【C/C++开发】容器set和multiset,C++11对vector成员函数的扩展(cbegin()、cend()、crbegin()、crend()、emplace()、data())
一、set和multiset基础
set和multiset会根据特定的排序准则,自动将元素进行排序。不同的是后者允许元素重复而前者不允许。

需要包含头文件:
#include <set>
set和multiset都是定义在std空间里的类模板:
- template<class _Kty,
- class _Pr = less<_Kty>,
- class _Alloc = allocator<_Kty> >
- class set
- template<class _Kty,
- class _Pr = less<_Kty>,
- class _Alloc = allocator<_Kty> >
- class multiset
只要是可复赋值、可拷贝、可以根据某个排序准则进行比较的型别都可以成为它们的元素。第二个参数用来定义排序准则。缺省准则less是一个仿函数,以operator<对元素进行比较。
所谓排序准则,必须定义strict weak ordering,其意义如下:
1、必须使反对称的。
对operator<而言,如果x<y为真,则y<x为假。
2、必须使可传递的。
对operator<而言,如果x<y为真,且y<z为真,则x<z为真。
3、必须是非自反的。
对operator<而言,x<x永远为假。
因为上面的这些特性,排序准则可以用于相等性检验,就是说,如果两个元素都不小于对方,则它们相等。
二、set和multiset的功能
和所有关联式容器类似,通常使用平衡二叉树完成。事实上,set和multiset通常以红黑树实作而成。
自动排序的优点是使得搜寻元素时具有良好的性能,具有对数时间复杂度。但是造成的一个缺点就是:
不能直接改变元素值。因为这样会打乱原有的顺序。
改变元素值的方法是:先删除旧元素,再插入新元素。
存取元素只能通过迭代器,从迭代器的角度看,元素值是常数。
三、操作函数
构造函数和析构函数

set的形式可以是:

有两种方式可以定义排序准则:
1、以template参数定义:
- set<int,greater<int>> col1;
此时,排序准则就是型别的一部分。型别系统确保只有排序准则相同的容器才能被合并。
程序实例:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <set>
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- set<int> s1;
- set<int,greater<int> > s2;
- for (int i = 1;i < 6;++i)
- {
- s1.insert(i);
- s2.insert(i);
- }
- if(s1 == s2)
- cout << "c1 equals c2 !" << endl;
- else
- cout << "c1 not equals c2 !" << endl;
- }
程序运行会报错。但是如果把s1的排序准则也指定为greater<int>便运行成功。
2、以构造函数参数定义。
这种情况下,同一个型别可以运用不同的排序准则,而排序准则的初始值或状态也可以不同。如果执行期才获得排序准则,而且需要用到不同的排序准则,这种方式可以派上用场。
程序实例:
- #include <iostream>
- #include "print.hpp"
- #include <set>
- using namespace std;
- template <class T>
- class RuntimeCmp{
- public:
- enum cmp_mode{normal,reverse};
- private:
- cmp_mode mode;
- public:
- RuntimeCmp(cmp_mode m = normal):mode(m){}
- bool operator()(const T &t1,const T &t2)
- {
- return mode == normal ? t1 < t2 : t2 < t1;
- }
- bool operator==(const RuntimeCmp &rc)
- {
- return mode == rc.mode;
- }
- };
- typedef set<int,RuntimeCmp<int> > IntSet;
- void fill(IntSet& set);
- int main()
- {
- IntSet set1;
- fill(set1);
- PRINT_ELEMENTS(set1,"set1:");
- RuntimeCmp<int> reverse_order(RuntimeCmp<int>::reverse);
- IntSet set2(reverse_order);
- fill(set2);
- PRINT_ELEMENTS(set2,"set2:");
- set1 = set2;//assignment:OK
- set1.insert(3);
- PRINT_ELEMENTS(set1,"set1:");
- if(set1.value_comp() == set2.value_comp())//value_comp <span style="font-family: verdana, arial, helvetica, sans-serif; ">Returns the comparison object associated with the container</span>
- cout << "set1 and set2 have the same sorting criterion" << endl;
- else
- cout << "set1 and set2 have the different sorting criterion" << endl;
- }
- void fill(IntSet &set)
- {
- set.insert(4);
- set.insert(7);
- set.insert(5);
- set.insert(1);
- set.insert(6);
- set.insert(2);
- set.insert(5);
- }
运行结果:

虽然set1和set2的而比较准则本身不同,但是型别相同,所以可以进行赋值操作。
非变动性操作

注意:元素比较操作只能用于型别相同的容器。
特殊的搜寻函数


赋值
赋值操作两端的容器必须具有相同的型别,但是比较准则本身可以不同,但是其型别必须相同。如果比较准则的不同,准则本身也会被赋值或交换。
迭代器相关函数

元素的插入和删除

注意:插入函数的返回值不完全相同。
set提供的插入函数:
- pair<iterator,bool> insert(const value_type& elem);
- iterator insert(iterator pos_hint, const value_type& elem);
multiset提供的插入函数:
- iterator insert(const value_type& elem);
- iterator insert(iterator pos_hint, const value_type& elem);
返回值型别不同的原因是set不允许元素重复,而multiset允许。当插入的元素在set中已经包含有同样值的元素时,插入就会失败。所以set的返回值型别是由pair组织起来的两个值:
第一个元素返回新元素的位置,或返回现存的同值元素的位置。第二个元素表示插入是否成功。
set的第二个insert函数,如果插入失败,就只返回重复元素的位置!
但是,所有拥有位置提示参数的插入函数的返回值型别是相同的。这样就确保了至少有了一个通用型的插入函数,在各种容器中有共通接口。
注意:还有一个返回值不同的情况是:作用于序列式容器和关联式容器的erase()函数:
序列式容器的erase()函数:
- iterator erase(iterator pos);
- iterator erase(iterator beg, iterator end);
关联式容器的erase()函数:
- void erase(iterator pos);
- void erase(iterator beg, iterator end);
这完全是为了性能的考虑。因为关联式容器都是由二叉树实现,搜寻某元素并返回后继元素可能很费时。
五、set应用示例:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <set>
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- typedef set<int,greater<int> > IntSet;
- IntSet s1;
- s1.insert(4);
- s1.insert(3);
- s1.insert(5);
- s1.insert(1);
- s1.insert(6);
- s1.insert(2);
- s1.insert(5);
- //the inserted element that has the same value with a element existed is emitted
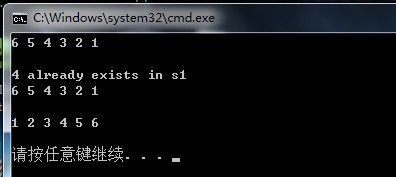
- copy(s1.begin(),s1.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
- cout << endl << endl;
- pair<IntSet::iterator,bool> status = s1.insert(4);
- if(status.second)
- cout << "4 is inserted as element "
- << distance(s1.begin(),status.first) + 1 << endl;
- else
- cout << "4 already exists in s1" << endl;
- copy(s1.begin(),s1.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
- cout << endl << endl;
- set<int> s2(s1.begin(),s1.end());//default sort criterion is less<
- copy(s2.begin(),s2.end(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout," "));
- cout << endl << endl;
- }
上述程序最后新产生一个set:s2,默认排序准则是less。以s1的元素作为初值。
注意:s1和s2有不同的排序准则,所以他们的型别不同,不能直接进行相互赋值或比较。
运行结果:
|
Defined in header
<iterator> |
||
| (1) | ||
| template< class C > auto rbegin( C& c ) -> decltype(c.rbegin()); |
(since C++14) (until C++17) |
|
|
template< class C > constexpr auto rbegin( C& c ) -> decltype(c.rbegin()); |
(since C++17) | |
| (1) | ||
| template< class C > auto rbegin( const C& c ) -> decltype(c.rbegin()); |
(since C++14) (until C++17) |
|
|
template< class C > constexpr auto rbegin( const C& c ) -> decltype(c.rbegin()); |
(since C++17) | |
| (2) | ||
| template< class T, size_t N > reverse_iterator<T*> rbegin( T (&array)[N] ); |
(since C++14) (until C++17) |
|
|
template< class T, size_t N > constexpr reverse_iterator<T*> rbegin( T (&array)[N] ); |
(since C++17) | |
| (3) | ||
| template< class C > auto crbegin( const C& c ) -> decltype(std::rbegin(c)); |
(since C++14) (until C++17) |
|
|
template< class C > constexpr auto crbegin( const C& c ) -> decltype(std::rbegin(c)); |
(since C++17) | |
Returns an iterator to the reverse-beginning of the given container c or array array.
c.c.Parameters
| c | - | a container with a rbegin method |
| array | - | an array of arbitrary type |
Return value
An iterator to the reverse-beginning of c or array
Notes
In addition to being included in <iterator>, std::rbegin and std::crbegin are
guaranteed to become available if any of the following headers are included: <array>, <deque>, <forward_list>, <list>, <map>, <regex>, <set>, <string>,
<string_view> (since C++17), <unordered_map>, <unordered_set>,
and <vector>.
Overloads
Custom overloads of rbegin may be provided for classes that do not expose a suitable rbegin() member
function, yet can be iterated. The following overload is already provided by the standard library:
|
(C++14)
|
specializes std::rbegin (function) |
Example
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <iterator>int main(){std::vector<int> v = { 3, 1, 4 };auto vi = std::rbegin(v);std::cout << *vi << '\n';int a[] = { -5, 10, 15 };auto ai = std::rbegin(a);std::cout << *ai << '\n';}
Output:
415
所以这篇博客就是想罗列一下C++11对vector容器的扩充。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
<codeclass="hljs>#include#includeint{ std::vector<int>10,20,30,40,50}; std::cout"myvector; for std::cout' std::cout'\n'; return;}Output:myvector10</int></vector></iostream></code> |
如何使用:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<codeclass="hljs>#include#includeint{ std::vector<int>10,20,30}; auto1,100 myvector.emplace200 myvector.emplace300 std::cout"myvector; for std::cout' std::cout'\n'; return;}Output:myvector10</int></vector></iostream></code> |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<codeclass="hljs>#include#includeint{ std::vector<int>5); int* *p10; ++p; *p20; p[2]100; std::cout"myvector; for0;""""""\n';=""="";=""""""""""=""=""=""=""</int></vector></iostream></code> |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
<codeclass="hljs><codeclass="hljs>#include#includeint{ std::vector<int>100); std::cout"1. '\n'; std::cout"1. '\n'; myvector.resize(10); std::cout"2. '\n'; std::cout"2. '\n'; myvector.shrink_to_fit(); std::cout"3. '\n'; std::cout"3. '\n'; return;}//输出1.1001.1002.1002.103.103.10</int></vector></iostream></code></code> |
此时,就是要明白size和capacity的区别,也就会更加理解resize和reserve的区别了!
【C/C++开发】容器set和multiset,C++11对vector成员函数的扩展(cbegin()、cend()、crbegin()、crend()、emplace()、data())的更多相关文章
- 面向UI编程:ui.js 1.0 粗糙版本发布,分布式开发+容器化+组件化+配置化框架,从无到有的艰难创造
时隔第一次被UI思路激励,到现在1.0的粗糙版本发布,掐指一算整整半年了.半年之间,有些细节不断推翻重做,再推翻再重做.时隔今日,终于能先出来个东西了,这个版本很粗糙,主体功能大概能实现了,但是还是有 ...
- 【Cocos2d-x游戏开发】细数Cocos2d-x开发中那些常用的C++11知识
自从Cocos2d-x3.0开始,Cocos2dx就正式的使用了C++11标准.C++11简洁方便的特性使程序的可拓展性和可维护性大大提高,也提高了代码的书写速度. 下面我们就来一起学习一下Cocos ...
- c++ stl容器set成员函数介绍及set集合插入,遍历等用法举例
c++ stl集合set介绍 c++ stl集合(Set)是一种包含已排序对象的关联容器.set/multiset会根据待定的排序准则,自动将元素排序.两者不同在于前者不允许元素重复,而后者允许. 1 ...
- 容器大小的改变以及容器操作可能使迭代器失效、vector对象的容量变化
1 改变容器的大小 我们可以使用resize来增加或缩小容器,与往常一样,array不支持resize.如果当前大小大于所要求的大小,容器后面的元素会被删除:如果当前大小小于新大小,会将新元素添加到容 ...
- 银弹谷零代码开发V百科|使用技巧:OMG!这些时间日期函数太好用了吧,盘它
银弹谷零代码开发V百科|使用技巧:OMG!这些时间日期函数太好用了吧,盘它 Hello~everybody!小V又来咯!这次小V给大家带来的是零代码开发V平台常用的时间日期函数.小V知道我们平时常常会 ...
- Hi3559AV100 NNIE开发(2)-RFCN(.wk)LoadModel及NNIE Init函数运行过程分析
之后随笔将更多笔墨着重于NNIE开发系列,下文是关于Hi3559AV100 NNIE开发(2)-RFCN(.wk)LoadModel及NNIE Init函数运行过程分析,通过对LoadModel函数及 ...
- C++ STL学习之容器set和multiset (补充材料)
一.set和multiset基础 set和multiset会根据特定的排序准则,自动将元素进行排序.不同的是后者允许元素重复而前者不允许. 需要包含头文件: #include <set> ...
- 08--STL关联容器(set/multiset)
一:set/multiset的简介 set是一个集合容器,其中所包含的元素是唯一的,集合中的元素按一定的顺序排列.元素插入过程是按排序规则插入,所以不能指定插入位置. set采用红黑树变体的数据结构实 ...
- STL标准库-容器-set与multiset
技术在于交流.沟通,转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. set与multiset关联容器 结构如下 set是一种关联容器,key即value,value即key.它是自动排序,排序特点依据key se ...
随机推荐
- gentelella 开源后台使用记录
前言 gentelella是一款开源后台,github地址是:https://github.com/ColorlibHQ/gentelella 使用 表单验证 parsley 验证 在form.htm ...
- 一道Common Lisp 宏的练习题
这是<ANSI Common Lisp>第10章“宏”的习题第6题: 定义一个宏,接受一变量列表以及一个代码主体,并确保变量在代码主体被求值后恢复 (revert)到原本的数值
- 转:Windows系统环境下安装dlib
原文链接 因为今天安装Face Recognition,需要先按照 dlib .需要在windows环境下做一些图片处理,所以需要在pycharm中配置环境,而其中需要的主要是dlib的安装: 下面说 ...
- C# 中using 用来释放资源的用法
using(...) {........} 定义了一个范围,等范围结束以后进行资源的释放. 例如: using(SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(" ...
- 很全的vue插件汇总,赶紧收藏下(转)
Vue是一个构建数据驱动的 web 界面的渐进式框架.Vue.js 的目标是通过尽可能简单的 API 实现响应的数据绑定和组合的视图组件特别整理了常用的vue插件,来了个大汇总,方便查找使用,便于工作 ...
- 关于html的相关讲解
浏览器chrome Chrome它内部有一个解析器,这个解析器就是解析我们的代码,各个浏览器的内核不一样,所以存在浏览器的兼容.这个内核是一个引擎. 谷歌的内核是webkit 引擎是v8. 客户端的请 ...
- make CMake 来龙去脉
理论上说,任意一个C++程序都可以用g++来编译. 大家都知道,写程序大体步骤如下: 1.用编辑器编写源代码,如.c文件. 2.用编译器编译代码生成目标文件,如.o. 3.用链接器连接目标代码生成可执 ...
- Android 9.0网络权限适配
在做Android开发时,使用华为的p20和平板(均为Android 9.0)测试时,发现不能使用WIFI网络,一番郁闷纠结查找后 直接上方法: 在res文件夹下创建xml文件夹,在xml里面创建文件 ...
- 使用 Python 生成二维码
在“一带一路”国际合作高峰论坛举行期间, 20 国青年投票选出中国的“新四大发明”:高铁.扫码支付.共享单车和网购.其中扫码支付指手机通过扫描二维码跳转到支付页面,再进行付款.这种新的支付方式,造就二 ...
- Django rest framework ---- 权限
Django rest framework ---- 权限 添加权限 api/utils文件夹下新建premission.py文件,代码如下: message是当没有权限时,提示的信息 # FileN ...

