Using Internal EEPROM of PIC Microcontroller
There are commonly three types of memories in a PIC Microcontroller, Flash Program Memory, Data Memory (RAM) and EEPROM Data Memory. We write Programs in the Flash Program Memory of a microcontroller. Flash memory makes it possible to program a microcontroller many times before installing to device and even after the installation we can change the program. RAM Data Memory is used for storing data temporarily during program execution and it is volatile. That is, this memory is cleared when the power is gone or after CPU reset. RAM Data Memory locations are also called General Purpose Registers (GPR). These two memories have faster response time. The third memory is EEPROM memory which is an abbreviation for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. EEPROM memory can be read and write electrically, can be accessed through program. It is a non volatile memory but has slower response time. EEPROM memory can be used to store data such as sensor logs, device parameters which should not be loss during power loss or CPU reset. Here I using PIC 16F877A for explanation.

EEPROM Special Function Registers
The data in the EEPROM and Flash Program Memory can be read/write during normal operations (over full VDD range). These memories are not mapped in the register file space, instead of it can be accessed through the following six Special Function Registers (SFR) for read and write operations.
- EECON1
- EECON2
- EEDATA
- EEDATH
- EEADR
- EEADRH
EEDATA register hold 8-bit data for read/write and EEADR holds the address of EEPROM memory location to be accessed. PIC Microcontrollers usually have 128/256 bytes of data EEPROM memory with address ranging from 00h to FFh. On devices having 128 bytes, memory locations from 80h to FFh are unimplemented and will be wraparound to beginning of the data EEPROM memory. On-Chip charge pump (used while writing data to EEPROM) is turned off when writing these unimplemented locations. EEDATH and EEADRH registers are used when interfacing program memory block with Program Flash Memory. Here we deals only with EEPROM data memory.
EEPROM data memory allows only single byte read and write. When a data byte is written in to EEPROM, automatically erases the particular location first and then writes the new data (erase before write). The write time is controlled by and on-chip timer and write/erase voltages are generated automatically by an on-chip charge pump. When the device is code protected, program or data memory will not be accessible to programmer but CPU may read or write data EEPROM memory.
EECON1 is the control register used for memory access.
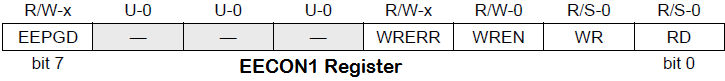
EEPGD control bit is used to select Program Memory or Data Memory access. If it is set Program Memory is selected and vice versa. Control bits RD, WR are used to initiate read, write, erase operations. These bit cannot be cleared in program, only able to set. These bits are cleared in hardware on the completion of read or write operations.
The WREN control bit is the Write Enable bit, when set it enables write or erase operation. On power-up, the WREN bit will be automatically cleared. The WRERR bit is the Write Error Flag bit, it sets when a write (or erase) operation is interrupted by a MCLR or a WDT Time-out Reset during normal operation. In these situations, we can check the WRERR bit and rewrite the location as the data and address will be unchanged in the EEDATA and EEADR registers.
On the completion of write operation Interrupt flag bit, EEIF in the PIR2 register is set. It must be cleared in program.
EECON2 register is not a physical register and it is used exclusively in the EEPROM write sequence. Reading EECON2 will read all zeros.
Reading from Data EEPROM Memory
- Write the address of the memory location to be read to EEADR register.
- To select EEPROM data memory, clear the EEPGD control bit.
- Set the RD bit to initiate the read cycle.
- Then we can read data from EEDATA register.
Writing to Data EEPROM Memory
- Write the address of the memory location to write to EEADR register.
- Write the 8-bit data to be written in the EEDATA register.
- To select EEPROM data memory, clear the EEPGD control bit.
- Set the WREN control bit to enable write operations.
- Disable Interrupts if enabled in your program. (You may store interrupt register (INTCON) to enable interrupts)
- Then the special five instruction sequence is executed.
- Enable Interrupts if using.
- Disable the program operations by clearing WREN control bit.
- WR control bit is cleared and EEIF interrupt flag bit is set after completion of the write operation. EEIF bit must be cleared in the program.
MikroC Programming
Functions Developed by Us
MikroC Function to Read Data from Internal EEPROM :
unsigned char readEEPROM(unsigned char address)
{
EEADR = address; //Address to be read
EECON1.EEPGD = 0;//Selecting EEPROM Data Memory
EECON1.RD = 1; //Initialise read cycle
return EEDATA; //Returning data
}
MikroC Function to Write Data to Internal EEPROM :
void writeEEPROM(unsigned char address, unsigned char datas)
{
unsigned char INTCON_SAVE;//To save INTCON register value
EEADR = address; //Address to write
EEDATA = datas; //Data to write
EECON1.EEPGD = 0; //Selecting EEPROM Data Memory
EECON1.WREN = 1; //Enable writing of EEPROM
INTCON_SAVE=INTCON;//Backup INCON interupt register
INTCON=0; //Diables the interrupt
EECON2=0x55; //Required sequence for write to internal EEPROM
EECON2=0xAA; //Required sequence for write to internal EEPROM
EECON1.WR = 1; //Initialise write cycle
INTCON = INTCON_SAVE;//Enables Interrupt
EECON1.WREN = 0; //To disable write
while(PIR2.EEIF == 0)//Checking for complition of write operation
{
asm nop; //do nothing
}
PIR2.EEIF = 0; //Clearing EEIF bit
}
To read or write data to EEPROM, you may use built-in MikroC Libraries or user defined functions as following.
Using MikroC EEPROM Libraries
MikroC PRO for PIC Microcontrollers provides library to work with Internal EEPROM. We can easily read/write form EEPROM using the following library functions.
- Eeprom_Read
- Eeprom_Write
Eeprom_Read
Prototype: unsigned short EEPROM_Read(unsigned int address);
Eeprom_Read function reads data from a specified address. Note that parameter address is of integer type, which implies that this functions supports microcontrollers with more than 256 bytes of EEPROM. There must me atleast 20ms delay between successive using of these routines.
Eeprom_Write
Prototype: void EEPROM_Write(unsigned int address, unsigned short data);
EEPROM_Write function write data to the specified address. As I said above, since the address parameter is of integer type, it supports microcontrollers with more than 256 bytes of EEPROM. There must me atleast 20ms delay between successive using of these routines. Beware that all Interrupts will be disabled during the execution of this function.
Note: Address ranges from 00h to FFh for devices having 256 bytes while for 128 bytes devices it is 00h to 7Fh.
Mikro Code
void main()
{
unsigned int a, i;
TRISC = 0;
do
{
for(i=0,a=1;i<8;i++)
{
EEPROM_Write(i, a);
a = a<<1;
} for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
PORTC = EEPROM_Read(i);
Delay_ms(1000);
}
}while(1);
}
Circuit Diagram

Note: VDD and VSS of the pic microcontroller is not shown in the circuit diagram. VDD should be connected to +5V and VSS to GND.
In this example we writes 00000001 to the first memory location, 00000010 to second, 000000100 to third etc sequentially up to 10000000. Then it is read sequentially and output through PORTC.
Download Here
You can download the hex file, MikroC source code, Proteus files etc here.
文章来源: https://electrosome.com/internal-eeprom-pic-microcontroller/
Using Internal EEPROM of PIC Microcontroller的更多相关文章
- RFID 仿真/模拟/监控/拦截/检测/嗅探器
Sound card based RFID sniffer/emulator (Too tired after recon.cx to do draw the schematics better th ...
- PID控制器(比例-积分-微分控制器)- I
形象解释PID算法 小明接到这样一个任务: 有一个水缸点漏水(而且漏水的速度还不一定固定不变),要求水面高度维持在某个位置,一旦发现水面高度低于要求位置,就要往水缸里加水. 小明接到任务后就一直守在水 ...
- LPCScrypt, DFUSec : USB FLASH download, programming, and security tool, LPC-Link 2 Configuration tool, Firmware Programming
What does this tool do? The LPC18xx/43xx DFUSec utility is a Windows PC tool that provides support f ...
- introduction to my business card
http://www.t4f.org/projects/business-card/ After 4 years working in an international IT consulting c ...
- Android 笔记
一.MTK Android version在文件下build/core/version_defaults.xml下定义. 二.Android 重新编译frameworks/base/core/res资 ...
- Django整合Keras报错:ValueError: Tensor Tensor("Placeholder:0", shape=(3, 3, 1, 32), dtype=float32) is not an element of this graph.解决方法
本人在写Django RESful API时,碰到一个难题,老出现,整合Keras,报如下错误:很纠结,探索找资料近一个星期,皇天不负有心人,解决了 Internal Server Error: /p ...
- 编译android framework的例子【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/brucexu1978/article/details/7610358 在开发过程中,尤其是Framework相关开发时,有时候需要重新编译资源文 ...
- 在屏幕上搜索图片并返回图片所在位置的坐标的AutoHotkey脚本源代码(类似大漠插件)
;~ 在屏幕上搜索图片并返回图片所在位置的坐标的AutoHotkey脚本源代码(类似大漠插件) ; https://www.autohotkey.com/boards/viewtopic.php?t ...
- PIC XC8 EEPROM操作
要做一个报警功能的东东,要求可以通过遥控来改变遥控内容.由于对系统的稳定性要求很高,所以用了看门狗. 可是看门狗复位会引起所有寄存器重置,恢复到默认状态.遥控要改变的内容也被复位了,所以只能借助EEP ...
随机推荐
- DrawSVG - SVG 路径动画 jQuery 插件
jQuery DrawSVG 使用了 jQuery 内置的动画引擎实现 SVG 路径动画,用到了 stroke-dasharray 和 stroke-dashoffset 属性.DrawSVG 是完全 ...
- Promise和$.Deferred总结
语法对比: Promise .then(f).catch(f)是.then(f,f)的语法糖 .all([A,B,C])等最慢的 .race([A,B,C])最快的 $.Deferred .d ...
- IIS6.0添加上.net4.0后,以前的.net系统出现“服务器应用程序不可用”的错误提示解决办法
把VS2010开发的网站.net4.0部署到Windows Server 2003的服务器上去, Windows Server 2003操作系统自带的为IIS 6.0,IIS 6.0一般只支持.NET ...
- php每天一题:怎么在不使用第三个变量的情况下交换两个变量的值
$a = 'php'; $b = 'my'; list($a,$b) = array($b,$a); echo $a,$b; 很简单,大家试一下是不是交换了!
- iOS 设置状态栏的背景颜色
设置状态栏的背景颜色 - (void)setStatusBarBackgroundColor:(UIColor *)color { UIView *statusBar = [[[UIApplicati ...
- Android 监听ScrollView的滑动
我们需要监听ScroView的滑动情况,比如滑动了多少距离,是否滑到布局的顶部或者底部.可惜的是SDK并没有相应的方法,不过倒是提供了一个 protected void onScrollChanged ...
- AndroidStudio配置gradle,让App自动签名
最近开发关于微信一系列功能,发现分享.支付必须要打包签名才能测试,太耽误事了,耗时耗力...在网上扒拉扒拉资料,发现有很多前辈都处理过类似问题,非常感谢大家的分享,参考链接:http://blog.c ...
- js(javascript)与OC(Objective-C)交互
实质上oc与js的通信交互就是发送消息,也即函数调用,iOS7以后官方公布JavaScriptCore framework中很方便我们对他们之间的相互调用.在以前我们只能通过UIWebView的UIW ...
- SQL SERVER如何通过SQL语句获服务器硬件和系统信息
在SQL SERVER中如何通过SQL语句获取服务器硬件和系统信息呢?下面介绍一下如何通过SQL语句获取处理器(CPU).内存(Memory).磁盘(Disk)以及操作系统相关信息.如有不足和遗漏,敬 ...
- (转载)SQL Reporting Services (Expression Examples)
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms157328(v=SQL.100).aspx Expressions are used frequently in ...
