TCP connection status
A TCP connection progresses through a series of states during its lifetime. The following diagram illustrates the possible states for a TCP connection and how the states transition based on various events from either the network or from the local TCP sockets application.
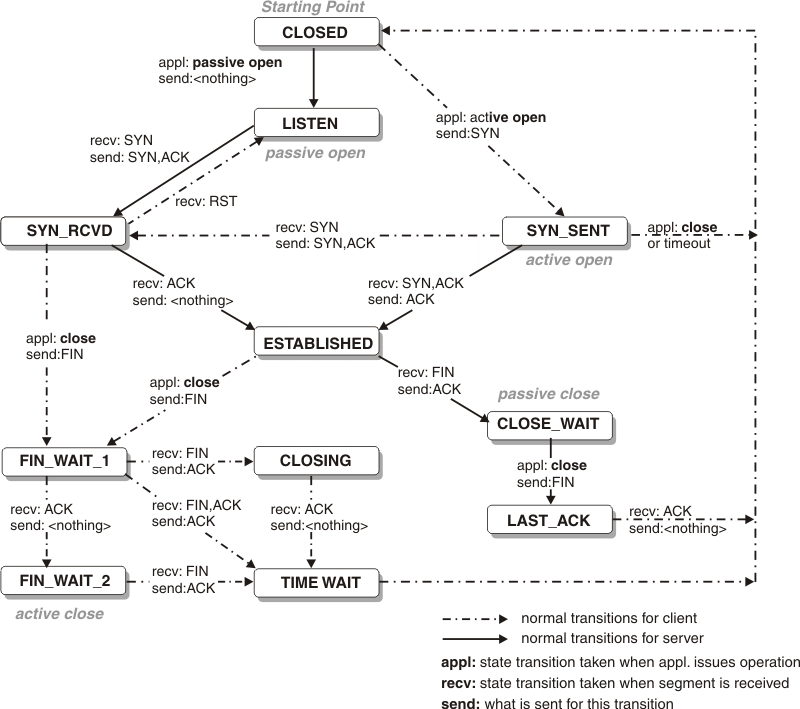
| TCP connection state | Abbreviation in MVS™ console | Abbreviation in TSO or UNIX shell | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LISTEN | Listen | Listen | Waiting for a connection request from a remote TCP application. This is the state in which you can find the listening socket of a local TCP server. |
| SYN-SENT | SynSent | SynSent | Waiting for an acknowledgment from the remote endpoint after having sent a connection request. Results after step 1 of the three-way TCP handshake. |
| SYN-RECEIVED | SynRcvd | SynRcvd | This endpoint has received a connection request and sent an acknowledgment. This endpoint is waiting for final acknowledgment that the other endpoint did receive this endpoint's acknowledgment of the original connection request. Results after step 2 of the three-way TCP handshake. |
| ESTABLISHED | Estblsh | Establsh | Represents a fully established connection; this is the normal state for the data transfer phase of the connection. |
| FIN-WAIT-1 | FinWt1 | FinWait1 | Waiting for an acknowledgment of the connection termination request or for a simultaneous connection termination request from the remote TCP. This state is normally of short duration. |
| FIN-WAIT-2 | FinWt2 | FinWait2 | Waiting for a connection termination request from the remote TCP after this endpoint has sent its connection termination request. This state is normally of short duration, but if the remote socket endpoint does not close its socket shortly after it has received information that this socket endpoint closed the connection, then it might last for some time. Excessive FIN-WAIT-2 states can indicate an error in the coding of the remote application. |
| CLOSE-WAIT | ClosWt | ClosWait | This endpoint has received a close request from the remote endpoint and this TCP is now waiting for a connection termination request from the local application. |
| CLOSING | Closing | Closing | Waiting for a connection termination request acknowledgment from the remote TCP. This state is entered when this endpoint receives a close request from the local application, sends a termination request to the remote endpoint, and receives a termination request before it receives the acknowledgment from the remote endpoint. |
| LAST-ACK | LastAck | LastAck | Waiting for an acknowledgment of the connection termination request previously sent to the remote TCP. This state is entered when this endpoint received a termination request before it sent its termination request. |
| TIME-WAIT | TimeWt | TimeWait | Waiting for enough time to pass to be sure the remote TCP received the acknowledgment of its connection termination request. |
| CLOSED | Closed | Closed | Represents no connection state at all. |
- Clients or Users
- For various reasons, TCP/IP refers to MVS jobs or address spaces that use TCP/IP services as clients or users of TCP/IP services. The term client in this context has nothing to do with the traditional client/server roles of a network application. Both local server programs and local client programs on z/OS® are clients or users of TCP/IP services. For most purposes you can substitute Client name, User ID, and User in the Netstat reports with MVS jobname.
- UDP socket status
- UDP, unlike TCP, does not operate with strict states. The state that is shown in the various Netstat reports is always UDP for UDP sockets.
- Client ID or Connection number
- A generated number that uniquely identifies a socket endpoint that might represent a connection on this TCP/IP host. This number can be used to drop a socket or connection with the Netstat DROP/-D parameter.
- Client name or User ID
- The client name from a TCP/IP perspective is in general the job name of the address space that owns the socket. For batch jobs this is the job name. For TSO users, this is the TSO user ID. For UNIX processes this is the job name as determined during process creation, either by appending a digit to the job name (INETD creates INETD1) of the parent process or by setting the job name to the value of the _BPX_JOBNAME environment variable. For started tasks, the job name is generally the procedure name. If a procedure is started with the JOBNAME keyword (S procname,JOBNAME=myjob), then the job name becomes the value that was specified on that JOBNAME keyword. If a procedure is started with a start modifier (S procname.modif), then the modifier is what is shown as the TCP/IP client name.
- Local IP address
- A socket might have no address information at all (right after it has been created by a program using the socket() call); it might have just a local address (a local IP address and/or a local port number) that was set using a bind() socket call; or it might have both a local address and a remote address, in which case it represents a connected socket (a socket that is in connection with a remote socket).
The local IP address of a socket is either zero (not bound to any local IP address) or it is an IP address that is in the HOME list of this TCP/IP host.
The listening socket of a server program has only the local address filled in. If the local IP address of the server's listening socket is zero, then remote clients are allowed to send connection requests to any IP address that is in this TCP/IP host's HOME list. If the local IP address of the server's listening socket is nonzero, then remote clients can connect to this server only by sending connection requests to that specific IP address. A connected socket has both the local and the remote address filled in.
- Foreign/remote IP address
- The remote IP address is present for connected sockets and represents the IP address that is associated with the remote socket endpoint to which this socket is connected. A connected socket might be one of the following sockets:
- A server socket where the remote client that is represented by this remote IP address connected to a server on this TCP/IP host.
- A socket belonging to a client program on this TCP/IP host that is connected to a server on the remote TCP/IP host that is represented by this remote IP address.
- Local port
- The local port is part of the local address of a socket. For a server's listening socket, the port represents the specific server. If remote clients need to use the services of this server, they send a connection request to this TCP/IP host to this server's specific port number.
Connected sockets might represent one of the following case:
- A connection with a local server from a remote client, for example, the local port number is the same port number that appears on the server's listening socket.
- A local client connected to a remote server, for example, the port number could be any port number the TCP/IP host found available when the connection was being established (also known as an ephemeral or short-lived port number). This is typically a port number higher than 1024.
- Foreign/remote port
- The remote port is part of the remote address of a socket and is present only for connected sockets. It represents the port number of the remote socket that is connected to this socket. If the connected socket belongs to a client program on this TCP/IP host, then the remote port number identifies the server on the remote TCP/IP host to which this client program is connected.
- Local socket
- The IP address and port number to which the application on the local stack was bound.
- Foreign socket
- The IP address and port number to which the application on the remote host was bound. For UDP sockets, the foreign socket field that is shown in the various Netstat reports is displayed as *..* if the socket is not connected. For connected UDP sockets, the foreign socket field shows the remote IP address and port specified on the connect request. When a UDP socket is connected, it accepts packets only from the specified remote IP address and port.
- Last touched time
- For TCP, the last time one of the following events occurred to the connection:
- The server side receives a connection request.
- The server side accepts the connection request.
- Either the server or client side of a connection receives a packet.
- Either the server or client side of a connection sends a packet.
For UDP, the last time one of the following events occurred to the connection:
- Either the server or client side of a connection receives a packet.
- Either the server or client side of a connection sends a packet.
- Redirecting Netstat output:
- Netstat screen output can be redirected for all Netstat reports. The following example uses the BYTEINFO report:
- From TSO environment:
-
- You can redirect TSO NETSTAT screen output to a disk file by appending a REPORT option.
- NETSTAT BYTEINFO REPORT
- The data set MVSUSER.NETSTAT.BYTEINFO (where MVSUSER is the user ID) is created containing the screen output from a BYTEINFO command. See Netstat command output for more description of the REPORT option.
- You can also redirect TSO NETSTAT screen output to the TSO data stack by appending a STACK option.
- NETSTAT BYTEINFO STACK
- Causes the report, stripped of title lines, to be placed in the TSO data stack containing the screen output from a BYTEINFO command. See Netstat command output for more description of the STACK option.
- You can redirect TSO NETSTAT screen output to a disk file by appending a REPORT option.
- From z/OS UNIX shell environment:
-
You can redirect the netstat screen output to a file by using the redirect function (>) in the following format:
netstat -b > byteinfoThe file byteinfo is created in your current directory containing the screen output shown previously.
- Time stamp
- The time stamp displayed in the header for each Netstat report is in local time. The time field displayed in reports ALL/-A, BYTEinfo/-b, CLients/-e, HOME/-h, RESCache/-q, ROUTe/-r, SLAP/-j, UP/-u, and VIPADyn/-v is Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). UTC time does not take leap seconds into account.
TCP connection status的更多相关文章
- RabbitMQ问题解决:TCP connection succeeded but Erlang distribution failed
说明 本来是要先把Hystrix 仪表盘更完的,但是出现了Turbine.Dashboard.RabbitMQ整合实现监控. 所以先在学RabbitMq的基本操作,在安装过程中出现了 E:\Rabbi ...
- linux上TCP connection timeout的原因查找
linux上TCP connection timeout的原因查找 好久没有写文章了, 今天解决了一个网络连接超时的问题, 记录以备查看. 最近在线上nginx经常出现输出connection tim ...
- TCP Connection Establishment and Termination
Three-Way Handshake The following scenario occurs when a TCP connection is established: The server m ...
- RT:How HTTP use TCP connection
In HTTP/0.9 (not used anymore), each request uses a separate TCP connection, and the end of a respon ...
- RobotFramework自动化测试框架-移动手机自动化测试Get Network Connection Status和Set Network Connection Status关键字的使用
Get Network Connection Status关键字用来获取手机的网络连接状态.在获取到连接状态后,会返回不同的数字. Set Network Connection Status关键字用来 ...
- tcp connection
三次握手与四次挥手的原因 https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/7435?spm=5176.8091938.0.0.N4v33a linux里的backlog详解 tcp co ...
- Exception in thread "RMI TCP Connection(idle)" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space
在Eclipse 调试 springside showcase项目中,tomcat报异常 Exception in thread "RMI TCP Connection(idle)" ...
- the age of the TCP connection TCP Slow Start
w防止网络过载和拥塞 HTTP The Definitive Guide The performance of TCP data transfer also depends on the age of ...
- A TCP connection is distinguished by four values
4个值唯一地定义一条TCP连接. HTTP The Definitive Guide A computer might have several TCP connections open at any ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ2310 : ParkII
单路径最大和问题,设f[i][j][S]表示到达(i,j),轮廓线状态为S的最优解. S用4进制m+1位数表示,0表示无插头,1表示左括号,2表示右括号,3表示独立插头. 在DP之前先进行一次预处理, ...
- POJ 3281 (最大流+匹配+拆点)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3281 题目大意:有一些牛,一堆食物,一堆饮料.一头牛要吃一份食物喝一份饮料才算满足,而且牛对某些食物和饮料才有好感,问最多有多少头牛是 ...
- 我的第一个 Mono for Android 应用
创建 Mono for Android 应用 打开 MonoDevelop , 选择新建解决方案, 左边的分类选择 "Mono for Android" , 右边选择 " ...
- TYVJ P1077 有理逼近 Label:坑,tle的好帮手 不懂
描述 对于一个素数P,我们可以用一系列有理分数(分子.分母都是不大于N的自然数)来逼近sqrt(p),例如P=2,N=5的时候:1/1<5/4<4/3<sqrt(2)<3/2& ...
- Dijkstra堆优化与SPFA模板
Dijkstra+优先队列 #include<cstdio> #include<cctype> #include<queue> #include<cstrin ...
- jQuery 写的插件图片上下切换幻灯效果
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- winform学习之----进程和线程
Process[] pros = Process.GetProcesses();//获取多个进程 foreach(var item in pros) { ...
- Mock模拟后台数据接口--再也不用等后端的API啦
ok,在开发中经常需要从后台获取数据,那么有时候后台的数据接口并没有写好,所以这时候,就需要自己模拟数据接口,来实现前端逻辑, 今天数的就是阿里巴巴的一款mock产品,很好用的哦!!!! ok!这是我 ...
- [译]- 6-1 排列窗体上的控件(Laying Out Widgets on a Form)
排列窗体上的控件(Laying Out Widgets on a Form) 中英文对照:form(窗体),layout(布局或者排列,意思是进行窗体上控件的排列的过程,如大小位置等) absolu ...
- dtd语法之定义属性
1.语法: <!ATTLIST 元素名称 属性名称 属性类型 默认值> 属性类型: l CDATA :文本数据 l (en1|en2|……) :属性值任选其一 l ID :属性值必须是唯 ...
