Thread.join方法的解析(转)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/huangzejun/p/7908898.html
1. join() 的示例和作用
1.1 示例

1 // 父线程
2 public class Parent extends Thread {
3 public void run() {
4 Child child = new Child();
5 child.start();
6 child.join();
7 // ...
8 }
9 }


1 // 子线程
2 public class Child extends Thread {
3 public void run() {
4 // ...
5 }
6 }

上面代码展示了两个类:Parent(父线程类),Child(子线程类)。
在 Parent.run() 中,通过 Child child = new Child(); 新建 child 子线程(此时 child 处于 NEW 状态);
然后再调用 child.start()(child 转换为 RUNNABLE 状态);
再调用 child.join()。
在 Parent 调用 child.join() 后,child 子线程正常运行,Parent 父线程会等待 child 子线程结束后再继续运行。
下图是我总结的 Java 线程状态转换图:
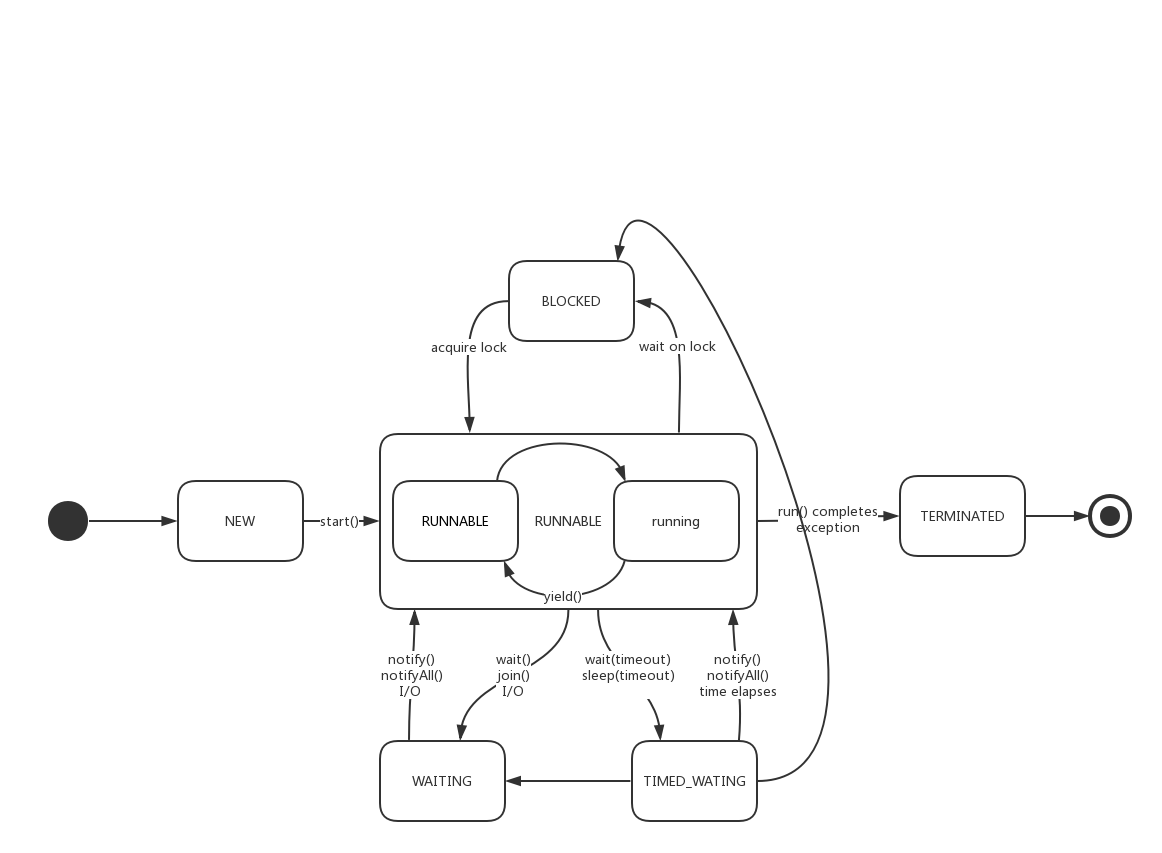
1.2 join() 的作用
让父线程等待子线程结束之后才能继续运行。
我们来看看在 Java 7 Concurrency Cookbook 中相关的描述(很清楚地说明了 join() 的作用):
Waiting for the finalization of a thread
In some situations, we will have to wait for the finalization of a thread. For example, we may have a program that will begin initializing the resources it needs before proceeding with the rest of the execution. We can run the initialization tasks as threads and wait for its finalization before continuing with the rest of the program. For this purpose, we can use the join() method of the Thread class. When we call this method using a thread object, it suspends the execution of the calling thread until the object called finishes its execution.
当我们调用某个线程的这个方法时,这个方法会挂起调用线程,直到被调用线程结束执行,调用线程才会继续执行。
2. join() 源码分析
以下是 JDK 8 中 join() 的源码:

1 public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
2 join(0);
3 }
4
5 public final synchronized void join(long millis)
6 throws InterruptedException {
7 long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
8 long now = 0;
9
10 if (millis < 0) {
11 throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
12 }
13
14 if (millis == 0) {
15 while (isAlive()) {
16 wait(0);
17 }
18 } else {
19 while (isAlive()) {
20 long delay = millis - now;
21 if (delay <= 0) {
22 break;
23 }
24 wait(delay);
25 now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
26 }
27 }
28 }
29
30 public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos)
31 throws InterruptedException {
32
33 if (millis < 0) {
34 throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
35 }
36
37 if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
38 throw new IllegalArgumentException(
39 "nanosecond timeout value out of range");
40 }
41
42 if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {
43 millis++;
44 }
45
46 join(millis);
47 }

我们可以看到 join() 一共有三个重载版本(都是 final method,无法被子类覆盖):
1 public final void join() throws InterruptedException;
2
3 public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
4
5 public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException;
其中
a. join() 和 join(long millis, int nanos) 最后都调用了 join(long millis)。
b. 带参数的 join() 都是 synchronized method。
c. join() 调用了 join(0),从源码可以看到 join(0) 不断检查当前线程(join() 所属的线程实例,非调用线程)是否是 Active。
d. join() 和 sleep() 一样,都可以被中断(被中断时,会抛出 InterrupptedException 异常);不同的是,join() 内部调用了 wait(),会出让锁,而 sleep() 会一直保持锁。
以本文开头的代码为例,我们分析一下代码逻辑:
Parent 调用 child.join(),child.join() 再调用 child.join(0) (此时 Parent 会获得 child 实例作为锁,其他线程可以进入 child.join() ,但不可以进入 child.join(0), 因为无法获取锁)。child.join(0) 会不断地检查 child 线程是否是 Active。
如果 child 线程是 Active,则循环调用 child.wait(0)(为了防止 Spurious wakeup, 需要将 wait(0) 放入 for 循环体中;此时 Parent 会释放 child 实例锁,其他线程可以竞争锁并进入 child.join(0)。我们可以得知,可以有多个线程等待某个线程执行完毕)。
一旦 child 线程不为 Active (状态为 TERMINATED), child.join(0) 会直接返回到 child.join(), child.join() 会直接返回到 Parent 父线程,Parent 父线程就可以继续运行下去了。
超下来,说不定下次会看看,为别人引一点流,哈哈
Thread.join方法的解析(转)的更多相关文章
- Thread.join()方法
thread.Join把指定的线程加入到当前线程,可以将两个交替执行的线程合并为顺序执行的线程.比如在线程B中调用了线程A的Join()方法,直到线程A执行完毕后,才会继续执行线程B.t.join() ...
- Java Thread.join()方法
一.使用方式. join是Thread类的一个方法,启动线程后直接调用,例如: Thread t = new AThread(); t.start(); t.join(); 二.为什么要用join() ...
- JAVA THREAD.JOIN方法详解
一.使用方式. join是Thread类的一个方法,启动线程后直接调用,例如: Thread t = new AThread(); t.start(); t.join(); 二.为什么要用join() ...
- 多线程--Thread.join方法
在Thread类的Api中,Join的作用是让当前线程等待目标线程结束之后才继续执行. thread.Join把指定的线程加入到当前线程,可以将两个交替执行的线程合并为顺序执行的线程. 比如在线程B ...
- Java java.lang.Thread#join()方法分析
结论:A 线程调用 B 线程对象的 join 方法,则 A 线程会被阻塞,直到 B 线程 挂掉 (Java Doc 原话: Watis for this thread to die). 一.分析 查看 ...
- thread.join() 方法存在的必要性是什么?
好久远的问题,为什么关注这个问题的人这么少? 或许是用到这个功能的情形比较少吧. 1.等待处理结果 为什么要用join()方法在很多情况下,主线程生成并起动了子线程,如果子线程里要进行大量的耗时的运算 ...
- Thread join方法的用途
主线程中会创建多个子线程做一些事情,主线程要用到这些子线程处理的数据,因此它需要等待所有的子线程处理完之后才继续运行.这就要用到join方法了.
- 浅析Thread的join() 方法
Thread中的 join() 方法在实际开发过程中可能用的不是很多,但是在面试中作为考察基本功知识的扎实与否,经常会被用到.因此,对于 Thread 的 join() 方法进行了一定的研究. 常见的 ...
- Thread的join方法
一个线程在执行的过程中,可能调用另一个线程,前者可以称为调用线程,后者成为被调用线程. Thread.Join方法的使用场景:调用线程挂起,等待被调用线程执行完毕后,继续执行. 如下案列: 当NewT ...
随机推荐
- c# HTML中提取图片地址
public class HtmlHelper { /// <summary> /// HTML中提取图片地址 /// </summa ...
- C# 编写WCF简单的服务端与客户端
http://www.wxzzz.com/1860.html Windows Communication Foundation(WCF)是由微软开发的一系列支持数据通信的应用程序框架,可以翻译为Win ...
- 文件上传MultipartBody使用方法
最近有使用一个文件上传的功能,需要在请求中添加文件,一起传给服务器 Okhttp提供了这个文件添加然后上传的功能 下面给出核心的代码,然后分析一下 //多个文件上传,Filelist private ...
- 父子元素select悬浮代码,兼容火狐
//公共切换方法 function SwitchCommon() { //悬浮显示 $(document.body).on("mouseenter", "[hex-eid ...
- JavaScript动态加载资源
//动态加载样式 function dynamicLoadingCss(path){ if(!path || path.length === 0){ return false; } var head ...
- HDOJ-1806 ( Frequent values ) 线段树区间合并
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1806 线段树维护区间出现频率最高的出现次数.为了维护上者,需要维护线段前后缀的出现次数,当和其他线段在端点处的字 ...
- vux,vue 苹果手机使用position:fixed有问题,如何解决
苹果手机真是各种坑,导致我都想摔手机呀,但没办法,用苹果的人太多,程序员还是继续在坑的路上行走! 上一篇文章介绍了一些组件,就是使用vux可以解决,苹果手机使用position:fixed的问题 给需 ...
- php字符串转成数组
/* 4.$m = “woxihuanphp”,编程实现:将字符串分割为单个字符存放到一个数组中,并打印数组? */ $m='woxihuanphp'; echo $res=trim(chunk_sp ...
- 区间逼近 牛客寒假1 小a的排列
做法:模拟 萌区间也就是这个区间里的数是一段连续的数 做法的话是先找出题目x,y的位置,记为l,r,然后找出l,r内的最大最小值,又因为萌区间要求数是连续的,就从这段连续数最小的开始到最大的,确定缩放 ...
- MySQL使用的常见问题
(一)是否启动了服务器 如果没有启动报错:ERROR 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on ‘localhost' (10061) 解决方法:启 ...
