[Scikit-learn] 1.4 Support Vector Classification
Ref: http://sklearn.lzjqsdd.com/modules/svm.html
Ref: CS229 Lecture notes - Support Vector Machines
Ref: Lecture 6 | Machine Learning (Stanford) youtube
Ref: 《Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis》
Ref: SVM教程:支持向量机的直观理解【插图来源于此链接,写得不错】
支持向量机


其实就是最大间隔分类器,而且是软间隔,加正则。

对于时间充裕的年轻人,建议SVM的原理推导一遍,过程中设计了大部分的数学优化基础,而且SVM是自成体系的sol,大有裨益。
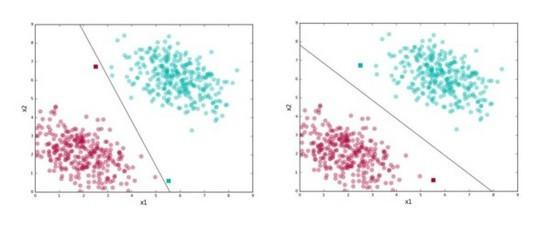
Figure, SVM试图找到右图中的“分割线”
Support vector machines (SVMs) are a set of supervised learning methods used for classification (分类), regression (回归) and outliers detection ( 异常检测).
优势
- Effective in high dimensional spaces. 【高维好操作】
- Still effective in cases where number of dimensions is greater than the number of samples. 【高维,例如语言模型,但效果好不好是另一码事】
- Uses a subset of training points in the decision function (called support vectors), so it is also memory efficient. 【通过子集判断】
- Versatile: different Kernel functions can be specified for the decision function. Common kernels are provided, but it is also possible to specify custom kernels.
劣势
- If the number of features is much greater than the number of samples, the method is likely to give poor performances.
- SVMs do not directly provide probability estimates, these are calculated using an expensive five-fold cross-validation.
什么是支持向量
支持向量(support vector):距离最接近的数据点。
间隔(margin):支持向量定义的沿着分隔线的区域。
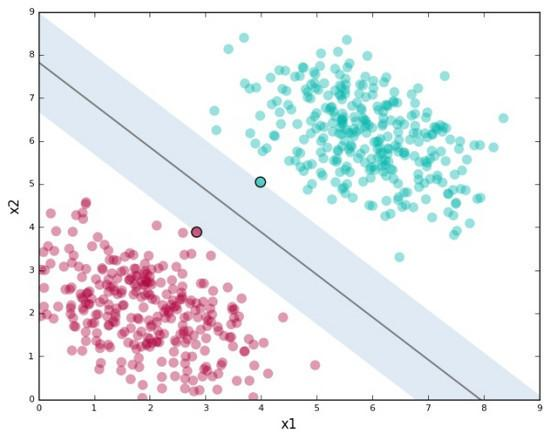
有间隔就会影响分类结果中的误差大小
SVM允许我们通过参数 C 指定愿意接受多少误差,让我们可以指定以下两者的折衷:
- 较宽的间隔。正确分类 训练数据 。
- C值较高,意味着训练数据上容许的误差较少
什么是核
升维使其可分
一般而言,很难找到这样的特定投影。
不过,感谢Cover定理,我们确实知道,投影到高维空间后,数据 更可能线性可分。
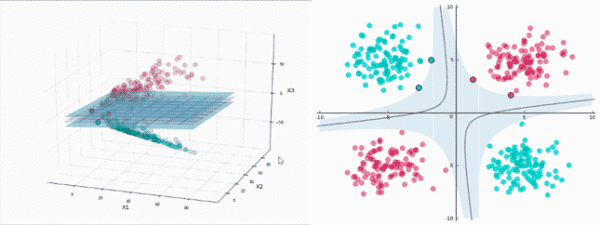
谁来做高维投影
SVM将使用一种称为 核(kernels)的东西进行投影,这相当迅速。
升维且高效
需要几次运算?在二维情形下计算内积需要2次乘法、1次加法,然后平方又是1次乘法。所以总共是 4次运算,仅仅是之前先投影后计算的 运算量的31% 。
看来用核函数计算所需内积要快得多。在这个例子中,这点提升可能不算什么:4次运算和13次运算。然而,如果数据点有许多维度,投影空间的维度更高,在大型数据集上,核函数节省的算力将飞速累积。这是核函数的巨大优势。
大多数SVM库内置了流行的核函数,比如 多项式(Polynomial)、 径向基函数(Radial Basis Function,RBF) 、 Sigmoid 。当我们不进行投影时(比如本文的第一个例子),我们直接在原始空间计算点积——我们把这叫做使用 线性核(linear kernel) 。
径向基函数 RBF
例:RBF kernel 【径向基函数 (Radial Basis Function 简称 RBF), 就是某种沿径向对称的标量函数,也是默认kernel】
"""
==============
Non-linear SVM
============== Perform binary classification using non-linear SVC
with RBF kernel. The target to predict is a XOR of the
inputs. The color map illustrates the decision function learned by the SVC.
"""
print(__doc__) import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm
# 生成网格型数据
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-3, 3, 500), np.linspace(-3, 3, 500))
np.random.seed(0)
X = np.random.randn(300, 2)
Y = np.logical_xor(X[:, 0] > 0, X[:, 1] > 0) # fit the model
clf = svm.NuSVC()
clf.fit(X, Y) # plot the decision function for each datapoint on the grid
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) plt.imshow(Z, interpolation='nearest',
extent=(xx.min(), xx.max(), yy.min(), yy.max()), aspect='auto',
origin='lower', cmap=plt.cm.PuOr_r)
contours = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2, linetypes='--')
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=30, c=Y, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.axis([-3, 3, -3, 3])
plt.show()
变量:xx, yy
xx
Out[140]:
array([[-3. , -2.98797595, -2.9759519 , ..., 2.9759519 ,
2.98797595, 3. ],
[-3. , -2.98797595, -2.9759519 , ..., 2.9759519 ,
2.98797595, 3. ],
[-3. , -2.98797595, -2.9759519 , ..., 2.9759519 ,
2.98797595, 3. ],
...,
[-3. , -2.98797595, -2.9759519 , ..., 2.9759519 ,
2.98797595, 3. ],
[-3. , -2.98797595, -2.9759519 , ..., 2.9759519 ,
2.98797595, 3. ],
[-3. , -2.98797595, -2.9759519 , ..., 2.9759519 ,
2.98797595, 3. ]]) yy
Out[141]:
array([[-3. , -3. , -3. , ..., -3. ,
-3. , -3. ],
[-2.98797595, -2.98797595, -2.98797595, ..., -2.98797595,
-2.98797595, -2.98797595],
[-2.9759519 , -2.9759519 , -2.9759519 , ..., -2.9759519 ,
-2.9759519 , -2.9759519 ],
...,
[ 2.9759519 , 2.9759519 , 2.9759519 , ..., 2.9759519 ,
2.9759519 , 2.9759519 ],
[ 2.98797595, 2.98797595, 2.98797595, ..., 2.98797595,
2.98797595, 2.98797595],
[ 3. , 3. , 3. , ..., 3. ,
3. , 3. ]])
np.c_ 降维后的元素的reconstruct
np.c_[np.array([1,2,3]), np.array([4,5,6])]
Out[142]:
array([[1, 4],
[2, 5],
[3, 6]]) np.c_[np.array([[1,2,3]]), 0, 0, np.array([[4,5,6]])]
Out[143]: array([[1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 5, 6]])
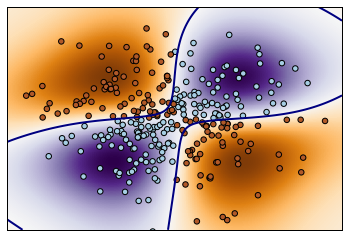
不同的核:Various kernels
可见,RBF 的分割更为细致。
"""
================================
SVM Exercise
================================ A tutorial exercise for using different SVM kernels. This exercise is used in the :ref:`using_kernels_tut` part of the
:ref:`supervised_learning_tut` section of the :ref:`stat_learn_tut_index`.
"""
print(__doc__) import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets, svm iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target X = X[y != 0, :2]
y = y[y != 0] n_sample = len(X) np.random.seed(0)
order = np.random.permutation(n_sample)
X = X[order]
y = y[order].astype(np.float)
# shuffle
X_train = X[:.9 * n_sample]
y_train = y[:.9 * n_sample]
X_test = X[ .9 * n_sample:]
y_test = y[ .9 * n_sample:] # fit the model
for fig_num, kernel in enumerate(('linear', 'rbf', 'poly')):
clf = svm.SVC(kernel=kernel, gamma=10)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train) plt.figure(fig_num)
plt.clf()
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, zorder=10, cmap=plt.cm.Paired) # Circle out the test data
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], s=80, facecolors='none', zorder=10) plt.axis('tight')
x_min = X[:, 0].min()
x_max = X[:, 0].max()
y_min = X[:, 1].min()
y_max = X[:, 1].max() XX, YY = np.mgrid[x_min:x_max:200j, y_min:y_max:200j]
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()]) # Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(XX.shape)
plt.pcolormesh(XX, YY, Z > 0, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.contour(XX, YY, Z, colors=['k', 'k', 'k'], linestyles=['--', '-', '--'],
levels=[-.5, 0, .5]) plt.title(kernel)
plt.show()
Result:
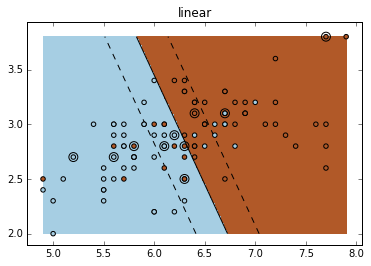
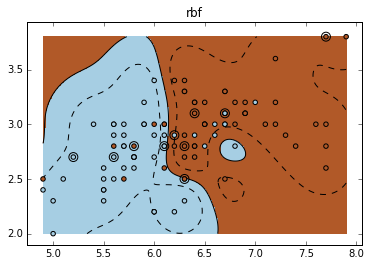
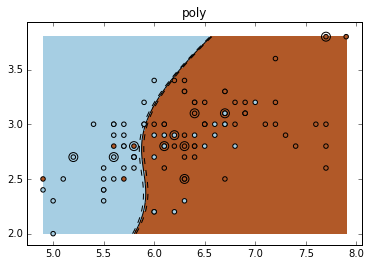
End.
[Scikit-learn] 1.4 Support Vector Classification的更多相关文章
- [Scikit-learn] 1.4 Support Vector Machines - Linear Classification
Outline: 作为一种典型的应用升维的方法,内容比较多,自带体系,以李航的书为主,分篇学习. 函数间隔和几何间隔 最大间隔 凸最优化问题 凸二次规划问题 线性支持向量机和软间隔最大化 添加的约束很 ...
- 支持向量机 support vector machine
SVM(support Vector machine) (1) SVM(Support Vector Machine)是从瓦普尼克(Vapnik)的统计学习理论发展而来的,主要针对小样本数据进行学习. ...
- A glimpse of Support Vector Machine
支持向量机(support vector machine, 以下简称svm)是机器学习里的重要方法,特别适用于中小型样本.非线性.高维的分类和回归问题.本篇希望在正篇提供一个svm的简明阐述,附录则提 ...
- [Scikit-learn] 1.4 Support Vector Regression
SVM算法 既可用于回归问题,比如SVR(Support Vector Regression,支持向量回归) 也可以用于分类问题,比如SVC(Support Vector Classification ...
- Support Vector Machines for classification
Support Vector Machines for classification To whet your appetite for support vector machines, here’s ...
- (原创)(四)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的Logistic回归初探
目录 5.3 使用LogisticRegressionCV进行正则化的 Logistic Regression 参数调优 一.Scikit Learn中有关logistics回归函数的介绍 1. 交叉 ...
- Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习
转自:http://my.oschina.net/u/175377/blog/84420#OSC_h2_23 Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习 Warning 警告:有些没能理解的 ...
- (原创)(三)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的线性回归模型初探
一.Scikit Learn中使用estimator三部曲 1. 构造estimator 2. 训练模型:fit 3. 利用模型进行预测:predict 二.模型评价 模型训练好后,度量模型拟合效果的 ...
- Support vector machine
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine In machine learning, support vector machines (S ...
随机推荐
- Java字节码方法表结构深度剖析
继续上一次[https://www.cnblogs.com/webor2006/p/9459681.html]的字节码分析,这次来分析一下最为复杂的方法表的信息,如下: 而上一次分析到了属性表的位置在 ...
- 【NOIP/CSP2019】D2T1 Emiya 家今天的饭
这个D2T1有点难度啊 原题: 花了我一下午的时间,作为D2T1的确反常 条件很奇怪,感觉不太直观,于是看数据范围先写了个暴力 写暴力的时候我就注意到了之前没有仔细想过的点,烹饪方式必须不同 虽然a很 ...
- cas的客户端配置
知识点:cas的客户端配置 一:cas客户端配置 二:cas认证流程原理(图) 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/suiyueqiannian/p/9359597.html 源码: ...
- java之spring
Spring Spring中的基本概念1.IOC/DI对象的属性由自己创建,为正向流程,而由Spring创建,为控制反转.DI(依赖注入)为实现IOC的一种方式,通过配置文件或注解包含的依赖关系创建与 ...
- tomcat配置CA证书后,https的接口url请求很慢,大概率会超时
背景:项目需要使用websocket长连接,走nginx反向代理会断开,所以决定要直连项目 [websocket连接https需要使用wss] 项目端口: 项目名:biubiu https证书端口: ...
- Windows Dialog对话框
一.MessageBox弹出框 MessageBox.Show(<字符串> Text, <字符串> Title, <整型> nType,MessageBoxIcon ...
- BackGroundWorker组件使用、Winform控件的Invoke安全调用
BackgroundWorker是·net里用来执行多线程任务的控件,它允许编程者在一个单独的线程上执行一些操作. 可以通过编程方式创建 BackgroundWorker,也可以将它从"工具 ...
- Why GPU Program is expensive in CPU
对于非morden API这部分开销比较大的原因 1. state validation -验证state API 调用的合法性 CPU开销 -encode API state 到hardware ...
- js中in关键字的使用方法
1.for...in 对数组或对象的循环/迭代操作 对于数组循环出来的是数组元素:对于对象循环出来的是对象属性 2.判断对象是否是数组/对象的元素/属性 格式:(变量 in 对象) 当‘对象’是数组时 ...
- elk with docker-compose
version: '2' services: elasticsearch: image: docker.calix.local:18080/docker-elasticsearch:6.2.2-1 # ...
