https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2014/03/how-hashmap-works-in-java.html
Most common interview questions are “How HashMap works in java”, “How get and put method of HashMap work internally”. Here I am trying to explain internal functionality with an easy example. Rather than going through theory, we will start with example first, so that you will get better understanding and then we will see how get and put function work in java.
Lets take a very simple example. I have a Country class, we are going to use Country class object as key and its capital name(string) as value. Below example will help you to understand, how these key value pair will be stored in hashmap.
1. Country.java
01 |
package org.arpit.javapostsforlearning; |
02 |
public class Country { |
07 |
public Country(String name, long population) { |
10 |
this.population = population; |
12 |
public String getName() { |
15 |
public void setName(String name) { |
18 |
public long getPopulation() { |
21 |
public void setPopulation(long population) { |
22 |
this.population = population; |
25 |
// If length of name in country object is even then return 31(any random number) and if odd then return 95(any random number). |
26 |
// This is not a good practice to generate hashcode as below method but I am doing so to give better and easy understanding of hashmap. |
28 |
public int hashCode() { |
29 |
if(this.name.length()%2==0) |
35 |
public boolean equals(Object obj) { |
37 |
Country other = (Country) obj; |
38 |
if (name.equalsIgnoreCase((other.name))) |
If you want to understand more about hashcode and equals method of object, you may refer hashcode() and equals() method in java
2. HashMapStructure.java(main class)
01 |
import java.util.HashMap; |
02 |
import java.util.Iterator; |
04 |
public class HashMapStructure { |
07 |
* @author Arpit Mandliya |
09 |
public static void main(String[] args) { |
11 |
Country india=new Country("India",1000); |
12 |
Country japan=new Country("Japan",10000); |
14 |
Country france=new Country("France",2000); |
15 |
Country russia=new Country("Russia",20000); |
17 |
HashMap<country,string> countryCapitalMap=new HashMap<country,string>(); |
18 |
countryCapitalMap.put(india,"Delhi"); |
19 |
countryCapitalMap.put(japan,"Tokyo"); |
20 |
countryCapitalMap.put(france,"Paris"); |
21 |
countryCapitalMap.put(russia,"Moscow"); |
23 |
Iterator<country> countryCapitalIter=countryCapitalMap.keySet().iterator();//put debug point at this line |
24 |
while(countryCapitalIter.hasNext()) |
26 |
Country countryObj=countryCapitalIter.next(); |
27 |
String capital=countryCapitalMap.get(countryObj); |
28 |
System.out.println(countryObj.getName()+"----"+capital); |
34 |
</country></country,string></country,string> |
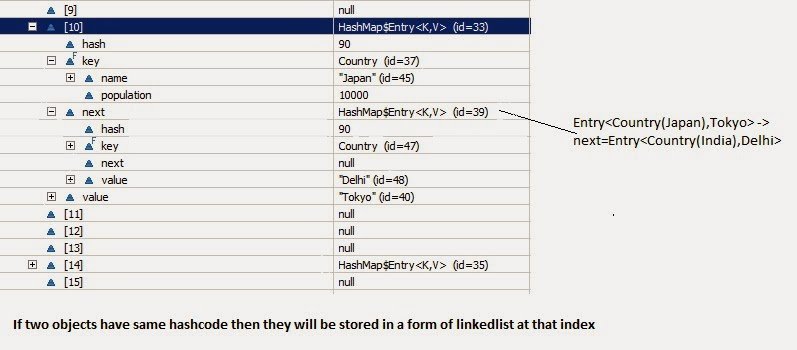
Now put debug point at line 23 and right click on project->debug as-> java application. Program will stop execution at line 23 then right click on countryCapitalMap then select watch.You will be able to see structure as below.

Now From above diagram, you can observe following points
- There is an Entry[] array called table which has size 16.
- This table stores Entry class’s object. HashMap class has a inner class called Entry.This Entry have key value as instance variable. Lets see structure of entry class Entry Structure.
1 |
static class Entry implements Map.Entry |
7 |
...//More code goes here |
- Whenever we try to put any key value pair in hashmap, Entry class object is instantiated for key value and that object will be stored in above mentioned Entry[](table). Now you must be wondering, where will above created Enrty object get stored(exact position in table). The answer is, hash code is calculated for a key by calling Hascode() method. This hashcode is used to calculate index for above Entry[] table.
- Now, If you see at array index 10 in above diagram, It has an Entry object named HashMap$Entry.
- We have put 4 key-values in hashmap but it seems to have only 2!!!!This is because if two objects have same hashcode, they will be stored at same index. Now question arises how? It stores objects in a form of LinkedList(logically).
So how hashcode of above country key-value pairs are calculated.
1 |
Hashcode for Japan = 95 as its length is odd. |
2 |
Hashcode for India =95 as its length is odd |
3 |
HashCode for Russia=31 as its length is even. |
4 |
HashCode for France=31 as its length is even. |
Below diagram will explain LinkedList concept clearly.
So now if you have good understanding of hashmap structure,Lets go through put and get method.
Put :
Lets see implementation of put method:
02 |
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. If the |
03 |
* map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old value is |
07 |
* key with which the specified value is to be associated |
09 |
* value to be associated with the specified key |
10 |
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or <tt>null</tt> |
11 |
* if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. (A <tt>null</tt> return |
12 |
* can also indicate that the map previously associated |
13 |
* <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) |
15 |
public V put(K key, V value) { |
17 |
return putForNullKey(value); |
18 |
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); |
19 |
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); |
20 |
for (Entry<k , V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { |
22 |
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { |
31 |
addEntry(hash, key, value, i); |
now lets understand above code step by step
- Key object is checked for null. If key is null then it will be stored at table[0] because hashcode for null is always 0.
- Key object’s hashcode() method is called and hash code is calculated. This hashcode is used to find index of array for storing Entry object. It may happen sometimes that, this hashcode function is poorly written so JDK designer has put another function called hash() which takes above calculated hash value as argument.If you want to learn more about hash() function, you can refer hash and indexFor method in hashmap.
- indexFor(hash,table.length) is used to calculate exact index in table array for storing the Entry object.
- As we have seen in our example, if two key objects have same hashcode(which is known as collision) then it will be stored in form of linkedlist.So here, we will iterate through our linkedlist.
- If there is no element present at that index which we have just calculated then it will directly put our Entry object at that index.
- If There is element present at that index then it will iterate until it gets Entry->next as null.Then current Entry object become next node in that linkedlist
- What if we are putting same key again, logically it should replace old value. Yes,it will do that.While iterating it will check key equality by calling equals() method(key.equals(k)), if this method returns true then it replaces value object with current Entry’s value object.
Get:
Lets see implementation of get now:
02 |
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or {@code null} |
03 |
* if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
06 |
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key {@code k} to a |
07 |
* value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null : |
08 |
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns |
09 |
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) |
12 |
* A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i> indicate that |
13 |
* the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also possible that the map |
14 |
* explicitly maps the key to {@code null}. The {@link #containsKey |
15 |
* containsKey} operation may be used to distinguish these two cases. |
17 |
* @see #put(Object, Object) |
19 |
public V get(Object key) { |
21 |
return getForNullKey(); |
22 |
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); |
23 |
for (Entry<k , V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { |
25 |
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) |
As you got the understanding on put functionality of hashmap. So to understand get functionality is quite simple. If you pass any key to get value object from hashmap.
- Key object is checked for null. If key is null then value of Object resides at table[0] will be returned.
- Key object’s hashcode() method is called and hash code is calculated.
- indexFor(hash,table.length) is used to calculate exact index in table array using generated hashcode for getting the Entry object.
- After getting index in table array, it will iterate through linkedlist and check for key equality by calling equals() method and if it returns true then it returns the value of Entry object else returns null.
Key points to Remeber:
- HashMap has a inner class called Entry which stores key-value pairs.
- Above Entry object is stored in Entry[ ](Array) called table
- An index of table is logically known as bucket and it stores first element of linkedlist
- Key object’s hashcode() is used to find bucket of that Entry object.
- If two key object ‘s have same hashcode , they will go in same bucket of table array.
- Key object ‘s equals() method is used to ensure uniqueness of key object.
- Value object ‘s equals() and hashcode() method is not used at all
- How HashMap works in Java
https://www.javainterviewpoint.com/hashmap-works-internally-java/ How a HashMap Works internally has ...
- HashMap如何工作 - Java
大多数人应该会同意HashMap是现在面试最喜欢问的主题之一.我和同事常常进行讨论,并很有帮助.现在,我继续和大家讨论. 我假设你对HashMap的内部工作原理感兴趣,并且你已经知道了基本的HashM ...
- SpringMvc中Hashmap操作遇到 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException: null
代码按照网上修改为类似,还不能解决问题 for (Iterator<String> it = target.keySet().iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) { i ...
- HashTable HashMap HashSet区别(java)
Hashtable: 1. key和value都不许有null值 2. 使用enumeration遍历 3. 同步的,每次只有一个线程能够访问 4. 在java中Hashtable是H大写,t小写,而 ...
- HashMap如何在Java中工作?
通过优锐课学习笔记分享,我们可以看到HashMap问题在工作面试中很常见. 这也是HashMaps在Java内部如何工作的一些深入说明,分享给大家参考学习. HashMap在内部如何工作已成为几乎所有 ...
- JSONObject JSONArray json字符串 HashMap ArryList 在java开发中用到的数据结构
1.JSONObject 长成这样的: { "key1":value1, "key2":value2, "key3":value3} ...
- Understanding How Graal Works - a Java JIT Compiler Written in Java
https://chrisseaton.com/truffleruby/jokerconf17/ https://chrisseaton.com/truffleruby/tenthings/ http ...
- LRU hashMap(拉链) + 双向链表 java实现
//基于 hash (拉链法) + 双向链表,LRUcache //若改为开放寻址,线性探测法能更好使用cpuCache public class LRU { private class Node { ...
- Java集合框架(Collection Framework)学习之 HashMap
从API文档可以得到HashMap的以下几个特点: 基于哈希表(hash table)实现,并且是链式哈希表 允许空值和空键(null=null 键值对) HashMap与Hashtable基本相同, ...
随机推荐
- MySQL复制以及调优
一. 简介 MySQL自带复制方案,带来好处有: 数据备份. 负载均衡. 分布式数据. 概念介绍: 主机(master):被复制的数据库. 从机(slave):复制主机数据的数据库. 复制步骤: (1 ...
- jQuery找到GridView控件ItemTemplate模版内的控件
可以使用下面的方法,jQuery找到GridView控件ItemTemplate模版内的CheckBox: 使用jQuery的find()方法:
- 控制器中获取Field值
在ASP.NET MVC程序中,我们需要POST Data到制器中,是有很多方法.但是我们想在控制器中,获取Feild值呢?怎样获取?你可以留意到有一个类FormCollection.它能帮助到我们解 ...
- thinkphp save() 跟新失败
一.失败案例 $data = I(); $rs = $this->typeModel->data($data)->save(); 二.正确案例 正确一 $rs=$this->t ...
- vb.net連接Oracle数据库
Imports Oracle.DataAccess.Client '導入命名空間 Public Class Form1 Dim Sql As String Public SqlTP As Oracle ...
- 【Linux】安装openssh-server依赖openssh-client版本错误的解决办法
这是因为,openssh-server是依赖于openssh-clien的,ubuntu自带了openssh-client,自带的openssh-clien与所要安装的openssh-server所依 ...
- Jave Web阿里云短信服务发送验证码
首先得在阿里云根据流程开通短信服务,申请签名和模版,具体看文档 因为这是个web项目,用到了thymeleaf模板,所以在pom.xml中加入如下依赖 <dependency> <g ...
- 数据定义语句(DDL语句)
建立表 create table 表名( 字段名1 类型, 字段名2 类型, ........ 字段名n 类型): 类型有: char(n) 是一个类型,叫定长字符串,数据不够就补空格 v ...
- ORM--Entity Framework 学习(01)
关键词:Entity Framework:微软官方提供的ORM工具,ORM让开发人员节省数据库访问的代码时间,将更多的时间放到业务逻辑层代码上.EF提供变更跟踪.唯一性约束.惰性加载.查询事物等.开发 ...
- javascript中常见错误类型
js中控制台报错主分两大类: 第一类:语法错误,这一类错误在javascript预解析的过程中如果遇到,则会导致整个js文件都无法执行. 另一类:统称为异常,这一类的错误会导致在错误出现的那一行之后的 ...


