Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A,B,C,D
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
According to an old legeng, a long time ago Ankh-Morpork residents did something wrong to miss Fortune, and she cursed them. She said that at some time n snacks of distinct sizes will fall on the city, and the residents should build a Snacktower of them by placing snacks one on another. Of course, big snacks should be at the bottom of the tower, while small snacks should be at the top.
Years passed, and once different snacks started to fall onto the city, and the residents began to build the Snacktower.
However, they faced some troubles. Each day exactly one snack fell onto the city, but their order was strange. So, at some days the residents weren't able to put the new stack on the top of the Snacktower: they had to wait until all the bigger snacks fell. Of course, in order to not to anger miss Fortune again, the residents placed each snack on the top of the tower immediately as they could do it.
Write a program that models the behavior of Ankh-Morpork residents.
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the total number of snacks.
The second line contains n integers, the i-th of them equals the size of the snack which fell on the i-th day. Sizes are distinct integers from 1 to n.
Print n lines. On the i-th of them print the sizes of the snacks which the residents placed on the top of the Snacktower on the i-th day in the order they will do that. If no snack is placed on some day, leave the corresponding line empty.
3
3 1 2
3
2 1
5
4 5 1 2 3
5 4
3 2 1
In the example a snack of size 3 fell on the first day, and the residents immediately placed it. On the second day a snack of size 1 fell, and the residents weren't able to place it because they were missing the snack of size 2. On the third day a snack of size 2 fell, and the residents immediately placed it. Right after that they placed the snack of size 1 which had fallen before.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x,y) cout<<"bug"<<x<<" "<<y<<endl;
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=2e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
int a[N];
int flag[N];
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
int en=n;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
flag[a[i]]=;
while(flag[en]==)
{
printf("%d ",en);
en--;
}
printf("\n");
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Finally! Vasya have come of age and that means he can finally get a passport! To do it, he needs to visit the passport office, but it's not that simple. There's only one receptionist at the passport office and people can queue up long before it actually opens. Vasya wants to visit the passport office tomorrow.
He knows that the receptionist starts working after ts minutes have passed after midnight and closes after tf minutes have passed after midnight (so that (tf - 1) is the last minute when the receptionist is still working). The receptionist spends exactly t minutes on each person in the queue. If the receptionist would stop working within t minutes, he stops serving visitors (other than the one he already serves).
Vasya also knows that exactly n visitors would come tomorrow. For each visitor Vasya knows the point of time when he would come to the passport office. Each visitor queues up and doesn't leave until he was served. If the receptionist is free when a visitor comes (in particular, if the previous visitor was just served and the queue is empty), the receptionist begins to serve the newcomer immediately.
 "Reception 1"
"Reception 1"
For each visitor, the point of time when he would come to the passport office is positive. Vasya can come to the office at the time zero (that is, at midnight) if he needs so, but he can come to the office only at integer points of time. If Vasya arrives at the passport office at the same time with several other visitors, he yields to them and stand in the queue after the last of them.
Vasya wants to come at such point of time that he will be served by the receptionist, and he would spend the minimum possible time in the queue. Help him!
The first line contains three integers: the point of time when the receptionist begins to work ts, the point of time when the receptionist stops working tf and the time the receptionist spends on each visitor t. The second line contains one integer n — the amount of visitors (0 ≤ n ≤ 100 000). The third line contains positive integers in non-decreasing order — the points of time when the visitors arrive to the passport office.
All times are set in minutes and do not exceed 1012; it is guaranteed that ts < tf. It is also guaranteed that Vasya can arrive at the passport office at such a point of time that he would be served by the receptionist.
Print single non-negative integer — the point of time when Vasya should arrive at the passport office. If Vasya arrives at the passport office at the same time with several other visitors, he yields to them and queues up the last. If there are many answers, you can print any of them.
10 15 2
2
10 13
12
8 17 3
4
3 4 5 8
2
In the first example the first visitor comes exactly at the point of time when the receptionist begins to work, and he is served for two minutes. At 12 minutes after the midnight the receptionist stops serving the first visitor, and if Vasya arrives at this moment, he will be served immediately, because the next visitor would only come at 13 minutes after midnight.
In the second example, Vasya has to come before anyone else to be served.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x,y) cout<<"bug"<<x<<" "<<y<<endl;
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=2e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
ll a[N];
map<ll,int>mp;
int main()
{
ll ts,tf,t,n;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&ts,&tf,&t);
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lld",&a[i]),mp[a[i]]=;
ll ans=a[]-;
ll st=ts;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(ts>tf)break;
if(a[i]<=ts)
ts+=t;
else
{
printf("%lld\n",ts);
return ;
}
}
if(tf-ts>=t)
return *printf("%lld\n",ts);
ll wait=INF;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i]<=||mp[a[i]-])continue;
if(st+(i-)*t<=tf&&wait>st+(i-)*t-a[i]+)
{
wait=st+(i-)*t-a[i]+;
ans=a[i]-;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
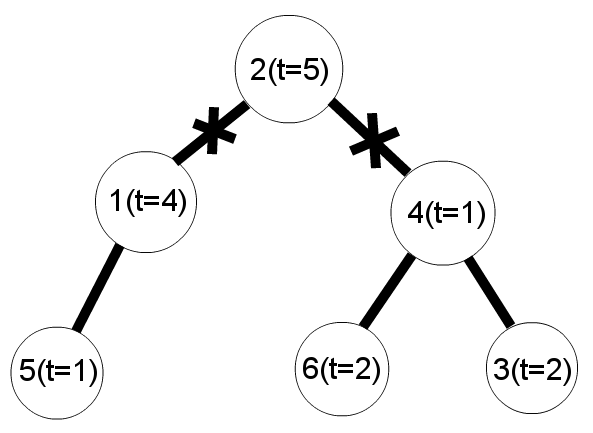
Once at New Year Dima had a dream in which he was presented a fairy garland. A garland is a set of lamps, some pairs of which are connected by wires. Dima remembered that each two lamps in the garland were connected directly or indirectly via some wires. Furthermore, the number of wires was exactly one less than the number of lamps.
There was something unusual about the garland. Each lamp had its own brightness which depended on the temperature of the lamp. Temperatures could be positive, negative or zero. Dima has two friends, so he decided to share the garland with them. He wants to cut two different wires so that the garland breaks up into three parts. Each part of the garland should shine equally, i. e. the sums of lamps' temperatures should be equal in each of the parts. Of course, each of the parts should be non-empty, i. e. each part should contain at least one lamp.

Help Dima to find a suitable way to cut the garland, or determine that this is impossible.
While examining the garland, Dima lifted it up holding by one of the lamps. Thus, each of the lamps, except the one he is holding by, is now hanging on some wire. So, you should print two lamp ids as the answer which denote that Dima should cut the wires these lamps are hanging on. Of course, the lamp Dima is holding the garland by can't be included in the answer.
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 106) — the number of lamps in the garland.
Then n lines follow. The i-th of them contain the information about the i-th lamp: the number lamp ai, it is hanging on (and 0, if is there is no such lamp), and its temperature ti ( - 100 ≤ ti ≤ 100). The lamps are numbered from 1 to n.
If there is no solution, print -1.
Otherwise print two integers — the indexes of the lamps which mean Dima should cut the wires they are hanging on. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
6
2 4
0 5
4 2
2 1
1 1
4 2
1 4
6
2 4
0 6
4 2
2 1
1 1
4 2
-1
The garland and cuts scheme for the first example:
/*
题意:给你一棵树,删掉两条边,分成三部分,权值和相等;
思路:dfs,回溯的时候判子树和是否等于平均值,坑点:根不算;
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x,y) cout<<"bug"<<x<<" "<<y<<endl;
const int N=1e6+,M=1e6+,inf=2e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
struct is
{
int v,next;
}edge[N<<];
int head[N],edg;
int n,sum[N],a[N];
void init()
{
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
edg=;
}
void add(int u,int v)
{
edg++;
edge[edg].v=v;
edge[edg].next=head[u];
head[u]=edg;
}
int ave;
vector<int>ans;
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
sum[u]=a[u];
for(int i=head[u];i!=-;i=edge[i].next)
{
int v=edge[i].v;
if(v==fa)continue;
dfs(v,u);
sum[u]+=sum[v];
}
if(fa!=-&&sum[u]==ave)
{
sum[u]=;
ans.push_back(u);
}
}
int main()
{
int root;
init();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int u;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&a[i]);
if(u)
add(u,i),add(i,u);
else
root=i;
ave+=a[i];
}
if(ave%)return puts("-1");
ave/=;
dfs(root,-);
if(ans.size()<)
printf("-1\n");
else
{
for(int i=;i<;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Olya likes milk very much. She drinks k cartons of milk each day if she has at least k and drinks all of them if she doesn't. But there's an issue — expiration dates. Each carton has a date after which you can't drink it (you still can drink it exactly at the date written on the carton). Due to this, if Olya's fridge contains a carton past its expiry date, she throws it away.
Olya hates throwing out cartons, so when she drinks a carton, she chooses the one which expires the fastest. It's easy to understand that this strategy minimizes the amount of cartons thrown out and lets her avoid it if it's even possible.
 Milk. Best before: 20.02.2017.
Milk. Best before: 20.02.2017.
The main issue Olya has is the one of buying new cartons. Currently, there are n cartons of milk in Olya's fridge, for each one an expiration date is known (how soon does it expire, measured in days). In the shop that Olya visited there are m cartons, and the expiration date is known for each of those cartons as well.
Find the maximum number of cartons Olya can buy so that she wouldn't have to throw away any cartons. Assume that Olya drank no cartons today.
In the first line there are three integers n, m, k (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 106, 1 ≤ k ≤ n + m) — the amount of cartons in Olya's fridge, the amount of cartons in the shop and the number of cartons Olya drinks each day.
In the second line there are n integers f1, f2, ..., fn (0 ≤ fi ≤ 107) — expiration dates of the cartons in Olya's fridge. The expiration date is expressed by the number of days the drinking of this carton can be delayed. For example, a 0 expiration date means it must be drunk today, 1 — no later than tomorrow, etc.
In the third line there are m integers s1, s2, ..., sm (0 ≤ si ≤ 107) — expiration dates of the cartons in the shop in a similar format.
If there's no way for Olya to drink the cartons she already has in her fridge, print -1.
Otherwise, in the first line print the maximum number x of cartons which Olya can buy so that she wouldn't have to throw a carton away. The next line should contain exactly x integers — the numbers of the cartons that should be bought (cartons are numbered in an order in which they are written in the input, starting with 1). Numbers should not repeat, but can be in arbitrary order. If there are multiple correct answers, print any of them.
3 6 2
1 0 1
2 0 2 0 0 2
3
1 2 3
3 1 2
0 0 0
1
-1
2 1 2
0 1
0
1
1
In the first example k = 2 and Olya has three cartons with expiry dates 0, 1 and 1 (they expire today, tomorrow and tomorrow), and the shop has 3 cartons with expiry date 0 and 3 cartons with expiry date 2. Olya can buy three cartons, for example, one with the expiry date 0 and two with expiry date 2.
In the second example all three cartons Olya owns expire today and it means she would have to throw packets away regardless of whether she buys an extra one or not.
In the third example Olya would drink k = 2 cartons today (one she alreay has in her fridge and one from the shop) and the remaining one tomorrow.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
#define bug(x,y) cout<<"bug"<<x<<" "<<y<<endl;
const int N=1e6+,M=1e6+,inf=2e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
int a[N];
struct is
{
int b,pos;
bool operator <(const is &a)const
{
return b<a.b;
}
}b[N];
vector<int>ans;
int main()
{
int n,m,k;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i].b),b[i].pos=i;
sort(a+,a++n);
sort(b+,b++m);
int en1=n,en2=m;
for(int i=1e7;i>=;i--)
{
int flag=k;
while(flag)
{
if(en1>=&&a[en1]>=i)
en1--;
else break;
flag--;
}
if(en1>=&&a[en1]>=i)
return puts("-1");
while(flag)
{
if(en2>=&&b[en2].b>=i)
{
ans.push_back(b[en2].pos);
en2--;
}
else break;
flag--;
}
//while(en2>=1&&b[en2].b>=i)
// en2--;
}
printf("%d\n",ans.size());
for(int i=;i<ans.size();i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
According to an old legeng, a long time ago Ankh-Morpork residents did something wrong to miss Fortune, and she cursed them. She said that at some time n snacks of distinct sizes will fall on the city, and the residents should build a Snacktower of them by placing snacks one on another. Of course, big snacks should be at the bottom of the tower, while small snacks should be at the top.
Years passed, and once different snacks started to fall onto the city, and the residents began to build the Snacktower.

However, they faced some troubles. Each day exactly one snack fell onto the city, but their order was strange. So, at some days the residents weren't able to put the new stack on the top of the Snacktower: they had to wait until all the bigger snacks fell. Of course, in order to not to anger miss Fortune again, the residents placed each snack on the top of the tower immediately as they could do it.
Write a program that models the behavior of Ankh-Morpork residents.
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the total number of snacks.
The second line contains n integers, the i-th of them equals the size of the snack which fell on the i-th day. Sizes are distinct integers from 1 to n.
Print n lines. On the i-th of them print the sizes of the snacks which the residents placed on the top of the Snacktower on the i-th day in the order they will do that. If no snack is placed on some day, leave the corresponding line empty.
3
3 1 2
3
2 1
5
4 5 1 2 3
5 4
3 2 1
In the example a snack of size 3 fell on the first day, and the residents immediately placed it. On the second day a snack of size 1 fell, and the residents weren't able to place it because they were missing the snack of size 2. On the third day a snack of size 2 fell, and the residents immediately placed it. Right after that they placed the snack of size 1 which had fallen before.
Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A,B,C,D的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A.Snacktower 模拟 我和官方题解的命名神相似...$has$ #include <iostream> #inclu ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A. Snacktower 模拟
A. Snacktower 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/767/problem/A Description According to an old lege ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) C. Garland —— DFS
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/767/problem/C 题解:类似于提着一串葡萄,用剪刀剪两条藤,葡萄分成了三串.问怎样剪才能使三串葡萄的质量相等. 首先要做 ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (div.2)简要题解
这场cf时间特别好,周六下午,于是就打了打(谁叫我永远1800上不去div1) 比以前div2的题目更均衡了,没有太简单和太难的...好像B题难度高了很多,然后卡了很多人. 然后我最后做了四题,E题感 ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A B C D 模拟 细节 dfs 贪心
A. Snacktower time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) B,C
B. The Queue time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input o ...
- 【DFS】Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) C. Garland
设sum是所有灯泡的亮度之和 有两种情况: 一种是存在结点U和V,U是V的祖先,并且U的子树权值和为sum/3*2,且U不是根,且V的子树权值和为sum/3. 另一种是存在结点U和V,他们之间没有祖先 ...
- 【枚举】【贪心】 Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) B. The Queue
卡题意……妈的智障 一个人的服务时间完整包含在整个工作时间以内. 显然,如果有空档的时间,并且能再下班之前完结,那么直接输出即可,显然取最左侧的空档最优. 如果没有的话,就要考虑“挤掉”某个人,就是在 ...
- 【暴力】Codeforces Round #398 (Div. 2) A. Snacktower
题意不复述. 用个bool数组记录一下,如果某一天,当前剩下的最大的出现了的话,就输出一段. #include<cstdio> using namespace std; int n; bo ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ4452】[Cerc2015]Export Estimate 并查集
[BZOJ4452][Cerc2015]Export Estimate Description 给你一个n个点m条边的无向图,每条边有权值,我们可以选择一个整数lim来生成一个新的图,过程如下: 1 ...
- asp.net 下载文件几种方式
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { /* 微软为Response对象提供了一个新的方法TransmitFile来解决使 ...
- 浙江工业大学校赛 XiaoWei的战斗力
XiaoWei的战斗力 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Tota ...
- Code Forces 652D Nested Segments(离散化+树状数组)
Nested Segments time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- APM最佳实践: 诊断平安城市视频网性能问题
前言: 平安城市已经是一个关系你我他的民生工程,但由于本身系统的复杂性,给运维工作带来了极大的挑战.如何保障摄像头在线率?如何在系统中找到视频系统故障的问题所在?在我们某一次项目经历中,APM在发现问 ...
- linux 如何查看防火墙是否开启
service iptables status可以查看到iptables服务的当前状态.但是即使服务运行了,防火墙也不一定起作用,你还得看防火墙规则的设置 iptables -L在此说一下关于启动和关 ...
- AE开发的一个想法
基于字典进行GIS图形进行编辑. 图层信息 大类别 字典项(属性字段) 居民点 控制点 GPS控制点 线状道路 铁路 省道 国道 一般公路 名称 长度 等级 备注 线状水系 面状道路 面状水系 湖泊 ...
- (转)《SSO CAS单点系列》之 实现一个SSO认证服务器是这样的!
上篇我们引入了SSO这个话题<15分钟了解SSO是个什么鬼!>.本篇我们一步步深入分析SSO实现机理,并亲自动手实现一个线上可用的SSO认证服务器!首先,我们来分析下单Web应用系统登录登 ...
- 数据挖掘-KNN-K最近邻算法
1. 算法核心思想: 通过计算每个训练样本到待分类样本的距离,选取和待分类样本的距离最近的 K 个训练样本,K个样本中那个类别的训练样本占据着多数, 则表明待分类的样本就属于哪一个类别. KNN算法在 ...
- 1.1 、Django 后台
Django 后台 与后台相关文件:每个app中的 admin.py 文件与后台相关. 一,新建一个 名称为 HelloDjango 的项目 django-admin.py startproject ...
