go理论知识总结
基于const常量理解个中类型的内存分配引入参考
官方:Constant expressions may contain only constant operands and are evaluated at compile time.
Using constants can often be more efficient than using variables where possible because any references to the constant will be replaced at compile time使用常量通常比在可能的情况下使用变量更有效,因为对常量的任何引用都将在编译时被替换;理解:如const A=7 m:=A 编译后就直接是m:=7用数字替换完了自然没有那个所谓A的地址
In many popular programming environments the stack usually refers to the call stack of a thread;A call stack is a LIFO stack data structure that stores arguments, local variables, and other data tracked as a thread executes functions
在许多流行的编程环境中,堆栈通常是指线程的调用堆栈
We must be able to safely free the memory of the most recent stack frame when it’s popped. We therefore can’t store anything on the stack that later needs to be referenced elsewhere.
Since threads are managed by the OS, the amount of memory available to a thread stack is typically fixed,e.g. a default of 8MB in many Linux environments。This means we also need to be mindful of how much data ends up on the stack, particularly in the case of deeply-nested recursive functions. If the stack pointer in the diagram above passes the stack guard, the program will crash with a stack overflow error.由于线程由操作系统管理,线程堆栈可用的内存量通常是固定的
The heap is a more complex area of memory . We can use the heap on demand to store data needed in our program. Memory allocated here can’t simply be freed when a function returns, and needs to be carefully managed to avoid leaks and fragmentation. 我们可以按需使用堆来存储程序所需的数据,这里分配的内存不能简单地在函数返回时释放,需要小心管理以避免泄漏和碎片
The Go stack and heap
Threads managed by the OS are completely abstracted away from us by the Go runtime, and we instead work with a new abstraction: goroutines. Goroutines are conceptually very similar to threads, but they exist within user space. This means the runtime, and not the OS, sets the rules of how stacks behave。操作系统管理的线程被 Go 运行时完全抽象出来,我们使用一个新的抽象来工作:goroutines。 Goroutines 在概念上与线程非常相似,但它们存在于用户空间中。 这意味着运行时而不是操作系统设置堆栈行为的规则
Rather than having hard limits set by the OS, goroutine stacks start with a small amount of memory (currently 2KB),Before each function call is executed, a check within the function prologue is executed to verify that a stack overflow won’t occur。This means that stacks in Go are dynamically sized, and can typically keep growing as long as there’s enough memory available to feed them。与操作系统设置硬限制不同,goroutine 堆栈以少量内存(当前为 2KB)开始,在执行每个函数调用之前,会执行函数序言中的检查以验证不会发生堆栈溢出,这意味着 Go 中的堆栈是动态大小的,并且只要有足够的可用内存来喂它们,通常就可以保持增长
The Go heap。All goroutines share a common heap and anything that can’t be stored on the stack will end up there.所有 goroutine 共享一个公共堆,任何不能存储在堆栈上的东西都将最终存储在那里。
①线程-堆栈-内存
go数组和切片,参考https://go.dev/blog/slices-intro
Go’s arrays are values. An array variable denotes the entire array; it is not a pointer to the first array element (as would be the case in C).This means that when you assign or pass around an array value you will make a copy of its contents.而切片A slice is a descriptor of an array segment. It consists of a pointer to the array, the length of the segment, and its capacity (the maximum length of the segment).
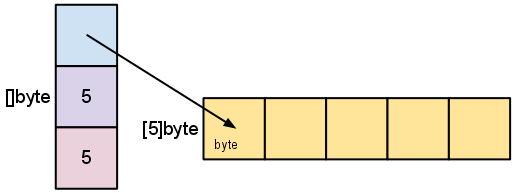
The length is the number of elements referred to by the slice. The capacity is the number of elements in the underlying array (beginning at the element referred to by the slice pointer). The distinction between length and capacity will be made clear as we walk through the next few examples.
As we slice s, observe the changes in the slice data structure and their relation to the underlying array:s = s[2:4]
Slicing does not copy the slice’s data. It creates a new slice value that points to the original array.
This makes slice operations as efficient as manipulating array indices.
Therefore, modifying the elements (not the slice itself) of a re-slice modifies the elements of the original slice:
关于切片引用数组导致整个数组不释放问题
As mentioned earlier, re-slicing a slice doesn’t make a copy of the underlying array. The full array will be kept in memory until it is no longer referenced. Occasionally this can cause the program to hold all the data in memory when only a small piece of it is needed.
For example, this FindDigits function loads a file into memory and searches it for the first group of consecutive numeric digits, returning them as a new slice.
var digitRegexp = regexp.MustCompile("[0-9]+")
func FindDigits(filename string) []byte {
b, _ := ioutil.ReadFile(filename)
return digitRegexp.Find(b)
}
This code behaves as advertised, but the returned []byte points into an array containing the entire file. Since the slice references the original array, as long as the slice is kept around the garbage collector can’t release the array; the few useful bytes of the file keep the entire contents in memory.
To fix this problem one can copy the interesting data to a new slice before returning it:
func CopyDigits(filename string) []byte {
b, _ := ioutil.ReadFile(filename)
b = digitRegexp.Find(b)
c := make([]byte, len(b))
copy(c, b)
return c
}
A more concise version of this function could be constructed by using append. This is left as an exercise for the reader.
go理论知识总结的更多相关文章
- js中函数的一些理论知识
函数的一些理论知识 1. 函数: 执行一个明确的动作并提供一个返回值的独立代码块.同时函数也是javascript中的一级公民(就是函数和其它变量一样). 2.函数的 ...
- 用VC进行COM编程所必须掌握的理论知识
一.为什么要用COM 软件工程发展到今天,从一开始的结构化编程,到面向对象编程,再到现在的COM编程,目标只有一个,就是希望软件能象积方块一样是累起来的,是组装起来的,而不是一点点编出来的.结构化编程 ...
- 图形学理论知识 BRDF 双向反射分布函数(Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function)
图形学理论知识 BRDF 双向反射分布函数 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function BRDF理论 BRDF表示的是双向反射分布函数(Bidire ...
- TestNG学习-001-基础理论知识
此 文主要讲述用 TestNG 的基础理论知识,TestNG 的特定,编写测试过程三步骤,与 JUnit4+ 的差异,以此使亲对 TestNG 测试框架能够有一个简单的认知. 希望能对初学 TestN ...
- [转] DDD领域驱动设计(三) 之 理论知识收集汇总
最近一直在学习领域驱动设计(DDD)的理论知识,从网上搜集了一些个人认为比较有价值的东西,贴出来和大家分享一下: 我一直觉得不要盲目相信权威,比如不能一谈起领域驱动设计,就一定认为国外的那个Eric ...
- Winsock网络编程笔记(4)----基本的理论知识
前面的笔记记录了Winsock的入门编程,领略了Winsock编程的乐趣..但这并不能算是掌握了Winsock,加深理论知识的理解才会让后续学习更加得心应手..因此,这篇笔记将记录一些有关Winsoc ...
- Android初级教程对大量数据的做分页处理理论知识
有时候要加载的数据上千条时,页面加载数据就会很慢(数据加载也属于耗时操作).因此就要考虑分页甚至分批显示.先介绍一些分页的理论知识.对于具体用在哪里,会在后续博客中更新. 分页信息 1,一共多少条数据 ...
- Android初级教程理论知识(第四章内容提供器)
之前第三章理论知识写到过数据库.数据库是在程序内部自己访问自己.而内容提供器是访问别的程序数据的,即跨程序共享数据.对访问的数据也无非就是CRUD. 内容提供者 应用的数据库是不允许其他应用访问的 内 ...
- 关于mpi的理论知识以及编写程序来实现数据积分中的梯形积分法。
几乎所有人的第一个程序是从“hello,world”程序开始学习的 #include "mpi.h" #include <stdio.h> int main(int a ...
- 线程概念( 线程的特点,进程与线程的关系, 线程和python理论知识,线程的创建)
参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/xiao987334176/p/9041318.html 线程概念的引入背景 进程 之前我们已经了解了操作系统中进程的概念,程序并不能单独运 ...
随机推荐
- 虚拟机搭建linux环境&&使用winscp连接搭建好的linux环境步骤
一.需要的工具 虚拟机应用程序.一个镜像(ubuntu等).winscp可执行程序 二.安装虚拟机以及插入镜像 1)选择虚拟机 我安装的是VMware 就是这个,因为之前用的都是vitualbox现在 ...
- 记录安装perl-Verilog过程
开始,编译带Verilog::Netlist的脚本,报 YumRepo Error: All mirror URLs are not using ftp, http[s] or file.centos ...
- supervisord and pm2 进程守护工具
目录 安装 pm2 config pm2是一个带有负载均衡功能的应用进程管理器,类似有Supervisor,forever supervisor 特点: 代码修改,实时重启 安装 npm instal ...
- linux安装Elasticsearch的单节点
一.基础环境 操作系统环境:Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.4 (Santiago) ES版本:elasticsearch-7.8.0-linux- ...
- ServiceEntry与WorkloadEntry
ServiceEntry: 用于将未能自动添加至网格中的服务,以手形式使得内发 现机制能够访问或路由到这些服务.网格外部的服务 运行于 Kubernetes 上,但却非为 Istio 网格 ...
- vue打包后打开index.html文件显示空白页问题
通过网上的资料发现在vue.config.js中写入再重新打包就可以再index.html中显示. https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51060602/article/details/ ...
- TIDB-DM数据迁移第三部(集群管理)
1.对现在 dm 集群进行缩容,将 free 状态的 worker 下线. tiup dm display dm-test 查看 free 状态节点 tiup dm scale-in dm 172.1 ...
- 在windows上搭建spark遇到的问题
报错如下: The root scratch dir: /tmp/hive on HDFS should be writable. Current permissions are: --------- ...
- DSL语言思想的应用
背景 DSL语言的认知 DSL思想的应用 DSL的拓展思考 目标 业务限定 简化逻辑 提高效率 实现 业务提取 业务共性抽离 语法生成 语法实施
- easyui subGrid实现
$(function(){ $('#dg').datagrid({ view: detailview, detailFormatter:function(index,row){ return '< ...
