多线程——Executor、ExecutorService、Executors三者的区别
Executor、ExecutorService、Executors三者的区别:
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {}
public abstract class AbstractExecutorService implements ExecutorService {}
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService {}
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService {}
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor implements ScheduledExecutorService {}
shutDown() 方法终止线程池。 newSingleThreadExecutor() 创建一个只有一个线程的线程池, newFixedThreadPool(int numOfThreads)来创建固定线程数的线程池, newCachedThreadPool()创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
void shutdown();
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
boolean isShutdown();
boolean isTerminated();
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException;
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, throws InterruptedException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException,ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
public class Executors {
/** Cannot instantiate. */
private Executors() {}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism) {
return new ForkJoinPool (parallelism,ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,null, true);
}
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool() {
return new ForkJoinPool (Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(), ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,null, true);
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),threadFactory);
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(), threadFactory));
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),threadFactory);
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService (new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService (new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, threadFactory));
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory);
}
public static ExecutorService unconfigurableExecutorService(ExecutorService executor) {
if (executor == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new DelegatedExecutorService(executor);
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService unconfigurableScheduledExecutorService(ScheduledExecutorService executor) {
if (executor == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService(executor);
}
public static ThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory();
}
public static ThreadFactory privilegedThreadFactory() {
return new PrivilegedThreadFactory();
}
public static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new RunnableAdapter<T>(task, result);
}
public static Callable<Object> callable(Runnable task) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new RunnableAdapter<Object>(task, null);
}
public static Callable<Object> callable(final PrivilegedAction<?> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new Callable<Object>() {
public Object call() { return action.run(); }};
}
public static Callable<Object> callable(final PrivilegedExceptionAction<?> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new Callable<Object>() {
public Object call() throws Exception { return action.run(); }};
}
public static <T> Callable<T> privilegedCallable(Callable<T> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new PrivilegedCallable<T>(callable);
}
public static <T> Callable<T> privilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader(Callable<T> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new PrivilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader<T>(callable);
}
}
/** 表示异步计算的结果。 */
public interface Future<V> { /**
* 试图取消对此任务的执行
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning); /**
*如果在任务正常完成前将其取消,则返回 true。
*/
boolean isCancelled(); /**
* 如果任务已完成,则返回 true。
*/
boolean isDone(); /**
*如有必要,等待计算完成,然后获取其结果。
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; /**
*如有必要,最多等待为使计算完成所给定的时间之后,获取其结果(如果结果可用)。
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
多线程——Executor、ExecutorService、Executors三者的区别的更多相关文章
- Executor ExecutorService Executors
Executor public interface Executor { void execute(Runnable command); } ExecutorService ExecutorServi ...
- Executor、Executors、ExecutorService多线程操作
Executor:一个接口,其定义了一个接收Runnable对象的方法executor,其方法签名为executor(Runnable command),该方法接收一个Runable实例,它用来执行一 ...
- Executor, ExecutorService 和 Executors 间的区别与联系
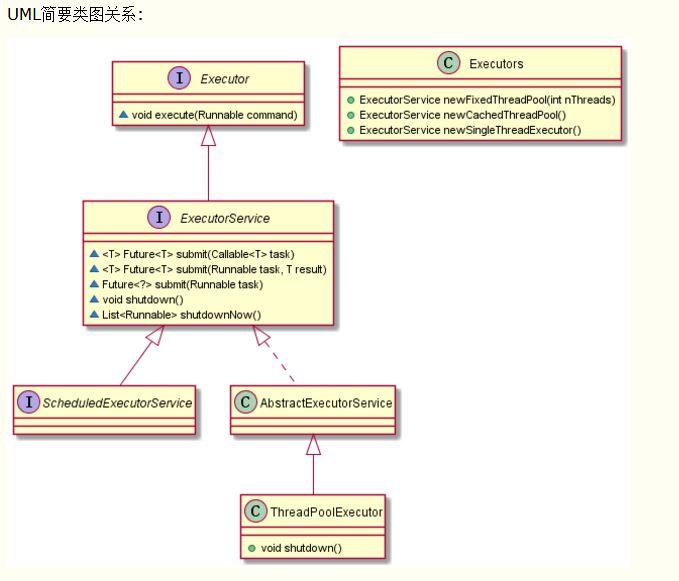
UML简要类图关系: 下面详细看一下三者的区别: Executor vs ExecutorService vs Executors 正如上面所说,这三者均是 Executor 框架中的一部分.Java ...
- java并发编程:Executor、Executors、ExecutorService
1.Executor和ExecutorService Executor:一个接口,其定义了一个接收Runnable对象的方法executor,其方法签名为executor(Runnable comma ...
- Executor, ExecutorService 和 Executors 间的不同
java.util.concurrent.Executor, java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService, java.util.concurrent. Executors ...
- Java并发编程 - Executor,Executors,ExecutorService, CompletionServie,Future,Callable
一.Exectuor框架简介 Java从1.5版本开始,为简化多线程并发编程,引入全新的并发编程包:java.util.concurrent及其并发编程框架(Executor框架). Executor ...
- 【Java多线程】ExecutorService和ThreadPoolExecutor
ExecutorService Java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService接口代表一种异步执行机制,它能够在后台执行任务.因此ExecutorService与thread ...
- java并发编程框架 Executor ExecutorService invokeall
首先介绍两个重要的接口,Executor和ExecutorService,定义如下: public interface Executor { void execute(Runnable command ...
- String,StringBuilder,StringBuffer三者的区别
参考 String,StringBuilder,StringBuffer三者的区别 这三个类之间的区别主要是在两个方面,即运行速度和线程安全这两方面. 1.运行速度 首先说运行速度,或者说是执行速 ...
随机推荐
- 【JS加密库】SJCL :斯坦福大学JS加密库
斯坦福大学Javascript加密库简称SJCL,是一个由斯坦福大学计算机安全实验室创立的项目,旨在创建一个安全.快速.短小精悍.易使用.跨浏览器的JavaScript加密库. 斯坦福大学下载地址:h ...
- Failed to resolve: com.android.support:appcompat-v7:27.0.1问题解决
今天,在毫无征兆的情况下AndroidStudio又抽风了,搞了大半天,试了网上众多方案,终于解决了这个问题.咱们一步一步来 第一步:这是最开始的bug Error:Failed to resolve ...
- mac yarn 安装
通过HomeBrew安装 brew install yarn 升级yarn brew upgrade yarn 查看版本 yarn -v 1.15.2
- JS中判断一个对象是否为null、undefined、0
1.判断undefined: var tmp = undefined; if (typeof(tmp) == "undefined"){ alert("undefined ...
- eclipse无法连接到makertplace
Eclipse需要安装一个Jcoco的插件,但是连接Eclipse Market的时候,总是出现如下的报错: Cannot open Eclipse Marketplace Cannot instal ...
- vb学习基础之val函数与val(&HFFFF) 的理解
在VB语言中,val函数可以把数值字符串==转为==>数值的函数,在它不能识别为数字的第一个字符上,停止读入字符串. 那些被认为是数值的一部分的符号和字符,例如美元号与逗号,都不能被识别.但是能 ...
- 第八天py
我发现这个老师讲的太基础只是我懒得跳过而已想慢慢听 列表公共功能 索引 切片 for 长度 特有功能 翻转 排序 追加 插入 索引位置 删除
- day_6.20动态加载py文件
__import__() 魔法方法! 关于动态网站打开的 代码流程!
- 【Vue】---编写Vue插件流程---【巷子】
一.在Vue中编写插件流程 1.创建组件 components/message.vue <template> <div class="message" v-if= ...
- thinkphp或thinkcmf 《文章编辑,文章添加》 访问另一个表的分类,添加入另一个表时将id值以(,)逗号分隔储存,编辑时以(,)逗号分隔并且相等的id值被选中
首页 显示 的控制器//网贷评级 public function grade(){ $archives = $this->archives_model->where(array('de ...
