android学习2——RelativeLayout
相对布局管理器,一个View的位置是相对于另外一个View定义的.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/btn1"/>
</RelativeLayout>
当只有一个按钮的时候,位置和线性布局管理器一样.在左上角.如下图所示:

android:layout_below用于指定当前的View在指定view的下面.代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_below="@id/btn1"/>
</RelativeLayout>
效果如下所示:
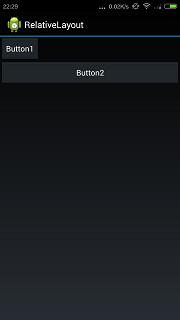
android:layout_alignRight用于表示和指定view右对齐.代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_below="@id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_below="@id/btn2"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/btn2"/>
</RelativeLayout>
右对齐的效果如下所示:
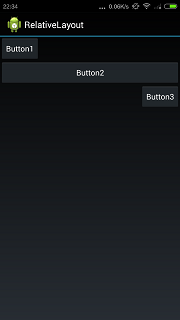
layout_alignParentRight表示和父组件的右边缘对齐.代码如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_below="@id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_below="@id/btn2"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/btn2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button4"
android:id="@+id/btn4"
android:layout_below="@id/btn3"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
代码产生的效果如下所示:
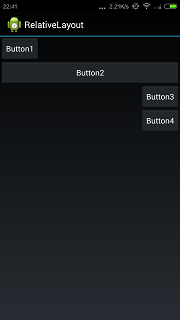
android:layout_centerHorizontal表示水平方向居中,代码如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_below="@id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_below="@id/btn2"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/btn2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button4"
android:id="@+id/btn4"
android:layout_below="@id/btn3"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button5"
android:id="@+id/btn5"
android:layout_below="@id/btn4"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
代码产生的效果如下所示:
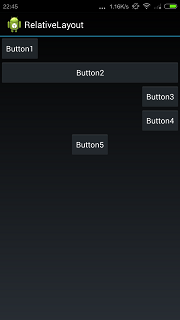
另外注意相对布局管理器默认是以左上为参照排列的.看下面的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_below="@id/button1"/>
</RelativeLayout>
代码的效果如下所示:
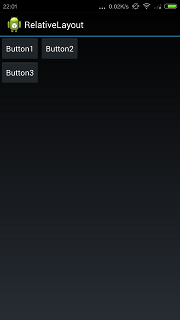
android:layout_toRightOf表示在view的右边.现在加一个按钮,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_below="@id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button4"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button3"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
直观感觉按钮4应该在按钮3的右边.但实际上的效果如下所示:
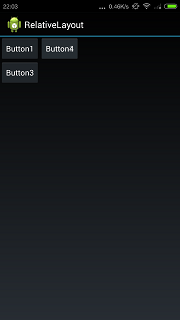
按钮4把按钮2遮住了.为什么?因为只指定了按钮4在按钮3的右边,没有指定上面的位置.默认是尽量向左上排,所以按钮4把按钮2遮住了.
所以想得到按钮4在按钮3右边的效果,要再指定上下的位置,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button1"
android:id="@+id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button2"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button3"
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_below="@id/button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button4"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/button3"
android:layout_below="@+id/button2"/>
</RelativeLayout>
效果如下所示:
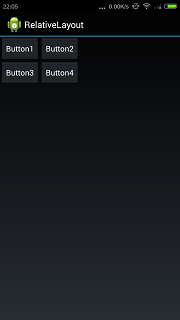
android学习2——RelativeLayout的更多相关文章
- [Android学习笔记]RelativeLayout的使用
RelativeLayout是相对布局控件,在屏幕适配的时候非常有用,在此记录一些它的常用属性 第一类:属性值为true或falseandroid:layout_centerHrizontal ...
- Android学习笔记(九) 视图的应用布局效果
最近少了写博客,可能最近忙吧,工作上忙,因为工作原因也忙于学习,也没记录什么了,也没有按照之前的计划去学习了.现在就记录一下最近学到的. 要做Android应用,界面设计少不了,可惜之前一直在用Win ...
- 三、Android学习第三天——Activity的布局初步介绍(转)
(转自:http://wenku.baidu.com/view/af39b3164431b90d6c85c72f.html) 三.Android学习第三天——Activity的布局初步介绍 今天总结下 ...
- Android – 学习操作NFC – 2
在<Android – 学习操作NFC – 1>说明了Android在处理NFC tag的机制.tag dispatch system的运作流程,以及三种ACTION_NDEF_DISCO ...
- Android 学习笔记之如何实现简单相机功能
PS:看来算法和数据结构还是非常有用的,以后每天都练习两道算法题目...这次忘了对代码进行折叠了..导致篇幅过长... 学习内容: 1.Android如何实现相机功能... 2.如何实现音频的录制.. ...
- Android 学习笔记之SurfaceView的使用+如何实现视频播放...
学习内容: 1.掌握Surface的使用... 2.Android中如何实现视频播放... 1.SurfaceView类的使用 在Android中,一般播放音频时我们可以去使用Android提供的 ...
- Android学习随笔--ListView的分页功能
第一次写博客,可能格式,排版什么的会非常不美观,不过我主要是为了记录自己的Android学习之路,为了以后能有些东西回顾.既然是为了学习,那我肯定会吸收各位大大们的知道经验,有不足的地方请指出. 通过 ...
- Android学习系列(23)--App主界面实现
在上篇文章<Android学习系列(22)--App主界面比较>中我们浅略的分析了几个主界面布局,选了一个最大众化的经典布局.今天我们就这个经典布局,用代码具体的实现它. 1.预览图先看下 ...
- android学习日记03--常用控件button/imagebutton
常用控件 控件是对数据和方法的封装.控件可以有自己的属性和方法.属性是控件数据的简单访问者.方法则是控件的一些简单而可见的功能.所有控件都是继承View类 介绍android原生提供几种常用的控件bu ...
随机推荐
- 安卓 listview与arrayadapter
今天有感于群里讨论的一个问题,很简单,但是问题还真是需要仔细看一下 问题:定义了一个最简单的arrayadapter,和listview结合使用,灭个item就显示个最简单的textView,一共6个 ...
- Django form模块使用心得
最近用Django 写了一个网站,现在来分享一下对Django form 的一些心得. 一,创建一个表单 创建一个Form表单有两种方式: 第一种方式是继承于forms.Form,的一个子类,通过在f ...
- 学习swing界面
最近做自动数据平台,没有界面.周末于是想用java实现一个可视化的界面. package cn.wuwenfu.swing; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import ja ...
- Struts2配置dtd约束
Struts2和Struts1的区别: 一.elclipse-ee开发 搭建环境eclipse-ee 1.加入jar包 apps/struts2-blank.war解压 2.在web.xml文件中配 ...
- 【蓝牙数据采集模块】-01-Sensor Controller 功能介绍
一. CC2650芯片内部的结构框图如图,内部包含: 一个Cortex-M3主控制器,用来做整个芯片的功能与任务实现 一个Cortex-M0射频控制器,用来驱动RF相关电路 一个Sensor Cont ...
- C#的显式接口和隐式接口(转载)
接口的实现分为:隐式实现和显式实现.如果类或者结构要实现的是单个接口,可以使用隐式实现,如果类或者结构继承了多个接口那么接口中相同名称成员就要显式实现.显示实现是通过使用接口的完全限定名来实现接口成员 ...
- MYSQL外键的使用以及优缺点
主键和索引是不可少的,不仅可以优化数据检索速度,开发人员还省不其它的工作, 矛盾焦点:数据库设计是否需要外键.这里有两个问题:一个是如何保证数据库数据的完整性和一致性:二是第一条对性能的影响. 正方观 ...
- GCD教程(二):多核心的性能
接上一篇,原帖地址:http://www.dreamingwish.com/dream-2012/of-of-of-performance-of-of-of-of-of-of-of-gcd-intro ...
- AIX上面Oracle数据库相关启动
1,启动停止Oracle实例 (1) su -oracle (2) echo $ORACLE_SID (3) sqlplus /nolog //以不登录到数据库的方式进入sqlplus环境 (4) c ...
- JSP和JSTL
JSP页面由Web服务器上的JSP引擎执行,该引擎会把JSP转成Servlet代码源文件,并以一般的Servlet方式载入执行:JSP引擎介绍客户端对JSP页面的请求,生成JSP页面给客户端的响应,该 ...
