How to install Mysql in the CentOS
This article will walk through you the process of installing and updating latest MySQL 5.7.9 version onRHEL/CentOS 7/6/5 and Fedora 23/22/21 using MySQL Yum repository via YUM utility.
Step 1: Adding the MySQL Yum Repository
1. We will use official MySQL Yum software repository, which will provides RPM packages for installing the latest version of MySQL server, client, MySQL Utilities, MySQL Workbench, Connector/ODBC, and Connector/Python for the RHEL/CentOS 7/6/5 and Fedora 23-21.
Important: These instructions only works on fresh installation of MySQL on the server, if there is already a MySQL installed using a third-party-distributed RPM package, then I recommend you to upgrade or replace the installed MySQL package using the MySQL Yum Repository”.
Before Upgrading or Replacing old MySQL package, don’t forget to take all important databases backup and configuration files.
2. Now download and add the following MySQL Yum repository to your respective Linux distribution system’s repository list to install the latest version of MySQL (i.e. 5.7.9 released on 21 October 2015).
--------------- On RHEL/CentOS 7 ---------------
# wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-el7-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On RHEL/CentOS 6 ---------------
# wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-el6-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On RHEL/CentOS 5 ---------------
# wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-el5-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On Fedora 23 ---------------
# wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-fc23-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On Fedora 22 ---------------
# wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-fc22-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On Fedora 21 ---------------
# wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql57-community-release-fc21-7.noarch.rpm
3. After downloading the package for your Linux platform, now install the downloaded package with the following command.
--------------- On RHEL/CentOS 7 ---------------
# yum localinstall mysql57-community-release-el7-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On RHEL/CentOS 6 ---------------
# yum localinstall mysql57-community-release-el6-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On RHEL/CentOS 5 ---------------
# yum localinstall mysql57-community-release-el5-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On Fedora 23 ---------------
# dnf localinstall mysql57-community-release-fc23-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On Fedora 22 ---------------
# dnf localinstall mysql57-community-release-fc22-7.noarch.rpm
--------------- On Fedora 21 ---------------
# yum localinstall mysql57-community-release-fc21-7.noarch.rpm
The above installation command adds the MySQL Yum repository to system’s repository list and downloads the GnuPG key to verify the integrity of the packages.
4. You can verify that the MySQL Yum repository has been added successfully by using following command.
# yum repolist enabled | grep "mysql.*-community.*"
# dnf repolist enabled | grep "mysql.*-community.*" [On Fedora 22+ versions]
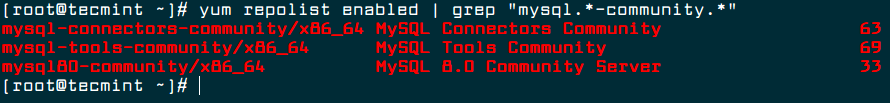
Verify MySQL Yum Repository
Step 2: Installing Latest MySQL Version
5. Install latest version of MySQL (currently 5.7) using the following command.
# yum install mysql-community-server
# dnf install mysql-community-server [On Fedora 22+ versions]
The above command installs all the needed packages for MySQL server mysql-community-server, mysql-community-client, mysql-community-common and mysql-community-libs.
Step 3: Installing MySQL Release Series
6. You can also install different MySQL version using different sub-repositories of MySQL Community Server. The sub-repository for the recent MySQL series (currently MySQL 5.7) is activated by default, and the sub-repositories for all other versions (for example, the MySQL 5.6 or 5.5 series) are deactivated by default.
To install specific version from specific sub-repository, you can use --enable or --disable options usingyum-config-manager or dnf config-manager as shown:
# yum-config-manager --disable mysql57-community
# yum-config-manager --enable mysql56-community
------------------ Fedora 22+ Versions ------------------
# dnf config-manager --disable mysql57-community
# dnf config-manager --enable mysql56-community
Step 4: Starting the MySQL Server
7. After successful installation of MySQL, it’s time to start the MySQL server with the following command:
# service mysqld start
You can verify the status of the MySQL server with the help of following command.
# service mysqld status
This is the sample output of running MySQL under my CentOS 7 box.
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl status mysqld.service
mysqld.service - MySQL Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service; enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2015-10-29 05:15:19 EDT; 4min 5s ago
Process: 5314 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/mysqld --daemonize $MYSQLD_OPTS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 5298 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/mysqld_pre_systemd (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 5317 (mysqld)
CGroup: /system.slice/mysqld.service
└─5317 /usr/sbin/mysqld --daemonize Oct 29 05:15:19 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started MySQL Server.
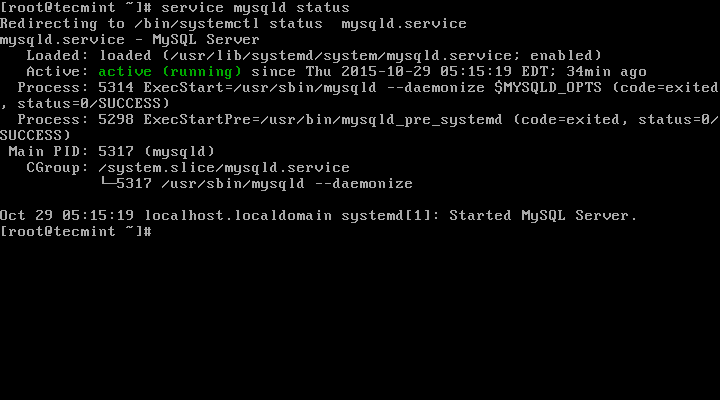
Check Mysql Status
8. Now finally verify the installed MySQL version using following command.
# mysql --version mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.9, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper

Check MySQL Installed Version
Step 5: Securing the MySQL Installation
9. The command mysql_secure_installation allows you to secure your MySQL installation by performing important settings like setting the root password, removing anonymous users, removing root login, and so on.
# mysql_secure_installation
Now follow the onscreen instructions carefully, for reference see the output of the above command below.
Sample Output
Securing the MySQL server deployment. Enter password for user root: Enter New Root Password VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN can be used to test passwords
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD plugin? Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y There are three levels of password validation policy: LOW Length >= 8
MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters
STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 2
Using existing password for root. Estimated strength of the password: 50
Change the password for root ? ((Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y New password: Set New MySQL Password Re-enter new password: Re-enter New MySQL Password Estimated strength of the password: 100
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user,
allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have
a user account created for them. This is intended only for
testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother.
You should remove them before moving into a production
environment. Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success. Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success. By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
and should be removed before moving into a production
environment. Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
- Dropping test database...
Success. - Removing privileges on test database...
Success. Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success. All done!
Step 6: Connecting to MySQL Server
10. Connecting to newly installed MySQL server by providing username and password.
# mysql -u root -p
Sample Output:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 19
Server version: 5.7.9 MySQL Community Server (GPL) Copyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
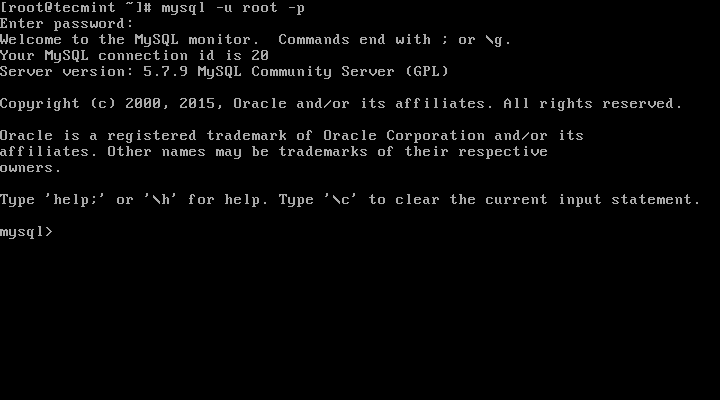
Connect to MySQL Server
Step 7: Updating MySQL with Yum
11. Besides fresh installation, you can also do updates for MySQL products and components with the help of following command.
# yum update mysql-server
# dnf update mysql-server [On Fedora 22+ versions]
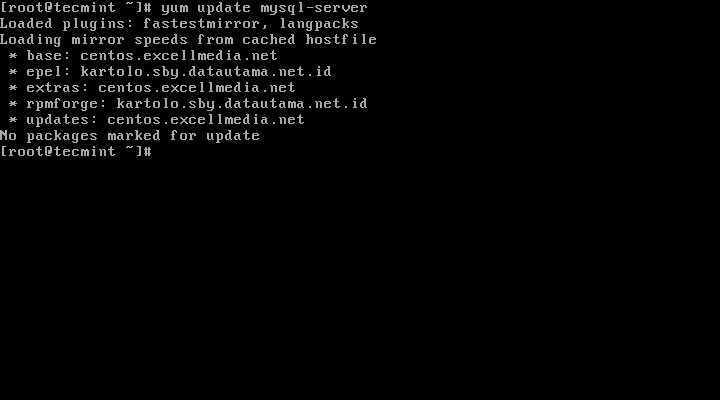
Update MySQL Version
When new updates are available for MySQL, it will auto install them, if not you will get a message saying NO packages marked for updates.
That’s it, you’ve successfully installed MySQL 5.7.9 on your system. If you’re having any trouble installing feel free to use our comment section for solutions.
How to install Mysql in the CentOS的更多相关文章
- Install MySQL 5.7 on Fedora 25/24, CentOS/RHEL 7.3/6.8/5.11
MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that runs as a server providing multi-user ...
- Install MySql on CentOS
Installing & Configuring MySQL Server This Howto will show you how to install MySQL 5.x, start t ...
- How to Install MySQL on CentOS 7
CentOS 7的yum源中貌似没有正常安装mysql时的mysql-sever文件,需要去官网上下载 # wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-communit ...
- Installing MySQL Server on CentOS
MySQL is an open-source relational database. For those unfamiliar with these terms, a database is wh ...
- linux下安装多个mysql实例(摘自国外:How to create multiple mysql instance in CentOS 6.4 and Red Hat 6.4)
How to create multiple mysql instance in CentOS 6.4 and Red Hat 6.4 from:http://sharadchhetri.com/20 ...
- Mysql 5.7 CentOS 7 安装MHA
Table of Contents 1. MHA简介 1.1. 功能 1.2. MHA切换逻辑 1.3. 工具 2. 环境 2.1. 软件 2.2. 环境 3. Mysql 主从复制 3.1. Mys ...
- Install MySQL on Mac by Homebrew
1. 安装mysql brew update brew install mysql 2. 启动mysql mysql.server start 3. 登录mysql mysql -uroot -p ...
- yum install mysql
rpm -qa|grep -i mysqlmysql-libs-5.1.52-1.1.alios6.1.x86_64mysql-5.1.52-1.1.alios6.1.x86_64mysql-deve ...
- 在OSX狮子(Lion)上安装MYSQL(Install MySQL on Mac OSX)
这篇文章简述了在Mac OSX狮子(Lion)上安装MySQL Community Server最新版本v10.6.7的过程. MySQL是最流行的开源数据库管理系统.首先,从MySQL的下载页面上下 ...
随机推荐
- C语言学习笔记:14_内部函数和外部函数
/* * 14_内部函数和外部函数.c * * Created on: 2015年7月5日 * Author: zhong */ #include <stdio.h> #include & ...
- C++中无法解析的外部符号错误
在编译C++程序的时候,如果引用了对应的头文件,但是调用一个函数的时候仍然出现" 无法解析的外部符号错误"的编译错误,比如: 无法解析的外部符号__imp__PathFileE ...
- 在Foreda上安装apache-tomcat-7.0.42.tar.gz
开发环境JDK和Tomcat应该和部署环境一致,要不容易出现奇奇怪怪的问题.所以Aspire机器上的Tomcat要装一个新版本了. 装Tomcat基本等于一个解压和移动的过程,确实简单. 第一步:解压 ...
- Python访问PostGIS(建表、空间索引、分区表)
#encoding: utf-8 __author__ = 'Administrator' import psycopg2 import ppygis import datetime import s ...
- Appium Python 二:理论概念理解
简介 Appium 是一个开源的自动化测试工具,支持 iOS 平台和 Android 平台上的原生应用,web 应用和混合应用. “移动原生应用”是指那些用 iOS 或者 Android SDK 写的 ...
- UITabBarController 的配置
UITabBarController --> UITabBar Customizing Appearance backgroundImage 背景图片 selectedImageTintCol ...
- Java从零开始学十三(封装)
一.什么是封装,为什么要封装 对面向对象而言:封装就是将方法和属性包装到一个程序单元中,并且这个单元以类的形式实现. 简单讲:封闭就是将属性私有化,提供公有方法来访问私有属性 封装的作用: 封装反映和 ...
- PHP MySQL 连接数据库
PHP连接MySQL的小实例 <?php /*时间:2014-09-14 *作者:葛崇 *功能:PHP连接MySQL小实例 * */ /* SQL 脚本.直接贴到命令行运行. DROP ...
- 转:Windows消息机制要点
Windows消息机制要点 1. 窗口过程 每个窗口会有一个称为窗口过程的回调函数(WndProc),它带有四个参数,分别为:窗口句柄(Window Handle),消息ID(Message ...
- TP3.2批量上传文件(图片),解决同名冲突问题
1.html <form action="{:U('Upload/index')}" enctype="multipart/form-data" meth ...
