【javaFX学习】(二) 面板手册--1
移至http://blog.csdn.net/qq_37837828/article/details/78732591 更新
找了好几个资料,没找到自己想要的,自己整理下吧,方便以后用的时候挑选,边学边记。以学习笔记为主,所以会写的会偏个人记忆性。非教程,有什么问题一起讨论啊。
各个不同的控件放入不同的面板中有不同的效果,挨个开撸。这里可以把面板当作容器来理解,就是装各种东西的,容器装容器、装控件等等。
面板列表:
Accordion
手风琴面板:就是一个折叠展开功能,一般与TitledPane一起用)
AnchorPane
相对位置控制面板:锚布局:可以设置容器里面的控件的各种相对位置,主要用于界面大小改变而控件相对位置不变的情况
BorderPane
区域面板:划分为了5个区域:上、下、左、右、中
FlowPane
流面板:会随着界面大小而改变控件布局
GridPane
网格面板 :面板中的控件可以设置按网格坐标分布,就当作一个棋盘吧,控件就是棋子,指哪放哪
HBox
水平排列面板:顾名思义,水平排列,与垂直排列VBox对应
Pane
所有面板的爸爸:当作java的Object来理解就好了
ScrollPane
滚动面板:瞄一眼你的网页右边有没有一个滚动条→_→,注意滚动面板里面只能放一个元素,所以一般是把需要的控件都装到一个其他面板里面,再把那个叫其他的面板扔到这个滚动面板里面-_-
SplitPane
分割面板:里面存放的其他面板可以自由拖动大小)
StackPane
层级面板:放入进StackPane的子模块会根据放入顺序的不同形成不同的层级关系.
TabPane
标签面板: 用来放标签
TilePane
片面板: 就是特殊的流面板,里面每个元素的网格大小都是相同的,测试发现取最大的,详见示例
TitledPane
标题面板:用法见Accordion
VBox
竖直面板:用法见HBox示例
Accordion(折叠面板):
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Accordion;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.ListView;
import javafx.scene.control.TitledPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
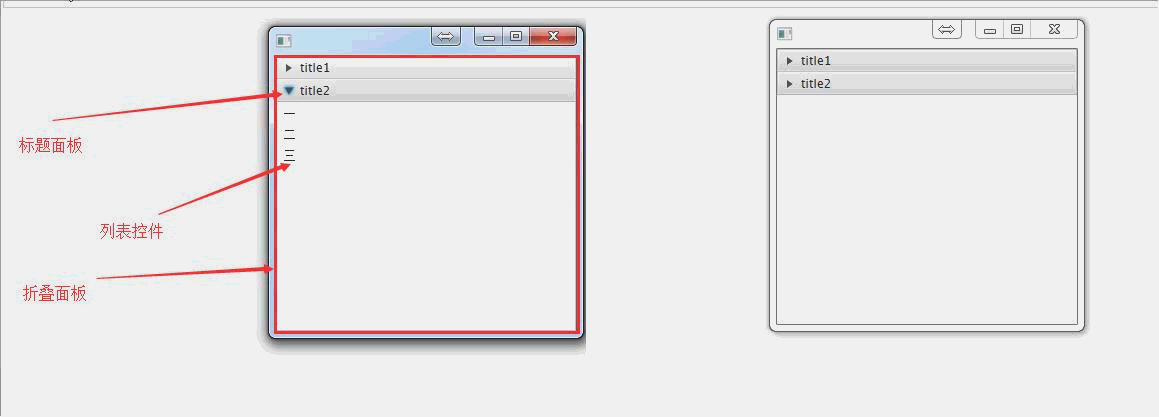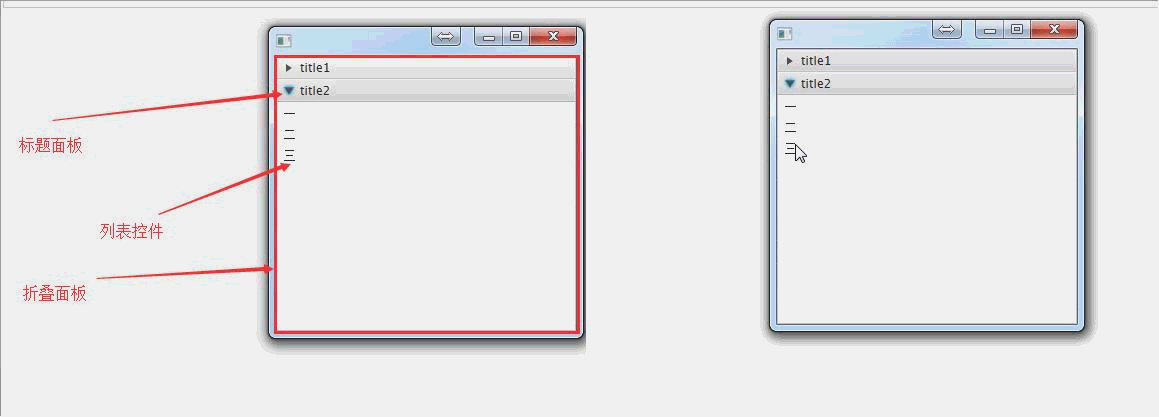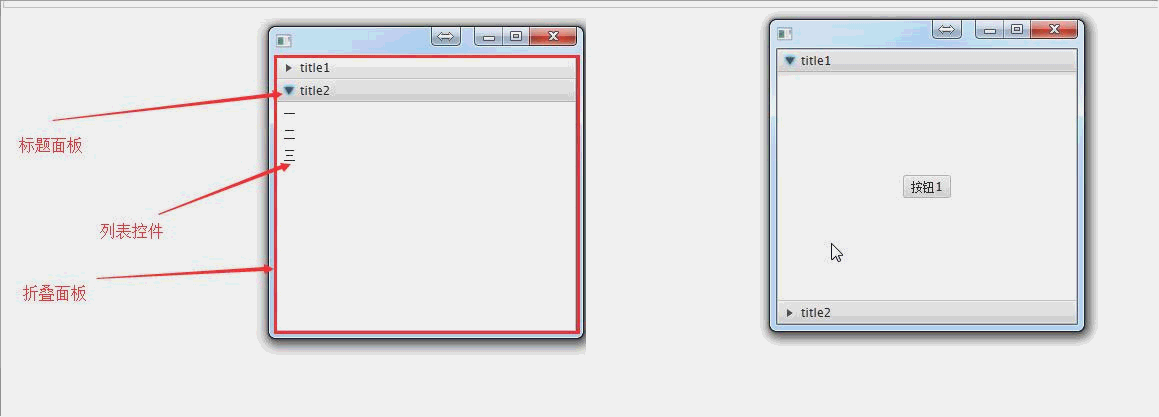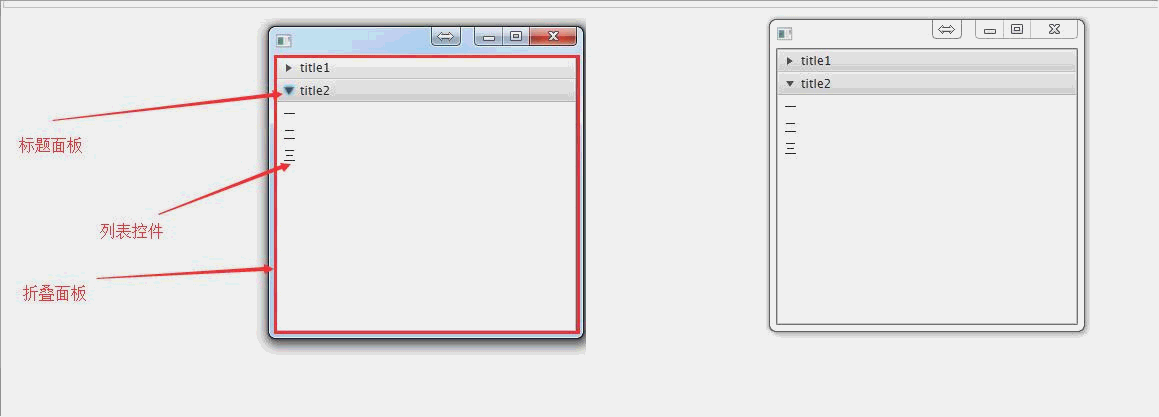
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception{ //创建标题面板1
TitledPane titledPane1 = new TitledPane("title1",new Button("按钮1")); //创建一个列表控件
ListView<String> listView = new ListView<>();
ObservableList<String> ob = FXCollections.observableArrayList();
ob.addAll("一","二","三");
listView.setItems(ob); //创建标题面板2
TitledPane titledPane2 = new TitledPane("title2",listView); //创建折叠面板
Accordion accordion = new Accordion(); //将标题面板添加到折叠面板中
accordion.getPanes().addAll(titledPane1,titledPane2); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(accordion, 300, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
AnchorPane(控件位置控制面板):
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.AnchorPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个anchorPane面板,
AnchorPane anchorPane = new AnchorPane(); //创建按钮控件
Button button1 = new Button("靠右按钮");
Button button2 = new Button("靠左按钮");
Button button3 = new Button("靠下按钮"); //将按钮控件添加入面板(容器)
anchorPane.getChildren().addAll(button1,button2,button3); //设置边距为
AnchorPane.setRightAnchor(button1, 10.0);//设置右边距为10
AnchorPane.setLeftAnchor(button2,10.0);//左
AnchorPane.setBottomAnchor(button3,10.0);//下 primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(anchorPane, 300, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
BorderPane:区域面板,将界面划分为了5个区域

import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.BorderPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个区域控制面板
BorderPane borderPane = new BorderPane(); //创建5个按钮,洗净,备用
Button button1 = new Button("左按钮");
Button button2 = new Button("右按钮");
Button button3 = new Button("上按钮");
Button button4 = new Button("下按钮");
Button button5 = new Button("中按钮"); //将按钮放入相应区域
borderPane.setLeft(button1);
borderPane.setRight(button2);
borderPane.setTop(button3);
borderPane.setBottom(button4);
borderPane.setCenter(button5); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(borderPane, 300, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}

FlowPane(流面板):
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.FlowPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个流面板
FlowPane flowPane = new FlowPane(); //创建一堆按钮或其他什么东西
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
Button button4 = new Button("button4");
Button button5 = new Button("button5");
Button button6 = new Button("button6"); //把按钮都扔进去
flowPane.getChildren().addAll(button1,button2,button3,button4,button5,button6); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(flowPane, 400, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}

GridPane(网格布局):
创建6个按钮,前3个放第一行,后3个放第二行
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.GridPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个网格面板
GridPane gridPane = new GridPane(); //创建一堆按钮或其他什么东西
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
Button button4 = new Button("button4");
Button button5 = new Button("button5");
Button button6 = new Button("button6"); //把按钮按照网格坐标扔进去
gridPane.add(button1,0,0);
gridPane.add(button2,0,1);
gridPane.add(button3,0,2);
gridPane.add(button4,1,0);
gridPane.add(button5,1,1);
gridPane.add(button6,1,2); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(gridPane, 400, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
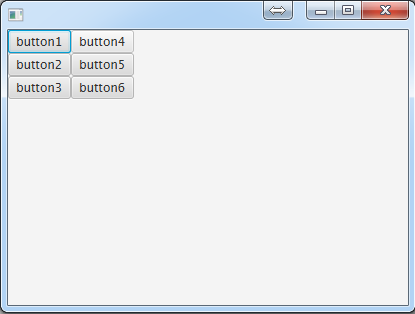
HBox(水平排列)
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个水平排列面板
HBox hBox = new HBox(); //创建一堆按钮或其他什么东西
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
Button button4 = new Button("button4");
Button button5 = new Button("button5");
Button button6 = new Button("button6"); //把按钮扔进去
hBox.getChildren().addAll(button1,button2,button3,button4,button5,button6); //设置一下各个按钮的间隔。
hBox.setSpacing(10.0); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(hBox, 500, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
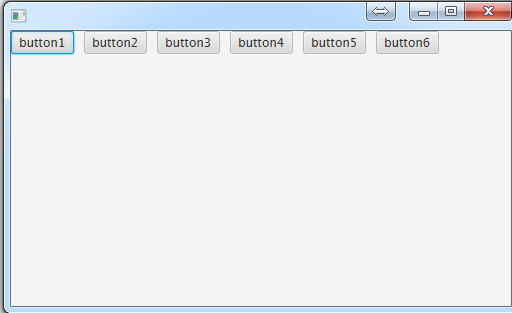
Pane:
由于是所有面板的"父类",所以不具备其他面板已经设置好的的布局属性,故而加进去的控件要记得自己设置在面板中的坐标,否则就会挤在一堆,像这样:

设置一下控件的坐标:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个面板
Pane pane = new Pane(); //创建一堆按钮或其他什么东西
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
Button button4 = new Button("button4");
Button button5 = new Button("button5");
Button button6 = new Button("button6"); //设置按钮在控件中的坐标
button1.setLayoutX(50);button1.setLayoutY(50);
button2.setLayoutX(200);button2.setLayoutY(50);
button3.setLayoutX(350);button3.setLayoutY(50);
button4.setLayoutX(50);button4.setLayoutY(100);
button5.setLayoutX(200);button5.setLayoutY(100);
button6.setLayoutX(350);button6.setLayoutY(100); //把按钮扔进去
pane.getChildren().addAll(button1,button2,button3,button4,button5,button6); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(pane, 500, 275));
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
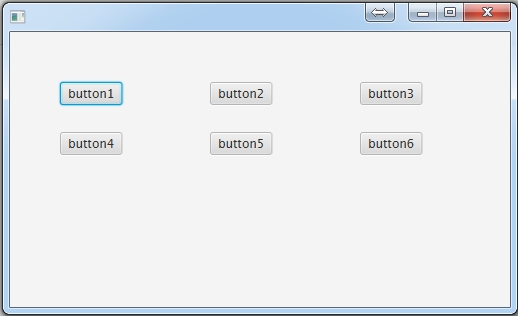
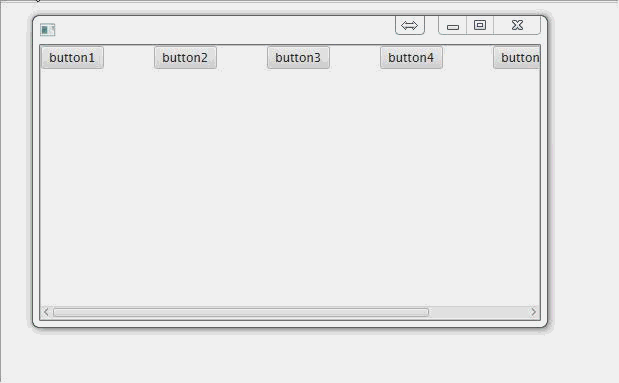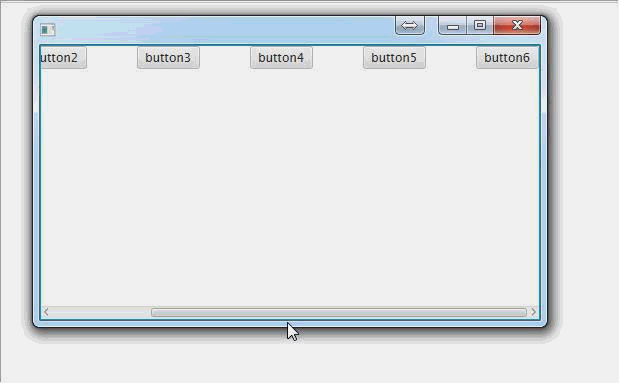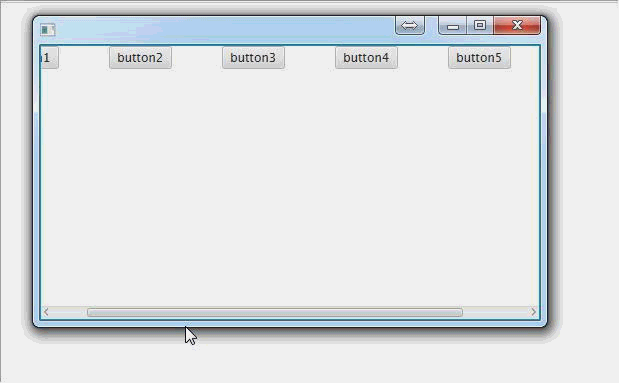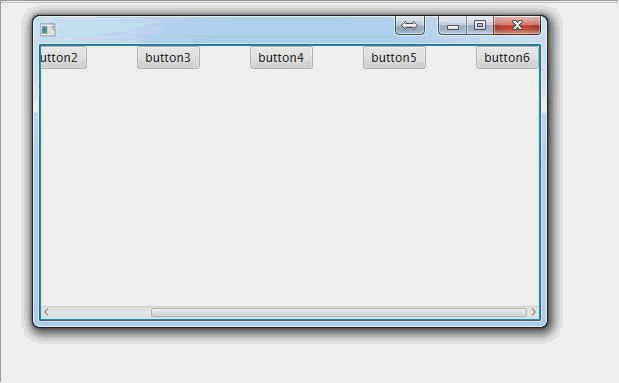
ScrollPane(滚动面板):
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.ScrollPane;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个滚动面板
ScrollPane scrollPane = new ScrollPane(); //创建一个水平排列面板,用来装按钮,如果想测试垂直滚动,就换成垂直排列面板
HBox hBox = new HBox(); //创建一堆按钮或其他什么东西
Button button1 = new Button("button1");
Button button2 = new Button("button2");
Button button3 = new Button("button3");
Button button4 = new Button("button4");
Button button5 = new Button("button5");
Button button6 = new Button("button6"); //把按钮放在行面板里面
hBox.getChildren().addAll(button1,button2,button3,button4,button5,button6);
//为了少装几个东西而出现滚动条,我们把按钮间隔设大一点
hBox.setSpacing(50); //把行面板放到滚动面板里面
scrollPane.setContent(hBox); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(scrollPane, 500, 275));
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
SplitPane(分割面板):
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.SplitPane;
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个滚动面板
SplitPane splitPane = new SplitPane(); //创建两个普通面板
Pane pane1 = new Pane(new Button("左边的面板"));
Pane pane2 = new Pane(new Button("右边的面板")); //添加到滚动面板中
splitPane.getItems().addAll(pane1,pane2); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(splitPane, 500, 275));
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}

StackPane(层级面板):
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.Background;
import javafx.scene.layout.BackgroundFill;
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane;
import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个层级面板
StackPane stack = new StackPane(); //创建一个普通面板,并设置背景为黑色
Pane pane = new Pane();
pane.setBackground(new Background(new BackgroundFill(Color.BLACK,null,null))); //创建一个按钮
Button button = new Button("按钮2"); //将按钮和普通面板添加到stackPane面板中
//stack.getChildren().addAll(pane,button);
stack.getChildren().addAll(button,pane); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(stack, 300, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
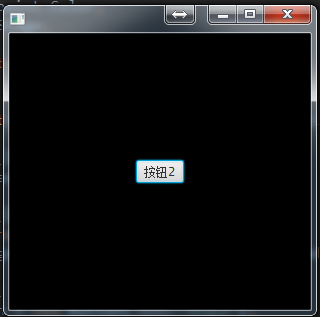
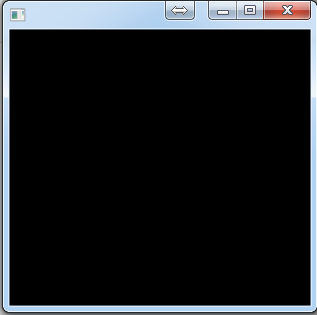
如图所示,先添加pane时,pane在下面,按钮在pane的上面;先添加button时,button在下面,pane在上面,所以将button盖住了。
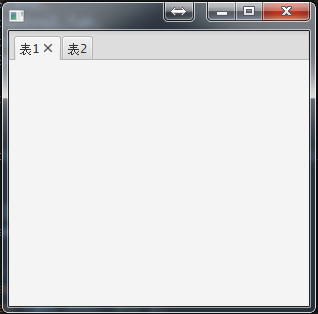
TabPane(标签面板):
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Tab;
import javafx.scene.control.TabPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建一个标签面板
TabPane tabPane = new TabPane(); //创建两个标签,放入标签面板
Tab tab1 = new Tab("表1");
Tab tab2 = new Tab("表2");
tabPane.getTabs().addAll(tab1,tab2); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(tabPane, 300, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
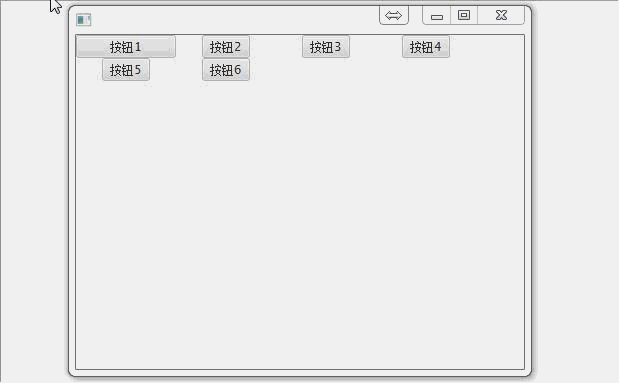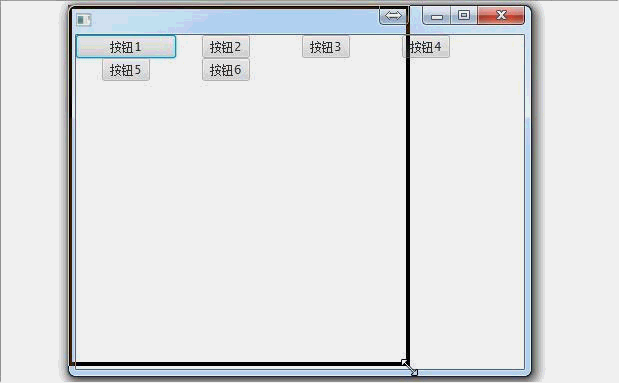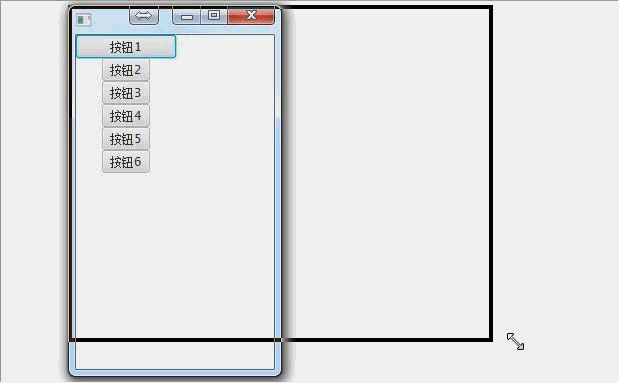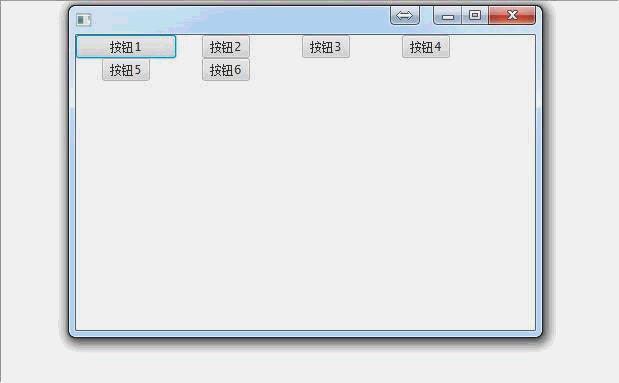
TilePane(片面板):
特殊的流面板,里面的元素都在网格中,每个网格大小相同,默认取最大的网格大小.例如下面把按钮1设成100宽,则所有的网格都变成了100宽
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.TilePane;
import javafx.stage.Stage; public class Main extends Application { @Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception { //创建片面板
TilePane tilePane = new TilePane(); Button button1 = new Button("按钮1");
button1.setPrefWidth(100);
Button button2 = new Button("按钮2");
Button button3 = new Button("按钮3");
Button button4 = new Button("按钮4");
Button button5 = new Button("按钮5");
Button button6 = new Button("按钮6"); tilePane.getChildren().addAll(button1,button2,button3,button4,button5,button6); primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(tilePane, 300, 275));
primaryStage.show();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
【javaFX学习】(二) 面板手册--1的更多相关文章
- Android JNI学习(二)——实战JNI之“hello world”
本系列文章如下: Android JNI(一)——NDK与JNI基础 Android JNI学习(二)——实战JNI之“hello world” Android JNI学习(三)——Java与Nati ...
- JavaFX学习之道:JavaFX之TableView
TableView表 TableColumn列 构建一个表主要有TableView,TableColumn,ObservableList,Bean. 加入列table.getColumns ...
- emberjs学习二(ember-data和localstorage_adapter)
emberjs学习二(ember-data和localstorage_adapter) 准备工作 首先我们加入ember-data和ember-localstorage-adapter两个依赖项,使用 ...
- ReactJS入门学习二
ReactJS入门学习二 阅读目录 React的背景和基本原理 理解React.render() 什么是JSX? 为什么要使用JSX? JSX的语法 如何在JSX中如何使用事件 如何在JSX中如何使用 ...
- TweenMax动画库学习(二)
目录 TweenMax动画库学习(一) TweenMax动画库学习(二) TweenMax动画库学习(三) Tw ...
- Hbase深入学习(二) 安装hbase
Hbase深入学习(二) 安装hbase This guidedescribes setup of a standalone hbase instance that uses the local fi ...
- Struts2框架学习(二) Action
Struts2框架学习(二) Action Struts2框架中的Action类是一个单独的javabean对象.不像Struts1中还要去继承HttpServlet,耦合度减小了. 1,流程 拦截器 ...
- Python学习二:词典基础详解
作者:NiceCui 本文谢绝转载,如需转载需征得作者本人同意,谢谢. 本文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/NiceCui/p/7862377.html 邮箱:moyi@moyib ...
- Quartz学习--二 Hello Quartz! 和源码分析
Quartz学习--二 Hello Quartz! 和源码分析 三. Hello Quartz! 我会跟着 第一章 6.2 的图来 进行同步代码编写 简单入门示例: 创建一个新的java普通工程 ...
- SpringCloud学习(二):微服务入门实战项目搭建
一.开始使用Spring Cloud实战微服务 1.SpringCloud是什么? 云计算的解决方案?不是 SpringCloud是一个在SpringBoot的基础上构建的一个快速构建分布式系统的工具 ...
随机推荐
- Django(二)
QuerySet与惰性机制: 所谓惰性机制:Publisher.objects.all()或者所谓惰性机制:Publisher.objects.all()或者.filter()等都只是返回了一个Que ...
- zabbix杂文
ps:这是从我原来记录的地方直接copy的,很杂乱,不过主要我想记录当时的思路,乱就乱了...... 背景: 这是进公司的第一个正式任务(之前在测试环境熟悉),所以基本上最近一段时间都在弄这个东西,一 ...
- 【转】深度分析NandFlash—物理结构及地址传送(以TQ2440开发板上的K9F2G08U0A为例)
K9F2G08U0A是三星公司生产的总容量为256M的NandFlash,常用于手持设备等消费电子产品.还是那句话,搞底层就得会看datasheet,我们就从它的datasheet看起. 这就是 K9 ...
- Git相关操作四
1.克隆远程仓库 git clone remote_location clone_name remote_location为仓库地址,clone_name为要克隆到本地的仓库名称. 2.显示对应克隆地 ...
- ASP.NET MVC 分页
概述:数据比较多的时候,常使用分页.这里使用bootpag.js和PagedList这两个插件实现. 准备JS的引用 1.这个是bootstrap 中pagination的库 2..NET后台ToPa ...
- input输入框校验,字母,汉字,数字等
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta http-e ...
- 打包zip下载
//首先引入的文件为org.apache的切记不是jdk的import org.apache.tools.zip.ZipOutputStream;import org.apache.tools.zip ...
- lua State加载部分库
lua State加载部分库 在lua中,通常我们用luaL_openlibs(L)加载所有的lub标准库,但是有时候我们想只加载部分,有没有什么好的办法呢?在luaproc看到如下办法: stati ...
- win7旗舰版安装IIS
1.在控制面板中:程序->打开或关闭Windows功能 2.在弹出的对话窗中,在“Internet服务信息”中作如下勾选(打钩的为全选) 点击确定后安装. 3.安装成功后回到控制面板->系 ...
- java工程师学习线路图
