Python 之RabbitMQ使用
1. IO 多路复用
# select 模拟socket server
# server 端
import select
import socket
import sys
import queue
server = socket.socket()
server.setblocking(False)
server_addr = ('localhost', 10000)
print('starting up on %s port %s' % server_addr)
server.bind(server_addr)
server.listen(5)
inputs = [server, ]
outputs = []
message_queues = {}
while True:
print('waiting for next event...')
readable, writeable, exeptional = select.select(inputs, outputs, inputs)
for s in readable: # 每个 s 就是一个socket
if s in server:
conn, client_addr = s.accept()
print('new connection from', client_addr)
conn.setblocking(False)
inputs.append(conn)
message_queues[conn] = queue.Queue()
else:
data = s.recv(1024)
if data:
print('收到来自[%s]的数据:' % s.getpeername()[0], data)
message_queues[s].put[data]
if s not in outputs:
outputs.append(s)
else:
print('客户端断开了', s)
if s in outputs:
outputs.remove(s)
inputs.remove(s)
del message_queues[s]
for s in writeable:
try:
next_msg = message_queues[s].get_nowait()
except queue.Empty:
print('client [%s]' % s.getpeername()[0], 'queue is empty...')
outputs.remove(s)
else:
print('sending msg to [%s]' % s.getpeername()[0], next_msg)
s.send(next_msg.upper())
for s in exceptional:
print('handling exception for', s.getpeername())
inputs.remove(s)
if s in outputs:
outputs.remove(s)
s.close()
del message_queues[s]
# client 端
import socket
import sys
messages = [b'This is the message ',
b'It will be sent',
b'in parts']
server_address = ('localhost', 10000)
socks = [socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM),
socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM),]
print('connecting to %s port %s' % server_address)
for s in socks:
s.connect(server_address)
for message in messages:
for s in socks:
print('%s: sending "%s"' % (s.getsockname(), message))
s.send(message)
for s in socks:
data = s.recv(1024)
print('%s: received "%s"' % (s.getsockname(), data))
if not data:
print(sys.stderr, 'closing socket', s.getsockname())
2. RabbitMQ
2.1 RabbitMQ 准备工作(以mac为例)
- 安装
RabbitMQ:brew install rabbitmq - 安装
pika:pip3 install pika - 启动
RabbitMQ:/usr/local/Cellar/rabbitmq/3.7.4/sbin/rabbitmq-server
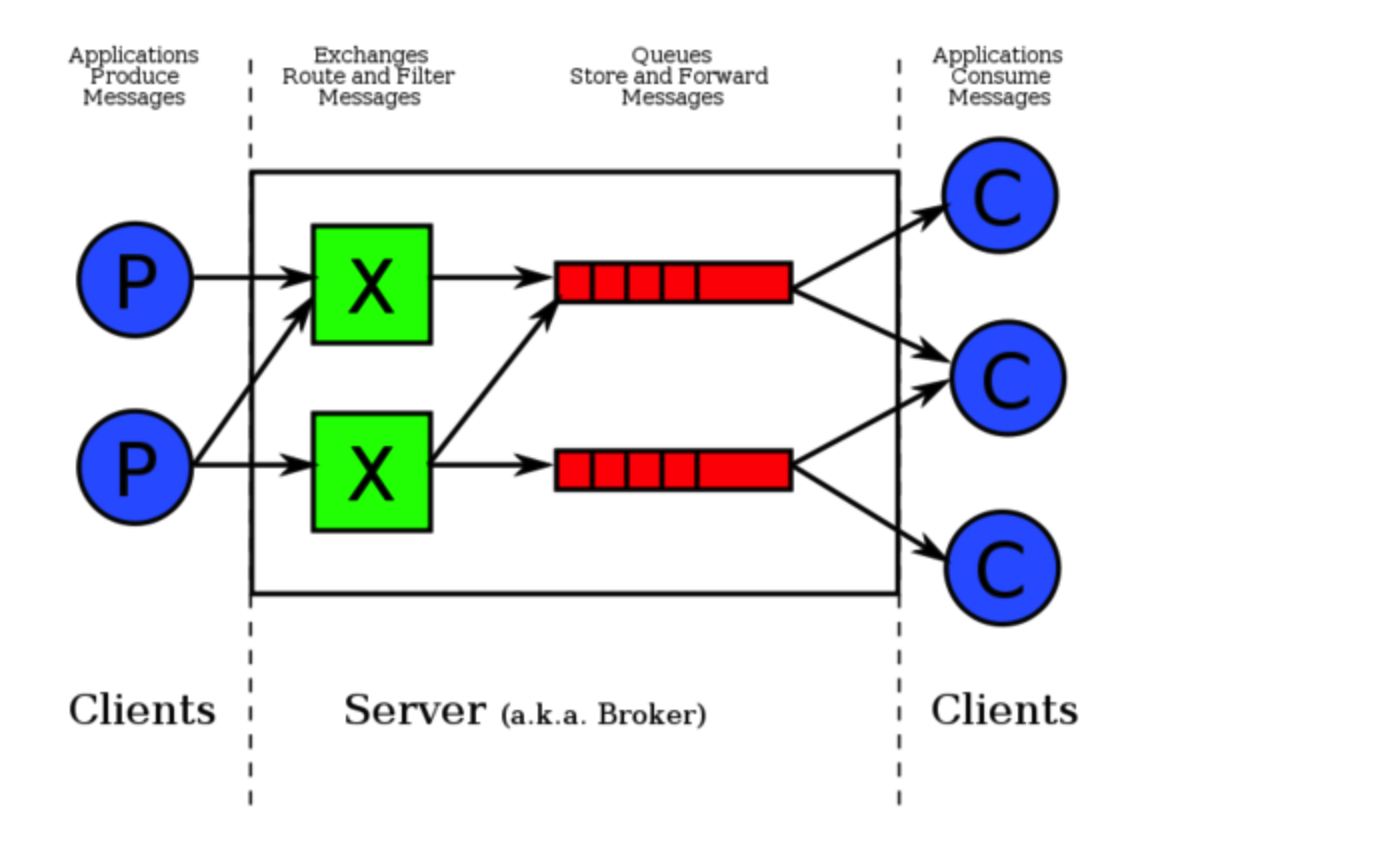
# 示例:
# 发送端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('localhost'))
channel = connection.channel() # 声明一个管道
# 声明queue
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
# 需要 exchange 作为中转站
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello', # queue 名字
body='Hello World!')
print("' [x] Sent 'Hello World!'")
connection.close()
# 接收端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters('localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] Received %r" % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback, # 如果收到消息,就调用 CALLBACK 函数来处理消息
queue='hello',
no_ack=True) # no acknowledgement 不确认
print(' [*] Waiting fo messages. To exit press CTRL+C')
channel.start_consuming()
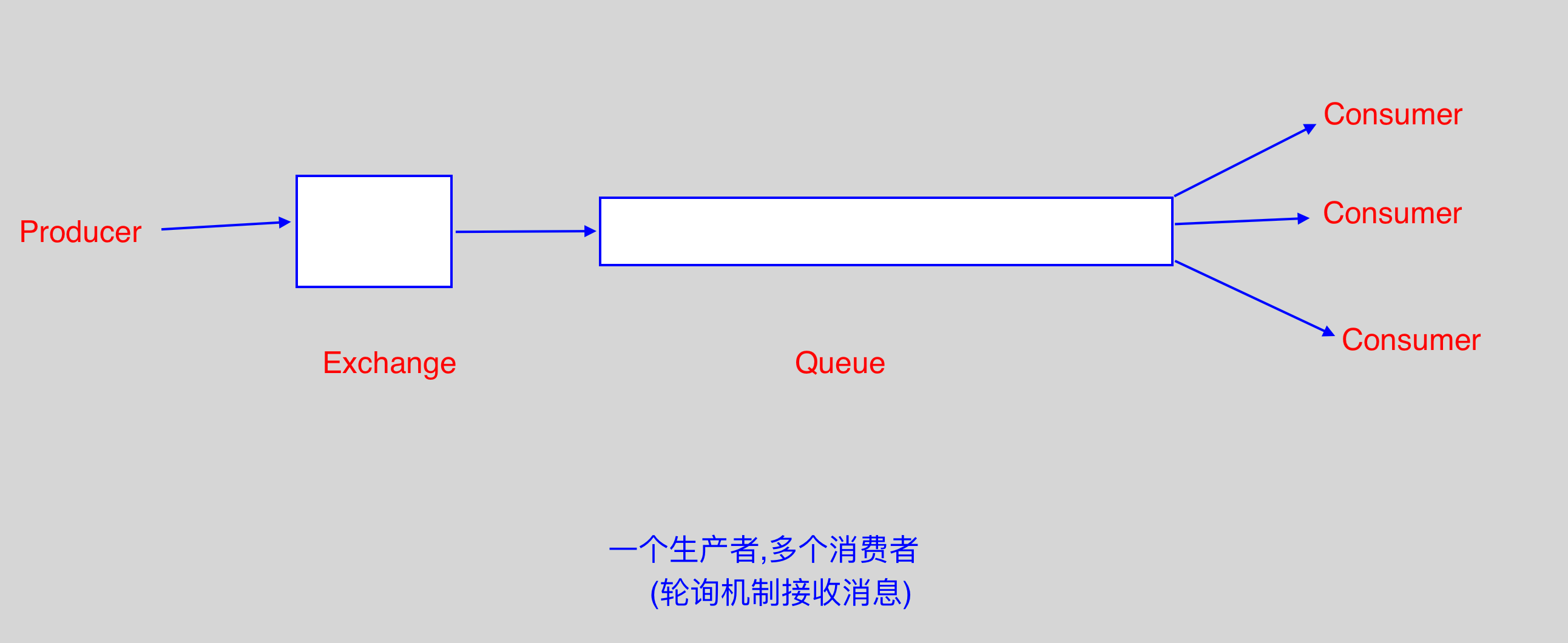
2.2 RabbitMQ 消息分发轮询
- 先启动消息生产者,然后再分别启动3个消费者,通过生产者多发送几条消息,这几条消息会依次分配到各个消费者身上;
2.3 RabbitMQ 消息持久化(发送端)
# 示例:
`channel.queue_declare(queue='hello', durable=True)`: 队列持久化;
# 示例二: 消息持久化
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello',
body='Hello World!',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(delivery_mode=2,) # 将消息持久化
)
2.4 RabbitMQ fanout广播模式
- 如果Rabbit只管按顺序把消息发到各个消费者身上,不考虑消费者负载的话,很可能出现,一个配置不高的机器的消费者那里
堆积了很多消息处理不完,同时配置高的消费者却一直很轻松; - 为解决上述问题,可以在各个消费者端,配置
perfetch=1,意思是告诉RabbitMQ,消费者当前消息还没处理完的时候,就不
要再向该消费者发送新消息了。
# 示例:
# 发送端:
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello', durable=True)
message='Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='hello',
body=message,
properties=pika.BasicProperties(delivery_mode=2,))
print(' [x] Sent %r' % message)
connection.close()
# 消费者端
import pika
import time
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='hello', durable=True)
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(' [x] Received %r' % body)
time.sleep(body.count(b'.'))
print(' [x] Done')
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue='hello')
channel.start_consuming()
2.5 RabbitMQ (发布/订阅模式)
- 发布/订阅模式,需要使用
Exchange; Exchange在定义的时候是有类型的,以决定到底是哪些Queue符合条件,可以接收消息:fanout: 所有bind到此exchange的queue都可以接收消息;direct: 通过routingKey和exchange决定的那个唯一的queue可以接收消息;topic: 所有符合routingKey(此时可以是一个表达式)的routingKey所bind的queue可以接收消息;headers: 通过headers来决定把消息发给哪些queue;
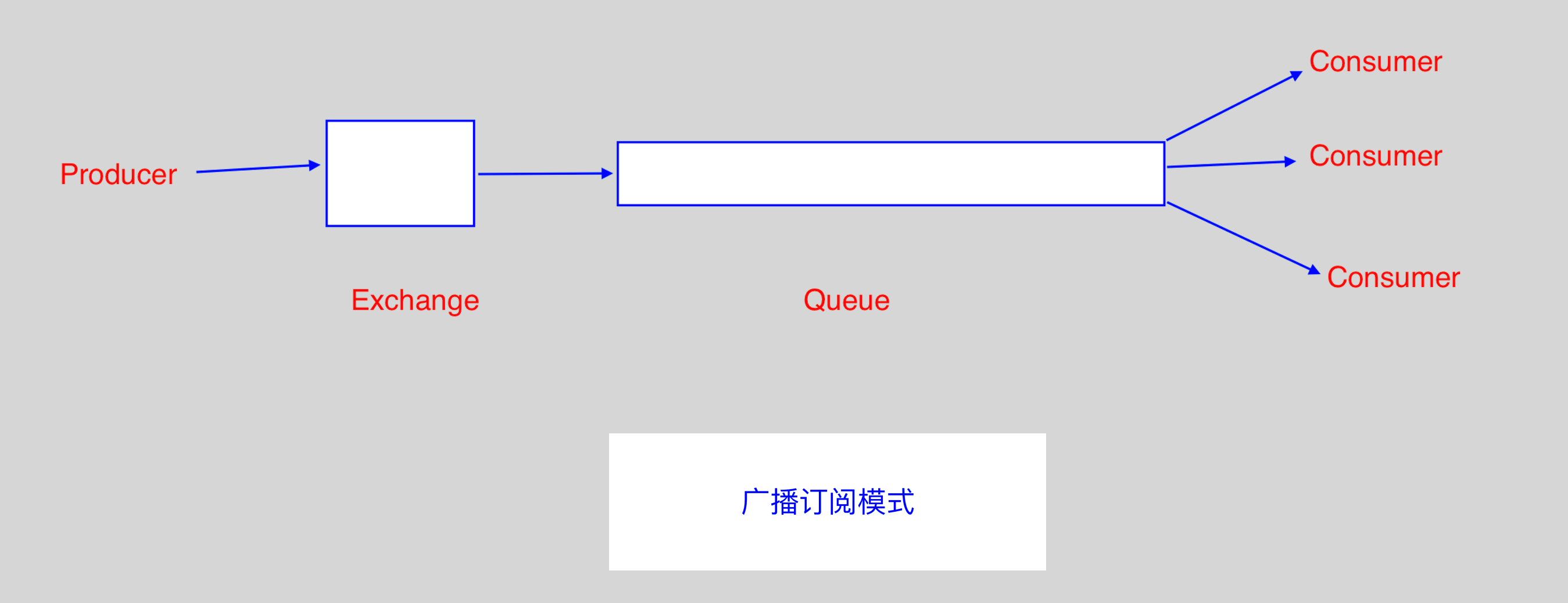
# 表达式符号说明: # 代表一个或多个字符, * 代表任何字符
# 例: #.a 会匹配 a.a, aa.a, aaa.a 等
# *.a 会匹配 a.a, b.a, c.a 等
# 示例: fanout模式,一方发送,多方同时接收
# 发送端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
exchange_type='fanout')
message = 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='logs',
routing_key='',
body=message)
print(' [x] Sent %r' % message)
connection.close()
# 接收端
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs',
exchange_type='fanout')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True) # 不指定queue名字,rabbit会随机分配一个名字, exclusive=True
# 会在使用此queue的消费者断开后,自动将queue删除
queue_name = result.method.queue
channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs',
queue=queue_name)
print(' [*]Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(' [x] %r' % body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
# 示例二: direct 模式(有选择的接收消息)
# 发送端(server.py)
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
exchange_type='direct')
severity = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='direct_logs',
routing_key=severity,
body=message)
print(' [x] Sent %r:%r' % (severity, message))
connection.close()
# 接收端(client.py)
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='direct_logs',
exchange_type='direct')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
severities = sys.argv[1:]
if not severities:
sys.stderr.write('Usage: %s [info] [warning] [error]\n' % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for severity in severities:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='direct_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=severity)
print(' [*]Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(' [x] %r:%r' % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
# 说明:
# 以上操作在terminal启动: python3 client.py info (info级别的接收方)
# python3 server.py info (info级别的发送方)
# python3 client.py error (error级别的接收方)
# python3 server.py error (error级别的发送方)
# 示例三: 更细致的消息过滤(topic 模式)
# 划分为不同应用程序(例如mysql,python等),不同级别(error, info, debug)
# 发送端
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
exchange_type='topic')
routing_key = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'anonymous.info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='topic_logs',
routing_key=routing_key,
body=message)
print(' [x] Sent %r:%r' % (routing_key, message))
connection.close()
# 接收端
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
exchange_type='topic')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
binding_keys = sys.argv[1:]
if not binding_keys:
sys.stderr.write('Usage: %s [binding_key]...\n' % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for binding_key in binding_keys:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='topic_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=binding_key)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(' [x] %r:%r' % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
# 说明:
# 以上操作在terminal启动: python3 client.py mysql.* (接收任何以mysql开头的消息)
# python3 server.py mysql.error (发送mysql的报错日志)
2.6 RabbitMQ rpc实现
# 示例:
# RPC server
import pika
import time
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='rpc_queue')
def fib(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
def on_request(ch, method, props, body):
n = int(body)
print(' [.] fib(%s)' % n)
response = fib(n)
ch.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key=props.reply_to,
properties=pika.BasicProperties(correlation_id = \
props.correlation_id),
body=str(response))
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag = method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)
channel.basic_consume(on_request, queue='rpc_queue')
print(' [x] Awaiting RPC requests')
channel.start_consuming()
# RPC client
import pika
import uuid
class FibonacciRpcClient(object):
def __init__(self):
self.connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='localhost'))
self.channel = self.connection.channel()
result = self.channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
self.callback_queue = result.method.queue # 生成随机Queue
self.channel.basic_consume(self.on_response, # 只要一收到消息,就调用 on_response
no_ack=True,
queue=self.callback_queue)
def on_response(self, ch, method, props, body):
if self.corr_id == props.correlation_id:
self.response = body
def call(self, n):
self.response = None
self.corr_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
self.channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='rpc_queue',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(
reply_to = self.callback_queue,
correlation_id = self.corr_id,
),
body=str(n))
while self.response is None:
self.connection.process_data_events() # 非阻塞版的start_consuming
print('no message')
return int(self.response)
fibonacci_rpc = FibonacciRpcClient()
print(' [x] Requesting fib(30)')
response = fibonacci_rpc.call(30)
print(' [.] Got %r' % response)
参考资料:
Python 之RabbitMQ使用的更多相关文章
- Python操作RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ介绍 RabbitMQ是一个由erlang开发的AMQP(Advanced Message Queue )的开源实现的产品,RabbitMQ是一个消息代理,从“生产者”接收消息并传递消 ...
- 用 Python、 RabbitMQ 和 Nameko 实现微服务
用 Python. RabbitMQ 和 Nameko 实现微服务 原创 07-17 17:57 首页 Linux中国 "微服务是一股新浪潮" - 现如今,将项目拆分成多个独立的. ...
- python之RabbitMQ
一.安装RabbitMQ 1. 安装erlang 1 2 3 4 tar xf otp_src_18.3.tar.gz cd otp_src_18.3 ./configure --prefix=/ma ...
- Python之路【第九篇】:Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache、SQLAlchemy
Python之路[第九篇]:Python操作 RabbitMQ.Redis.Memcache.SQLAlchemy Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用 ...
- python - 操作RabbitMQ
python - 操作RabbitMQ 介绍 RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统.他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议.MQ全称为Mess ...
- 文成小盆友python-num12 Redis发布与订阅补充,python操作rabbitMQ
本篇主要内容: redis发布与订阅补充 python操作rabbitMQ 一,redis 发布与订阅补充 如下一个简单的监控模型,通过这个模式所有的收听者都能收听到一份数据. 用代码来实现一个red ...
- Python之路第十二天,高级(4)-Python操作rabbitMQ
rabbitMQ RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统.他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议. MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(M ...
- Python与RabbitMQ交互
RabbitMQ 消息队列 成熟的中间件RabbitMQ.ZeroMQ.ActiveMQ等等 RabbitMQ使用erlang语言开发,使用RabbitMQ前要安装erlang语言 RabbitMQ允 ...
- python中RabbitMQ的使用(安装和简单教程)
1,简介 RabbitMQ是一个由erlang开发的AMQP(Advanced Message Queue )的开源实现的产品,RabbitMQ是一个消息代理,从"生产者"接收消息 ...
- Python之RabbitMQ的使用
今天总结一下Python关于Rabbitmq的使用 RabbitMQ官网说明,其实也是一种队列,那和前面说的线程queue和进程queue有什么区别呢? 线程queue只能在同一个进程下进行数据交互 ...
随机推荐
- 在form action中滥用绝对路径导致session的attribute丢失(无法正常保存)
症状: 刚才在做一个利用session的attribute保存用户的id的实验,login.jsp输入用户id,提交给LoginServlet去数据库验证,然后LoginServlet根据验证情况跳转 ...
- NFC读卡APP
# 设计文档 ### 简介----------------------------- 这个APP的功能是使用手机的NFC读卡器功能,做到读取卡片支持M1卡和CPU卡. ### 功能列表-------- ...
- tiny4412 u-boot 启动参数的设置
参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/chenfulin5/p/5887552.html 制作SD卡 u-boot 编译完之后, 进入 u-boot 目录里面的 sd_fuse cd ~ ...
- IOS设备信息与机型对照表
http://blog.csdn.net/olsQ93038o99S/article/details/78374343 参考别人的文章吧....
- Spring Boot自动配置类
http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/api/overview-summary.html http://docs.spring.io/sprin ...
- 股票指数kdj,sar,macd
http://blog.eastmoney.com/gulingqianketong2011/blog_120832611.html http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_a3 ...
- JAVA学习资源网站
中文java技术网——http://www.cn-java.com/ 灰狐动力(http://www.huihoo.com/)—— 该站点有许多的开源的项目的介绍和学习,涉及操作系统,数据库等许多方向 ...
- linux的tcz文件怎么安装?
.tcz文件是Tiny core linux 应用安装包文件启动Tiny core linux后,可以使用tce-load命令安装软件如: tce-load -i /tmp/bftpd.tcz 转自: ...
- gomobile build
You need to set the NDK path in gomobile init using the -ndk flag - if you follow these instructions ...
- 搭建 Docker-Registry 私有仓库
官方已经提供了很多版本的 Linux 镜像,直接从官方仓库(Public Repositories)下载就可以了.如果考虑到安全性和速度,我们可能会想在自己局域网里架设一个私有仓库(Private R ...
