CF581C Developing Skills 模拟
Petya loves computer games. Finally a game that he's been waiting for so long came out!
The main character of this game has n different skills, each of which is characterized by an integer ai from 0 to 100. The higher the number ai is, the higher is the i-th skill of the character. The total rating of the character is calculated as the sum of the values of 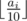 for all i from 1 to n. The expression ⌊ x⌋ denotes the result of rounding the number x down to the nearest integer.
for all i from 1 to n. The expression ⌊ x⌋ denotes the result of rounding the number x down to the nearest integer.
At the beginning of the game Petya got k improvement units as a bonus that he can use to increase the skills of his character and his total rating. One improvement unit can increase any skill of Petya's character by exactly one. For example, if a4 = 46, after using one imporvement unit to this skill, it becomes equal to 47. A hero's skill cannot rise higher more than 100. Thus, it is permissible that some of the units will remain unused.
Your task is to determine the optimal way of using the improvement units so as to maximize the overall rating of the character. It is not necessary to use all the improvement units.
The first line of the input contains two positive integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ k ≤ 107) — the number of skills of the character and the number of units of improvements at Petya's disposal.
The second line of the input contains a sequence of n integers ai (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100), where ai characterizes the level of the i-th skill of the character.
The first line of the output should contain a single non-negative integer — the maximum total rating of the character that Petya can get using k or less improvement units.
2 4
7 9
2
3 8
17 15 19
5
2 2
99 100
20
In the first test case the optimal strategy is as follows. Petya has to improve the first skill to 10 by spending 3 improvement units, and the second skill to 10, by spending one improvement unit. Thus, Petya spends all his improvement units and the total rating of the character becomes equal to lfloor frac{100}{10} rfloor + lfloor frac{100}{10} rfloor = 10 + 10 = 20.
In the second test the optimal strategy for Petya is to improve the first skill to 20 (by spending 3 improvement units) and to improve the third skill to 20 (in this case by spending 1 improvement units). Thus, Petya is left with 4 improvement units and he will be able to increase the second skill to 19 (which does not change the overall rating, so Petya does not necessarily have to do it). Therefore, the highest possible total rating in this example is 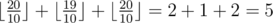 .
.
In the third test case the optimal strategy for Petya is to increase the first skill to 100 by spending 1 improvement unit. Thereafter, both skills of the character will be equal to 100, so Petya will not be able to spend the remaining improvement unit. So the answer is equal to 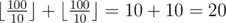 .
.
注意一些坑点即可;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 1000005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9 + 7;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-4
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
inline ll rd() {
ll x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ int n, k;
int a[maxn];
struct node {
int dt;
int org;
}d[maxn];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.dt < b.dt;
}
int main() {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)rdint(a[i]), d[i].org = a[i];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (d[i].org % 10 != 0) {
int tp = (d[i].org / 10 + 1) * 10;
d[i].dt = tp - d[i].org;
}
else if (d[i].org != 0 && d[i].org % 10 == 0)d[i].dt = 0;
else if (d[i].org == 0)d[i].dt = 10;
} sort(d + 1, d + 1 + n, cmp);
int cnt = 1;
int sy = 0;
while (k > 0) {
if (cnt == 1) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (k >= d[i].dt) {
k -= d[i].dt;
d[i].org += d[i].dt;
ans += (d[i].org / 10);
if (d[i].org <= 100) {
sy += 100 - (d[i].org);
}
}
else {
ans += (d[i].org / 10);
}
}
cnt++;
if (k <= 0)break;
}
else {
ans += (min(sy, k)) / 10;
k = 0;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
CF581C Developing Skills 模拟的更多相关文章
- cf581C Developing Skills
Petya loves computer games. Finally a game that he's been waiting for so long came out! The main cha ...
- Codeforces Round #322 (Div. 2) C. Developing Skills 优先队列
C. Developing Skills Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/581/p ...
- codeforces 581C. Developing Skills 解题报告
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/581/C 题目意思:给出 n 个数:a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100).给出值 ...
- Developing Skills
题目传送门:点击打开链接 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include < ...
- 【Henu ACM Round#19 C】 Developing Skills
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 优先把不是10的倍数的变成10的倍数. (优先%10比较大的数字增加 如果k还有剩余. 剩下的数字都是10的倍数了. 那么先加哪一个 ...
- Codeforces Round #322 (Div. 2)
水 A - Vasya the Hipster /************************************************ * Author :Running_Time * C ...
- codeforces581C
Developing Skills CodeForces - 581C 你在玩一个游戏.你操作的角色有n个技能,每个技能都有一个等级ai.现在你有k次提升技能的机会(将其中某个技能提升一个等级,可以重 ...
- How do I learn mathematics for machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-mathematics-for-machine-learning How do I learn mathematics f ...
- 每日英语:A Better Way To Treat Anxiety
Getting up the nerve to order in a coffee shop used to be difficult for 16-year-old Georgiann Steely ...
随机推荐
- ORACLE——日期时间格式化参数详解 之二
2.8 DD 指定日期在当月中第几天(范围:1-31) SQL> select to_char(sysdate,'DD YYYY-MM-DD PM hh24:mi:ss ') from dual ...
- 用JS实现,图片放大和缩小
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- 如何在Eclipse下查看JDK源代码以及java源代码阅读方法(转载)
不会看JDK源代码,相当于没学过Java. 网上不容易找到一篇帮助我解决了如何在Eclipse下查看JDK源代码 的文章. 核心提示:在Eclipse中查看JDK类库的源代码!!! 设置: 1.点 w ...
- Android 数据库 OrmLite Failed to open database
04-01 16:49:32.720: E/SQLiteLog(1894): (14) cannot open file at line 30204 of [00bb9c9ce4]04-01 16:4 ...
- 定位程序问题出现的原因工具-jstack
jstack还可以生成线程快照 如何使用jstack: 1.打开命令行,输入jstack 在任务管理器中就可看到对应进程id 2.在命令行中输入 jstack -l 进程id 这样就可得到进程中所有的 ...
- sqlplus 连接数据库执行SP
.bashrc export HOME= export LANG="C" .bash_profile #明码 #export LOG_USER=lhcx #export LOG_P ...
- Java-马士兵设计模式学习笔记-工厂模式-模拟Spring读取Properties文件
一.目标:读取properties文件,获得类名来生成对象 二.类 1.Movable.java public interface Movable { void run(); } 2.Car.java ...
- 红帽企业版RHEL7.1在研域工控板上,开机没有登陆窗口 -- 编写xorg.conf 简单三行解决Ubuntu分辩率不可调的问题
红帽企业版RHEL7.1在研域工控板上,开机没有登陆窗口 没有登陆窗口 的原因分析: 没有登陆窗口的原因是因为有多个屏幕在工作,其中一个就是build-in 屏幕(内置的虚拟屏幕)和外接的显示器,并且 ...
- linux deb及rpm格式软件安装
deb格式软件安装 deb包是debian,ubuntu等LINUX发行版的软件安装包,是类似于rpm的软件包,而非debian,ubuntu系统不推荐使用deb软件包,因为要解决软件包依赖问题,安装 ...
- linux下top命令参数解释
top命令是Linux下常用的性能分析工具,能够实时显示系统中各个进程的资源占用状况,类似于Windows的任务管理器.下面详细介绍它的使用方法. top - 01:06:48 up 1:22, 1 ...
