关于c++ string类的一些使用
主要最近要用的上 才整理一下
用string类别忘了导入头文件
#include <string>
注意这个细节:cout 可直接输出 string 类的对象的内容 但是printf不可以 需要转化成char指针
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h> using namespace std; int main()
{
string strOutput = "Hello World"; cout << "[cout] strOutput is: " << strOutput << endl; // string 转换为 char*
const char* pszOutput = strOutput.c_str(); printf("[printf] strOutput is: %s\n", pszOutput); return 0;
}
string s1; 默认构造函数,s1为空串
string s2(s1); 将s2初始化为s1的一个副本
string s3("value"); 将s3初始化为一个字符串字面值副本
string s4(n,'c') 将s4初始化为字符'c'的n个副本
对于对象的操作
s.empty()如果s为空串,则返回true,否则返回false
s.size()返回s 中字符的字符个数
s[n]
返回s中位置为n的字符,位置从0开始计数
s1+s2把s1和s2链接成一个新的字符串,返回新生成的字符串
s1=s2把s1内容替换为s2的副本
v1==v2判断v1与v2的内容,相等则返回true,否则返回false
!=, <, <=, >, >=保持这些操作的惯有含义
s.size()返回的类型是string::size_type()类型,而不是int形,string::size_type 的类型长度是int的俩倍所以尽量让s.size()的返 回值给string::size_type 类型
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio> using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("value");
string::size_type it;
it=s.size();
cout<<it<<endl;//5
return 0;
}
注意:除了一些特殊操作,string类型提供与vector容器相同的操作。string类型和vector容器不同的是,它不支持以栈方式操纵容器:在string类型中不能使用front,back,pop_back操作
string 是支持push_back()的,因为string也是顺序容器
String的遍历
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<string>
3 #include<cstdio>
4
5 using namespace std;
6 int main()
7 {
8 string s("Helloworld");
9 string::iterator it;
10 for(it=s.begin();it!=s.end();++it)
11 cout<<*it<<endl;
12 for(int i=0;s[i];i++)
13 cout<<s[i]<<endl;
14 cout<<s<<endl;
15 return 0;
16 }
下面举几个例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ( )
{
string str; //定义了一个空字符串str
str = "Hello world"; // 给str赋值为"Hello world"
char cstr[] = "abcde"; //定义了一个C字符串
string s1(str); //调用复制构造函数生成s1,s1为str的复制品
cout<<s1<<endl;
string s2(str,6); //将str内,开始于位置6的部分当作s2的初值
cout<<s2<<endl;
string s3(str,6,3); //将str内,开始于6且长度顶多为3的部分作为s3的初值
cout<<s3<<endl;
string s4(cstr); //将C字符串作为s4的初值
cout<<s4<<endl;
string s5(cstr,3); //将C字符串前3个字符作为字符串s5的初值。
cout<<s5<<endl;
string s6(5,'A'); //生成一个字符串,包含5个'A'字符
cout<<s6<<endl;
string s7(str.begin(),str.begin()+5); //区间str.begin()和str.begin()+5内的字符作为初值
cout<<s7<<endl;
return 0;
}
程序执行结果为:
Hello world
world
wor
abcde
abc
AAAAA
Hello
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cout << "Please input your name:"<<endl;
cin >> str;
if( str == "Li" ) // 字符串相等比较
cout << "you are Li!"<<endl;
else if( str != "Wang" ) // 字符串不等比较
cout << "you are not Wang!"<<endl;
else if( str < "Li") // 字符串小于比较,>、>=、<=类似
cout << "your name should be ahead of Li"<<endl;
else
cout << "your name should be after of Li"<<endl;
str += ", Welcome!"; // 字符串+=
cout << str<<endl;
for(int i = 0 ; i < str.size(); i ++)
cout<<str[i]; // 类似数组,通过[]获取特定的字符
return 0;
}
程序执行结果为:
Please input your name:
Zhang
you are not Wang!
Zhang, Welcome!
Zhang, Welcome!
对于string的特性描述:
int capacity()const; //返回当前容量(即string中不必增加内存即可存放的元素个数)
int max_size()const; //返回string对象中可存放的最大字符串的长度
int size()const; //返回当前字符串的大小
int length()const; //返回当前字符串的长度
bool empty()const; //当前字符串是否为空
void resize(int len,char c); //把字符串当前大小置为len,多去少补,多出的字符c填充不足的部分
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
if (str.empty())
cout<<"str is NULL."<<endl;
else
cout<<"str is not NULL."<<endl;
str = str + "abcdefg";
cout<<"str is "<<str<<endl;
cout<<"str's size is "<<str.size()<<endl;
cout<<"str's capacity is "<<str.capacity()<<endl;
cout<<"str's max size is "<<str.max_size()<<endl;
cout<<"str's length is "<<str.length()<<endl;
str.resize(20,'c');
cout<<"str is "<<str<<endl;
str.resize(5);
cout<<"str is "<<str<<endl;
return 0;
}
程序执行结果为:
str is NULL.
str is abcdefg
str's size is 7
str's capacity is 15
str's max size is 4294967294
str's length is 7
str is abcdefgccc
str is abcde
string的查找比较丰富:
size_type find( const basic_string &str, size_type index ); //返回str在字符串中第一次出现的位置(从index开始查找),如果没找到则返回string::npos
size_type find( const char *str, size_type index ); // 同上
size_type find( const char *str, size_type index, size_type length ); //返回str在字符串中第一次出现的位置(从index开始查找,长度为length),如果没找到就返回string::npos
size_type find( char ch, size_type index ); // 返回字符ch在字符串中第一次出现的位置(从index开始查找),如果没找到就返回string::npos
注意:查找字符串a是否包含子串b,不是用 strA.find(strB) > 0 而是 strA.find(strB) != string:npos
int idx = str.find("abc");
if (idx == string::npos);
上述代码中,idx的类型被定义为int,这是错误的,即使定义为 unsigned int 也是错的,它必须定义为 string::size_type。npos 是这样定义的: static const size_type npos = -1; 因为 string::size_type (由字符串配置器 allocator 定义) 描述的是 size,故需为无符号整数型别。因为缺省配置器以型别 size_t 作为 size_type,于是 -1 被转换为无符号整数型别,npos 也就成了该型别的最大无符号值。不过实际数值还是取决于型别 size_type 的实际定义。不幸的是这些最大值都不相同。事实上,(unsigned long)-1 和 (unsigned short)-1 不同(前提是两者型别大小不同)。因此,比较式 idx == string::npos 中,如果 idx 的值为-1,由于 idx 和字符串string::npos 型别不同,比较结果可能得到 false。因此要想判断 find()等查找函数的结果是否为npos,最好的办法是直接比较。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int loc;
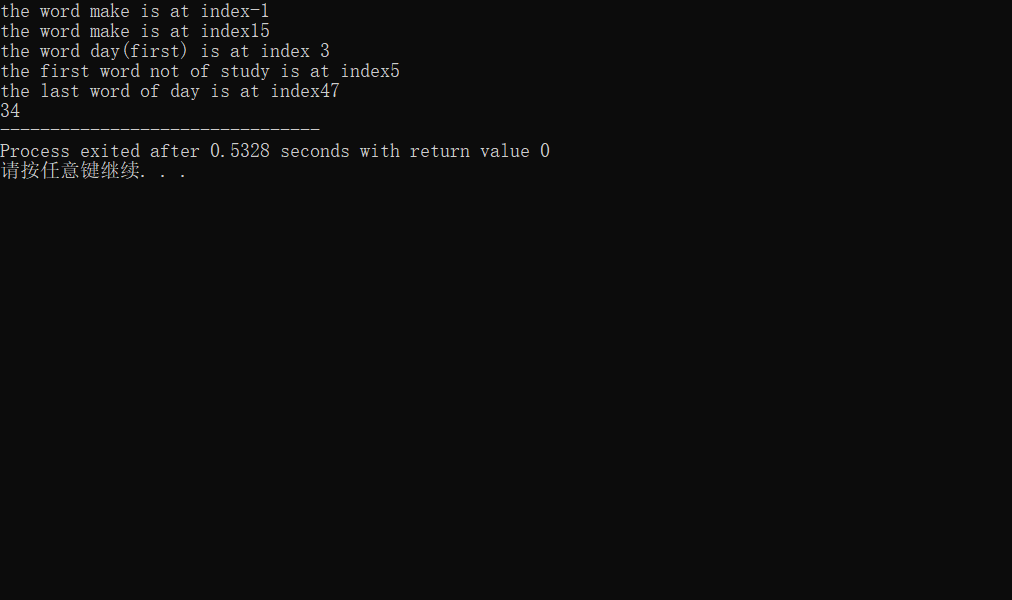
string s="study hard and make progress everyday! every day!!";
loc=s.rfind("make",10);
cout<<"the word make is at index"<<loc<<endl;//-1表示没找到
loc=s.rfind("make");//缺省状态下,从最后一个往前找
cout<<"the word make is at index"<<loc<<endl;
loc=s.find_first_of("day");
cout<<"the word day(first) is at index "<<loc<<endl;
loc=s.find_first_not_of("study");
cout<<"the first word not of study is at index"<<loc<<endl;
loc=s.find_last_of("day");
cout<<"the last word of day is at index"<<loc<<endl;
loc=s.find("day");//缺陷状态下从第一个往后找
cout<<loc;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
其他常用函数
string &insert(int p,const string &s); //在p位置插入字符串s
string &replace(int p, int n,const char *s); //删除从p开始的n个字符,然后在p处插入串s
string &erase(int p, int n); //删除p开始的n个字符,返回修改后的字符串
string substr(int pos = 0,int n = npos) const; //返回pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
void swap(string &s2); //交换当前字符串与s2的值
string &append(const char *s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
void push_back(char c) //当前字符串尾部加一个字符c
const char *data()const; //返回一个非null终止的c字符数组,data():与c_str()类似,用于string转const char*其中它返回的数组是不以空字符终止,
const char *c_str()const; //返回一个以null终止的c字符串,即c_str()函数返回一个指向正规C字符串的指针, 内容与本string串相同,用于string转const char*
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1 = "abc123defg";
string str2 = "swap!";
cout<<str1<<endl;
cout<<str1.erase(3,3)<<endl; //从索引3开始的3个字符,即删除掉了"123"
cout<<str1.insert(0,"123")<<endl; //在头部插入
cout<<str1.append("123")<<endl; //append()方法可以添加字符串
str1.push_back('A'); //push_back()方法只能添加一个字符
cout<<str1<<endl;
cout<<str1.replace(0,3,"hello")<<endl; //即将索引0开始的3个字符替换成"hello"
cout<<str1.substr(5,7)<<endl; //从索引5开始7个字节
str1.swap(str2);
cout<<str1<<endl;
const char* p = str.c_str();
printf("%s\n",p);
return 0;
}
程序执行结果为:
abc123defg
abcdefg
123abcdefg
123abcdefg123
123abcdefg123A
helloabcdefg123A
abcdefg
swap!
swap!
关于c++ string类的一些使用的更多相关文章
- 标准库String类
下面的程序并没有把String类的所有成员方法实现,只参考教程写了大部分重要的成员函数. [cpp] view plain copy #include<iostream> #include ...
- 自己实现简单的string类
1.前言 最近看了下<C++Primer>,觉得受益匪浅.不过纸上得来终觉浅,觉知此事须躬行.今天看了类类型,书中简单实现了String类,自己以前也学过C++,不过说来惭愧,以前都是用C ...
- C++ string类的实现
c++中string类的实现 今天面试被考到了, 全给忘记了!!! //string类的实现 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> ...
- String类的功能
String类 标红的为较少出现的 1.判断功能 boolean equals(Object obj) :比较字符串内容是否相同,区分大小写 boolean equalsIg ...
- java基础复习:final,static,以及String类
2.final 1)为啥String是final修饰的呢? 自己答: 答案: 主要是为了“效率” 和 “安全性” 的缘故.若 String允许被继承, 由于它的高度被使用率, 可能会降低程序的性能,所 ...
- String类和StringBuffer类的区别
首先,String和StringBuffer主要有2个区别: (1)String类对象为不可变对象,一旦你修改了String对象的值,隐性重新创建了一个新的对象,释放原String对象,StringB ...
- 05_整理String类的Length()、charAt()、 getChars()、replace()、 toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase()、trim()、toCharArray()使用说明
Question: 整理String类的Length().charAt(). getChars().replace(). toUpperCase(). toLowerCase().trim().toC ...
- 标准C++中的string类的用法总结
标准C++中的string类的用法总结 相信使用过MFC编程的朋友对CString这个类的印象应该非常深刻吧?的确,MFC中的CString类使用起来真的非常的方便好用.但是如果离开了MFC框架,还有 ...
- String类常用方法
1.String类的特点,字符串一旦被初始化就不会被改变. 2.String对象定义的两种方式 ①String s = "affdf";这种定义方式是在字符串常量池中创建一个Str ...
- 运用String类实现一个模拟用户登录程序
package Test; import java.util.Scanner; // 模拟用户登录程序 // 思路: // 1.用两个String类分别接收用户名和密码 // 2.判断输入的用户名和密 ...
随机推荐
- 永久激活(idea,pycharm等推荐使用)
二.永久激活(推荐使用)激活码激活总是过期,永久激活后,一劳永逸,不需要每次都在网上搜索激活码了. 1.下载激活插件:jetbrains-agent.jar(关注公号[吾非同]回复pycharm获取) ...
- Java中的常见锁(公平和非公平锁、可重入锁和不可重入锁、自旋锁、独占锁和共享锁)
公平和非公平锁 公平锁:是指多个线程按照申请的顺序来获取值.在并发环境中,每一个线程在获取锁时会先查看此锁维护的等待队列,如果为空,或者当前线程是等待队列的第一个就占有锁,否者就会加入到等待队列中,以 ...
- 这10道springboot常见面试题你需要了解下
1.什么是Spring Boot? 多年来,随着新功能的增加,spring变得越来越复杂.只需访问https://spring.io/projects页面,我们就会看到可以在我们的应用程序中使用的 ...
- Oracle学习(六)存储过程
一.简介 1.定义 所谓存储过程,就是一段存储在数据库中执行某块业务功能的程序模块. 它是由一段或者多段的PL/SQL代码块或者SQL语句组成的一系列代码块. 2.结构分析 create [or re ...
- MFC DLL中如何响应PreTranslateMessage消息
最近项目中使用到MFC,由于工程是DLL的,在使用ToolTip时碰到非模态对话框无法显示的问题.查了一番资料,发现原因是由于:虽然MFC Regular DLL派生了CWinApp类,并有一个the ...
- 刷题[网鼎杯 2020 朱雀组]phpweb
解题思路 打开是一个蛮有意思的背景,众生皆懒狗,是自己没错了.源代码看一看,啥都没有.抓个包 诶,一看到func和p两个参数,想到了call_user_func(). 尝试着把date改成system ...
- zabbix安装要求
zabbix server 和 zabbix Agent都在一个压缩包中,可以从官网上下载源码包,www.zabbix.com/download.php zabbix是C语言编写,压缩包的文件夹介绍: ...
- 渗透测试方法论(qf总结)
渗透测试(penetration testing , pentest)是实施安全评估(即审计)的具体手段.方法论是在指定.实施信息安全审计方案时,需要遵循的规则.惯例和过程.人们在评估网路.应用.系统 ...
- react 中发布订阅模式使用
react 中发布订阅模式使用 场景 怎么能将设计模式应用到我们的 React 项目中?以前一直在思考这个问题. 场景一 模块 A 模块 B 需要用到同一个数据 data,A 和 B 都会修改这份数据 ...
- 坐标下降(Coordinate descent)
坐标下降法属于一种非梯度优化的方法,它在每步迭代中沿一个坐标的方向进行线性搜索(线性搜索是不需要求导数的),通过循环使用不同的坐标方法来达到目标函数的局部极小值.
