[编织消息框架][netty源码分析]11 UnpooledHeapByteBuf 与 ByteBufAllocator

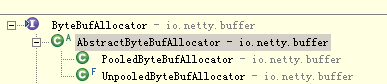
每种ByteBuf都有相应的分配器ByteBufAllocator,类似工厂模式。我们先学习UnpooledHeapByteBuf与其对应的分配器UnpooledByteBufAllocator
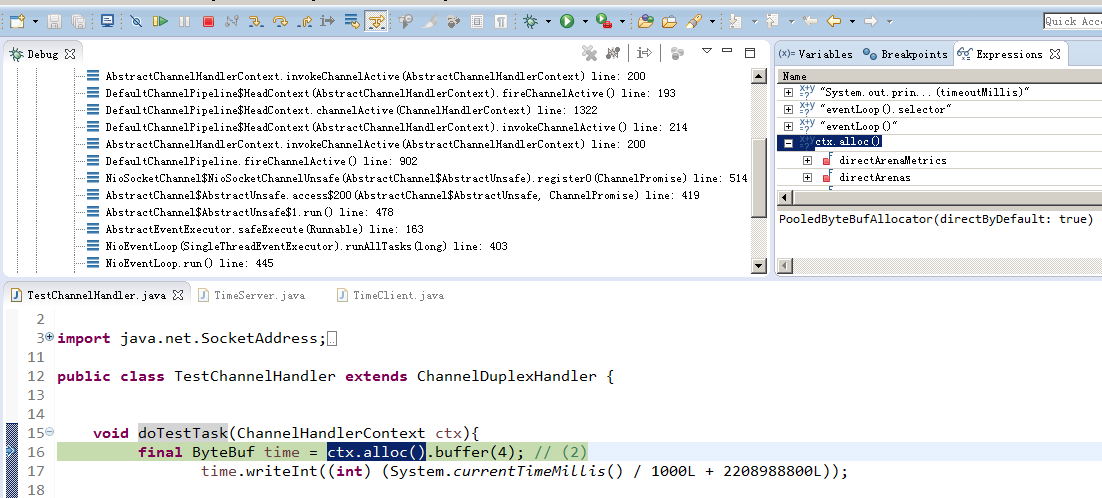
如何知道alloc分配器那是个?
可以从官方下载的TimeServer 例子来学习,本项目已有源码可在 TestChannelHandler.class里断点追踪
从图可以看出netty 4.1.8默认的ByteBufAllocator是PooledByteBufAllocator,可以参过启动参数-Dio.netty.allocator.type unpooled/pooled 设置
细心的读者可以看出分配ByteBuf只有pool跟unpool,但ByteBuf有很多类型,可能出于使用方面考虑,有时不一定设计太死板,太规范反而使学习成本很大
public final class ByteBufUtil {
static final ByteBufAllocator DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR;
static {
String allocType = SystemPropertyUtil.get(
"io.netty.allocator.type", PlatformDependent.isAndroid() ? "unpooled" : "pooled");
allocType = allocType.toLowerCase(Locale.US).trim();
ByteBufAllocator alloc;
if ("unpooled".equals(allocType)) {
alloc = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
} else if ("pooled".equals(allocType)) {
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
} else {
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
}
DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR = alloc;
}
}
AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf是统计引用总数处理,用到Atomic*技术。
refCnt是从1开始,每引用一次加1,释放引用减1,当refCnt变成1时执行deallocate由子类实现
public abstract class AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf extends AbstractByteBuf {
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf> refCntUpdater =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf.class, "refCnt");
private volatile int refCnt = 1;
@Override
public ByteBuf retain() {
return retain0(1);
}
private ByteBuf retain0(int increment) {
for (;;) {
int refCnt = this.refCnt;
final int nextCnt = refCnt + increment;
if (nextCnt <= increment) {
throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(refCnt, increment);
}
if (refCntUpdater.compareAndSet(this, refCnt, nextCnt)) {
break;
}
}
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean release() {
return release0(1);
}
private boolean release0(int decrement) {
for (;;) {
int refCnt = this.refCnt;
if (refCnt < decrement) {
throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(refCnt, -decrement);
}
if (refCntUpdater.compareAndSet(this, refCnt, refCnt - decrement)) {
if (refCnt == decrement) {
deallocate();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
protected abstract void deallocate();
}
对于ByteBuf I/O 操作经常用的是 writeByte readByte两种
由于ByteBuf支持多种bytes对象,如 OutputStream、GatheringByteChannel、ByteBuffer、ByteBuf等,
我们只拿两三种常用的API来做分析,其它逻辑大同小异
如果读者有印象的话,通常底层只负责流程控制,实现交给应用层/子类处理,AbstractByteBuf.class writeByte/readByte 也是这种处理方式
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
//分配器
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;
//数据
byte[] array;
//临时ByteBuffer,用于内部缓存
private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf;
private UnpooledHeapByteBuf(
ByteBufAllocator alloc, byte[] initialArray, int readerIndex, int writerIndex, int maxCapacity) {
//省去部分代码同边界处理
super(maxCapacity);
this.alloc = alloc;
array = initialArray;
this.readerIndex = readerIndex;
this.writerIndex = writerIndex;
}
//获取ByteBuffer容量
@Override
public int capacity() {
ensureAccessible();
return array.length;
}
@Override
public boolean hasArray() {
return true;
}
//获取原始数据
@Override
public byte[] array() {
ensureAccessible();
return array;
}
//扩容/缩容
@Override
public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) {
ensureAccessible();
//newCapacity参数边界判断
if (newCapacity < 0 || newCapacity > maxCapacity()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("newCapacity: " + newCapacity);
}
int oldCapacity = array.length;
//扩容处理,直接cp到新的array
if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) {
byte[] newArray = new byte[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, array.length);
setArray(newArray);
} else if (newCapacity < oldCapacity) {
//减容处理
//这里有两种处理情况
//1.readerIndex > newCapacity 说明还有数据未处理直接将 readerIndex,writerIndex相等 newCapacity
//2.否则 writerIndex =Math.min(writerIndex,newCapacity),取最少值,然后直接复制数据
//可以看出netty处理超出readerIndex、writerIndex 限界直接丢弃数据。。。。。。
byte[] newArray = new byte[newCapacity];
int readerIndex = readerIndex();
if (readerIndex < newCapacity) {
int writerIndex = writerIndex();
if (writerIndex > newCapacity) {
writerIndex = newCapacity
this.writerIndex = writerIndex;
}
System.arraycopy(array, readerIndex, newArray, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex);
//System.arraycopy(复制来源数组, 来源组起始坐标, 目标数组, 目标数组起始坐标, 复制数据长度);
} else {
this.readerIndex = newCapacity;
this.writerIndex = newCapacity;
}
setArray(newArray);
}
return this;
}
}
AbstractByteBuf.class readBytes 调用子类实现 getBytes方法,区别是调用readBytes会改变readerIndex记录
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf {
@Override
public ByteBuf readBytes(ByteBuffer dst) {
int length = dst.remaining();
//checkReadableBytes(length);
if (readerIndex > (writerIndex - length)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format(
"readerIndex(%d) + length(%d) exceeds writerIndex(%d): %s",
readerIndex, length, writerIndex, this));
}
//调用子类实现
getBytes(readerIndex, dst);
//记录已读长度
readerIndex += length;
return this;
}
@Override
public ByteBuf readBytes(ByteBuf dst, int dstIndex, int length) {
checkReadableBytes(length);
getBytes(readerIndex, dst, dstIndex, length);
readerIndex += length;
return this;
}
//这里如果index不为负的话只需要 capacity - (index + length) < 0 判断就可以
//用到 | 运算 如果 index为-1的话 index | length 还是负数 第二个 | (index + length)运算有可能 index + length相加为负
public static boolean isOutOfBounds(int index, int length, int capacity) {
return (index | length | (index + length) | (capacity - (index + length))) < 0;
}
}
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
//支持ByteBuffer读取
@Override
public ByteBuf getBytes(int index, ByteBuffer dst) {
//checkIndex(index, dst.remaining());
if (isOutOfBounds(index, dst.remaining(), capacity())) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format(
"index: %d, length: %d (expected: range(0, %d))", index, dst.remaining(), capacity()));
}
dst.put(array, index, dst.remaining());
return this;
}
//支持ByteBuf读取
@Override
public ByteBuf getBytes(int index, ByteBuf dst, int dstIndex, int length) {
checkDstIndex(index, length, dstIndex, dst.capacity());
//是unsafe类型,要调用jdk unsafe方法复制
if (dst.hasMemoryAddress()) {
PlatformDependent.copyMemory(array, index, dst.memoryAddress() + dstIndex, length);
} else if (dst.hasArray()) { //如果是数组即 heap类型,直接复制过去
getBytes(index, dst.array(), dst.arrayOffset() + dstIndex, length);
} else {
dst.setBytes(dstIndex, array, index, length);
}
return this;
}
//支持数组读取
@Override
public ByteBuf getBytes(int index, byte[] dst, int dstIndex, int length) {
checkDstIndex(index, length, dstIndex, dst.length);
System.arraycopy(array, index, dst, dstIndex, length);
return this;
}
}
AbstractByteBuf.class writeBytes 调用子类实现 setBytes方法,区别是调用writeBytes会改变writerIndex记录
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf {
@Override
public ByteBuf writeBytes(ByteBuf src) {
writeBytes(src, src.readableBytes());
return this;
}
@Override
public ByteBuf writeBytes(ByteBuf src, int length) {
if (length > src.readableBytes()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format(
"length(%d) exceeds src.readableBytes(%d) where src is: %s", length, src.readableBytes(), src));
}
writeBytes(src, src.readerIndex(), length);
//读取src数据到this.ByteBuf 所以要更改src readerIndex
src.readerIndex(src.readerIndex() + length);
return this;
}
@Override
public ByteBuf writeBytes(ByteBuf src, int srcIndex, int length) {
ensureAccessible();
//是否扩容处理
ensureWritable(length);
//调用子类实现
setBytes(writerIndex, src, srcIndex, length);
//记录已写长度
writerIndex += length;
return this;
}
private void ensureWritable0(int minWritableBytes) {
if (minWritableBytes <= writableBytes()) {
return;
}
//写入数据长度大于最大空间剩余长度抛异常
if (minWritableBytes > maxCapacity - writerIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format(
"writerIndex(%d) + minWritableBytes(%d) exceeds maxCapacity(%d): %s",
writerIndex, minWritableBytes, maxCapacity, this));
}
//通过分配器计算,参数1写完后的writerIndex记录,参数2最大容量长度
int newCapacity = alloc().calculateNewCapacity(writerIndex + minWritableBytes, maxCapacity);
//子类实现
capacity(newCapacity);
}
//////////////////////////////AbstractByteBufAllocator.class//////////////////////////////////////
@Override
public int calculateNewCapacity(int minNewCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
if (minNewCapacity < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("minNewCapacity: " + minNewCapacity + " (expectd: 0+)");
}
if (minNewCapacity > maxCapacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"minNewCapacity: %d (expected: not greater than maxCapacity(%d)",
minNewCapacity, maxCapacity));
}
final int threshold = 1048576 * 4; // 4 MiB page
if (minNewCapacity == threshold) {
return threshold;
}
//如果新容量大于4M,不走双倍扩大算法,数值范围取 minNewCapacity <= maxCapacity
if (minNewCapacity > threshold) {
// 除以threshold再乘以threshold得出的结果是 threshold的倍数,可以理解是去掉余数
int newCapacity = minNewCapacity / threshold * threshold;
//如果剩余容量不够4M直接给maxCapacity,否则自增4M
if (newCapacity > maxCapacity - threshold) {
newCapacity = maxCapacity;
} else {
newCapacity += threshold;
}
return newCapacity;
}
//newCapacity <<= 1 意思是 newCapacity*2,双倍自增
int newCapacity = 64;
while (newCapacity < minNewCapacity) {
newCapacity <<= 1;
}
return Math.min(newCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
}
//setBytes逻辑跟getBytes一样
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
@Override
public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, ByteBuf src, int srcIndex, int length) {
checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.capacity());
if (src.hasMemoryAddress()) {
PlatformDependent.copyMemory(src.memoryAddress() + srcIndex, array, index, length);
} else if (src.hasArray()) {
setBytes(index, src.array(), src.arrayOffset() + srcIndex, length);
} else {
src.getBytes(srcIndex, array, index, length);
}
return this;
} @Override
public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) {
checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.length);
System.arraycopy(src, srcIndex, array, index, length);
return this;
}
}
总结:
1.writeBytes跟setBytes、readBytes跟getBytes区别是前者有记录,后者没有,而后者是子类的实现
2.扩容算法是两种策略:
2.1.大于4M时不走double自增,数值范围取 minNewCapacity <= maxCapacity
2.2.少于4M时从64开始double自增
3.更改容量也是每个子类实现,要考虑两种情况
3.1.大于当前容量
3.2.小于当前容量,当小于的时候要考虑 readerIndex、writerIndex边界,当超过 readerIndex、writerIndex边界heap的策略是丢去原来的数据
4.heap是继承 AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf的,当refCnt记录为1时释放数据
[编织消息框架][netty源码分析]11 UnpooledHeapByteBuf 与 ByteBufAllocator的更多相关文章
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]11 ByteBuf 实现类UnpooledHeapByteBuf职责与实现
每种ByteBuf都有相应的分配器ByteBufAllocator,类似工厂模式.我们先学习UnpooledHeapByteBuf与其对应的分配器UnpooledByteBufAllocator 如何 ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]1分析切入点
在分析源码之前有几个疑问 1.BOSS线程如何转交给handle(业务)线程2.职业链在那个阶段执行3.socket accept 后转给上层对象是谁4.netty控流算法 另外要了解netty的对象 ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]2 eventLoop
eventLoop从命名上看是专门处理事件 事件系统主要由线程池同队列技术组成,有以下几个优点 1.任务出队有序执行,不会出现错乱,当然前提执行线程池只有一个 2.解偶系统复杂度,这是个经典的生产者/ ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]6 ChannelPipeline 实现类DefaultChannelPipeline职责与实现
ChannelPipeline 负责channel数据进出处理,如数据编解码等.采用拦截思想设计,经过A handler处理后接着交给next handler ChannelPipeline 并不是直 ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]10 ByteBuf 与 ByteBuffer
因为jdk ByteBuffer使用起来很麻烦,所以netty研发出ByteBuf对象维护管理内存使用ByteBuf有几个概念需要知道1.向ByteBuf提取数据时readerIndex记录最后读取坐 ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]4 eventLoop 实现类NioEventLoop职责与实现
NioEventLoop 是jdk nio多路处理实现同修复jdk nio的bug 1.NioEventLoop继承SingleThreadEventLoop 重用单线程处理 2.NioEventLo ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]5 eventLoop 实现类NioEventLoopGroup职责与实现
分析NioEventLoopGroup最主有两个疑问 1.next work如何分配NioEventLoop 2.boss group 与child group 是如何协作运行的 从EventLoop ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]8 Channel 实现类NioSocketChannel职责与实现
Unsafe是托委访问socket,那么Channel是直接提供给开发者使用的 Channel 主要有两个实现 NioServerSocketChannel同NioSocketChannel 致于其它 ...
- [编织消息框架][netty源码分析]9 Promise 实现类DefaultPromise职责与实现
netty Future是基于jdk Future扩展,以监听完成任务触发执行Promise是对Future修改任务数据DefaultPromise是重要的模板类,其它不同类型实现基本是一层简单的包装 ...
随机推荐
- jdbc(2)
create table account ( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), money double);insert int ...
- linux vi 报错 E37: No write since last change (add ! to override)
用 vi 命令编辑文本文件,没有文件写入权限的时候会报这个错.:q :wq 怎么都不能退出. 这时只需 ctrl+z 即可,或者在退出命令后加 ! 忽略提示 :q!
- 习惯的PHP命名规则
从C++转PHP也已经很长一段时间了,一直有点代码洁癖,对于文件名,接口名,类名,方法名等都使用严格的驼峰命名法, 但是有时候会犹豫到底用首字母大写区分还是用下划线区分.今天简单总结和规约一下. 1 ...
- Swift学习笔记(4):字符串
目录: 初始化 常用方法或属性 字符串索引 初始化 创建一个空字符串作为初始值: var emptyString = "" // 空字符串字面量 var anotherEmptyS ...
- GTD:让大脑用来思考,而不是用来记事!
前段时间听刘润大师分享了一套GTD时间管理方法理论,感觉非常受用!现拿来跟大家分享下,这套方法是刘润老师践行20多年总结提炼的精华,经亲自实践确实行之有效. 俗话说:工欲善其事,必先利其器!人生也是如 ...
- Linux services, runlevels, and rc.d scripts
Reference: [1] https://www.linux.com/news/introduction-services-runlevels-and-rcd-scripts A Linux se ...
- 《Android进阶》之第四篇 ViewPagerIndicator的使用
1.先将这个开源框架下载到本地: Administrator@QH-20141231RFQJ /d/hixin $ cd ViewPagerIndicator/ Administrator@QH-20 ...
- motor和servo
程序简单易读,不再做注释 motor.py from gpiozero import Motor from gpiozero import LED led = LED(2) motor = Motor ...
- spring service层单元测试
service层测试较简单,目前大多数测试主要是针对public方法进行的.依据测试方法划分,可以分为两种:基于mock的隔离测试和基于dbunit的普通测试. mock隔离测试 配置pom.xml ...
- SonarQube+Jenkins,搭建持续交付平台
前言 Kurt Bittner曾说过,如果敏捷仅仅只是开始,那持续交付就是头条! "If Agile Was the Opening Act, Continuous Delivery is ...
