[LeetCode] Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针之二
Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example:
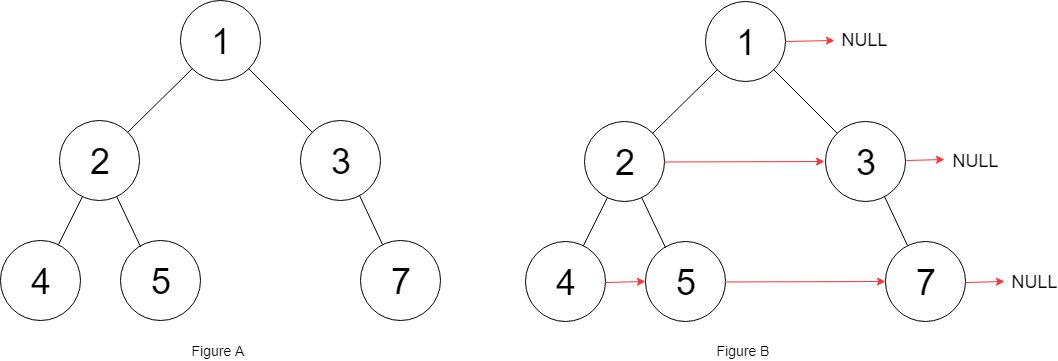
Input: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":4},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":5},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"val":3},"val":1}
Output: {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":null,"next":{"$id":"4","left":null,"next":{"$id":"5","left":null,"next":null,"right":null,"val":7},"right":null,"val":5},"right":null,"val":4},"next":{"$id":"6","left":null,"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"5"},"val":3},"right":{"$ref":"4"},"val":2},"next":null,"right":{"$ref":"6"},"val":1}
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B.
Note:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- Recursive approach is fine, implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
这道是之前那道 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node 的延续,原本的完全二叉树的条件不再满足,但是整体的思路还是很相似,仍然有递归和非递归的解法。我们先来看递归的解法,这里由于子树有可能残缺,故需要平行扫描父节点同层的节点,找到他们的左右子节点。代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
Node *p = root->next;
while (p) {
if (p->left) {
p = p->left;
break;
}
if (p->right) {
p = p->right;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
if (root->right) root->right->next = p;
if (root->left) root->left->next = root->right ? root->right : p;
connect(root->right);
connect(root->left);
return root;
}
};
对于非递归的方法,我惊喜的发现之前的方法直接就能用,完全不需要做任何修改,算法思路可参见之前的博客 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node,代码如下:
解法二:
// Non-recursion, more than constant space
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int len = q.size();
for (int i = ; i < len; ++i) {
Node *t = q.front(); q.pop();
if (i < len - ) t->next = q.front();
if (t->left) q.push(t->left);
if (t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
虽然以上的两种方法都能通过OJ,但其实它们都不符合题目的要求,题目说只能使用constant space,可是OJ却没有写专门检测space使用情况的test,那么下面贴上constant space的解法,这个解法也是用的层序遍历,只不过没有使用queue了,我们建立一个dummy结点来指向每层的首结点的前一个结点,然后指针cur用来遍历这一层,我们实际上是遍历一层,然后连下一层的next,首先从根结点开始,如果左子结点存在,那么cur的next连上左子结点,然后cur指向其next指针;如果root的右子结点存在,那么cur的next连上右子结点,然后cur指向其next指针。此时root的左右子结点都连上了,此时root向右平移一位,指向其next指针,如果此时root不存在了,说明当前层已经遍历完了,我们重置cur为dummy结点,root此时为dummy->next,即下一层的首结点,然后dummy的next指针清空,或者也可以将cur的next指针清空,因为前面已经将cur赋值为dummy了。那么现在想一想,为什么要清空?因为我们用dummy的目的就是要指到下一行的首结点的位置即dummy->next,而一旦将root赋值为dummy->next了之后,这个dummy的使命就已经完成了,必须要断开,如果不断开的话,那么假设现在root是叶结点了,那么while循环还会执行,不会进入前两个if,然后root右移赋空之后,会进入最后一个if,之前没有断开dummy->next的话,那么root又指向之前的叶结点了,死循环诞生了,跪了。所以一定要记得清空哦,呵呵哒~
这里再来说下dummy结点是怎样指向每层的首结点的前一个结点的,过程是这样的,dummy是创建出来的一个新的结点,其目的是为了指向root结点的下一层的首结点的前一个,具体是这么做到的呢,主要是靠cur指针,首先cur指向dummy,然后cur再连上root下一层的首结点,这样dummy也就连上了。然后当root层遍历完了之后,root需要往下移动一层,这样dummy结点之后连接的位置就正好赋值给root,然后cur再指向dummy,dummy之后断开,这样又回到了初始状态,以此往复就可以都连上了,代码如下:
解法三:
// Non-recursion, constant space
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
Node *dummy = new Node(, NULL, NULL, NULL), *cur = dummy, *head = root;
while (root) {
if (root->left) {
cur->next = root->left;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (root->right) {
cur->next = root->right;
cur = cur->next;
}
root = root->next;
if (!root) {
cur = dummy;
root = dummy->next;
dummy->next = NULL;
}
}
return head;
}
};
类似题目:
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)
[LeetCode] Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针之二的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针 II
Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given tre ...
- 117 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 每个节点的右向指针 II
这是“每个节点的右向指针”问题的进阶.如果给定的树可以是任何二叉树,该怎么办?你以前的解决方案仍然有效吗?注意: 你只能使用恒定的空间.例如,给定以下二叉树, 1 / ...
- LeetCode: Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II 解题报告
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node IIFollow up for problem "Populating Next Right Poin ...
- LeetCode——Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given tre ...
- [leetcode]Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II @ Python
原题地址:https://oj.leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/ 题意: Follow up ...
- LeetCode - Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
题目: Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given ...
- [LeetCode] [LeetCode] Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Follow up for problem "Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node". What if the given tre ...
- leetCode 116.Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node (为节点填充右指针) 解题思路和方法
Given a binary tree struct TreeLinkNode { TreeLinkNode *left; TreeLinkNode *right; TreeLinkNode *nex ...
- [Leetcode] Populating next right pointer in each node 填充每个节点的右指针
Given a binary tree struct TreeLinkNode { TreeLinkNode *left; TreeLinkNode *right; TreeLinkNode *nex ...
随机推荐
- 把UI图里的小图标制作成icon font
一个交互比较多的UI图里面可能会有很多小图标,一般可用sprites图将多个小图标弄成一张大图,或者其它的办法,各种方法的比较可参见博主的另外一篇博客使用css3新属性clip-path制作小图标,本 ...
- Rafy 框架 - 执行SQL或存储过程
有时候,开发者不想通过实体来操作数据库,而是希望通过 SQL 语句或存储过程来直接访问数据库.Rafy 也提供了一组 API 来方便实现这类需求. IDbAccesser 接口 为了尽量屏蔽各数据库中 ...
- Node学习笔记(二):事件驱动
接触Node,提得最多的可能就是回调,异步非阻塞处理,思前想后,JavaScript从前端语言过渡到服务器端,最大的劣势可能就是线程,当然这方面的不足现在也被慢慢弥补起来了(很多第三方的npm包可供下 ...
- [SQL Server] 特殊字符、上标、下标处理
今天遇到一个问题是往 SQL Server 中导入像m².m³这样的单位数据,可是在 SQL Server 中查看到的都是 m2.m3,于是在网上查了一下资料,顺便摘录下来供日后查阅. 一 Wind ...
- MongoDB初识
参考: MongoDB资料汇总专题:
- gearman 安装
yum install gperfyum install libevent-develyum install libuuid-develwget https://launchpad.net/gearm ...
- [连载]《C#通讯(串口和网络)框架的设计与实现》- 14.序列号的设计,不重复的实现一机一码
目 录 第十四章 序列号的设计... 2 14.1 设计原则... 2 14.2 设计思想... 3 14.3 代码实现... 4 14. ...
- javascript冒泡排序
数组冒泡排序算法(升序) 升序:小数在前,大数在后 冒泡排序的原则:每次比较相邻两个元素,如果前一个数>后一个数,说明违反升序的要求,就将两数交换位置.否则,保持不变.继续比较下一对. 例如:玩 ...
- js对象和继承总结
创建对象方式: [工厂模式]:无法解决对象识别问题 [构造函数模式]:每个方法都要在每个实例上创建一遍 [原型模式]:原型上属性为引用类型的问题,见例子 [组合模式]:解决上述问题 [动态原型模式]: ...
- xampp与Hbuilder、phpstorm配置
1.xampp的安装就不用多说了,安装完按之后出现这个界面. 2.点击中间那个按钮,运行三个选项,全部正常之后是这样的,这样xampp就不用管了,但是要记下安装的路径,之后需要用 3.首先说Hbuil ...
