机器学习作业(三)多类别分类与神经网络——Matlab实现
题目太长了!下载地址【传送门】
第1题
简述:识别图片上的数字。
第1步:读取数据文件:
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this part of the exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10) % Load Training Data
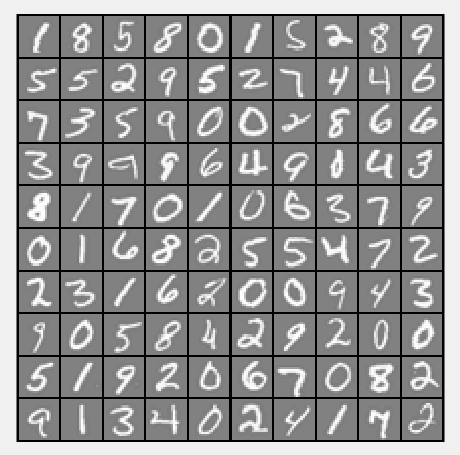
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n') load('ex3data1.mat'); % training data stored in arrays X, y
m = size(X, 1); % Randomly select 100 data points to display
rand_indices = randperm(m);
sel = X(rand_indices(1:100), :); displayData(sel);
第2步:实现displayData函数:
function [h, display_array] = displayData(X, example_width) % Set example_width automatically if not passed in
if ~exist('example_width', 'var') || isempty(example_width)
example_width = round(sqrt(size(X, 2)));
end % Gray Image
colormap(gray); % Compute rows, cols
[m n] = size(X);
example_height = (n / example_width); % Compute number of items to display
display_rows = floor(sqrt(m));
display_cols = ceil(m / display_rows); % Between images padding
pad = 1; % Setup blank display
display_array = - ones(pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad), ...
pad + display_cols * (example_width + pad)); % Copy each example into a patch on the display array
curr_ex = 1;
for j = 1:display_rows
for i = 1:display_cols
if curr_ex > m,
break;
end
% Copy the patch % Get the max value of the patch
max_val = max(abs(X(curr_ex, :)));
display_array(pad + (j - 1) * (example_height + pad) + (1:example_height), ...
pad + (i - 1) * (example_width + pad) + (1:example_width)) = ...
reshape(X(curr_ex, :), example_height, example_width) / max_val;
curr_ex = curr_ex + 1;
end
if curr_ex > m,
break;
end
end % Display Image
h = imagesc(display_array, [-1 1]); % Do not show axis
axis image off drawnow; end
运行结果:
第3步:计算θ:
lambda = 0.1;
[all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda);
其中oneVsAll函数:
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda) % Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2); % You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; for c = 1:num_labels,
initial_theta = zeros(n+1, 1);
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
[theta] = ...
fmincg(@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y==c), lambda)), initial_theta, options);
all_theta(c,:) = theta;
end; end
第4步:实现lrCostFunction函数:
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda) % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); theta2 = theta(2:end,1);
h = sigmoid(X*theta);
J = 1/m*(-y'*log(h)-(1-y')*log(1-h)) + lambda/(2*m)*sum(theta2.^2);
theta(1,1) = 0;
grad = 1/m*(X'*(h-y)) + lambda/m*theta; grad = grad(:); end
第5步:实现sigmoid函数:
function g = sigmoid(z)
g = 1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z));
end
第6步:计算预测的准确性:
pred = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);
其中predictOneVsAll函数:
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X) m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; g = zeros(size(X, 1), num_labels);
for c = 1: num_labels,
theta = all_theta(c, :);
g(:, c) = sigmoid(X*theta');
end [value, p] = max(g, [], 2); end
运行结果:

第2题
简介:使用神经网络实现数字识别(Θ已提供)
第1步:读取文档数据:
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25; % 25 hidden units
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10) % Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n') load('ex3data1.mat');
m = size(X, 1); % Randomly select 100 data points to display
sel = randperm(size(X, 1));
sel = sel(1:100); displayData(X(sel, :)); % Load the weights into variables Theta1 and Theta2
load('ex3weights.mat');
第2步:实现神经网络:
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);
其中predict函数:
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X) % Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); X = [ones(m,1) X];
z2 = X*Theta1';
a2 = sigmoid(z2);
a2 = [ones(size(a2, 1), 1) a2];
z3 = a2*Theta2';
a3 = sigmoid(z3)
[values, p] = max(a3, [], 2) end
运行结果:
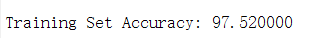
第3步:实现单个数字识别:
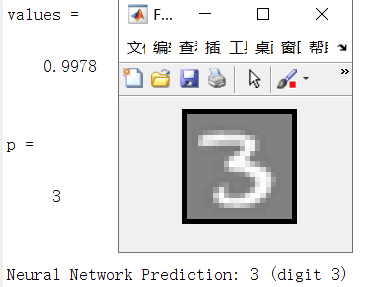
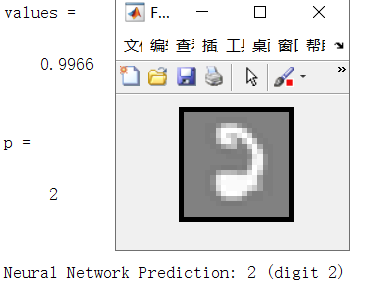
rp = randperm(m); for i = 1:m
% Display
fprintf('\nDisplaying Example Image\n');
displayData(X(rp(i), :)); pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X(rp(i),:));
fprintf('\nNeural Network Prediction: %d (digit %d)\n', pred, mod(pred, 10)); % Pause with quit option
s = input('Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:','s');
if s == 'q'
break
end
end
运行结果:

机器学习作业(三)多类别分类与神经网络——Matlab实现的更多相关文章
- 机器学习作业(三)多类别分类与神经网络——Python(numpy)实现
题目太长了!下载地址[传送门] 第1题 简述:识别图片上的数字. import numpy as np import scipy.io as scio import matplotlib.pyplot ...
- 机器学习入门16 - 多类别神经网络 (Multi-Class Neural Networks)
原文链接:https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/multi-class-neural-networks/ 多类别分类, ...
- 機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations) 机器学习基石 作业三 课后习题解答
今天和大家分享coursera-NTU-機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations)-作业三的习题解答.笔者在做这些题目时遇到非常多困难,当我在网上寻找答案时却找不到,而林 ...
- 机器学习实验报告:利用3层神经网络对CIFAR-10图像数据库进行分类
PS:这是6月份时的一个结课项目,当时的想法就是把之前在Coursera ML课上实现过的对手写数字识别的方法迁移过来,但是最后的效果不太好… 2014年 6 月 一.实验概述 实验采用的是CIFAR ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络
Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7365730.html 前言 ...
- 斯坦福深度学习与nlp第四讲词窗口分类和神经网络
http://www.52nlp.cn/%E6%96%AF%E5%9D%A6%E7%A6%8F%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E4%B8%8Enlp%E7%A ...
- 用Python开始机器学习(2:决策树分类算法)
http://blog.csdn.net/lsldd/article/details/41223147 从这一章开始进入正式的算法学习. 首先我们学习经典而有效的分类算法:决策树分类算法. 1.决策树 ...
- 吴恩达《深度学习》-第一门课 (Neural Networks and Deep Learning)-第三周:浅层神经网络(Shallow neural networks) -课程笔记
第三周:浅层神经网络(Shallow neural networks) 3.1 神经网络概述(Neural Network Overview) 使用符号$ ^{[
- 基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,详解自然语言处理
摘要:这篇文章将详细讲解自然语言处理过程,基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,并进行了各种分类算法(SVM.RF.LR.Boosting)对比 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python人工智能] ...
随机推荐
- pikachu-服务器端请求伪造SSRF(Server-Side Request Forgery)
一.SSRF概述(部分内容来自pikachu平台) SSRF(Server-Side Request Forgery:服务器端请求伪造),其形成的原因大都是由于服务端提供了从其他服务器应用获取数据的功 ...
- SpringCloud之Ribbon负载均衡的入门操作
使用Ribbon进行负载均衡 在使用Ribbon之前,我们先想一个之前的问题,之前我们将服务提供者注册进了eureka注册中心,但是在消费者端,我们还是使用的restTemplate调用的时候,其中写 ...
- iOS 中事件的响应链和传递链
iOS事件链有两条:事件的响应链:Hit-Testing事件的传递链 响应链:由离用户最近的view向系统传递.initial view –> super view –> ….. –> ...
- redis 5.0.7 源码阅读——压缩列表ziplist
redis中压缩列表ziplist相关的文件为:ziplist.h与ziplist.c 压缩列表是redis专门开发出来为了节约内存的内存编码数据结构.源码中关于压缩列表介绍的注释也写得比较详细. 一 ...
- python 语言打印直角三角形的几种方法
方法1:全部打印语句 print('*') print('**') print('***') print('****') 方法2:简单使用循环 for i in range(5): print('*' ...
- [CodeIgniter4]讲解-启动流程
https://codeigniter.org.cn/forums/thread-31030-1-1.html CodeIgniter 是一个小巧但功能强大的 PHP 框架,作为一个简单而“优雅”的工 ...
- opencv —— imread、namedWindow & imshow、cvtColor、imwrite 加载、显示、修改、保存图像
加载图像:imread 函数 Mat imread(const string& filename, int flags = 1): filename:需要载入的图像的路径名. flags:加载 ...
- C# SQLITE 使用文档
https://www.devart.com/dotconnect/sqlite/docs/Devart.Data.SQLite~Devart.Data.SQLite_namespace.html 有 ...
- 解决问题:当redis服务端断开的时候`进程会崩溃(转载6哥笔记)
package main import ( "fmt" "github.com/astaxie/beego/logs" "github.com/gar ...
- Math, Date,JSON对象
Math 对象 Math是 JavaScript 的原生对象,提供各种数学功能.该对象不是构造函数,不能生成实例,所有的属性和方法都必须在Math对象上调用. 静态属性 Math对象的静态属性,提供以 ...
