Solution -「LOCAL」大括号树
\(\mathcal{Description}\)
OurTeam & OurOJ.
给定一棵 \(n\) 个顶点的树,每个顶点标有字符 ( 或 )。将从 \(u\) 到 \(v\) 的简单有向路径上的字符串成括号序列,记其正则匹配的子串个数为 \(\operatorname{ans}(u,v)\)。求:
\]
\(n\le2\times10^5\)。
\(\mathcal{Solution}\)
可以先回忆一下括号树嗷。
来看看链怎么做 owo,现有结点按 \(1\sim n\) 从左到右编号,记 \(s(i,j)\) 表示从 \(i\) 到 \(j\) 串成的括号序列。令 \(\operatorname{match}(i)\) 为最大的 \(j<i\),满足 \(s(j,i)\) 正则匹配。定义状态 \(f(i)\) 表示 \(s(1,i)\) 中,以 \(i\) 结尾的正则子串贡献。那么:
\]
即,先保证最短的以 \(i\) 结尾的正则,起点就可以在前面任选了。而事实上,终点也能任选,那么答案为:
\]
需要正反分别做一次嗷。
那么,搬到树上,一个正则会贡献多少次呢?如图(混V的请告诉我背景是谁吖~):

不难发现,\((u,v)\)(或 \((v,u)\))若正则匹配,则它对答案的贡献为 \(siz_u\times siz_v\)。
好啦,开始 \(\text{DSU on Tree}\) 吧!
注意到我们只关心一些子树大小的信息,所以这样设计状态:
- \(f(u,i)\) 表示 \(u\) 子树内某一点 \(v\) 到 \(u\),构成的串有 \(i\) 个
(失配,且所有)被匹配的 \(siz_v\) 之和。 - \(g(u,i)\) 表示 \(u\) 到其子树内某一点 \(v\),构成的串有 \(i\) 个
)失配,且所有(被匹配的 \(siz_v\) 之和。
好奇怪的定义 qwq,该怎样理解呢?
考虑一条 \(v-u-w\) 的有向树链,其中 \(u\) 是 \(v\) 与 \(w\) 的 \(\text{LCA}\)。若 \(v-u\) 长成 (...((...(,\(u-w\) 长成 ...)...)...)),其中 ... 是已匹配的括号。可见 \(v-u-w\) 是正则匹配的,而这正对应了我们的状态 \(f(u,4)\) 和 \(g(u,4)\)!
接着考虑轻重儿子信息对答案的贡献,如图:
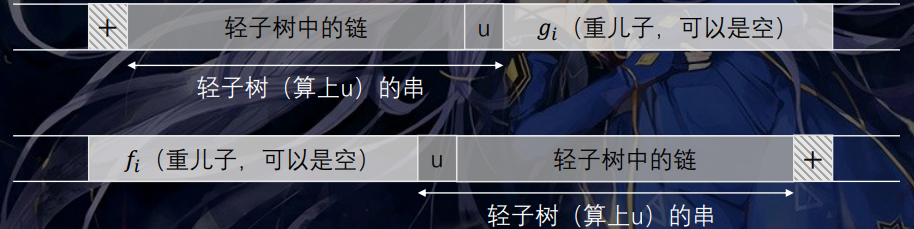
\(\text{DFS}\) 轻儿子的时候,用线段树动态维护前缀的 ),后缀的 ( 是否出现失配的情况,若一个点加入后不存在失配,则用 DP 信息更新答案。合并信息时类似,但加入最后一个点 \(u\) 时:
\(s_u=\texttt{'('}\),\(f(u,i+1)=f(v,i)\),\(g(u,i-1)=f(v,i)\)。
\(s_u=\texttt{')'}\),\(f(u,i-1)=f(v,i)\),\(g(u,i+1)=f(v,i)\)。
这……总不可能 \(\mathcal O(siz)\) 地遍历第二维吧 qwq。事实上,发现这只是一个单纯的数组位移,初始时开两倍数组,用一个指针指向数组实际的 \(0\) 号为即可 \(\mathcal O(1)\) 实现了。
以上两幅配图来自 Lucky_Glass 的题解。
\(\mathcal{Code}\)
#include <cstdio>
const int MAXN = 2e5, MOD = 998244353;
int n, ecnt, head[MAXN + 5], siz[MAXN + 5], son[MAXN + 5];
int ans, aryf[MAXN * 2 + 5], aryg[MAXN * 2 + 5], *f, *g;
char s[MAXN + 5];
inline int add ( int a, const int b ) { return ( a += b ) < MOD ? a : a - MOD; }
inline int sub ( int a, const int b ) { return ( a -= b ) < 0 ? a + MOD : a; }
inline int mul ( long long a, const int b ) { return ( a *= b ) < MOD ? a : a % MOD; }
inline int rint () {
int x = 0; char s = getchar ();
for ( ; s < '0' || '9' < s; s = getchar () );
for ( ; '0' <= s && s <= '9'; s = getchar () ) x = x * 10 + ( s ^ '0' );
return x;
}
struct Edge { int to, nxt; } graph[MAXN + 5];
inline void link ( const int s, const int t ) {
graph[++ ecnt] = { t, head[s] };
head[s] = ecnt;
}
struct SegmentTree {
int mn[MAXN * 2 + 5], tag[MAXN * 2 + 5];
inline int id ( const int l, const int r ) { return ( l + r ) | ( l != r ); }
inline void pushad ( const int l, const int r, const int v ) {
int rt = id ( l, r );
mn[rt] += v, tag[rt] += v;
}
inline void pushdn ( const int l, const int r ) {
int rt = id ( l, r ), mid = l + r >> 1;
if ( ! tag[rt] ) return ;
pushad ( l, mid, tag[rt] ), pushad ( mid + 1, r, tag[rt] );
tag[rt] = 0;
}
inline void pushup ( const int l, const int r ) {
int rt = id ( l, r ), mid = l + r >> 1, lc = id ( l, mid ), rc = id ( mid + 1, r );
mn[rt] = mn[lc] < mn[rc] ? mn[lc] : mn[rc];
}
inline void update ( const int l, const int r, const int ul, const int ur, const int v ) {
if ( ul <= l && r <= ur ) return pushad ( l, r, v );
int mid = l + r >> 1; pushdn ( l, r );
if ( ul <= mid ) update ( l, mid, ul, ur, v );
if ( mid < ur ) update ( mid + 1, r, ul, ur, v );
pushup ( l, r );
}
inline bool check () { return mn[id ( 1, n )] >= 0; }
} preT, sufT; // ((... and ...)), preT->g, sufT->f.
inline void init ( const int u ) {
siz[u] = 1;
for ( int i = head[u], v; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) {
init ( v = graph[i].to ), siz[u] += siz[v];
if ( siz[son[u]] < siz[v] ) son[u] = v;
}
}
inline void update ( const int u, const int dep, const int k ) {
preT.update ( 1, n, 1, dep, s[u] == '(' ? k : -k );
sufT.update ( 1, n, 1, dep, s[u] == ')' ? k : -k );
}
inline void calc ( const int u, int cnt, const int dep ) {
cnt += s[u] == ')' ? 1 : -1, update ( u, dep, 1 );
if ( sufT.check () ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( siz[u], f[cnt] ) );
if ( preT.check () ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( siz[u], g[-cnt] ) );
for ( int i = head[u]; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) calc ( graph[i].to, cnt, dep + 1 );
update ( u, dep, -1 );
}
inline void coll ( const int u, int cnt, const int dep ) {
cnt += s[u] == '(' ? 1 : -1, update ( u, dep, -1 );
if ( sufT.check () ) f[cnt] = add ( f[cnt], siz[u] );
if ( preT.check () ) g[-cnt] = add ( g[-cnt], siz[u] );
for ( int i = head[u]; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) coll ( graph[i].to, cnt, dep + 1 );
update ( u, dep, 1 );
}
inline void solve ( const int u, const bool keep ) {
for ( int i = head[u], v; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) {
if ( ( v = graph[i].to ) ^ son[u] ) {
solve ( v, false );
}
}
if ( son[u] ) solve ( son[u], true );
if ( s[u] == '(' ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( g[1], n - siz[son[u]] ) );
if ( s[u] == ')' ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( f[1], n - siz[son[u]] ) );
for ( int i = head[u], v; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) {
if ( ( v = graph[i].to ) ^ son[u] ) {
*f = add ( *f, n - siz[v] ), g[0] = add ( *g, n - siz[v] );
update ( u, 1, 1 );
calc ( v, s[u] == ')' ? 1 : -1, 2 );
*f = sub ( *f, n - siz[v] ), g[0] = sub ( *g, n - siz[v] );
update ( u, 1, -1 );
coll ( v, 0, 1 );
}
}
if ( s[u] == '(' ) *f = add ( *f, siz[u] ), -- f, *g ++ = 0;
if ( s[u] == ')' ) *g = add ( *g, siz[u] ), -- g, *f ++ = 0;
if ( ! keep ) {
for ( int i = 0; i <= siz[u]; ++ i ) f[i] = g[i] = 0;
f = aryf + n, g = aryg + n;
}
}
int main () {
scanf ( "%d %s", &n, s + 1 );
for ( int i = 2; i <= n; ++ i ) link ( rint (), i );
init ( 1 );
f = aryf + n, g = aryg + n;
solve ( 1, true );
printf ( "%d\n", ans );
return 0;
}
\(\mathcal{Update}\)
然后你就发现……只需要维护前缀、后缀最大值,与当前前缀、后缀和比较就砍掉 \(\log\) 了 owo!
#include <cstdio>
const int MAXN = 2e5, MOD = 998244353;
int n, ecnt, head[MAXN + 5], siz[MAXN + 5], son[MAXN + 5];
int ans, aryf[MAXN * 2 + 5], aryg[MAXN * 2 + 5], *f, *g;
char s[MAXN + 5];
inline int add ( int a, const int b ) { return ( a += b ) < MOD ? a : a - MOD; }
inline int sub ( int a, const int b ) { return ( a -= b ) < 0 ? a + MOD : a; }
inline int mul ( long long a, const int b ) { return ( a *= b ) < MOD ? a : a % MOD; }
inline void chkmax ( int& a, const int b ) { if ( a < b ) a = b; }
inline int rint () {
int x = 0; char s = getchar ();
for ( ; s < '0' || '9' < s; s = getchar () );
for ( ; '0' <= s && s <= '9'; s = getchar () ) x = x * 10 + ( s ^ '0' );
return x;
}
struct Edge { int to, nxt; } graph[MAXN + 5];
inline void link ( const int s, const int t ) {
graph[++ ecnt] = { t, head[s] };
head[s] = ecnt;
}
inline void init ( const int u ) {
siz[u] = 1;
for ( int i = head[u], v; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) {
init ( v = graph[i].to ), siz[u] += siz[v];
if ( siz[son[u]] < siz[v] ) son[u] = v;
}
}
inline void calc ( const int u, int cnt, int pre, int suf ) {
cnt += s[u] == ')' ? 1 : -1;
chkmax ( pre, -cnt ), chkmax ( suf, cnt );
if ( suf == cnt ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( siz[u], f[cnt] ) );
if ( pre == -cnt ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( siz[u], g[-cnt] ) );
for ( int i = head[u]; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) calc ( graph[i].to, cnt, pre, suf );
}
inline void coll ( const int u, int cnt, int pre, int suf ) {
cnt += s[u] == '(' ? 1 : -1;
chkmax ( pre, -cnt ), chkmax ( suf, cnt );
if ( suf == cnt ) f[cnt] = add ( f[cnt], siz[u] );
if ( pre == -cnt ) g[-cnt] = add ( g[-cnt], siz[u] );
for ( int i = head[u]; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) coll ( graph[i].to, cnt, pre, suf );
}
inline void solve ( const int u, const bool keep ) {
for ( int i = head[u], v; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) {
if ( ( v = graph[i].to ) ^ son[u] ) {
solve ( v, false );
}
}
if ( son[u] ) solve ( son[u], true );
if ( s[u] == '(' ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( g[1], n - siz[son[u]] ) );
if ( s[u] == ')' ) ans = add ( ans, mul ( f[1], n - siz[son[u]] ) );
int pre = s[u] == '(' ? 1 : -1, suf = s[u] == ')' ? 1 : -1;
for ( int i = head[u], v; i; i = graph[i].nxt ) {
if ( ( v = graph[i].to ) ^ son[u] ) {
*f = add ( *f, n - siz[v] ), g[0] = add ( *g, n - siz[v] );
calc ( v, s[u] == ')' ? 1 : -1, pre, suf );
*f = sub ( *f, n - siz[v] ), g[0] = sub ( *g, n - siz[v] );
coll ( v, 0, 0, 0 );
}
}
if ( s[u] == '(' ) *f = add ( *f, siz[u] ), -- f, *g ++ = 0;
if ( s[u] == ')' ) *g = add ( *g, siz[u] ), -- g, *f ++ = 0;
if ( ! keep ) {
for ( int i = 0; i <= siz[u]; ++ i ) f[i] = g[i] = 0;
f = aryf + n, g = aryg + n;
}
}
int main () {
scanf ( "%d %s", &n, s + 1 );
for ( int i = 2; i <= n; ++ i ) link ( rint (), i );
init ( 1 );
f = aryf + n, g = aryg + n;
solve ( 1, true );
printf ( "%d\n", ans );
return 0;
}
Solution -「LOCAL」大括号树的更多相关文章
- Solution -「LOCAL」Drainage System
\(\mathcal{Description}\) 合并果子,初始果子的权值在 \(1\sim n\) 之间,权值为 \(i\) 的有 \(a_i\) 个.每次可以挑 \(x\in[L,R]\) ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」Burning Flowers
灼之花好评,条条生日快乐(假装现在 8.15)! \(\mathcal{Description}\) 给定一棵以 \(1\) 为根的树,第 \(i\) 个结点有颜色 \(c_i\) 和光亮值 ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」画画图
\(\mathcal{Description}\) OurTeam. 给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的树形随机的带边权树,求所有含奇数条边的路径中位数之和.树形生成方式为随机取不连通两点连边直到全 ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」ZB 平衡树
\(\mathcal{Description}\) OurOJ. 维护一列二元组 \((a,b)\),给定初始 \(n\) 个元素,接下来 \(m\) 次操作: 在某个位置插入一个二元组: 翻 ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」人口迁徙
\(\mathcal{Description}\) \(n\) 个点,第 \(i\) 个点能走向第 \(d_i\) 个点,但从一个点出发至多走 \(k\) 步.对于每个点,求有多少点能够走到它. ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」「cov. HDU 6864」找朋友
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link.(几乎一致) 给定 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的仙人掌和起点 \(s\),边长度均为 \(1\).令 \(d(u)\) 表 ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」模板
\(\mathcal{Description}\) OurOJ. 给定一棵 \(n\) 个结点树,\(1\) 为根,每个 \(u\) 结点有容量 \(k_u\).\(m\) 次操作,每次操作 ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」割海成路之日
\(\mathcal{Description}\) OurOJ. 给定 \(n\) 个点的一棵树,有 \(1,2,3\) 三种边权.一条简单有向路径 \((s,t)\) 合法,当且仅当走过一条 ...
- Solution -「LOCAL」二进制的世界
\(\mathcal{Description}\) OurOJ. 给定序列 \(\{a_n\}\) 和一个二元运算 \(\operatorname{op}\in\{\operatorname{ ...
随机推荐
- jquery 的 ajax 传输 数组 ,但后台无法获取的 原因 与 解决 办法
1.前言 js传输数组到服务器 ,controller无法解析 ,打印结果是 null 2.原因 jQuery会调用jQuery.param序列化参数,源码是 jQuery.param( obj, t ...
- SQL高级优化(六)之MySQL索引
一.索引概述 1. 索引的优点 为什么要创建索引?这是因为,创建索引可以大大提高系统的查询性能.如果不使用索引,查询时从第一行开始查询.如果使用了索引,所以就可以更加快速的找到希望的数据. 第一. ...
- 《剑指offer》面试题36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
问题描述 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向. 为了让您更好地理解问题,以下面的二叉搜索树为例: 我们希望将这个二叉搜 ...
- 《设计模式面试小炒》策略和工厂模式替代业务场景中复杂的ifelse
<设计模式面试小炒>策略和工厂模式替代业务场景中复杂的ifelse 我是肥哥,一名不专业的面试官! 我是囧囧,一名积极找工作的小菜鸟! 囧囧表示:小白面试最怕的就是面试官问的知识点太笼统, ...
- 花了半年时间,我把Pink老师的HTMLCSS视频课程,整理成了10万字的Markdown笔记!
说明:本文内容真实!!!不是推广!!! 学习前端的同学应该都或多或少听说过 Pink 老师,我个人觉得 Pink 老师的前端视频教程应该说是目前B站上最好的了,没有之一! Pink老师 HTML CS ...
- C++构造函数语义学(二)(基于C++对象模型)
带有虚函数的情况. 下面情况编译器也会在需要的时候为其合成. 1.如果一个类自己声明为虚函数. 1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 ...
- Maven常用设置
1,maven属性设置 <properties>设置maven的常用属性 <properties> 属性设置 <!--maven构建项目使用编码,避免中文乱码--> ...
- hexo博客如何插入图片
Hexo是一个静态的博客网站生成器,生成一个博客只需要分分钟的时间就能搞定. Hexo的博文是支持Markdown格式的,发表一篇文章只需要简简单单的几个命令. hexo new '文章'就会生成一个 ...
- [luoguP4139]上帝与集合的正确用法
\(\text{Description}\) \(\text{Given a number }p(p\leqslant10^7).\) \(\text{Output }2^{2^{2^{2^{\cdo ...
- 文本图Tranformer在文本分类中的应用
原创作者 | 苏菲 论文来源: https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-main.668/ 论文题目: Text Graph Transformer for Docum ...
