02Android用户界面优化之(一)Android Fragment
一、使用Fragment
1.AndroidManifest.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.shiyanshi.learningfragment"> <application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme.NoActionBar">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application> </manifest>
2.布局文件
(1)activity_main.xml
其中放置的是一个帧布局的布局容器,其id为container
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/container">
</FrameLayout>
(2)fragment_main.xml
主fargment布局文件,里面放置的按钮用于弹出另外一个fragment
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.shiyanshi.learningfragment.MainActivityFragment"
tools:showIn="@layout/activity_main"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="北京欢迎您!" /> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btnShowFragmentAnother"
android:text="显现另外一个Fragment"/> </LinearLayout>
(3)fragment_another.xml
从fragment布局文件,里面的按钮用于支持返回到上一个fragment界面
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/fragmentAnother"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
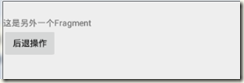
android:text="这是另外一个Fragment"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btnBackOperation"
android:text="后退操作"/> </LinearLayout>
3.Java源文件
(1)MainActivity.java
package com.example.shiyanshi.learningfragment; import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton;
import android.support.design.widget.Snackbar;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
if(savedInstanceState==null){
getSupportFragmentManager()
.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.container,new MainActivityFragment()) //add的第一个参数是布局容器,第二个参数是主Fragment的类
.commit();
}
} }
(2)MainActivityFragment.java
package com.example.shiyanshi.learningfragment;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup; /**
* A placeholder fragment containing a simple view.
*/
public class MainActivityFragment extends
Fragment
{ //注意其继承的是
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment
中的Fragment
public MainActivityFragment() {
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View rootView=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, container, false); //第一个参数:主fragment的布局文件,第二个:布局容器,第三个为布尔型attachToRoot
rootView.findViewById(R.id.btnShowFragmentAnother).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.addToBackStack(null) //加入后退栈,使其支持后退的功能
.replace(R.id.container,new AnotherFragment())
.commit();
}
});
return rootView;
}
}
(3)AnotherFragment.java
package com.example.shiyanshi.learningfragment; import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup; /**
* Created by shiyanshi on 2016/1/25.
*/
public class AnotherFragment extends
Fragment
{
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(final LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_another,container,false);
view.findViewById(R.id.btnBackOperation).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
getFragmentManager().popBackStack();
}
});
return view;
}
}
4.界面显示效果
二、Fragment的生命周期
02Android用户界面优化之(一)Android Fragment的更多相关文章
- Android编程权威指南笔记3:Android Fragment讲解与Android Studio中的依赖关系,如何添加依赖关系
Android Fragment 当我在学习时,了解了Fragment词汇 Fragment是一种控制器对象,我就把所了解的简单说一下.activity可以派fragment完成一些任务,就是管理用户 ...
- Android: Fragment编程指南
本文来自于www.lanttor.org Fragment代表了Activity里的一个行为,或者Activity UI的一部分.你可以在一个activity里构造多个Fragment,也可以在多个a ...
- 【Android自学日记】【转】Android Fragment 真正的完全解析(下)
上篇博客中已经介绍了Fragment产生原因,以及一些基本的用法和各种API,如果你还不了解,请看:Android Fragment 真正的完全解析(上). 本篇将介绍上篇博客提到的:如何管理Frag ...
- Android Fragment使用(四) Toolbar使用及Fragment中的Toolbar处理
Toolbar作为ActionBar使用介绍 本文介绍了在Android中将Toolbar作为ActionBar使用的方法. 并且介绍了在Fragment和嵌套Fragment中使用Toolbar作为 ...
- Android Fragment使用(三) Activity, Fragment, WebView的状态保存和恢复
Android中的状态保存和恢复 Android中的状态保存和恢复, 包括Activity和Fragment以及其中View的状态处理. Activity的状态除了其中的View和Fragment的状 ...
- Android Fragment使用(二) 嵌套Fragments (Nested Fragments) 的使用及常见错误
嵌套Fragment的使用及常见错误 嵌套Fragments (Nested Fragments), 是在Fragment内部又添加Fragment. 使用时, 主要要依靠宿主Fragment的 ge ...
- Android Fragment使用(一) 基础篇 温故知新
Fragment使用的基本知识点总结, 包括Fragment的添加, 参数传递和通信, 生命周期和各种操作. Fragment使用基础 Fragment添加 方法一: 布局里的标签 标识符: tag, ...
- Android Fragment应用实战
现在Fragment的应用真的是越来越广泛了,之前Android在3.0版本加入Fragment的时候,主要是为了解决Android Pad屏幕比较大,空间不能充分利用的问题,但现在即使只是在手机上, ...
- Android Fragment 真正的完全解析(下)
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/37992017 上篇博客中已经介绍了Fragment产生原因,以及一些基本的用法和 ...
随机推荐
- 全分布式环境下,DataNode不启动的问题解决
问题出现:机器重启之后,再次在master结点上面执行start-all.sh,发现有一个datanode没有启动,通过jps检查之后,发现slave1上面的datanode进程未启动 原因:每次na ...
- UIView和其子类的几个初始化函数执行的时机
-(id)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame - UIView的指定初始化方法; 总是发送给UIView去初始化, 除非是从一个nib文件中加载的; -(id)initWithCo ...
- 用canvas绘制一个时钟
实现一个时钟的绘制和时间的显示 一,首先是页面的搭建html部分以及一点点的css代码,因为css这块用的比较少,所以就没有单独出来: <!DOCTYPE html> <html l ...
- USACO 1.3... 虫洞 解题报告(搜索+强大剪枝+模拟)
这题可真是又让我找到了八数码的感觉...哈哈. 首先,第一次见题,没有思路,第二次看题,感觉是搜索,就这样写下来了. 这题我几乎是一个点一个点改对的(至于为什么是这样,后面给你看一个神奇的东西),让我 ...
- 关于jQuery中的attr和data问题
今天在使用data获取属性并且赋值时遇到一个小问题,写下来防止以后再跳坑. 在使用jQuery获取自定义属性值时,我们习惯用 $(selector).attr('data-value'); jQuer ...
- Python Tkinter canvas oval原理
Ovals, mathematically, are ellipses, including circles as a special case. The ellipse is fit into a ...
- Azure上如何在Linux下挂载数据磁盘
[原文首次发表于51cto http://cloudapps.blog.51cto.com/3136598/1653672] 在Azure上创建了虚拟机之后,我们在一些情况下会需要添加更多的数据磁盘来 ...
- Nginx 变量漫谈(五)
前面在 (二) 中我们已经了解到变量值容器的生命期是与请求绑定的,但是我当时有意避开了“请求”的正式定义.大家应当一直默认这里的“请求”都是指客户端发起的 HTTP 请求.其实在 Nginx 世界里有 ...
- 切图教程,APP切图实例
- linux之grep实例讲解
文件testgrep内容: 1.显示所有包含San的行 2.显示所有以J开始的人名所在的行 3.显示所有以700结尾的行 4.显示所有不包括834的行 5.显示所有生日在December的行 ...