[数据结构] 2.7 Heap 堆
* 注: 本文/本系列谢绝转载,如有转载,本人有权利追究相应责任。
1.堆是什么?
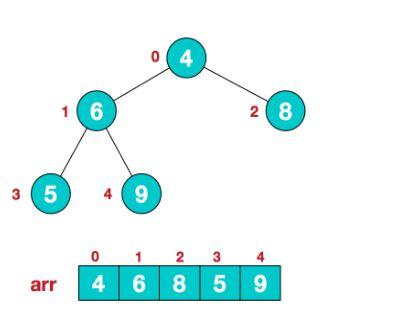
(如图所示是一个小堆)
1)堆是一颗完全二叉树,它的最后一层不是满的,其他每一层都是满的,最后一层从左到右也没有空隙。
简单的说? 完全二叉树也就是没有缝隙的二叉树。
2)堆常常通过数组实现,因为 父子节点直接的关系直接可以通过数组的索引换算
parent(i) = i/2
left child(i) = 2*i + 1
right child(i) = 2*i + 2
3)对于最大堆来说,每个节点的值都不大于其父节点的值,也就是根节点是最大的。
对于最小堆来说,每个节点的值都不小于其父节点的值,也就是根节点是最小的
4)堆进行插入和删除的时间复杂度均为 O(LogN)
2.堆的应用
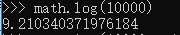
堆可以解决的首先就是topK问题,假设要从N大小的实数数组中找到topK,那么需要K*logN的时间。
当N=10000时
当N=10000*10000时
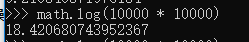
也就是说N可以放的足够大,K可以适当大一些,经过本机实验,堆在单机单线程下只需要14s就可以处理一亿数据的Top1W操作。
3.堆的实现
堆的操作主要是两个 add、remove,有些地方也会存在buildHeap的操作,我们分别捋一下它们的思路。
一下基于一个最大堆。
1) add操作,添加元素
思路:
将添加的元素放在数组尾部,进行“上浮”操作。也就是比较父元素,如果大于父元素则上浮。
实际长度 ++
/**
* 插入过程需要上浮比较
* @param node
*/
public void insert(Node node){
if(actualSize == MAX_N){
System.out.println("当前堆已满!");
return;
} // 插入
// 插入节点
nodes[actualSize] = node; // 上浮过程
// 调整堆,从这个节点开始与其夫节点进行比较,如果大于父节点则交换上浮
for(int i = actualSize; i > 0 ;i = getParentIndex(i)){
Node current = nodes[i];
Node parent = nodes[getParentIndex(i)];
if(parent.data < current.data){
nodes[i] = parent;
nodes[getParentIndex(i)] = current;
}
}
actualSize ++;
}
2) remove操作,删除元素
思路:
获得堆顶的值,然后用堆底节点替换堆顶节点。并针对此节点进行"下沉"操作,所谓下沉,就是如果比较当前元素与左右子节点的值,如果比它们小,则与最大者交换。
实际长度 --
/**
* 删除过程需要下沉比较
* @param node
*/
public void remove(Node node){
if(actualSize == 0){
System.out.println("当前堆已空!");
return;
} if(actualSize == 1){
actualSize --;
return;
} // 删除过程
// 使用最后一个节点替换掉顶点
Node tailNode = nodes[actualSize-1];
nodes[0] = tailNode;
actualSize --; // 下沉比较
for(int i = 0; i < actualSize;){
Node current = nodes[i]; Node leftChild = null;
if(getLeftChildIndex(i) < actualSize){
leftChild = nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)];
}
Node rightChild = null;
if(getRightChildIndex(i) < actualSize){
rightChild = nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)];
} if(leftChild == null && rightChild == null){
return;
} if(leftChild != null && leftChild.data > current.data){
if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > leftChild.data){ // 右枝最大
nodes[i] = rightChild;
nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current;
// i走右枝
i = getRightChildIndex(i);
continue;
}else{ // 左枝最大
nodes[i] = leftChild;
nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)] = current;
// i走左枝
i = getLeftChildIndex(i);
continue;
}
}else{
if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > current.data){ // 右枝最大
nodes[i] = rightChild;
nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current;
// i走右枝
i = getRightChildIndex(i);
continue;
}else if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data <= current.data){ // 当前点最大
//保持现状,直接结束循环
break;
}
}
}
}
3)buildHeap操作,给一个数组,进行建立堆操作
思路:
遍历数组的每一个节点,针对每个节点进行"上浮"操作.
Code:
package ds6.heap;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Heap {
static class Node{
long data;
public Node(long data) {
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
'}';
}
}
/**
* TopN最大值堆
*/
static class TopNMaxHeap{
int MAX_N = 10; // Top N ,指定堆的最大大小
Node[] nodes;
int actualSize = 0;
public TopNMaxHeap(int MAX_N) {
this.MAX_N = MAX_N;
nodes = new Node[MAX_N];
}
public void foreachPrint(){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nodes));
}
/**
* 删除过程需要下沉比较
* @param node
*/
public void remove(Node node){
if(actualSize == 0){
System.out.println("当前堆已空!");
return;
}
if(actualSize == 1){
actualSize --;
return;
}
// 删除过程
// 使用最后一个节点替换掉顶点
Node tailNode = nodes[actualSize-1];
nodes[0] = tailNode;
actualSize --;
// 下沉比较
for(int i = 0; i < actualSize;){
Node current = nodes[i];
Node leftChild = null;
if(getLeftChildIndex(i) < actualSize){
leftChild = nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)];
}
Node rightChild = null;
if(getRightChildIndex(i) < actualSize){
rightChild = nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)];
}
if(leftChild == null && rightChild == null){
return;
}
if(leftChild != null && leftChild.data > current.data){
if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > leftChild.data){ // 右枝最大
nodes[i] = rightChild;
nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current;
// i走右枝
i = getRightChildIndex(i);
continue;
}else{ // 左枝最大
nodes[i] = leftChild;
nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)] = current;
// i走左枝
i = getLeftChildIndex(i);
continue;
}
}else{
if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > current.data){ // 右枝最大
nodes[i] = rightChild;
nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current;
// i走右枝
i = getRightChildIndex(i);
continue;
}else{ // 当前点最大
//保持现状,直接结束循环
break;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 插入过程需要上浮比较
* @param node
*/
public void insert(Node node){
if(actualSize == MAX_N){
System.out.println("当前堆已满!");
return;
}
// 插入
// 插入节点
nodes[actualSize] = node;
// 上浮过程
// 调整堆,从这个节点开始与其夫节点进行比较,如果大于父节点则交换上浮
for(int i = actualSize; i > 0 ;i = getParentIndex(i)){
Node current = nodes[i];
Node parent = nodes[getParentIndex(i)];
if(parent.data < current.data){
nodes[i] = parent;
nodes[getParentIndex(i)] = current;
}
}
actualSize ++;
}
public int getParentIndex(int x){
return (x-1)/2;
}
public int getLeftChildIndex(int x){
return 2*x + 1;
}
public int getRightChildIndex(int x){
return 2*x + 2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TopNMaxHeap topNMaxHeap = new TopNMaxHeap(10);
topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(27));
topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(33));
topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(30));
topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(31));
Node nodeToRemove = new Node(40);
topNMaxHeap.insert(nodeToRemove);
topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(20));
topNMaxHeap.foreachPrint();
topNMaxHeap.remove(nodeToRemove);
topNMaxHeap.foreachPrint();
}
}
result:
[Node{data=40}, Node{data=33}, Node{data=30}, Node{data=27}, Node{data=31}, Node{data=20}, null, null, null, null]
[Node{data=33}, Node{data=31}, Node{data=30}, Node{data=27}, Node{data=20}, Node{data=20}, null, null, null, null]
4.堆排序
因为堆的这个特性,通过不断poll出堆顶元素就可以对元素列表进行排序。
测试:
public static void test2(){
int[] toSort = new int[]{
7,10,6,8,9,3,5,4
};
TopNMaxHeap heap = new TopNMaxHeap(toSort.length);
for(int i = 0 ; i < toSort.length; i++ ){
heap.insert(new Node(toSort[i]));
}
int[] result = new int[toSort.length];
for(int i = 0; i < toSort.length; i++ ){
result[i]=(int)heap.nodes[0].data;
heap.remove(heap.nodes[0]);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
result:
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3]
[数据结构] 2.7 Heap 堆的更多相关文章
- Stack栈 Heap堆
Stack(栈) 栈(stack) 又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表.其限制是仅允许在表的一端进行插入和删除运算.这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底.向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈.入栈或压栈 ...
- 栈 堆 stack heap 堆内存 栈内存 内存分配中的堆和栈 掌握堆内存的权柄就是返回的指针 栈是面向线程的而堆是面向进程的。 new/delete and malloc/ free 指针与内存模型
小结: 1.栈内存 为什么快? Due to this nature, the process of storing and retrieving data from the stack is ver ...
- Heap堆的理解以及在IAR中如何设置堆的大小
文章首发于浩瀚先森博客 堆栈的概念在脑海里已经存在有一段时间了,今天就测试来整理下Heap堆.栈以后再说. 堆区不像全局变量和局部变量总是有指定的内存大小,它是为了在程序运行时动态分配内存而设定的一块 ...
- java - Stack栈和Heap堆的区别
首先分清楚Stack,Heap的中文翻译:Stack—栈,Heap—堆. 在中文里,Stack可以翻译为“堆栈”,所以我直接查找了计算机术语里面堆和栈开头的词语: 堆存储 ...
- Heap(堆)和stack(栈)有的区别是什么。
java的内存分为两类,一类是栈内存,一类是堆内存.栈内存是指程序进入一个方法时,会为这个方法单独分配一块私属存储空间,用于存储这个方法内部的局部变量,当这个方法结束时,分配给这个方法的栈会释放,这个 ...
- JAVA Stack栈和Heap堆的区别(转)
首先分清楚Stack,Heap的中文翻译:Stack—栈,Heap—堆. 在中文里,Stack可以翻译为“堆栈”,所以我直接查找了计算机术语里面堆和栈开头的词语: ...
- 逻辑运算符、三元运算符、for循环、stack(栈),heap(堆),方法区,静态域
Lesson One 2018-04-17 19:58:39 逻辑运算符(用于逻辑运算,左右两边都是 true 或 false) 逻辑与-& 和 短路与-&& 区别: & ...
- linux heap堆分配
heap堆分配在用户层面:malloc函数用于heap内存分配 void* malloc(size_t size); 进程的虚拟内存地址布局: 对用户来说,主要关注的空间是User Space.将Us ...
- 如何给女朋友讲明白:Java 中 Stack(栈) 与 Heap(堆)
背景 Java 中 Stack(栈) 与 Heap(堆) 是面试中被经常问到的一个话题. 有没有对 Java 中 Stack(栈) 与 Heap(堆) 烂熟于心的童鞋,请举手!!!(怎么没人举手-) ...
随机推荐
- windows----------火狐浏览器访问所有https网站都显示链接不安全解决办法
1.如有以下情况,点右边的“高级”,看看自己的错误码是否为SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER 2.在地址栏键入"about:config" 点击“我了解此风险” 3. ...
- RSA算法的C++string实现(模幂算法和欧几里得算法的使用)后附思路
void resetNumA(string numAStr); //使用string重置numB void resetNumB(string numBStr); //将数组转换为字符串,用于输出 st ...
- JavaScript实现循环链表
单链表地址:点我 一.循环链表 节点的next指向下一个节点,节点的prev指向上一个节点 function loopList() { let length = 0, head = null, tai ...
- SQL死锁操作
这两天数据库经常被锁,所以记录一下操作: 查看被锁表:select request_session_id spid,OBJECT_NAME(resource_associated_entity_id) ...
- djanggo中自定义过滤器的步骤图解
- 畅捷通T+12.2升级时发生的错误及处理方法图解
前言:最近处理一个客户单位的财务数据,需要从2004年的U820版本的数据升级到畅捷通T+12.2版本.经查,该升级先要将原数据升级到T6,再从T6升级到畅捷通T+12.2版本.U820升级到T6很简 ...
- Python在终端通过pip安装好包以后,在Pycharm中依然无法使用的解决办法
在终端通过pip装好包以后,在pycharm中导入包时,依然会报错.新手不知道具体原因是什么,我把我的解决过程发出来. pip install 解决方案一: 在Pycharm中,依次打开File--- ...
- C# 反射 Type.GetType()
对于外部调用的动态库应用反射时要用到Assembly.LoadFile(),然后才是获取类型.执行方法等;当用反射创建当前程序集中对象实例或执行某个类下静态方法时只需通过Type.GetType(&q ...
- Oarcle之用户管理 与 DCL
用户管理 1.创建一个账户 create user zhangsan identified by123456: 2.修改账户的密码 alter user zhangsan identified by ...
- 《CSS世界》读书笔记(十三)
<!-- <CSS世界>张鑫旭著 --> margin 无效情形解析 (1)display 计算值 inline 的非替换元素的垂直 margin 是无效的.对于内联替换元素, ...
