C语言用两个栈实现队列(完整版)
队列是一种 先进先出(first in - first out, FIFO)的数据结构,队列中的元素都从后端(rear)入队(push),从前端(front)出队(pop)。
实现队列最直观的方法是用链表,但在这篇文章里我会介绍另一个方法 - 使用栈。
栈是一种 后进先出(last in - first out, LIFO)的数据结构,栈中元素从栈顶(top)压入(push),也从栈顶弹出(pop)。
为了满足队列的 FIFO 的特性,我们需要用到两个栈,用它们其中一个来反转元素的入队顺序,用另一个来存储元素的最终顺序。
方法一(使用两个栈 入队 - O(n)O(n), 出队 - O(1)O(1))
算法
入队(push)思路:考虑入队的元素是先进先出,后进后出,而你的栈是后进先出,那么你最新压入的元素(后进的)应该在栈底,也就是只要保证后进后出即可
一个队列是 FIFO 的,但一个栈是 LIFO 的。这就意味着最新压入的元素必须得放在栈底。为了实现这个目的,我们首先需要把 s1 中所有的元素移到 s2 中,接着把新元素压入 s2。最后把 s2 中所有的元素弹出,再把弹出的元素压入 s1。
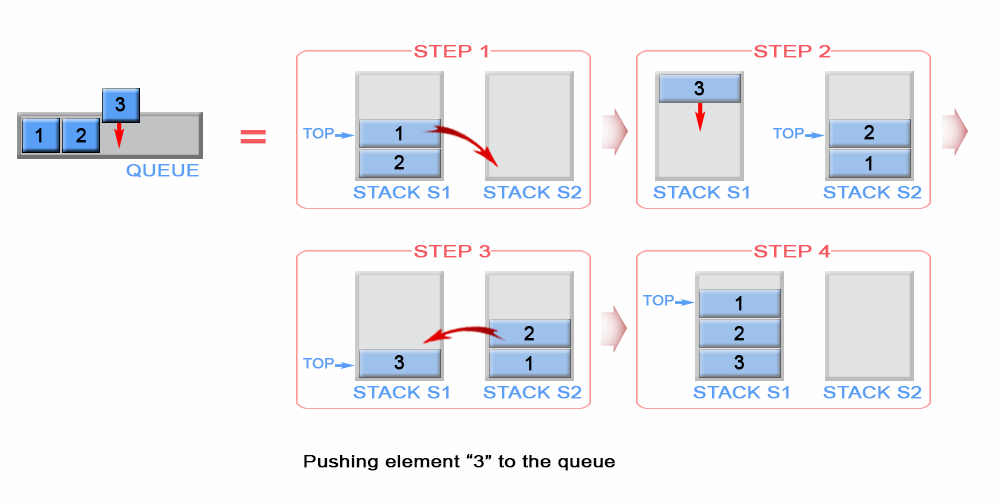
出队(pop)
直接从 s1 弹出就可以了,因为 s1 的栈顶元素就是队列的队首元素。同时我们把弹出之后 s1 的栈顶元素赋值给代表队首元素的 front 变量。

以上图片以及文字来自https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/solution/yong-zhan-shi-xian-dui-lie-by-leetcode/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxsize 100
//创建栈
struct Stack{
int data[maxsize];
int top;
};
typedef struct Stack MyStack;
//队列定义为双栈
typedef struct {
MyStack s1; //S1为主栈
MyStack s2; //S2为用来反转的栈
} MyQueue;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue * tempQueue =(MyQueue *)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
tempQueue->s1.top = -1 ;
tempQueue->s2.top = -1 ;
return tempQueue ;
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
if(obj->s1.top<maxsize)
{
while(obj->s1.top!=-1) //栈是否满
{
obj->s2.data[++(obj->s2.top)]=obj->s1.data[(obj->s1.top)--];////把S1栈中元素压入S2实现反转
}
obj->s1.data[++(obj->s1.top)]= x ; ////把push的元素压入S1栈(此时S1为空栈,因为它的元素已经全部给S2啦)
while(obj->s2.top!=-1)
{
obj->s1.data[++(obj->s1.top)]=obj->s2.data[(obj->s2.top)--];//再把S2栈中的元素全部反转压入S1
}
}
}
void show_myQueue(MyQueue * obj)
{
int temp =obj->s1.top ;
while(temp!=-1)
{
printf("%d ",obj->s1.data[temp--]);
}
printf("\n");
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
if(obj->s1.top!=-1)
{
return obj->s1.data[obj->s1.top--] ;
}
// return NULL ;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(obj->s1.top!=-1)
{
return obj->s1.data[obj->s1.top] ;
}
// return NULL ;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
if(obj->s1.top == -1)
return true ;
return false ;
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
free(obj);
}
int main()
{
int i ;
MyQueue * myQueue =NULL;
myQueue =myQueueCreate();
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
myQueuePush(myQueue,i);
}
show_myQueue(myQueue);
printf("出队的元素是:%d\n",myQueuePop(myQueue));
printf("此时队列内的首个的元素是:%d\n",myQueuePeek(myQueue));
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/
C语言用两个栈实现队列(完整版)的更多相关文章
- 【Java】 剑指offer(8) 用两个栈实现队列
本文参考自<剑指offer>一书,代码采用Java语言. 更多:<剑指Offer>Java实现合集 题目 用两个栈实现一个队列.队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数append ...
- 剑指Offer面试题:6.用两个栈实现队列
一.题目:用两个栈实现队列 题目:用两个栈实现一个队列.队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数appendTail和deleteHead,分别完成在队列尾部插入结点和在队列头部删除结点的功能. 原文是使用 ...
- 剑指OFFER之用两个栈实现队列(九度OJ1512)
题目描述: 用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作.队列中的元素为int类型. 输入: 每个输入文件包含一个测试样例.对于每个测试样例,第一行输入一个n(1<=n<=100 ...
- 九度OJ 1512 用两个栈实现队列 【数据结构】
题目地址:http://ac.jobdu.com/problem.php?pid=1512 题目描述: 用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作. 队列中的元素为int类型. 输入: 每 ...
- 两个栈实现队列+两个队列实现栈----java
两个栈实现队列+两个队列实现栈----java 一.两个栈实现一个队列 思路:所有元素进stack1,然后所有出s ...
- Algorithm --> 两个栈实现队列和两个队列实现栈
两个栈实现队列和两个队列实现栈 队列(queue)先进先出的线性表:栈(stack)先进后出的线性表. 两个栈实现队列 法一思路: s1是入栈的,s2是出栈的. 入队列:直接压入s1即可: 出队列:如 ...
- 二、 编写一个类,用两个栈实现队列,支持队列的基本操作(add,poll,peek)
请指教交流! package com.it.hxs.c01; import java.util.Stack; /* 编写一个类,用两个栈实现队列,支持队列的基本操作(add,poll,peek) */ ...
- 两个队列实现栈&两个栈实现队列(JAVA)
1,两个栈实现队列 题目描述 用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作. 队列中的元素为int类型. 思路:栈的特点时先进后出,队列的特点是先进先出. 若此时有两个队列stack1,st ...
- 剑指offer【05】- 用两个栈实现队列(java)
题目:用两个栈实现队列 考点:栈和队列 题目描述:用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作. 队列中的元素为int类型. 解题思路:每次psuh是时先将stack2清空放入stck1(保 ...
随机推荐
- Linux下安装nvidia显卡驱动
部署环境 操作系统:Centos 7.4 在线源:Centos 7.4镜像源 安装操作 1.安装系统插件 [root@localhost ~]# yum -y install gcc kernel-d ...
- Nutz | Nutz项目整合Spring实战
Nutz项目整合Spring实战 前言 Github地址 背景 实现步骤 加入springMvc与Spring 相关配置 新增Spring相关配置 新增SpringIocProvider 重写Nutz ...
- artTemplate--模板使用自定义函数(1)
案例 因为公司业务需要频繁调用接口,后端返回的都是json树对象,需要有些特殊的方法做大量判断和数据处理,显然目前简单语法已经不能满足业务需要了,需要自己定制一些 方法来处理业务逻辑. 例如后台返回的 ...
- <背包>solution-CF118D_Caesar's Legions
Caesar's Legions Gaius Julius Caesar, a famous general, loved to line up his soldiers. Overall the a ...
- 机器学习总结-bias–variance tradeoff
bias–variance tradeoff 通过机器学习,我们可以从历史数据学到一个\(f\),使得对新的数据\(x\),可以利用学到的\(f\)得到输出值\(f(x)\).设我们不知道的真实的\( ...
- Codeforces_723
A.取中间那个点即可. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ]; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio( ...
- CCF_201403-1_相反数
按绝对值排序,因为没相同的数,直接遍历比较一遍即可. #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> ...
- BZOJ 1601 [Usaco2008 Oct]灌水 (建图+mst)
题意: 300个坑,每个坑能从别的坑引水,或者自己出水,i从j饮水有个代价,每个坑自己饮水也有代价,问让所有坑都有谁的最少代价 思路: 先建一个n的完全图,然后建一个超级汇点,对每个点连w[i],跑m ...
- Linux命令行与Shell脚本编程大全
快来参加<Linux命令行与Shell脚本编程大全>学习吧,提升技能,展示自我. 点击链接即可进入学习:https://s.imooc.com/WTmCO6H 课程亮点适合零基础读者,从零 ...
- docker 镜像save和转换
docker save出来的tar包转成镜像 $ docker load < busybox.tar.gz 使用import转的镜像里面是空的,无法启动 报错如下Error: Error res ...
