POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA)
POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA)
Description
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
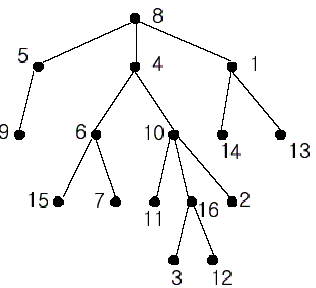
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,..., N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge --the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2
16
1 14
8 5
10 16
5 9
4 6
8 4
4 10
1 13
6 15
10 11
6 7
10 2
16 3
8 1
16 12
16 7
5
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 5
3 5
Sample Output
4
3
Http
POJ:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-1330
UVAlive:https://vjudge.net/problem/UVALive-2525
Source
最近公共祖先,LCA
题目大意
给出一棵树,求两点之间的公共祖先。
解决思路
求LCA有多种方法,那么本题我们用在线的倍增算法。
倍增算法基于的是非常高效的二分思想,即二分两个点的祖先,看是否是共同祖先,若是,则寻找更近的,若不是,则寻找更远的。
那么为了实现这个二分,我们定义一个Parent数组,Parent[u][i]表示u的(1 << i)祖先(即2i祖先),为什么要选择2i呢,因为我们用的是二分嘛。
另外,为了方便后面倍增,我们再定义一个Depth[u]数组表示u的深度。
那么首先我们用一个dfs求出Depth[u]和parent[u][0](即u的父亲,这是可以在dfs中求出来的)
然后,我们求出Parent的其他数组,Parent[u][i]=Parent[Parent[u][i-1]][i-1],这个很显然,u的2i祖先就是u的2(i-1)祖先的2^(i-1)祖先(自己可以手动模拟一下)
有了上面求出来的两组信息,我们就可以在线地求LCA啦。
现在假设我们要求LCA的是两个点a和b,并且Depth[a]>Depth[b](如果不是怎么办,swap(a,b)就可以了)。
那么,我们的第一步是把a与b提升到同一高度,这个较好理解。让k从大(一般是20)到小(0)循环,每次判断Depth[Parent[a][k]]与Depth[b]的大小关系,若Depth[Parent[a][k]]==Deptf[b],则a=Parent[a][k],相当于把a向上翻。
在a与b到达同一高度后,若此时ab说明已经找到了a,b的公共祖先,直接输出即可。若还不是,则把二者同时向上翻。注意,为了保证求得的是最近的公共祖先,这里的if判断不能写Parent[a][k]Parent[b][k],而要写Parent[a][k]!=Parent[b][k](自己想一想,为什么)
最后求得的解就是Parent[a][0](或者是Parent[b][0],两者是一样的)
LCA还有一些细节的地方需要注意,具体请看代码(都用注释标记出来了)
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxN=10011;
const int inf=2147483647;
int n;
int root;
vector<int> E[maxN];
int Parent[maxN][25];
int Depth[maxN];
bool vis[maxN];
int read();//读入优化
void LCA_init();
void dfs(int u);
int LCA(int a,int b);
int main()
{
int TT;
TT=read();
for (int ti=1;ti<=TT;ti++)
{
n=read();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
E[i].clear();
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int x=read(),y=read();
E[x].push_back(y);
vis[y]=1;
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (vis[i]==0)
root=i;
//cout<<root<<endl;
LCA_init();//LCA的初始化,即计算Depth和Parent数组
cout<<LCA(read(),read())<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
int read()
{
int x=0;
int k=1;
char ch=getchar();
while (((ch>'9')||(ch<'0'))&&(ch!='-'))
ch=getchar();
if (ch=='-')
{
k=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while ((ch<='9')&&(ch>='0'))
{
x=x*10+ch-48;
ch=getchar();
}
return x*k;
}
void LCA_init()
{
memset(Depth,0,sizeof(Depth));
Depth[root]=0;
memset(Parent,0,sizeof(Parent));
dfs(root);//首先用dfs计算出Depth和Parent[u][0]
int kk=0;
for (int j=1;j<=20;j++)//注意这里必须是j的循环在外面,i在里面,这是为了保证要计算某个值时它所需要的值已经计算出来了。
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
Parent[i][j]=Parent[Parent[i][j-1]][j-1];
/*for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<=kk;j++)
cout<<Parent[i][j]<<' ';
cout<<endl;
}
*/
}
void dfs(int u)
{
for (int i=0;i<E[u].size();i++)
{
int v=E[u][i];
Depth[v]=Depth[u]+1;
Parent[v][0]=u;
dfs(v);
}
return;
}
int LCA(int a,int b)
{
if (Depth[b]>Depth[a])//保证a的深度>=b的深度
swap(a,b);
for (int i=20;i>=0;i--)//把a提到与b高度一致
if ((Parent[a][i]!=0)&&(Depth[Parent[a][i]]>=Depth[b]))
a=Parent[a][i];
if (a==b)
return a;
for (int i=20;i>=0;i--)//把a和b同时向上提
if ((Parent[a][i]!=0)&&(Parent[b][i]!=0)&&(Parent[a][i]!=Parent[b][i]))
{
a=Parent[a][i];
b=Parent[b][i];
}
return Parent[a][0];注意返回值
}
POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors / UVALive 2525 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA)的更多相关文章
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors(最近公共祖先 LCA)
POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors(最近公共祖先 LCA) Description Write a program that takes as input a root ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors 【最近公共祖先LCA算法+Tarjan离线算法】
Nearest Common Ancestors Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 20715 Accept ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors【近期公共祖先LCA】
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/u013912596/article/details/35311489 题目链接:http://poj ...
- [leetcode]236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree二叉树最近公共祖先
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. Accordi ...
- 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree(最低公共祖先,难理解)
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. According ...
- LeetCode OJ:Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree(最近公共祖先)
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. According ...
- POJ 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA + 详解博客)
LCA问题的tarjan解法模板 LCA问题 详细 1.二叉搜索树上找两个节点LCA public int query(Node t, Node u, Node v) { int left = u.v ...
- HDU 1330 Nearest Common Ancestors(求两个点的近期公共祖先)
题目链接:id=1330">传送门 在线算法: #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstri ...
- POJ 1470 Closest Common Ancestors (最近公共祖先LCA 的离线算法Tarjan)
Tarjan算法的详细介绍,请戳: http://www.cnblogs.com/chenxiwenruo/p/3529533.html #include <iostream> #incl ...
随机推荐
- Akka(4): Routers - 智能任务分配
Actor模式最大的优点就是每个Actor都是一个独立的任务运算器.这种模式让我们很方便地把一项大型的任务分割成若干细小任务然后分配给不同的Actor去完成.优点是在设计时可以专注实现每个Actor的 ...
- No matching provisioning profiles found for "Applications/MyApp.app”问题解决
新开发的一个app打包报错,度娘谷歌了好久,废了不少时间,发现错误提示已经很明显了,只是自己没读懂而已,先说下问题和解决方法,给同意遇到这个问题的你: Failed to locate or gene ...
- JavaSE教程-01初识Java-思维导图
图片看不清楚时: 1)可以将图片另存为图片,保存在本地来查看 2)右击在新标签中打开放大查看. 分解: 1.计算机基本概念的普及 硬件 cpu.内存.硬盘等 软件 系统级软件 Windows.Linu ...
- css让文字在一行内显示
1.例如 p元素,里面的文字不换行显示,超出部分不隐藏 p{ width:100px; word-break:keep-all; white-space:nowrap; } 2.例如 p元素,里面的文 ...
- 工程师倾情奉献-Win7 ISO 精简操作说明
1.前提条件 a)本文档内容只适用于32bit win7 install ISO,其它OS不能保证兼容 b)示范文件为win7-ultimate-rtm-32-en-us-rdvd.iso 2.准备待 ...
- WCF入门的了解准备工作
了解WCF, 及WCF入门需要掌握哪里基本概念? 1.准备工作 >1.1 . XML >1.2 . Web Service >1.3 . 远程处理 (RPC) >1.4. 消 ...
- CSS中的尺寸单位
绝对单位 px: Pixel 像素 pt: Points 磅 pc: Picas 派卡 in: Inches 英寸 mm: Millimeter 毫米 cm: Centimeter 厘米 q: Qua ...
- github用法小结
共享仓库 bare 裸仓库 生成裸仓库时必须以.git结尾. 仓库就相当于一个服务器 ### 创建远程仓库 1. 创建以.git结尾的目录mkdir repo.git 2 ...
- linux下安装telnet
1:yum install telnet-server 2:编辑设置 /etc/xinetd.d/telnet ,将disable= yes设置成disable= no 3:service xine ...
- laydate时间插件更换皮肤
<script> ;!function(){ laydate.skin('molv'); laydate({ elem: '#demo' }) }();</script>
