shell 基本结构
就像其他的编程语言一样,shell也有三种基本的结构:顺序结构、分支结构、循环结构。顺序结构就是按照命令的出现顺序依次执行,比较简单。如下分别介绍分支结构和循环结构。
分支结构
格式1:
if command
then
commands
fi
# 或者
if command: then
commands
fi
说明:在其他编程语言中,if后面的command是一个等式,用来判断是true还是false;但是在bash shell中,该command是一个命令,if语句根据command执行结果的退出状态码是否为0来判断then部分是否需要执行[返回0表明命令执行成功,则执行then部分]。
如下使用grep命令在/etc/passwd文件中查找某个特定用户名是否在当前系统上使用,如果存在该用户,则显示该用户主目录的bash文件:
#! /bin/bash
# function: This script is to test structured commands
# author: benxintuzi
# date: -- user=benxintuzi if grep $user /etc/passwd
then
echo "The bash files for user $user are:"
ls -a /home/$user/.b*
fi
格式2:
if command
then
commands
else
commands
fi
user=123456 if grep $user /etc/passwd
then
echo "The bash files for user $user are:"
ls -a /home/$user/.b*
else
echo "The user $user does not exist on this system"
fi
格式3:
if command1
then
commands
elif command2
then
commands
elif ...
then
...
fi
注:if-then语句不能测试与命令退出码无关的条件,这个任务可以通过test命令来完成。
test命令的格式非常简单:test condition,用在if-then语句块中时,格式如下:
if test condition
then
commands
fi # 或者 # bash shell中可以使用方括号:
if [ condition ]
then
commands
fi
说明:方括号定义了test命令,但是括号内两侧必须有空格
test命令可以用于3类条件:数值比较、字符串比较、文件比较。
1 数值比较
|
操 作 |
描 述 |
|
n1 –eq n2 |
判断n1是否等于n2 |
|
n1 –ge n2 |
判断n1是否大于或等于n2 |
|
n1 –gt n2 |
判断n1是否大于n2 |
|
n1 –le n2 |
判断n1是否小于或等于n2 |
|
n1 –lt n2 |
判断n1是否小于n2 |
|
n1 –ne n2 |
判断n1是否不等于n2 |
val= if [ $val -gt ]
then
echo "The test value $val is greater than 5"
else
echo "sorry, you are so little"
fi
2 字符串比较
|
比 较 |
描 述 |
|
str1 = str2 |
是否相同 |
|
str1 != str2 |
是否不同 |
|
str1 < str2 |
是否小于 |
|
str1 > str2 |
是否大于 |
|
-n str1 |
str1的长度是否非0 |
|
-z str1 |
str1的长度是否为0 |
2.1 【=、!=】
user=benxintuzi if [ $USER = $user ]
then
echo "Welcome $user"
else
echo "The user $user is not exist"
fi
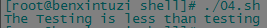
2.2 【>、<】这两个比较操作使用时必须转义,否则shell将其解释为重定向符号。
val1=Testing
val2=testing if [ $val1 \> $val2 ]
then
echo "The $val1 is greater than $val2"
else
echo "The $val1 is less than $val2"
fi
2.3 【-n、-z】
val1=testing
val2='' if [ -n val1 ]
then
echo "The string '$val1' is not empty"
else
echo "The string '$val1' is empty"
fi if [ -z val2 ]
then
echo "The string '$val2' is not empty"
else
echo "The string '$val2' is empty"
fi
3 文件比较
|
-d file |
检查file目录是否存在 |
|
-e file |
检查file是否存在 |
|
-f file |
检查file文件是否存在 |
|
-r file |
检查file是否存在并可读 |
|
-s file |
检查file是否存在并非空 |
|
-w file |
检查file是否存在并可写 |
|
-x file |
检查file是否存在并可执行 |
|
-O file |
检查file是否存在并属于当前用户所有 |
|
-G file |
检查file是否存在并且默认组与当前用户相同 |
|
file1 –nt file2 |
检查file1是否比file2新 |
|
file1 –ot file2 |
检查file1是否比file2旧 |
复合条件的编写
if-then语句可以使用布尔逻辑来组合测试,格式如下:
[ condition1 ] && [ condition2 ]
[ condition1 ] || [ condition2 ]
if-then高级特性
(( expression )) 用于对expression进行简单比较或计算,其中的比较操作符>等不需要转义
[[ expression ]] 主要用于字符串模式匹配
val1= if (( $val1 ** > ))
then
(( val2=$val1 ** ))
echo "The square of $val1 is $val2"
fi
if [[ $USER == benxin* ]]
then
echo "Hello, $USER"
else
echo "Sorry, I do not know you"
fi
当分支情况比较多时,可能需要编写多条if-then-elif-then-...语句,此时,可以使用case语句,格式如下:
case variable in
pattern1 | pattern2)
command1;;
pattern3)
commands;;
*)
commands;;
esac
说明:在一行中使用|来分割多个模式。
val=benxin case $val in
benxin | tuzi)
echo "You are alone";;
benxintuzi)
echo "Congratulations";;
*)
echo "go out now!";;
esac
循环结构
for命令
for var in list
do
commands
done # 或者 for var in list; do
commands
done
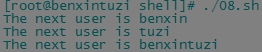
for var in benxin tuzi benxintuzi
do
echo "The next user is $var"
done
说明:for命令使用空格来划分列表中的不同值,如果单个数据值中也有空格,此时需要用双引号将这个值括起来,如下:
for var in benxin tuzi "benxin tuzi"
do
echo "The next user is $var"
done
通常的情况下,我们将一系列的值都存储在一个变量中,如:
list="benxin tuzi benxintuzi"
for var in $list
do
echo "The next user is $var"
done
bash shell中使用IFS(Internal Field Separator)环境变量作为字段分隔符,默认情况下IFS使用如下字符:空格符,制表符,换行符。
如果要将冒号:设定为分隔符,可以如下设置:
IFS=:
IFS=: list="benxin:tuzi:benxintuzi"
for var in $list
do
echo "The next user is $var"
done
如果需要指定多个IFS字符,只要将它们在赋值行中串起来就行了:
(IFS=$'\n:;')表示可以使用换行符、冒号、分号作为字段之间的分隔符。
IFS=$'\n:;' list="benxin
tuzi:benxintuzi
tuzi;"
for var in $list
do
echo "The next user is $var"
done
注:我们修改默认IFS一般只是为了处理一段特殊的脚本,因此处理完成后必须恢复默认值,如下:
IFS.OLD=$IFS
IFS=$’\n’
# user processing...
IFS=$IFS.OLD
while命令
while test command
do
commands
done
val= while [ $val -gt ]
do
echo $val
val=$[ $val - ]
done
until命令
until test command
do
commands
done
说明:until命令的执行刚好与while相反,其测试条件不成立时才执行。
循环控制命令
break命令
终止并退出循环;
break n
默认情况下,n为1,表示跳出当前循环;如果n为2,表示跳出上一级循环
for a in
do
echo "Outer loop: $a"
for (( b = ; b < ; b++ ))
do
if [ $b -gt ]
then
break
fi
echo "Inner loop: $b"
done
done

continue命令
跳过本次循环中的其余命令,继续执行下一轮循环
同理也有continue n
循环重定向
for a in
do
echo "Outer loop: $a"
for (( b = ; b < ; b++ ))
do
if [ $b -gt ]
then
break
fi
echo "Inner loop: $b"
done
done > output.txt
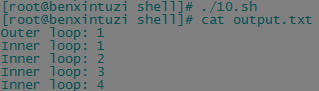
即直接在done后加上重定向符号即可,当然,也可以直接将循环输出重定向到一个命令的输入中:
for state in apple orange pear banana pineapple
do
echo "$state is my favourite fruit"
done | sort
shell 基本结构的更多相关文章
- Shell脚本、Shell脚本结构、date命令的用法、变量
1.Shell脚本: shell是一种脚本语言 目的:可以实现自动化运维,能大大增加运维的效率.2.Shell脚本结构: #!/bin/bash 以#!/bin/bash开头,即以/bin/ba ...
- centos shell脚本编程1 正则 shell脚本结构 read命令 date命令的用法 shell中的逻辑判断 if 判断文件、目录属性 shell数组简单用法 $( ) 和${ } 和$(( )) 与 sh -n sh -x sh -v 第三十五节课
centos shell脚本编程1 正则 shell脚本结构 read命令 date命令的用法 shell中的逻辑判断 if 判断文件.目录属性 shell数组简单用法 $( ) 和$ ...
- shell脚本介绍、shell脚本结构和执行、date命令用法、shell脚本中的变量
7月11日任务 20.1 shell脚本介绍20.2 shell脚本结构和执行20.3 date命令用法20.4 shell脚本中的变量 20.1 shell脚本介绍 1.shell脚本语言是linu ...
- Linux centosVMware shell脚本介绍、shell脚本结构和执行、date命令用法、shell脚本中的变量
一. shell脚本介绍 shell是一种脚本语言 aming_linux blog.lishiming.net 可以使用逻辑判断.循环等语法 可以自定义函数 shell是系统命令的集合 shell脚 ...
- For,while,case,shell循环结构
For,while,case,shell循环结构 案例1:使用for循环结构 案 ...
- Linux编程 24 shell编程(结构化 if [ condition ] 数值比较,字符串比较)
一.概述 接着上篇讲的结构化命令,最后讲到了test命令的另一种写法 if [ condition ],它的语法格式如下: --格式如下: if [ condition ] then commands ...
- Linux编程 23 shell编程(结构化条件判断 命令if -then , if-then ... elif-then ...else,if test)
一.概述 在上一篇里讲到了shell脚本,shell按照命令在脚本中出现的顺序依次进行处理,对于顺序操作已经足够了,但许多程序要求对shell脚本中的命令加入一些逻辑流程控制,这样的命令通常叫做 结构 ...
- shell脚本结构
echo $? 代表上一次命令的状态返回值,‘0’则代表为真<执行成功>,‘非零’则代表为假<执行失败>. shell脚本: <判断老男孩的年纪> [root@bo ...
- shell脚本结构化语句
本文中记录一下shell中的两种循环语句:for和while for循环 for循环是linux shell中最常用的结构,for循环有三种结构:1.列表for循环.2.不带列表for循环.3.C风格 ...
随机推荐
- 多XML追加操作
假设要统计当前系统中所有的试卷进行分析,试卷是以XML格式存储的,所有这就需要将所有零散的XML文件整合起来,处理成一个完整的XML文件,进行分析, 下面是简单额处理方法: 当前XML文件格式: &l ...
- leetcode 118
118. Pascal's Triangle Given numRows, generate the first numRows of Pascal's triangle. For example, ...
- .NET中的属性
1.What?什么是属性 属性是对字段的封装.当类中有了一个字段以后,为了控制这个字段对外的一些表现(例如可访问性,是只读?只写?或者对自读赋值做一些必要的验证等等)我们把这个字段私有化( ...
- libharu 源码编译 VS2010
最近项目中接过了一个libharu PDF 开源库的锅,哈哈.于是就自己编译了一套libharu 的MFC下的静态库和动态库. 编译libharu需要用到zlib库和libpng库,libpng库又依 ...
- input文本框实现宽度自适应代码实例,input文本框
本章节介绍一下如何让一个文本框的宽度能够随着文本框中的内容的宽度增长而增长,也就是能够实现宽度自适应效果. 代码实例如下: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> < ...
- POJ C++程序设计 编程题#1 编程作业—STL1
编程题#1 来源: POJ (Coursera声明:在POJ上完成的习题将不会计入Coursera的最后成绩.) 注意: 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 下面的程序输出结 ...
- iOS网络通讯——监测网络状态:Reachability(可达性)
1.iOS平台是按照一直有网络连接的思路来设计的,开发者利用这一特点创造了很多优秀的第三方应用.大多数的iOS应用都需要联网,甚至有些应用严重依赖网络,没有网络就无法正常工作. 2.在你的应用尝试通过 ...
- Application Designer Security
This wiki page covers how to manage and restrict Application Designer security through permission li ...
- 5.21_启程日本二面_1 vs 1
昨天上午刚群面完,晚上7点左右就接到了电话.面试官就两位菇凉,看来她们也是很辛苦.今天下午3点 1 vs 1,在一家咖啡店里,主要是询问下去日本的意愿是否足够强烈.太老实,这里实话实说,也没有表现出非 ...
- SQL Server编程(04)基本语法
一.定义变量 --简单赋值 declare @a int set @a=5 print @a --使用select语句赋值 declare @user1 nvarchar(50) select @ ...