SpringMVC 启动流程
首先看一下Web应用部署初始化过程 (Web Application Deployement),官方文档说明:
Web Application Deployment
When a web application is deployed into a container, the following steps must be performed, in this order, before the web application begins processing client requests.
■ Instantiate an instance of each event listener identified by a <listener> element in the deployment descriptor.
■ For instantiated listener instances that implement ServletContextListener, call the contextInitialized() method.
■ Instantiate an instance of each filter identified by a <filter> element in the deployment descriptor and call each filter instance’s init() method.
■ Instantiate an instance of each servlet identified by a <servlet> element that includes a <load-on-startup> element in the order defined by the load-onstartup
element values, and call each servlet instance’s init() method.大致说:
Web应用部署:当一个web应用被部署到一个容器(eg.tomcat),在web应用开始处理客户端请求前,以下步骤会按顺序执行:
1.初始化应用部署描述文件中每一个listener。
2.初始化ServletContextListener实现类,调用contextInitialized()方法。
3.初始化应用部署描述文件中每一个filter,并执行每一个的init()方法。
4.按照顺序<load-on-startup>来初始化servlet,并执行init()方法。
大致总结:先初始化lisener,再filter,最后servlet
SpringMVC启动过程:
常见SpringMVC配置:<web-app>
<display-name>Web Application</display-name>
<!--全局变量配置-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext-*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--解决乱码问题的filter-->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--Restful前端控制器-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
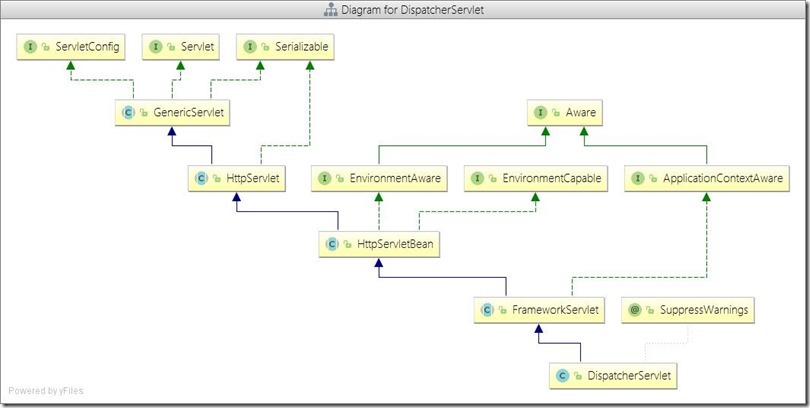
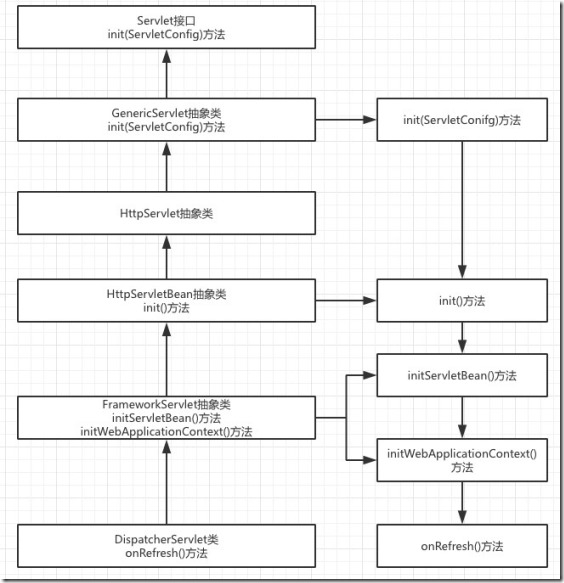
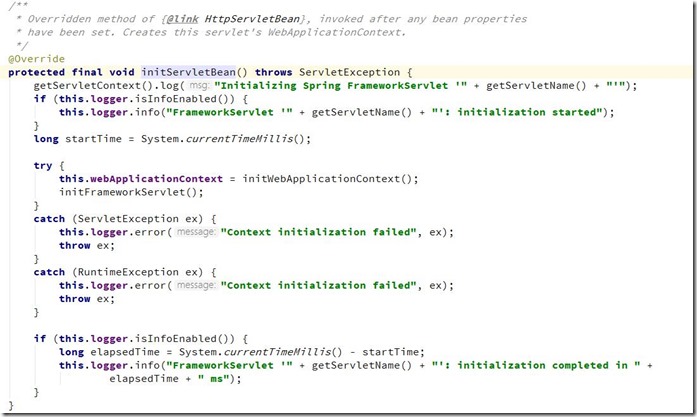
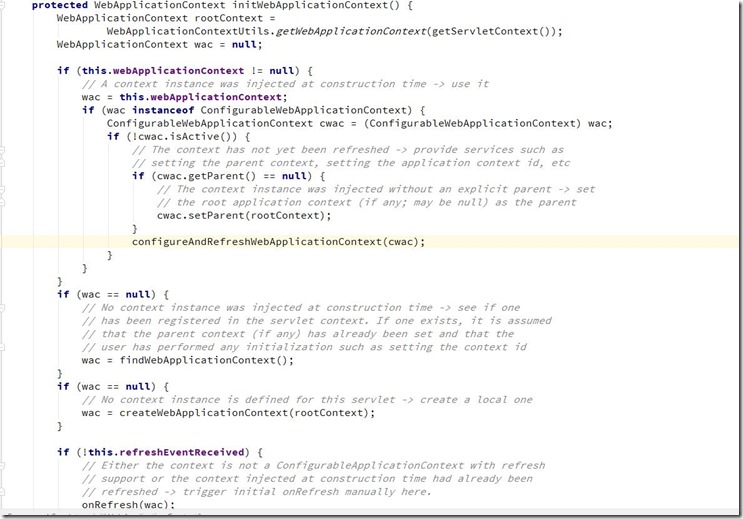
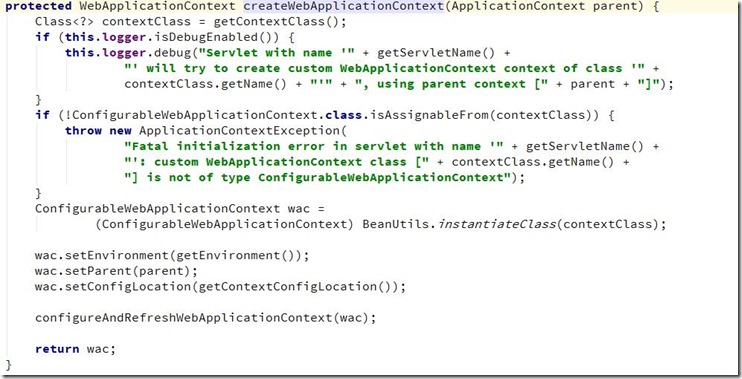
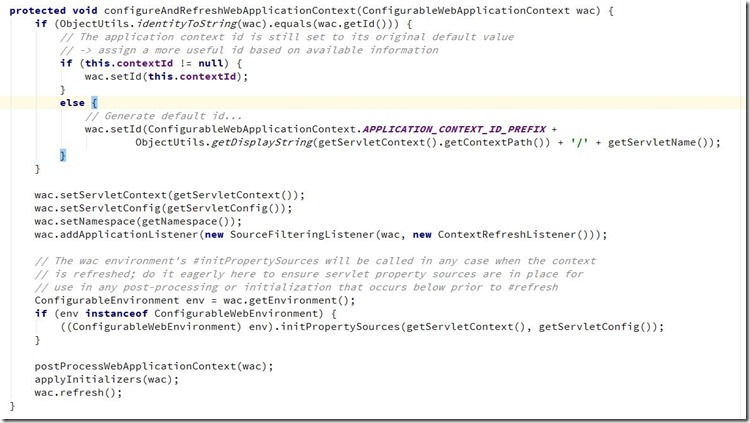
</web-app>DispatchServlet使用说明:其类图如下:可以明显看出DispatchServlet类间接父类实现了Servlet接口,因此其本质上依旧是一个Servlet。DispatchServlet类设计很巧妙,上层父类不同程度的实现了相关接口的部分方法,并留出相关方法用于子类覆盖,将不变的部分统一实现,将变化的部分预留方法用于子类实现。DispatchServlet类初始化过程函数调用图:通过类图和相关初始化函数调用的逻辑来看,DispatchServlet的初始化过程将模板方法,其父类完成不同的统一工作,并预留出相关方法用于子类覆盖去完成不同的可变工作。DispatchServlet类的本质是Servlet,在web应用部署到容器后进行Servelt初始化时会调用相关的init(ServletConfig)方法,因此,DispatchServlet类的初始化过程也由该方法开始。其中FrameworkServlet抽象类中的initServletBean()方法、initWebApplicationContext()方法以及DispatchServlet类中的onFresh()方法。FrameworkServlet initServletBean()方法源码,该方法重写了FrameworkServlet抽象类在执行,终于,initXXXContext的字眼出现了—initWebApplicationContext()方法会首先从ServletContext中获取到由ContextLoaderListener初始化完成并放进入的根容器对象引用(因为创建子容器必须将父容器作为参数传递进去),然后经过层层调用,最终在createWebApplicationContext()中完成了容器的创建工作,该方法的主要代码如下:好了,到此就初始化完成DispatchServlet处理请求流程:/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null; try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
} // Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
} if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
} // Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
} applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
SpringMVC 启动流程的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC源码解析-DispatcherServlet启动流程和初始化
在使用springmvc框架,会在web.xml文件配置一个DispatcherServlet,这正是web容器开始初始化,同时会在建立自己的上下文来持有SpringMVC的bean对象. 先从Dis ...
- SpringMVC启动和执行流程
Spring框架大家用得很多,相当熟悉,但是我对里面的运作比较好奇,例如bean的加载和使用,和我们定义的配置文件有什么联系;又例如aop在什么时候起作用,原理又是怎样.经过一个了解后,整理了启动和执 ...
- SpringMVC启动过程详解(li)
通过对SpringMVC启动过程的深入研究,期望掌握Java Web容器启动过程:掌握SpringMVC启动过程:了解SpringMVC的配置文件如何配置,为什么要这样配置:掌握SpringMVC是如 ...
- Spring基础系列-容器启动流程(1)
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/9870339.html 概述 我说的容器启动流程涉及两种情况,SSM开发模式和Spri ...
- SpringMVC 工作流程
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_36697353/article/details/64444147 SpringMVC 工 ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(六):IoC容器依赖注入
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程及其原理
Spring Boot.Spring MVC 和 Spring 有什么区别? 分别描述各自的特征: Spring 框架就像一个家族,有众多衍生产品例如 boot.security.jpa等等:但他们的 ...
- Spring MVC启动流程分析
本文是Spring MVC系列博客的第一篇,后续会汇总成贴子. Spring MVC是Spring系列框架中使用频率最高的部分.不管是Spring Boot还是传统的Spring项目,只要是Web项目 ...
- 面试高频SpringMVC执行流程最优解(源码分析)
文章已托管到GitHub,大家可以去GitHub查看阅读,欢迎老板们前来Star! 搜索关注微信公众号 码出Offer 领取各种学习资料! SpringMVC执行流程 SpringMVC概述 Spri ...
随机推荐
- unity中将多张图片进行椭圆运动
GameObject canvas; ; ; ; ; Dictionary<int,GO> storeItem; GameObject main; public static bool r ...
- LeetCode 总结,二叉树各种类型问题小结
三大遍历 前序遍历 中序遍历 后序遍历 关于三大基础遍历,必须要条件反射式的记住:三种遍历的迭代方式使用的都是栈,后序遍历必须使用了 两个栈,其余乱七八糟的解决方式统统就不要再记了. 广度遍历: 分析 ...
- spring对bean的高级装配之profile机制
最近在读spring实战一书,个人感觉内容通俗易懂,学到了一些之前并不知道的知识,于是打算在博客里记录一下这些知识点便于后期记忆: 今天要记录的就是spring的条件化创建bean,针对条件化创建be ...
- python2入门(2)
四.python条件语句 if语句基本语法if 判断条件: 执行语句块else if: 执行语句块else: 执行语句 五.循环语句 1 - while循环基本语法while 判断条件: 执行语句块w ...
- 如何利用 LTE/4G 伪基站+GSM 中间人攻击攻破所有短信验证
这次公开课请来的嘉宾对自己的简介是: 连续创业失败的创业导师:伪天使投资人:某非知名私立大学创办人兼校长:业余时间在本校通信安全实验室打杂. 自从他在黑客大会上演讲<伪基站高级利用技术——彻底攻 ...
- 集群容器管理之swarm ---服务管理
服务管理 # 创建服务docker service create --replicas 1 --name hello busybox # docker service update --args &q ...
- jupyter notebook中使用mpld3进行交互
用pycharm进行远程服务器debug可以说是非常的爽了,但是设置远程的图片在本地显示会非常的麻烦 jupyter可以用%matplotlib inline 来远程plt.show图片,但是有一个问 ...
- How to Install Tomcat 8.0.27 on CentOS/RHEL and Ubuntu【转】
https://tecadmin.net/install-tomcat-8-on-centos-rhel-and-ubuntu/ Apache Tomcat is an opensource web ...
- web-msg-send 学习 http://www.workerman.net/web-sender
WEB消息推送框架 web-msg-sender是一款web长连接推送框架,采用PHPSocket.IO开发,基于WebSocket长连接通讯,如果浏览器不支持WebSocket则自动转用comet推 ...
- IIS发布错误及解决
HTTP 错误 403.14 - Forbidden 解决办法: 打开iis管理器,找到对应网站,并找到目录浏览,双击打开. 点击启用即可. HTTP 错误 500.19 - Internal Se ...