
log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
a. 初始化Bootstrap对象
b. 根据具体的需求完成服务的加载、启动和关闭的功能
备注:这里运行或调试main方法的时候需要在VM arguments中填入类似-Dcatalina.home="C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\tomcat\apache-tomcat-6.0.43-src\output\build"这样的参数,具体操作参见《探秘Tomcat(一)——Myeclipse中导入Tomcat源码》

2.Bootstrap的初始化
2.1 init方法
public void init()
throws Exception
{ // Set Catalina path
setCatalinaHome();
setCatalinaBase(); initClassLoaders(); Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader); SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader); // Load our startup class and call its process() method
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
Class startupClass =
catalinaLoader.loadClass
("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.newInstance(); // Set the shared extensions class loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues); catalinaDaemon = startupInstance; }
a. 其中setCatalinaHome和setCatalinaBase分别用于为catalina.name和catalina.base赋值;
b. initClassLoaders用于初始类加载器,分别初始化了三个加载器CommonLoader、CatalinaLoader和SharedLoader,从代码可以发现CommonLoader是CatalinaLoader和SharedLoader的父类,最终初始化完成,两个子类都指向CommonLoader;
c. 通过反射机制生成一份org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina的实例用于启动。
2.2 createClassLoader方法
下面我们来看看init->initClassLoaders->createClassLoader这个方法,通过这个方法我们分别得到了三个加载器CommonLoader、CatalinaLoader和SharedLoader,我们加载所需要的目录和jar包等。
private ClassLoader createClassLoader(String name, ClassLoader parent)
throws Exception { String value = CatalinaProperties.getProperty(name + ".loader");//得到的value为${catalina.base}/lib,${catalina.base}/lib/*.jar,${catalina.home}/lib,${catalina.home}/lib/*.jar
if ((value == null) || (value.equals("")))
return parent; ArrayList repositoryLocations = new ArrayList();
ArrayList repositoryTypes = new ArrayList();
int i; StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(value, ",");//用于分隔String的类
while (tokenizer.hasMoreElements()) {//遍历value中的值
String repository = tokenizer.nextToken(); // Local repository
boolean replace = false;
String before = repository;
while ((i=repository.indexOf(CATALINA_HOME_TOKEN))>=0) {//这样的遍历说明如果value的每项里面包含了${catalina.home}或者${catalina.base}就将标记变量replace置为true,并且确确实实的替换这些变量,比如这里讲${catalina.base}替换为C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\tomcat\apache-tomcat-6.0.43-src\output\build。每次遍历完value值后,都会根据存储的repository的类型添加不同的值到repositoryTypes中去。
replace=true;
if (i>0) {
repository = repository.substring(0,i) + getCatalinaHome()
+ repository.substring(i+CATALINA_HOME_TOKEN.length());
} else {
repository = getCatalinaHome()
+ repository.substring(CATALINA_HOME_TOKEN.length());
}
}
while ((i=repository.indexOf(CATALINA_BASE_TOKEN))>=0) {
replace=true;
if (i>0) {
repository = repository.substring(0,i) + getCatalinaBase()
+ repository.substring(i+CATALINA_BASE_TOKEN.length());
} else {
repository = getCatalinaBase()
+ repository.substring(CATALINA_BASE_TOKEN.length());
}
}
if (replace && log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Expanded " + before + " to " + repository); // Check for a JAR URL repository
try {
URL url=new URL(repository);
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_URL);
continue;
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// Ignore
} if (repository.endsWith("*.jar")) {
repository = repository.substring
(0, repository.length() - "*.jar".length());
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_GLOB);
} else if (repository.endsWith(".jar")) {
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_JAR);
} else {
repositoryLocations.add(repository);
repositoryTypes.add(ClassLoaderFactory.IS_DIR);
}
} String[] locations = (String[]) repositoryLocations.toArray(new String[0]);
Integer[] types = (Integer[]) repositoryTypes.toArray(new Integer[0]);//分别将两个list集合转化为数组 ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader
(locations, types, parent);//调用createClassLoader方法,其中细加载到每个目录和具体的目录下面的文件,注意其中的加载的数据集使用LinkedHashSet,这是利用了set集合的特性,不允许重复元素的出现,因为这里面会有重复加载的情况,所以用set保证了唯一性。通过这个操作等于加载了所有的文件,具体类加载以及URLClassLoader的使用可以参见http://blog.csdn.net/mycomputerxiaomei/article/details/24470465 // Retrieving MBean server
MBeanServer mBeanServer = null;//得到一个MBean的对象
if (MBeanServerFactory.findMBeanServer(null).size() > 0) {
mBeanServer =
(MBeanServer) MBeanServerFactory.findMBeanServer(null).get(0);
} else {
mBeanServer = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
} // Register the server classloader
ObjectName objectName =
new ObjectName("Catalina:type=ServerClassLoader,name=" + name);
mBeanServer.registerMBean(classLoader, objectName);//将类加载器注册到mbean服务上,这样做的作用是,一旦classLoader有变化了,就会有notification。 return classLoader; }
这里有个小细节在createClassLoader方法中有调用方法getCatalinaBase,而getCatalinaBase又会去调用getCatalinaHome,而不是将getCatalinaHome中的具体功能代码又冗余的写一遍,这是一个很好的习惯^_^
至此,我们完成了Bootstrap对象的初始化,为catalina.home等,初始化了三个类加载器。
3.server的加载和启动
3.1 deamon.load方法
public void load() {
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
initDirs();
// Before digester - it may be needed
initNaming();
// Create and execute our Digester
Digester digester = createStartDigester();
InputSource inputSource = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
File file = null;
try {
file = configFile();
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
inputSource = new InputSource("file://" + file.getAbsolutePath());
} catch (Exception e) {
;
}
if (inputStream == null) {
try {
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(getConfigFile());
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource(getConfigFile()).toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
;
}
}
// This should be included in catalina.jar
// Alternative: don't bother with xml, just create it manually.
if( inputStream==null ) {
try {
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("server-embed.xml");
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource("server-embed.xml").toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
;
}
}
if ((inputStream == null) && (file != null)) {
log.warn("Can't load server.xml from " + file.getAbsolutePath());
if (file.exists() && !file.canRead()) {
log.warn("Permissions incorrect, read permission is not allowed on the file.");
}
return;
}
try {
inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);
digester.push(this);
digester.parse(inputSource);
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Catalina.start using "
+ getConfigFile() + ": " , e);
return;
}
// Stream redirection
initStreams();
// Start the new server
if (getServer() instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
getServer().initialize();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"))
throw new java.lang.Error(e);
else
log.error("Catalina.start", e);
}
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info("Initialization processed in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
a. 前面的完成一些初始化的工作;
b. createStartDigester方法很重要,用于声明要实例化的所有服务,当然这个工作需要与file = configFile();中声明的位于conf下的server.xml进行配合;
c. 通过digester.parse(inputSource)解析server.xml中的元素
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
// Initialize the digester
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setValidating(false);
digester.setRulesValidation(true);
HashMap<Class, List<String>> fakeAttributes = new HashMap<Class, List<String>>();
ArrayList<String> attrs = new ArrayList<String>();
attrs.add("className");
fakeAttributes.put(Object.class, attrs);
digester.setFakeAttributes(fakeAttributes);
digester.setClassLoader(StandardServer.class.getClassLoader());
// Configure the actions we will be using
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResources");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/GlobalNamingResources");
digester.addSetNext("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"setGlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResources");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service",
"addService",
"org.apache.catalina.Service");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
//Executor
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Executor",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardThreadExecutor",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Executor");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Executor",
"addExecutor",
"org.apache.catalina.Executor");
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector",
new ConnectorCreateRule());
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector",
new SetAllPropertiesRule(new String[]{"executor"}));
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector",
"addConnector",
"org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
// Add RuleSets for nested elements
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/GlobalNamingResources/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new EngineRuleSet("Server/Service/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new HostRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/"));
digester.addRuleSet(ClusterRuleSetFactory.getClusterRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Cluster/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context/"));
// When the 'engine' is found, set the parentClassLoader.
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Engine",
new SetParentClassLoaderRule(parentClassLoader));
digester.addRuleSet(ClusterRuleSetFactory.getClusterRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Cluster/"));
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Digester for server.xml created " + ( t2-t1 ));
return (digester);
}
从这里我们看到了很多熟悉的字眼比如StandardServer、Engine、Host、Context等,可以对比看下server.xml中的标签
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<!-- Note: A "Server" is not itself a "Container", so you may not
define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/server.html
-->
<Server port="" shutdown="SHUTDOWN"> <!--APR library loader. Documentation at /docs/apr.html -->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" />
<!--Initialize Jasper prior to webapps are loaded. Documentation at /docs/jasper-howto.html -->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JasperListener" />
<!-- Prevent memory leaks due to use of particular java/javax APIs-->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" />
<!-- JMX Support for the Tomcat server. Documentation at /docs/non-existent.html -->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.ServerLifecycleListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" /> <!-- Global JNDI resources
Documentation at /docs/jndi-resources-howto.html
-->
<GlobalNamingResources>
<!-- Editable user database that can also be used by
UserDatabaseRealm to authenticate users
-->
<Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container"
type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"
description="User database that can be updated and saved"
factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory"
pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" />
</GlobalNamingResources> <!-- A "Service" is a collection of one or more "Connectors" that share
a single "Container" Note: A "Service" is not itself a "Container",
so you may not define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/service.html
-->
<Service name="Catalina"> <!--The connectors can use a shared executor, you can define one or more named thread pools-->
<!--
<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-"
maxThreads="" minSpareThreads=""/>
--> <!-- A "Connector" represents an endpoint by which requests are received
and responses are returned. Documentation at :
Java HTTP Connector: /docs/config/http.html (blocking & non-blocking)
Java AJP Connector: /docs/config/ajp.html
APR (HTTP/AJP) Connector: /docs/apr.html
Define a non-SSL HTTP/1.1 Connector on port
-->
<Connector port="" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout=""
redirectPort="" />
<!-- A "Connector" using the shared thread pool-->
<!--
<Connector executor="tomcatThreadPool"
port="" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout=""
redirectPort="" />
-->
<!-- Define a SSL HTTP/1.1 Connector on port
This connector uses the JSSE configuration, when using APR, the
connector should be using the OpenSSL style configuration
described in the APR documentation -->
<!--
<Connector port="" protocol="HTTP/1.1" SSLEnabled="true"
maxThreads="" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS" />
--> <!-- Define an AJP 1.3 Connector on port -->
<Connector port="" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="" /> <!-- An Engine represents the entry point (within Catalina) that processes
every request. The Engine implementation for Tomcat stand alone
analyzes the HTTP headers included with the request, and passes them
on to the appropriate Host (virtual host).
Documentation at /docs/config/engine.html --> <!-- You should set jvmRoute to support load-balancing via AJP ie :
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="jvm1">
-->
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost"> <!--For clustering, please take a look at documentation at:
/docs/cluster-howto.html (simple how to)
/docs/config/cluster.html (reference documentation) -->
<!--
<Cluster className="org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster"/>
--> <!-- The request dumper valve dumps useful debugging information about
the request and response data received and sent by Tomcat.
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html -->
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RequestDumperValve"/>
--> <!-- This Realm uses the UserDatabase configured in the global JNDI
resources under the key "UserDatabase". Any edits
that are performed against this UserDatabase are immediately
available for use by the Realm. -->
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"
resourceName="UserDatabase"/> <!-- Define the default virtual host
Note: XML Schema validation will not work with Xerces 2.2.
-->
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"
xmlValidation="false" xmlNamespaceAware="false"> <!-- SingleSignOn valve, share authentication between web applications
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html -->
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SingleSignOn" />
--> <!-- Access log processes all example.
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html -->
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log." suffix=".txt" pattern="common" resolveHosts="false"/>
--> </Host>
</Engine>
</Service>
</Server>
web.xml
Digester就是根据web.xml中声明的标签生成对象,并把元素的属性赋值为对象的属性,并关联起他们之间的父子关系。
3.2 start方法
既然已经加载好了server以及所需要的service,那么就可以开始启动了。
public void start()
throws Exception {
if( catalinaDaemon==null ) init(); Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [] )null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null); }
通过反射机制,可是调用Catalina类下面的start方法。
下面我们看看Catalina中的start方法具体都做了什么
public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured.");
return;
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
if (getServer() instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) getServer()).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("Catalina.start: ", e);
}
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info("Server startup in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
try {
// Register shutdown hook
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// This will fail on JDK 1.2. Ignoring, as Tomcat can run
// fine without the shutdown hook.
}
if (await) {
await();
stop();
}
}
a. 首先判断这个server是否为空,如果为空则需要先加载load
b. 判断getServer是否是Lifecycle的实例,显然是,我们可以从StandardServer类的声明中
“public final class StandardServer implements Lifecycle, Server, MBeanRegistration”可以看出,StandardServer实现了LifeCycle的接口,Server接口。
而且当我们进入Server类的时候,可以看到类的注释上写了:一般而且如果某类实现了Server接口,同时也要实现LifeCycle接口,这也正好验证了这里StandardServer的声明;
c. 如果满足是LifeCycle的实例的条件,则执行StandardServer中的start方法,该方法主要用于启动所有前面解析出来的service,包括进入类Connector启动Connector服务,进入Container中依次通过Engine、Host、Context和Wrapper启动相应的服务。
至此,就完成了
- Bootstrap的初始化
- 加载server服务
- 启动server服务
最终实现了启动tomcat的目的,其实现在回头来看,启动一个服务器无非就是启动了一个server^^
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”将是我最大的写作动力!如果您想持续关注我的文章,请扫描二维码,关注JackieZheng的微信公众号,我会将我的文章推送给您,并和您一起分享我日常阅读过的优质文章。
友情赞助
如果你觉得博主的文章对你那么一点小帮助,恰巧你又有想打赏博主的小冲动,那么事不宜迟,赶紧扫一扫,小额地赞助下,攒个奶粉钱,也是让博主有动力继续努力,写出更好的文章^^。
1. 支付宝 2. 微信


探秘Tomcat——启动篇的更多相关文章
- 探秘Tomcat——连接篇
前两篇我们分别粗线条和细粒度的讲解了tomcat的服务是如何启动以及连接器Connector和容器Container又分别是如何被启动的. 本篇我们主要侧重tomcat中server.service以 ...
- 探秘Tomcat——连接器和容器的优雅启动
前言: 上篇<探秘Tomcat——启动篇>粗线条的介绍了在tomcat在启动过程中如何初始化Bootstrap类,加载并执行server,从而启动整个tomcat服务,一直到我们看到控制台 ...
- Tomcat 第二篇:启动流程
1 Tomcat 基本知识 首先介绍一些 Tomcat 的基本知识,防止有纯小白看的云里雾里的. 下面这张图是一个下载好二进制版的的 Tomcat ,直接解压得到的,虽然版本是 9.x ,但是这个目录 ...
- 探秘Tomcat——从一个简陋的Web服务器开始
前言: 无论是之前所在实习单位小到一个三五个人做的项目,还是如今一个在做的百人以上的产品,一直都能看到tomcat的身影.工作中经常遇到的操作就是启动和关闭tomcat服务,或者修改了摸个java文件 ...
- tomcat启动指定项目
看一下server.xml,conf/localhost/,web.xml是否配置了其他的WEBAPP应用,但实际地址已经被移除,清空WORK目录试试 http://blog.163.com/mous ...
- 探秘Tomcat(一)——Myeclipse中导入Tomcat源码
前言:有的时候自己不知道自己是井底之蛙,这并没有什么可怕的,因为你只要蜷缩在方寸之间的井里,无数次的生活轨迹无非最终归结还是一个圆形:但是可怕的是有一天你不得不从井里跳出来生活,需要重新审视井以外的生 ...
- Tomcat启动报错:Failed to initialize end point associated with ProtocolHandler ["http-apr-8080"]
在用MyEclipse做开发,启动Tomcat的时候,控制台老是报错Failed to initialize end point associated with ProtocolHandler [&q ...
- Tomcat启动时卡在“INFO: Deploying web application directory ”
今天在linux上的tomcat部署一个网站时,在刚启动tomcat的时候提示启动成功,然后也能访问成功. 可是第二次启动时虽然没有报错,但无法访问tomcat,查看了catalina.out日志,发 ...
- Linux配置tomcat (centos配置java环境 tomcat配置篇 总结三)
♣下载安装tomcat7 ♣设置启动和关闭 ♣设置用户名和密码 ♣发布java web项目 声明:这篇教程是建立在前两篇教程的基础上的,所以,还没安装工具和jdk,可以先看这个系列的前面两篇(去到文末 ...
随机推荐
- Python之路Day12--mysql介绍及操作
上节回顾: 1. RabbitMQ a. 平均分发 b. perfetch = 1 c. durable 队列持久化 deliver_mode = 2 消息持久化 d. 1对多广播 exchang ...
- 【noip 2016】 蚯蚓(earthworm)
100分程序,写了2天+1小时 →题目在这里← 大神就是厉害--写的程序居然看都看不懂,还有就是cena上过了但是luogu上一直是恶心的TLE 首先是考虑p=0时,数组大小开到了1100000,然后 ...
- 微信中一些常用的js事件积累
1.网页图片集左右滑动查看图片,如下样例: jjs效果 var pictures = []; angular.forEach(pitctures,function(k,i){ pict ...
- 【实战Java高并发程序设计6】挑战无锁算法:无锁的Vector实现
[实战Java高并发程序设计 1]Java中的指针:Unsafe类 [实战Java高并发程序设计 2]无锁的对象引用:AtomicReference [实战Java高并发程序设计 3]带有时间戳的对象 ...
- Your awesome titleHH
Welcome to Jekyll! Your awesome titleHH About Blogging Like a Hacker Welcome to Jekyll! Jan 9, 2016 ...
- Powershell 开启远程桌面
function Set-RemoteDesktop { while($InNumber -ne 6) { Write-Host " ###################### ...
- ABP理论学习之通知系统
返回总目录 本篇目录 介绍 订阅通知 发布通知 用户通知管理者 实时通知 通知存储 通知定义 介绍 通知(Notification)用于告知用户系统中的特定事件.ABP提供了基于实时通知基础设施的发布 ...
- ENode框架Conference案例分析系列之 - 上下文划分和领域建模
前面一片文章,我介绍了Conference案例的核心业务,为了方便后面的分析,我这里再列一下: 业务描述 Conference是这样一个系统,它提供了一个在线创建会议以及预订会议座位的平台.这个系统的 ...
- [Voice communications] 音量的控制
改变音频的音量是音频处理中最基础的部分,我们可以利用 GainNode 来构建 Mixers 的结构块.GainNode 的接口是很简单的: interface GainNode : AudioNod ...
- AMD and CMD are dead之js模块化黑魔法
var define, require, define2, require2; typeof JSON != "object" && (JSON = {}), fu ...

