KNN笔记
KNN笔记
先简单加载一下sklearn里的数据集,然后再来讲KNN。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
iris=datasets.load_iris()
看一下鸢尾花的keys:
iris.keys()
结果是:
dict_keys(['data', 'target', 'target_names', 'DESCR', 'feature_names'])
看一下文档:
print(iris.DESCR) #看看文档
文档结果:
Iris Plants Database
==================== Notes
-----
Data Set Characteristics:
:Number of Instances: 150 (50 in each of three classes)
:Number of Attributes: 4 numeric, predictive attributes and the class
:Attribute Information:
- sepal length in cm
- sepal width in cm
- petal length in cm
- petal width in cm
- class:
- Iris-Setosa
- Iris-Versicolour
- Iris-Virginica
:Summary Statistics: ============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
Min Max Mean SD Class Correlation
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
sepal length: 4.3 7.9 5.84 0.83 0.7826
sepal width: 2.0 4.4 3.05 0.43 -0.4194
petal length: 1.0 6.9 3.76 1.76 0.9490 (high!)
petal width: 0.1 2.5 1.20 0.76 0.9565 (high!)
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ==================== :Missing Attribute Values: None
:Class Distribution: 33.3% for each of 3 classes.
:Creator: R.A. Fisher
:Donor: Michael Marshall (MARSHALL%PLU@io.arc.nasa.gov)
:Date: July, 1988 This is a copy of UCI ML iris datasets.
http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Iris The famous Iris database, first used by Sir R.A Fisher This is perhaps the best known database to be found in the
pattern recognition literature. Fisher's paper is a classic in the field and
is referenced frequently to this day. (See Duda & Hart, for example.) The
data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a
type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the
latter are NOT linearly separable from each other. References
----------
- Fisher,R.A. "The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems"
Annual Eugenics, 7, Part II, 179-188 (1936); also in "Contributions to
Mathematical Statistics" (John Wiley, NY, 1950).
- Duda,R.O., & Hart,P.E. (1973) Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis.
(Q327.D83) John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-22361-1. See page 218.
- Dasarathy, B.V. (1980) "Nosing Around the Neighborhood: A New System
Structure and Classification Rule for Recognition in Partially Exposed
Environments". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, Vol. PAMI-2, No. 1, 67-71.
- Gates, G.W. (1972) "The Reduced Nearest Neighbor Rule". IEEE Transactions
on Information Theory, May 1972, 431-433.
- See also: 1988 MLC Proceedings, 54-64. Cheeseman et al"s AUTOCLASS II
conceptual clustering system finds 3 classes in the data.
- Many, many more ...
文档
看一下数据data:
iris.data #看看数据
数据为:
array([[ 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 4.9, 3. , 1.4, 0.2],
[ 4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2],
[ 4.6, 3.1, 1.5, 0.2],
[ 5. , 3.6, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 5.4, 3.9, 1.7, 0.4],
[ 4.6, 3.4, 1.4, 0.3],
[ 5. , 3.4, 1.5, 0.2],
[ 4.4, 2.9, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[ 5.4, 3.7, 1.5, 0.2],
[ 4.8, 3.4, 1.6, 0.2],
[ 4.8, 3. , 1.4, 0.1],
[ 4.3, 3. , 1.1, 0.1],
[ 5.8, 4. , 1.2, 0.2],
[ 5.7, 4.4, 1.5, 0.4],
[ 5.4, 3.9, 1.3, 0.4],
[ 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.3],
[ 5.7, 3.8, 1.7, 0.3],
[ 5.1, 3.8, 1.5, 0.3],
[ 5.4, 3.4, 1.7, 0.2],
[ 5.1, 3.7, 1.5, 0.4],
[ 4.6, 3.6, 1. , 0.2],
[ 5.1, 3.3, 1.7, 0.5],
[ 4.8, 3.4, 1.9, 0.2],
[ 5. , 3. , 1.6, 0.2],
[ 5. , 3.4, 1.6, 0.4],
[ 5.2, 3.5, 1.5, 0.2],
[ 5.2, 3.4, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 4.7, 3.2, 1.6, 0.2],
[ 4.8, 3.1, 1.6, 0.2],
[ 5.4, 3.4, 1.5, 0.4],
[ 5.2, 4.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[ 5.5, 4.2, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[ 5. , 3.2, 1.2, 0.2],
[ 5.5, 3.5, 1.3, 0.2],
[ 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[ 4.4, 3. , 1.3, 0.2],
[ 5.1, 3.4, 1.5, 0.2],
[ 5. , 3.5, 1.3, 0.3],
[ 4.5, 2.3, 1.3, 0.3],
[ 4.4, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2],
[ 5. , 3.5, 1.6, 0.6],
[ 5.1, 3.8, 1.9, 0.4],
[ 4.8, 3. , 1.4, 0.3],
[ 5.1, 3.8, 1.6, 0.2],
[ 4.6, 3.2, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 5.3, 3.7, 1.5, 0.2],
[ 5. , 3.3, 1.4, 0.2],
[ 7. , 3.2, 4.7, 1.4],
[ 6.4, 3.2, 4.5, 1.5],
[ 6.9, 3.1, 4.9, 1.5],
[ 5.5, 2.3, 4. , 1.3],
[ 6.5, 2.8, 4.6, 1.5],
[ 5.7, 2.8, 4.5, 1.3],
[ 6.3, 3.3, 4.7, 1.6],
[ 4.9, 2.4, 3.3, 1. ],
[ 6.6, 2.9, 4.6, 1.3],
[ 5.2, 2.7, 3.9, 1.4],
[ 5. , 2. , 3.5, 1. ],
[ 5.9, 3. , 4.2, 1.5],
[ 6. , 2.2, 4. , 1. ],
[ 6.1, 2.9, 4.7, 1.4],
[ 5.6, 2.9, 3.6, 1.3],
[ 6.7, 3.1, 4.4, 1.4],
[ 5.6, 3. , 4.5, 1.5],
[ 5.8, 2.7, 4.1, 1. ],
[ 6.2, 2.2, 4.5, 1.5],
[ 5.6, 2.5, 3.9, 1.1],
[ 5.9, 3.2, 4.8, 1.8],
[ 6.1, 2.8, 4. , 1.3],
[ 6.3, 2.5, 4.9, 1.5],
[ 6.1, 2.8, 4.7, 1.2],
[ 6.4, 2.9, 4.3, 1.3],
[ 6.6, 3. , 4.4, 1.4],
[ 6.8, 2.8, 4.8, 1.4],
[ 6.7, 3. , 5. , 1.7],
[ 6. , 2.9, 4.5, 1.5],
[ 5.7, 2.6, 3.5, 1. ],
[ 5.5, 2.4, 3.8, 1.1],
[ 5.5, 2.4, 3.7, 1. ],
[ 5.8, 2.7, 3.9, 1.2],
[ 6. , 2.7, 5.1, 1.6],
[ 5.4, 3. , 4.5, 1.5],
[ 6. , 3.4, 4.5, 1.6],
[ 6.7, 3.1, 4.7, 1.5],
[ 6.3, 2.3, 4.4, 1.3],
[ 5.6, 3. , 4.1, 1.3],
[ 5.5, 2.5, 4. , 1.3],
[ 5.5, 2.6, 4.4, 1.2],
[ 6.1, 3. , 4.6, 1.4],
[ 5.8, 2.6, 4. , 1.2],
[ 5. , 2.3, 3.3, 1. ],
[ 5.6, 2.7, 4.2, 1.3],
[ 5.7, 3. , 4.2, 1.2],
[ 5.7, 2.9, 4.2, 1.3],
[ 6.2, 2.9, 4.3, 1.3],
[ 5.1, 2.5, 3. , 1.1],
[ 5.7, 2.8, 4.1, 1.3],
[ 6.3, 3.3, 6. , 2.5],
[ 5.8, 2.7, 5.1, 1.9],
[ 7.1, 3. , 5.9, 2.1],
[ 6.3, 2.9, 5.6, 1.8],
[ 6.5, 3. , 5.8, 2.2],
[ 7.6, 3. , 6.6, 2.1],
[ 4.9, 2.5, 4.5, 1.7],
[ 7.3, 2.9, 6.3, 1.8],
[ 6.7, 2.5, 5.8, 1.8],
[ 7.2, 3.6, 6.1, 2.5],
[ 6.5, 3.2, 5.1, 2. ],
[ 6.4, 2.7, 5.3, 1.9],
[ 6.8, 3. , 5.5, 2.1],
[ 5.7, 2.5, 5. , 2. ],
[ 5.8, 2.8, 5.1, 2.4],
[ 6.4, 3.2, 5.3, 2.3],
[ 6.5, 3. , 5.5, 1.8],
[ 7.7, 3.8, 6.7, 2.2],
[ 7.7, 2.6, 6.9, 2.3],
[ 6. , 2.2, 5. , 1.5],
[ 6.9, 3.2, 5.7, 2.3],
[ 5.6, 2.8, 4.9, 2. ],
[ 7.7, 2.8, 6.7, 2. ],
[ 6.3, 2.7, 4.9, 1.8],
[ 6.7, 3.3, 5.7, 2.1],
[ 7.2, 3.2, 6. , 1.8],
[ 6.2, 2.8, 4.8, 1.8],
[ 6.1, 3. , 4.9, 1.8],
[ 6.4, 2.8, 5.6, 2.1],
[ 7.2, 3. , 5.8, 1.6],
[ 7.4, 2.8, 6.1, 1.9],
[ 7.9, 3.8, 6.4, 2. ],
[ 6.4, 2.8, 5.6, 2.2],
[ 6.3, 2.8, 5.1, 1.5],
[ 6.1, 2.6, 5.6, 1.4],
[ 7.7, 3. , 6.1, 2.3],
[ 6.3, 3.4, 5.6, 2.4],
[ 6.4, 3.1, 5.5, 1.8],
[ 6. , 3. , 4.8, 1.8],
[ 6.9, 3.1, 5.4, 2.1],
[ 6.7, 3.1, 5.6, 2.4],
[ 6.9, 3.1, 5.1, 2.3],
[ 5.8, 2.7, 5.1, 1.9],
[ 6.8, 3.2, 5.9, 2.3],
[ 6.7, 3.3, 5.7, 2.5],
[ 6.7, 3. , 5.2, 2.3],
[ 6.3, 2.5, 5. , 1.9],
[ 6.5, 3. , 5.2, 2. ],
[ 6.2, 3.4, 5.4, 2.3],
[ 5.9, 3. , 5.1, 1.8]])
数据data
可见data为150行,每行4列的数据。
看一下target:
iris.target #看看对应的目标值
target结果为:
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
看一下target_names:
iris.target_names #看看目标值对应的目标名称
arget_names结果为:
array(['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica'],
dtype='<U10')
也就是target的0,1,2分别对应的鸢尾花的名称就是这三个。
看一下4列数据(也就是data)分别是指什么
iris.feature_names #看看四个数据对应的是什么
可以看到结果为:
['sepal length (cm)',
'sepal width (cm)',
'petal length (cm)',
'petal width (cm)']
也就是4列数据分别代表花萼的长,花萼的宽,花瓣的长,花瓣的宽。
看一下花萼的数据,也就是前两列的数据:
#看一下花萼的散点图
X=iris.data[:,:2]
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1])
plt.xlabel("sepal length")
plt.ylabel("sepal width")
plt.title("DU's plot about speal")
plt.show()
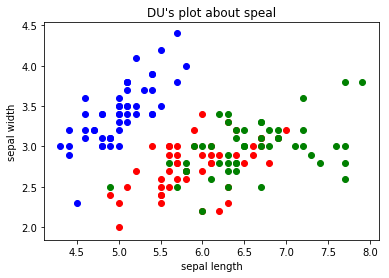
把三种花的散点图区分一下:
#把三种花的花萼的散点图画出来
y=iris.target
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1],color='b')
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1],color='r')
plt.scatter(X[y==2,0],X[y==2,1],color='g')
plt.xlabel("sepal length")
plt.ylabel("sepal width")
plt.title("DU's plot about speal")
plt.show()
再看一下花瓣的散点图:
Petal=iris.data[:,2:]
y=iris.target
plt.scatter(Petal[y==0,0],Petal[y==0,1],color='b')
plt.scatter(Petal[y==1,0],Petal[y==1,1],color='r')
plt.scatter(Petal[y==2,0],Petal[y==2,1],color='g')
plt.xlabel("Petal length")
plt.ylabel("Petal width")
plt.title("DU's plot about Petal")
plt.show()
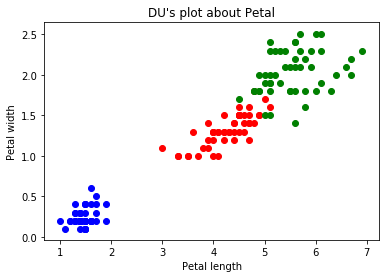
看到花瓣的散点图,那么就说一下KNN,那现在假设,花瓣散点图里来了一个长度为2cm,宽度主0.5cm的一个点,那么这个点代表的是哪个鸢尾呢?一般的人就能推出这个点应该是跟蓝色点是一类的,因为新进来的点是离蓝色的区域最近的,而离其他的红色或者绿色区域都很远。那么,这就是KNN的一个思想了。
比如现假设有如下场景,模拟有如下数据:
raw_X=[[1,2],
[2.8,2.5],
[4,3.2],
[2,1.5],
[6,7.8],
[8,5],
[9,7],
[7,8.5],
[10,9.7],
]
raw_y=[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1]
X_train=np.array(raw_X)
y_train=np.array(raw_y)
现在有一个数据x(设置为绿色的点)进来了,要判断这个数据是属于哪一类的:
x=np.array([7.5,6.5])
plt.scatter(X_train[y_train==0,0],X_train[y_train==0,1])
plt.scatter(X_train[y_train==1,0],X_train[y_train==1,1],color='r')
plt.scatter(x[0],x[1],color='g')
plt.show()
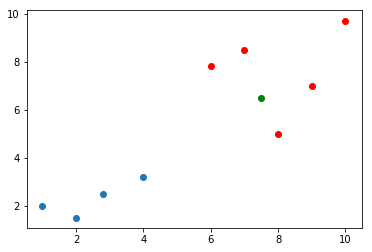
那么,按照KNN的思路就需求,求出这个里面,所有点离这个绿色点的距离了,看这个绿色的点离哪些是最近的。
那么,根据欧拉距离,一般程序员就可以写出这样的代码了:
from math import sqrt
distances=[]
for x_train in X_train:
d=sqrt(np.sum(x_train-x)**2)
distances.append(d)
当然,根据欧拉距离,不一般的程序员是会这么写:
distances=[sqrt(np.sum(x_train-x)**2) for x_train in X_train]
而结果distances都会是:
[11.0, 8.7, 6.8, 10.5, 0.20000000000000018, 1.0, 2.0, 1.5, 5.699999999999999]
接着,算出距离最近元素的索引,进而拿到距离最近的值:
nearest=np.argsort(distances)
topK_y=[y_train[i] for neighbor in nearest[:5]]
from collections import Counter
votes=Counter(topK_y)
predict_y=votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
predict_y
结果明显是1。
KNN笔记的更多相关文章
- 机器学习实战笔记(Python实现)-01-K近邻算法(KNN)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 本系列文章为<机器 ...
- 第2章KNN算法笔记_函数classify0
<机器学习实战>知识点笔记目录 K-近邻算法(KNN)思想: 1,计算未知样本与所有已知样本的距离 2,按照距离递增排序,选前K个样本(K<20) 3,针对K个样本统计各个分类的出现 ...
- opencv2.4.13+python2.7学习笔记--使用 knn对手写数字OCR
阅读对象:熟悉knn.了解opencv和python. 1.knn理论介绍:算法学习笔记:knn理论介绍 2. opencv中knn函数 路径:opencv\sources\modules\ml\in ...
- 机器学习笔记(5) KNN算法
这篇其实应该作为机器学习的第一篇笔记的,但是在刚开始学习的时候,我还没有用博客记录笔记的打算.所以也就想到哪写到哪了. 你在网上搜索机器学习系列文章的话,大部分都是以KNN(k nearest nei ...
- 学习笔记之k-nearest neighbors algorithm (k-NN)
k-nearest neighbors algorithm - Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-nearest_neighbors_algorith ...
- 机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————02.k-邻近算法(KNN)
机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————02.k-邻近算法(KNN) 关键字:邻近算法(kNN: k Nearest Neighbors).python.源 ...
- kNN算法笔记
kNN算法笔记 标签(空格分隔): 机器学习 kNN是什么 kNN算法是k-NearestNeighbor算法,也就是k邻近算法.是监督学习的一种.所谓监督学习就是有训练数据,训练数据有label标好 ...
- retrival and clustering: week 2 knn & LSH 笔记
华盛顿大学 <机器学习> 笔记. knn k-nearest-neighbors : k近邻法 给定一个 数据集,对于查询的实例,在数据集中找到与这个实例最邻近的k个实例,然后再根据k个最 ...
- 【cs231n作业笔记】一:KNN分类器
安装anaconda,下载assignment作业代码 作业代码数据集等2018版基于python3.6 下载提取码4put 本课程内容参考: cs231n官方笔记地址 贺完结!CS231n官方笔记授 ...
随机推荐
- C函数说明
输入函数scanf_s() 比如:char d[20];写成scanf_s("%s",d,20); 输出函数printf() 比如:printf("hell ...
- stm32寄存器版学习笔记10 SPI
SPI(Serial Peripheral Interface),串行外围设备接口.SPI是一种高速的.全双工.同步的通信总线. SPI接口一般使用4条线通信: MISO 主设备数据输入,从设备数据输 ...
- WebLogic配置JNDI数据源
一.什么是jndi数据源 JNDI是Java命名与目录接口(Java Naming and Directory Interface),在J2EE规范中是重要的规范之一. 我们平时开发web程序的时候, ...
- JanusGraph Server配置
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiyuqi/p/320267ff0b5052fad4613945e58ea1f1.html JanusGraph使用Gremlin Server ...
- 呵呵sql
INSERT INTO fnd_document_folder_structure_t (folder_name,parent_folder_id,company_type_id,inv_flag, ...
- 洛谷P1876开灯
题目描述 有n盏灯,一开始全是关闭的.来n个人, 第一个人把一的倍数的灯开着的关上,关上的打开. 第二个人把二的倍数的灯开着的关上,关上的打开. 第三个人把三的倍数的灯开着的关上,关上的打开. ... ...
- nginx+uwsgi 和nginx+gunicorn区别、如何部署
[线上环境部署Django,nginx+uwsgi 和nginx+gunicorn,这两种方案,应该如何选择?] 大家是采用的何种部署方式? 第一种,高并发稳定一点 我们公司使用的是nginx+gun ...
- BZOJ3261:最大异或和
浅谈\(Trie\):https://www.cnblogs.com/AKMer/p/10444829.html 题目传送门:https://lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem ...
- node编译安装
node应用编译安装 安装node编译环境 # apt-get install gcc make build-essential openssl g++ zlib1g-dev libssl-doc a ...
- 搭建基于hyperledger fabric的联盟社区(七) --升级chaincode
上个版本的chaincode有很多功能不完备,所以要部署新版本的chaincode.Fabric支持在保留现有状态的前提对chaincode进行升级. 一.新版chaincode 新版本的chainc ...
