LCT[Link-Cut-Tree学习笔记]
部分摘抄于
FlashHu
candy99
所以文章篇幅较长 请有足够的耐心(不是
其实不用学好splay再学LCT的…/kk (至少现在我平衡树靠fhq)
也许我菜吧…LCT靠背板子 pushup靠理解…没救了/kk
简单讲讲LCT
至于树链剖分 建议在LCT之前学(?
反正我blog里也有
一【理论知识】
-Link-Cut-Tree(简称LCT)是解决动态树类问题一种数据结构
-Preferred Child:重儿子,重儿子与父亲节点在同一棵Splay中,一个节点最多只能有一个重儿子
-Preferred Edge:重边,连接父亲节点和重儿子的边
-Preferred Path :重链,由重边及重边连接的节点构成的链
-Auxiliary Tree(辅助树)
由一条重链上的所有节点所构成的Splay称作这条链的辅助树
每个点的键值为这个点的深度,即这棵Splay的中序遍历是这条链从链顶到链底的所有节点构成的序列
辅助树的根节点的父亲指向链顶的父亲节点,然而链顶的父亲节点的儿子并不指向辅助树的根节点
(也就是说父亲不认轻儿子只认重儿子,儿子都认父亲)
这条性质为后来的操作提供了依据
原树与辅助树的关系
原树中的重链 -> 辅助树中两个节点位于同一棵Splay中
原树中的轻链 -> 辅助树中子节点所在Splay的根节点的father指向父节点
注意原树与辅助树的结构并不相同
辅助树的根节点≠原树的根节点
辅助树中的father≠原树中的father
辅助树是不断变化的,重链和轻链不断变化
二【实现】
LCT用到的Splay和通常的还是有点不同,没有权值v,不进行查找操作,点编号就是原树的编号
因为是一个Splay森林,多条重链多个根,所以用isRoot(x)判断是否为根,判断isRoot(x)相当于判断x的父亲存不存在
-rotate只是设置g的儿子时判断isRoot(f)就行了
-splay需要pushDown了(因为没有kth了),也是判断isRoot(pa)
-Access和Cut更新了儿子关系,所以需要update
-Access 将一个点与原先的重儿子切断,并使这个原树上点到根路径上的边全都变为重边
所以 这个节点到根的路径上的所有节点形成了一棵Splay
便于操作或查询节点到根路径上的所有节点
实现:不断把x splay到当前Atree的根,然后它的右子树就是重儿子了,修改;用y辅助 注意:Access后x不一定为这颗Splay的根,因为中途x变fa了 维护了节点信息别忘更新
MakeRoot 将x设为原树的根实现:Access后splay到根,然后全在x的左子树上(权值是深度),区间翻转即可
FindRoot 找x所在原树根,判连通性 实现:MakeRoot后不断往左找(不需要pushDown?加上也可以啊。不加也对因为只是来判连通,判断是不是在一棵原树上,都不pushDown找到的还是同一个点吧)
Link 实现:MakeRoot(x)然后t[x].fa=y
Cut 实现:MakeRoot(x)然后Access(y) splay(y) ,x就在y的左儿子了,t[y].ch[0]=t[x].fa=0;
维护了节点信息别忘更新
对x到y路径上的点进行修改或查询
只需要对x进行Move_To_Root操作,然后对y进行Access+Splay操作,那么x到y路径上的所有点都在以y为根的子树上
因为Access后x和y重链在一棵Splay上,x深度比y小
====================================================================== 以上是 candy99 巨佬的总结内容(?
像树剖一样……将某一个儿子的连边划分为实边,而连向其他子树的边划分为虚边。
区别在于虚实是可以动态变化的,因此要使用更高级、更灵活的Splay来维护每一条由若干实边连接而成的实链。
基于性质更加优秀的实链剖分,LCT(Link-Cut Tree)应运而生。
LCT维护的对象其实是一个森林。
在实链剖分的基础下,LCT资磁更多的操作
- 查询、修改链上的信息(最值,总和等)
- 随意指定原树的根(即换根)
- 动态连边、删边
- 合并两棵树、分离一棵树(跟上面不是一毛一样吗)
- 动态维护连通性(代替并查集)
边分为实边和虚边,实边包含在Splay中,而虚边总是由一棵Splay指向另一个节点(指向该Splay中中序遍历最靠前的点在原树中的父亲)。
因为性质2,当某点在原树中有多个儿子时,只能向其中一个儿子拉一条实链(只认一个儿子),而其它儿子是不能在这个Splay中的。
那么为了保持树的形状,我们要让到其它儿子的边变为虚边,由对应儿子所属的Splay的根节点的父亲指向该点,而从该点并不能直接访问该儿子(认父不认子)。
接着往下看…
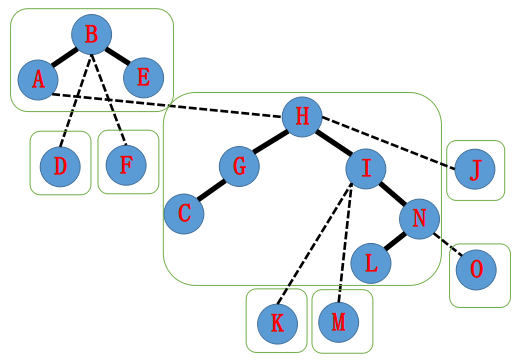
有一棵树,假设一开始实边和虚边是这样划分的(虚线为虚边)
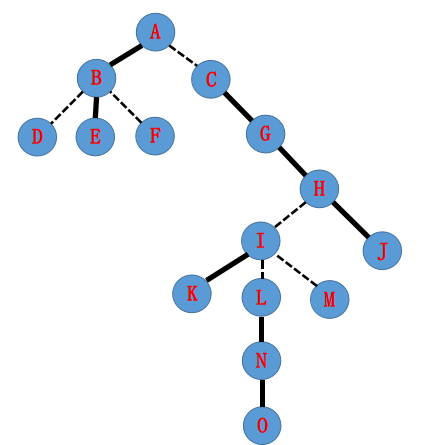
那么所构成的LCT可能会长这样(绿框中为一个Splay,可能不会长这样,但只要满足中序遍历按深度递增(性质1)就对结果无影响)
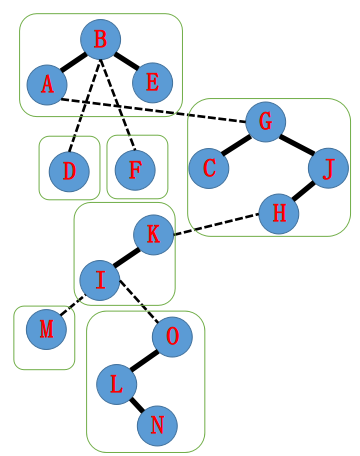
现在我们要access(N),把A−N的路径拉起来变成一条Splay。
因为性质2,该路径上其它链都要给这条链让路,也就是把每个点到该路径以外的实边变虚。
所以我们希望虚实边重新划分成这样。
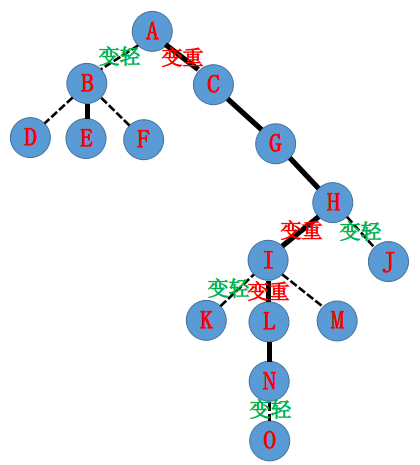
然后怎么实现呢?
我们要一步步往上拉。
首先把splay(N),使之成为当前Splay中的根。
为了满足性质2,原来N−O的重边要变轻。
因为按深度O在N的下面,在Splay中O在N的右子树中,所以直接单方面将N的右儿子置为0(认父不认子)
然后就变成了这样——

我们接着把N所属Splay的虚边指向的I(在原树上是L的父亲)也转到它所属Splay的根,splay(I)。
原来在I下方的重边I−K要变轻(同样是将右儿子去掉)。
这时候I−L就可以变重了。因为L肯定是在I下方的(刚才L所属Splay指向了I),所以I的右儿子置为N,满足性质1。
然后就变成了这样——
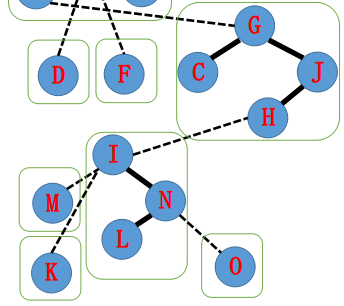
I指向H,接着splay(H),H的右儿子置为I。
H指向A,接着splay(A),A的右儿子置为H。
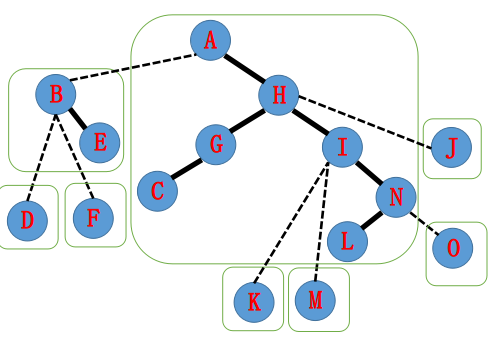
A−N的路径已经在一个Splay中了,大功告成!
代码其实很简单。循环处理,只有四步——
转到根;
换儿子;
更新信息;
当前操作点切换为轻边所指的父亲,转1
inline void access(int x) { for(int tp = 0 ; x ; x = fa[tp = x]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , pushup(x) ; }
只是把根到某个节点的路径拉起来并不能满足我们的需要。更多时候,我们要获取指定两个节点之间的路径信息。
然而一定会出现路径不能满足按深度严格递增的要求的情况。根据性质1,这样的路径不能在一个Splay中。
Then what can we do?
makeroot定义为换根,让指定点成为原树的根。
这时候就利用到access(x)和Splay的翻转操作。
access(x)后x在Splay中一定是深度最大的点对吧。
splay(x)后,x在Splay中将没有右子树(性质1)。于是翻转整个Splay,使得所有点的深度都倒过来了,x没了左子树,反倒成了深度最小的点(根节点),达到了我们的目的。
代码
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; pushr(x) ; }
findroot(x)
找x所在原树的树根,主要用来判断两点之间的连通性(findroot(x)==findroot(y)表明x,y在同一棵树中)
inline int findroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; while(ls(x)) { pushdown(x) ; x = ls(x) ; splay(x) ; } return x ; }
同样利用性质1,不停找左儿子,因为其深度一定比当前点深度小。
split(x,y)
神奇的makeroot已经出现,我们终于可以访问指定的一条在原树中的链啦!
split(x,y)定义为拉出x−y的路径成为一个Splay(本蒟蒻以y作为该Splay的根)
inline void split(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; }
Link 和 Cut 就是字面意思 连边建边 具体写法
inline void cut(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; if(findroot(y) == x && fa[y] == x && ! ls(y)) fa[y] = ls(x) = 0 , pushup(x) ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; if(findroot(y) != x) fa[x] = y ; }
下面给板子和题目(?
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;
int n , m , val[N] ;
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
class LCT {
public:
int ch[N][2] , fa[N] , sum[N] , rev[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline bool getr(int x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline void pushup(int x) { sum[x] = sum[ls(x)] ^ sum[rs(x)] ^ val[x] ; }
inline void pushr(int x) { rev[x] ^= 1 ; swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; }
inline void pushdown(int x) { if(rev[x]) { if(ls(x)) pushr(ls(x)) ; if(rs(x)) pushr(rs(x)) ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; } }
inline void rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] , k = getr(x) , w = ch[x][k ^ 1] ; if(! isroot(y)) ch[z][getr(y)] = x ;
fa[fa[fa[ch[ch[x][k ^ 1] = y][k] = w] = y] = x] = z ; pushup(y) ; pushup(x) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushdown(x) ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ; while(! isroot(x)) { int y = fa[x] ; if(! isroot(y)) rotate(getr(x) ^ getr(y) ? x : y) ; rotate(x) ; }
}
inline void access(int x) { for(int tp = 0 ; x ; x = fa[tp = x]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , pushup(x) ; }
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; pushr(x) ; }
inline void split(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; }
inline int findroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; while(ls(x)) { pushdown(x) ; x = ls(x) ; splay(x) ; } return x ; }
inline void cut(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; if(findroot(y) == x && fa[y] == x && ! ls(y)) fa[y] = ls(x) = 0 , pushup(x) ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; if(findroot(y) != x) fa[x] = y ; }
inline void change(int x , int y) { splay(x) ; val[x] = y ; }
inline int query(int x , int y) { return split(x , y) , sum[y] ; }
} lct ;
signed main() {
n = read() ; m = read() ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> val[i] ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
int opt = read() ;
if(opt == 0) { int x = read() , y = read() ; printf("%d\n" , lct.query(x , y)) ; }
if(opt == 1) { int x = read() , y = read() ; lct.link(x , y) ; }
if(opt == 2) { int x = read() , y = read() ; lct.cut(x , y) ; }
if(opt == 3) { int x = read() , y = read() ; lct.change(x , y) ; }
}
return 0 ;
}
[国家集训队]Tree II
带修的LCT 就直接像线段树一样放标记然后搞一下更新就可以了
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using uint = unsigned int ;
using namespace std ;
const int N = 1e5 + 5 ;
const int Mod = 51061 ;
uint n , q , fa[N] , ch[N][2] , val[N] , sum[N] , sz[N] , mul[N] , add[N] ;
bool rev[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline void Add(uint & x , uint y) { x += y ; x %= Mod ; }
inline void Mul(uint & x , uint y) { x *= y ; x %= Mod ; }
inline bool isroot(uint x) { return (ls(fa[x]) != x) && (rs(fa[x]) != x) ; }
inline void pushup(uint x) { sum[x] = (sum[ls(x)] + sum[rs(x)] + val[x]) ; sum[x] %= Mod ; sz[x] = (sz[ls(x)] + sz[rs(x)] + 1) ; }
inline void pushr(uint x) { swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; }
inline void pushm(uint x , uint v) { Mul(sum[x] , v) ; Mul(val[x] , v) ; Mul(mul[x] , v) ; Mul(add[x] , v) ; }
inline void pusha(uint x , uint v) { Add(sum[x] , v * sz[x]) ; Add(val[x] , v) ; Add(add[x] , v) ; }
inline void pushdown(uint x) {
if(mul[x] != 1) { pushm(ls(x) , mul[x]) ; pushm(rs(x) , mul[x]) ; mul[x] = 1 ; }
if(add[x]) { pusha(ls(x) , add[x]) ; pusha(rs(x) , add[x]) ; add[x] = 0 ; }
if(rev[x]) { if(ls(x)) pushr(ls(x)) ; if(rs(x)) pushr(rs(x)) ; rev[x] = 0 ; }
}
inline bool getr(uint x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline void rotate(uint x) { uint y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] , k = getr(x) , w = ch[x][k ^ 1] ;
if(! isroot(y)) ch[z][getr(y)] = x ;
ch[x][k ^ 1] = y ; ch[y][k] = w ;
if(w) fa[w] = y ; fa[y] = x ; fa[x] = z ;
pushup(y) ;
}
inline void pushall(uint x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushdown(x) ; }
inline void splay(uint x) { pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) { uint y = fa[x] ;
if(! isroot(y)) { rotate(getr(y) ^ getr(x) ? x : y) ; }
rotate(x) ;
} pushup(x) ;
}
inline void access(uint x) { for(uint tp = 0 ; x ; tp = x , x = fa[tp]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , pushup(x) ; }
inline void makeroot(uint x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; pushr(x) ; }
inline void split(uint x , uint y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; }
inline void link(uint x , uint y) { makeroot(x) ; fa[x] = y ; }
inline void cut(uint x , uint y) { split(x , y) ; fa[x] = ls(y) = 0 ; }
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false) ;
cin.tie(nullptr) ;
cout.tie(nullptr) ;
cin >> n >> q ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) val[i] = mul[i] = 1 ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n - 1 ; i ++) { uint u , v ; cin >> u >> v ; link(u , v) ; }
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= q ; i ++) {
char c ; cin >> c ;
if(c == '+') { uint u , v , w ; cin >> u >> v >> w ; split(u , v) ; pusha(v , w) ; }
if(c == '-') { uint u , v , u2 , v2 ; cin >> u >> v >> u2 >> v2 ; cut(u , v) ; link(u2 , v2) ; }
if(c == '*') { uint u , v , w ; cin >> u >> v >> w ; split(u , v) ; pushm(v , w) ; }
if(c == '/') { uint u , v ; cin >> u >> v ; split(u , v) ; cout << sum[v] << '\n' ; }
}
return 0 ;
}
板子…不说了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
#define csp rp++
inline int read() { register int x = 0 , f = 1 ; register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
int n ;
const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;
int val[N] ;
int ch[N][2] ; int fa[N] ; int sum[N] ; bool rev[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline bool getr(int x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline void pushup(int x) { sum[x] = sum[ls(x)] + sum[rs(x)] + val[x] ; }
inline void pushr(int x) {
if(! rev[x]) return ;
swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ;
rev[ls(x)] ^= 1 ; rev[rs(x)] ^= 1 ; rev[x] = 0 ;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ;
int k = getr(x) , w = ch[x][k ^ 1] ;
ch[y][k] = w ; fa[w] = y ;
if(! isroot(y)) ch[z][getr(y)] = x ;
fa[x] = z ; ch[x][k ^ 1] = y ; fa[y] = x ;
pushup(x) ; pushup(y) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushr(x) ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ;
if(! isroot(y)) rotate((ls(fa[x]) == x) ^ (ls(fa[y]) == y) ? x : y) ;
rotate(x) ;
} pushup(x) ;
}
inline void access(int x) { for( int tp = 0 ; x ; x = fa[tp = x]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , pushr(x) ; }
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; }
inline void split(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; }
inline int findroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; while(ls(x)) pushr(x) , x = ls(x) ; return x ; }
inline bool chk(int x , int y) { return findroot(x) == findroot(y) ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; fa[x] = y ; }
signed main() {
n = read() ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) val[i] = read() ;
for(register int t = read() ; t -- ; ) {
char op[20] ; scanf("%s" , op + 1) ;
int x = read() , y = read() ;
if(op[1] == 'p') splay(x) , val[x] = y ;
if(op[1] == 'b') { if(chk(x , y)) puts("no") ;
else puts("yes") , link(x , y) ;
}
if(op[1] == 'e') {
if(! chk(x , y)) puts("impossible") ;
else split(x , y) , printf("%d\n" , sum[y]) ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmax(T & x , T y) {
return x < y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmin(T & x , T y) {
return x > y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cabs(T & x) {
return x > 0 ? 1 : (x = - x) , 0 ;
}
inline int QP(int x , int y , int Mod) {
int ans = 1 ;
for( ; y ; y >>= 1 , x = (x * x) % Mod)
if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % Mod ;
return ans ;
}
int n , m ;
const static int N = 3e5 + 10 ;
int val[N] ;
class LCT {
public :
int ch[N][2] ; int fa[N] , sum[N] , rev[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline void push_up(int x) { sum[x] = sum[ls(x)] ^ sum[rs(x)] ^ val[x] ; }
inline void rever(int x) { swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; }
inline void push_down(int x) { if(rev[x]) {if(ls(x)) rever(ls(x)) ; if(rs(x)) rever(rs(x)) ; rev[x] = 0 ; } }
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline void rotate(int x) {
int fx = fa[x] , fy = fa[fx] , rs = (x == rs(fa[x])) , mus = ch[x][! rs] ;
if(! isroot(fx)) ch[fy][fx == rs(fy)] = x ;
ch[x][! rs] = fx ; ch[fx][rs] = mus ;
if(mus) fa[mus] = fx ; fa[x] = fy , fa[fx] = x ;
push_up(fx) , push_up(x) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; push_down(x) ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int fx = fa[x] , fy = fa[fx] ;
if(! isroot(fx)) rotate(((ls(fx) == x) ^ (ls(fy) == fx)) ? x : fx) ;
rotate(x) ;
}
}
inline void access(int x) { for(int tp = 0 ; x ; tp = x , x = fa[tp]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , push_up(x) ;}
inline void make_root(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; rever(x) ; }
inline int find_root(int x){ access(x) ; splay(x) ; while(ls(x)) push_down(x) , x = ls(x) ; splay(x) ; return x ; }
inline void split(int x , int y) { make_root(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; }
inline void cut(int x , int y) { make_root(x) ; if(find_root(y) == x && fa[y] == x && ! ls(y)) fa[y] = rs(x) = 0 , push_up(x) ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { make_root(x) ; if(find_root(y) != x) fa[x] = y ; }
} lct ;
inline int getopt() {
register char c = getchar() ;
string s = "" ;
while(isspace(c)) c = getchar() ;
while(! isspace(c)) s += c , c = getchar() ;
if(s == "Connect") return 1 ;
if(s == "Destroy") return 2 ;
if(s == "Query") return 3 ;
}
signed main() {
n = read() , m = read() ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
int opt = getopt() ;
int u = read() , v = read() ;
if(opt == 1) lct.link(u , v) ;
if(opt == 2) lct.cut(u , v) ;
if(opt == 3) puts(lct.find_root(u) == lct.find_root(v) ? "Yes" : "No") ;
}
return 0 ;
}
因为颜色不超过20种所以20个LCT不断删边加边就可以了……边用map存一下
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmax(T & x , T y) {
return x < y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmin(T & x , T y) {
return x > y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cabs(T & x) {
return x > 0 ? 1 : (x = - x) , 0 ;
}
inline int QP(int x , int y , int Mod) {
int ans = 1 ;
for( ; y ; y >>= 1 , x = (x * x) % Mod)
if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % Mod ;
return ans ;
}
int n , m , c , k ;
const int N = 1e4 + 10 ;
int val[N] ;
class LCT {
public :
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
int fa[N] , ch[N][2] , rev[N] , cnt[N] , mx[N] ; int s[N] ; int top ;
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline void pushup(int x){mx[x]=val[x];
if(ls(x)) cmax(mx[x],mx[ls(x)]);
if(rs(x)) cmax(mx[x],mx[rs(x)]);
}
inline void pushdown(int x){
if(x&&rev[x]){
swap(ls(x),rs(x));
rev[ls(x)]^=1,rev[rs(x)]^=1;
rev[x]=0;
}
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int y=fa[x],z=fa[y],d=rs(y)==x;
if(!isroot(y)) ch[z][rs(z)==y]=x;
fa[x]=z;fa[y]=x;fa[ch[x][d^1]]=y,ch[y][d]=ch[x][d^1];ch[x][d^1]=y;
pushup(y);
}
// inline void pushall(int x){if(!isroot(x))pushall(fa[x]);pushdown(x);}
inline void splay(int x){
// pushall(x);
s[top=1]=x;
for(int i=x;!isroot(i);i=fa[i])s[++top]=fa[i];
while(top)pushdown(s[top--]);
for(int y=fa[x],z=fa[y];!isroot(x);y=fa[x],z=fa[y]){
if(!isroot(y))rotate((rs(y)==x)^(rs(z)==y)?x:y);
rotate(x);
}pushup(x);
return ;
}
inline void access(int x){
for(register int y = 0; x ; x = fa[y=x])
splay(x),rs(x)=y,pushup(x);
return ;
}
inline void makeroot(int x){ access(x);splay(x);rev[x]^=1;}
inline void split(int x,int y){makeroot(x);access(y);splay(y);}
inline void link(int x,int y){++ cnt[x] , ++ cnt[y] , makeroot(x),fa[x]=y;splay(x);}
inline void cut(int x,int y){--cnt[x],--cnt[y],split(x,y),fa[x]=ls(y)=0,pushup(y);}
inline int findroot(int x){access(x),splay(x),pushdown(x);while(ls(x))pushdown(x=ls(x));return x;}
inline int query(int x,int y){split(x,y);return mx[y];}
} ;
LCT lct[15] ;
struct node{
int u,v;
inline bool operator <(const node & x) const {
return u < x.u || (u == x.u && v < x.v) ;
}
} ; map < node , int > mp ;
signed main() {
n = read() , m = read() , c = read() ,k = read();
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) val[i] = read() ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
int u = read() , v = read() , w = read() ;
node edge1 = {u,v};
node edge2 = {v,u};
mp[edge1]=mp[edge2]=w;
lct[w].link(u,v);
}
while(k -- ) {
int opt = read() ;
if(opt == 0) {
int x = read() , w = read() ;
val[x] = w ;
for(register int i = 0 ; i < c ; i ++)
lct[i].splay(x) ;
}
if(opt == 1) {
int u = read(),v=read(),w = read() ;
node edge1 = {u , v} ;
node edge2 = {v , u} ;
if(! mp.count(edge1)) { puts("No such edge.") ; continue ;}
int x = mp[edge1] ;
if(x == w) { puts("Success.") ; continue ;}
if(lct[w].cnt[u]>=2 || lct[w].cnt[v]>=2) {
puts("Error 1.") ;
continue ;
}
if(lct[w].findroot(u) == lct[w].findroot(v)){
puts("Error 2.") ;
continue ;
}
puts("Success.");
lct[x].cut(u , v) ;
lct[w].link(u , v);
mp[edge1]=mp[edge2]=w;
}
if(opt == 2){
int w = read() , u = read() , v = read() ;
if(lct[w].findroot(u) != lct[w].findroot(v)) {
puts("-1") ;
continue ;
}
printf("%lld\n" , lct[w].query(u,v)) ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
[AH2017/HNOI2017]单旋
这题有点烦 不太想讲…
每次单旋只会取maxormin,那么手玩发现,这样树的形态基本不变!
那么我们可以直接把x提上去,这是手动维护Spaly的形态,
我们想怎么统计答案呢?暴力跳显然是会T的,这里实质是查询点到根的距离,
可以考虑使用LCT维护,这样就直接查询点到根的路径长度就可以了
然后直接无脑set维护一下就可以了
// Isaunoya
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmax(T & x , T y) {
return x < y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmin(T & x , T y) {
return x > y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
inline int QP(int x , int y , int Mod){ int ans = 1 ;
for( ; y ; y >>= 1 , x = (x * x) % Mod)
if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % Mod ;
return ans ;
}
const int N = 1e6 + 10 ;
int ch[N][2] ;
int tot = 0 ;
int fa[N] , sub[N] , rt = 0 , cnt = 0 ;
bool rev[N] ; int size[N] , f[N] ;
int c[N][2] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline void pushup(int x) { size[x] = size[ls(x)] + size[rs(x)] + 1 ; }
inline void pushr(int x) { if(! rev[x]) return ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; rev[ls(x)] ^= 1 ; rev[rs(x)] ^= 1 ; swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; }
inline void rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ;
int qwq = rs(y) == x ? 1 : 0 ;
if(! isroot(y)) ch[z][rs(z) == y] = x ;
fa[x] = z ; fa[y] = x ; fa[ch[x][qwq ^ 1]] = y ; ch[y][qwq] = ch[x][qwq ^ 1] ;
ch[x][qwq ^ 1] = y ; pushup(y) ; pushup(x) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushr(x) ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ;
if(! isroot(y)) rotate((ls(y) == x) ^ (ls(z) == y) ? x : y) ;
rotate(x) ;
}
}
inline void access(int x) {
for( int tp = 0 ; x ; tp = x , x = fa[x]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , pushup(x) ;
}
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; }
inline void link(int x, int y) { if(! x || ! y) return ; makeroot(x) ; fa[x] = y ; }
inline void cut(int x , int y) { if(! x || ! y) return ; makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; ls(y) = fa[x] = 0 ; pushup(x) ; pushup(y) ; }
inline int query(int x) { makeroot(rt) ; access(x) ; splay(x) ; return size[x] ; }
set < int > s ;
typedef set <int> :: iterator IT ;
struct node { int flg , kk ; } a[N] ;
signed main() {
int t = read() ; s.insert(INT_MAX) ; s.insert(INT_MIN) ;
for( int i = 1 ; i <= t ; i ++ ) {
a[i].flg = read() ; if(a[i].flg == 1) {
a[i].kk = read() ;
sub[++ tot] = a[i].kk ;
}
}
sort(sub + 1 , sub + tot + 1) ;
tot = unique(sub + 1 , sub + tot + 1) - sub - 1 ;
for( int i = 1 ; i <= t ; i ++) {
if(a[i].flg == 1) {
a[i].kk = lower_bound(sub + 1 , sub + tot + 1 , a[i].kk) - sub ;
if(! cnt) { ++ cnt ; rt = a[i].kk ; s.insert(rt) ; printf("1\n") ; continue ; }
else {
IT it = s.upper_bound(a[i].kk) ;
int nxt = * it , dep = 0 , x ; -- it ;
int pre = * it ;
if(pre != INT_MIN) { int now = query(pre) ; if(now > dep) dep = now , x = pre ; }
if(nxt != INT_MAX) { int now = query(nxt) ; if(now > dep) dep = now , x = nxt ; }
printf("%lld\n" , dep + 1) ; c[x][a[i].kk > x] = a[i].kk ; f[a[i].kk] = x ;
++ cnt ; link(x , a[i].kk) ; s.insert(a[i].kk) ;
}
}
if(a[i].flg == 2) {
if(cnt == 1) { puts("1") ; continue ; }
IT it = s.begin() ; ++ it ; int x = * it , y = c[x][1] , z = f[x] , k = query(x) ;
if(rt != x) { cut(x , z) ; cut(x , y) ; link(x , rt) , link(z , y) ; f[x] = 0 ; c[x][1] = rt ; f[rt] = x ; rt = x ; c[z][0] = y ; f[y] = z ; }
printf("%lld\n", k) ;
}
if(a[i].flg == 3) {
if(cnt == 1) { puts("1") ; continue ; }
IT it = s.end() ; -- it , -- it ; int x = * it , y = c[x][0] , z = f[x] , k = query(x) ;
if(rt != x) { cut(x , z) ; cut(x , y) ; link(x , rt) ; link(z , y) ; f[x] = 0 ; c[x][0] = rt ; f[rt] = x ; rt = x ; c[z][1] = y ; f[y] = z ; }
printf("%lld\n" , k) ;
}
if(a[i].flg == 4) {
if(cnt == 1) { -- cnt ; puts("1") ; s.erase(s.find(rt)) ; rt = 0 ;continue ; }
IT it = s.begin() ; ++ it ; int x = * it , y = c[x][1] , z = f[x] , k = query(x) ;
cut(x , z) ; cut(x , y) ; link(y , z) ; cnt -- ; s.erase(s.find(x)) ;
if(x == rt) { rt = y ; }
c[x][0] = c[x][1] = f[x] = 0 ; c[z][0] = y ; f[y] = z ;
printf("%lld\n" , k) ;
}
if(a[i].flg == 5) {
if(cnt == 1) { cnt -- ; puts("1") ; s.erase(s.find(rt)) ; rt = 0 ; continue ; }
IT it = s.end() ; -- it ; -- it ; int x = * it , y = c[x][0] , z = f[x] , k = query(x) ;
cut(x , z) ; cut(x , y) ; link(y , z) ; cnt -- ; s.erase(s.find(x)) ;
printf("%lld\n" , k) ;
if(x == rt) { rt = y ; }
c[x][0] = c[x][1] = f[x] = 0 ; c[z][1] = y ; f[y] = z ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
题意大概是这样,有m条无向边按输入顺序标号,如果一段区间\([l,r]\)上的无向边包含环就称区间\([l,r]\)是“加强区间”,求每条边分别在多少个“加强区间”内。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long LL ;
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
template < typename T > inline void read(T & x) { x = 0 ; int f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
while(! isdigit(c)) {
if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
c = getchar() ;
}
while(isdigit(c)) { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ; c = getchar() ; }
x *= f ; return ;
}
const int N = 4e5 + 10 ;
struct Edge { int u , v ; } e[N] ;
template < > inline void read < Edge > (Edge & x) {
read(x.u) ; read(x.v) ; return void() ;
}
template < typename T > inline void print(T x) {
if(x == 0) return putchar('0') , void() ;
static int st[105] ;
if(x < 0) putchar('-') , x = -x ;
int tp = 0 ;
while(x) st[++ tp] = x % 10 , x /= 10 ;
while(tp) putchar(st[tp --] + '0') ;
return ;
}
template < typename T > inline void sort(vector < T > & v) { sort(v.begin() , v.end()) ; }
template < typename T > inline void unique(vector < T > & v) { v.erase(unique(v.begin() , v.end()) , v.end()) ; }
inline int getdigit() {
register char c = getchar() ;
while(! isdigit(c)) c = getchar() ;
return c - '0' ;
}
inline char getc() {
register char c = getchar() ;
while(! (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z')) c = getchar() ;
return c ;
}
inline int gcd(int x , int y) { return y == 0 ? x : gcd(y , x % y) ; }
const static LL Mod = LLONG_MAX ;
template < typename T , typename TT > inline void Add(T & x , TT y , T Mod = Mod) { x += y ; if(x >= Mod) x -= Mod ; }
template < typename T , typename TT > inline void Del(T & x , TT y , T Mod = Mod) { x -= y ; if(x < 0) x += Mod ; }
int n , m ;
int del[N] , del2[N] ;
template < typename T >
class LCT {
public :
int ch[N][2] , fa[N] ;
int rev[N] , sum[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline bool getr(int x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline void pushup(int x) { return void() ; }
inline void rever(int x) { rev[x] ^= 1 ; swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; }
inline void pushr(int x) {
if(! rev[x]) return ;
rev[x] ^= 1 ;
if(ls(x)) rever(ls(x)) ;
if(rs(x)) rever(rs(x)) ;
return void() ;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ; int k = getr(x) ;
if(! isroot(y)) ch[z][getr(y)] = x ;
fa[x] = z ;
ch[y][k] = ch[x][k ^ 1] ;
fa[ch[y][k]] = y ;
ch[x][k ^ 1] = y ;
fa[y] = x ;
// pushup(y) ; pushup(x) ;
return void() ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; return pushr(x) , void() ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ;
if(! isroot(y)) rotate((getr(x) ^ getr(y)) ? x : y) ;
rotate(x) ;
}
return void() ;
}
inline void acess(int x) { for( int tp = 0 ; x ; x = fa[tp = x]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp ; return void() ; }
inline void makeroot(int x) { acess(x) ; splay(x) ; rever(x) ; }
inline int findroot(int x) { acess(x) ; splay(x) ; while(ls(x)) pushr(x) , x = ls(x) ; splay(x) ; return x ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; fa[x] = y ; }
inline void cut(int x , int y) {makeroot(x) ; acess(y) ; splay(y) ; if((ls(y) != x) && (! rs(ls(y)))) return void() ; fa[x] = ls(y) = 0 ; }
// inline void query(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; acess(y) ; splay(y) ; return void() ; }
} ;
LCT < int > t ;
inline void solve(int l , int r , int _h , int _t) {
if(l > r) return void() ;
del[l ++] += _h ;
del[++ r] -= _h ;
del2[l] += _t ;
del2[r] -= _t ;
return void() ;
}
signed main() {
// freopen("testdata.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
read(m) ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) read(e[i]) ;
int r = 1 ;
for(register int l = 1 ; l <= m ; l ++) {
while(r <= m) {
int u = e[r].u , v = e[r].v ;
if(t.findroot(u) == t.findroot(v)) { solve(l , r , m - r + 1 , 0) ; solve(r + 1 , m , m - r , - 1) ; break ; }
else { t.link(u , v) ; } ++ r ;
}
t.cut(e[l].u , e[l].v) ;
}
int x = 0 , y = 0 ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
x += del[i] , y += del2[i] , x += y ;
print(x) , putchar(32) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
LCT 可以维护动态MST(动态最小生成树)
指最小生成树 思路大概是
如果不连通直接加 link一下的…
如果连通split提上去 然后判断大小关系来删边断边 如果满足最优性 则不变…
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmax(T & x , T y) {
return x < y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmin(T & x , T y) {
return x > y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cabs(T & x) {
return x > 0 ? 1 : (x = - x) , 0 ;
}
inline int QP(int x , int y , int Mod) {
int ans = 1 ;
for( ; y ; y >>= 1 , x = (x * x) % Mod)
if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % Mod ;
return ans ;
}
int n , m ;
const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;
struct node {
int u , v , w , w2 ;
inline bool operator <(const node & x ) const {
return w < x.w ;
}
} e[N] ;
int l[N] , r[N] ;
int f[N] ;
int idx ;
inline int find(int x) { return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]) ;}
inline void merge(int x , int y) { return f[find(x)] = find(y) , void() ;}
class LCT {
public :
int fa[N] , ch[N][2] , tag[N] ;
int w[N] , id[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool getr(int x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline void pushr(int x) { tag[x] ^= 1 ; swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; }
inline void pushup(int x) { id[x] = x ; if(w[id[ls(x)]] > w[id[x]]) id[x] = id[ls(x)] ; if(w[id[rs(x)]] > w[id[x]]) id[x] = id[rs(x)] ; }
inline void pushdown(int x) { if(tag[x]) { tag[x] = 0 ; if(ls(x)) pushr(ls(x)) ; if(rs(x)) pushr(rs(x)) ; }}
inline void rotate(int x) { int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] , k = getr(x) ;
if(!isroot(y)) ch[z][getr(y)] = x ;
fa[x] = z ; fa[y] = x ; fa[ch[x][k ^ 1]] = y ; ch[y][k] = ch[x][k ^ 1] ; ch[x][k ^ 1] = y ;
pushup(y) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushdown(x) ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int y = fa[x] ;
if(! isroot(y)) rotate(getr(x) ^ getr(y) ? x : y) ;
rotate(x) ;
} pushup(x) ;
}
inline void access(int x) { for( int tp = 0 ; x ; rs(x) = tp , tp = x , x = fa[tp]) splay(x) ; }
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; pushr(x) ; }
inline void split(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; }
inline int findroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; while(ls(x)) x = ls(x) ; splay(x) ; return x ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; if(findroot(y) != x) fa[x] = y ; }
inline void cut(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; if(ls(y) == x) ls(y) = fa[x] = 0 , pushup(y) ;}
inline int query(int x , int y) {
if(findroot(x) != findroot(y)) return INT_MAX ;
split(x , y) ;
return w[id[y]] ;
}
inline void Merge(int x , int y , int k) {
if(findroot(x) ^ findroot(y)) { w[++ idx] = k ; link(l[idx] = x , idx) ; link(r[idx] = y , idx) ; return ; }
split(x , y) ;
int s = id[y] ;
if(w[s] <= k) return ;
cut(s , l[s] ) ;
cut(s , r[s] ) ;
w[s] = k ;
link(l[s] = x , s) ;
link(r[s] = y , s) ;
}
} lct ;
signed main() {
// freopen("testdata.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
// freopen("testdata2.out" , "w" , stdout) ;
n = read() , m = read() ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
int u = read() , v = read() , w = read() , w2 = read() ;
e[i] = {u , v , w , w2} ;
}
sort(e + 1 , e + m + 1) ;
int ans = INT_MAX ;
idx = n ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) f[i] = i ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
lct.Merge(e[i].u , e[i].v , e[i].w2) ;
cmin(ans , e[i].w + lct.query(1 , n)) ;
}
if(ans == INT_MAX) ans = -1 ;
printf("%lld\n" , ans) ;
return 0 ;
}
[WC2006]水管局长
每次删边的LCT不太好维护MST
所以每次考虑倒着
离线先kruskal跑出来(为了复杂度)
然后再一步步动态加边 最后倒着输出(
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
// #define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmax(T & x , T y) {
return x < y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmin(T & x , T y) {
return x > y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cabs(T & x) {
return x > 0 ? 1 : (x = - x) , 0 ;
}
inline int QP(int x , int y , int Mod) {
int ans = 1 ;
for( ; y ; y >>= 1 , x = (x * x) % Mod)
if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % Mod ;
return ans ;
}
int n , m , q ;
int id ;
const int N = 3e5 + 5 ;
int l[N] , r[N] ;
struct node {
int u , v , w ;
inline bool operator < (const node& x ) const{ return w < x.w ; }
} e[1000005] ;
int f[100005] ;
map < int , int > p[100005] ;
struct que {
int op , x , y , w ;
} qs[100005] ;
class LCT {
public :
int fa[N] , ch[N][2] , tag[N] ;
pair < int , int > val[N] , mn[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool getr(int x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline void pushr(int x) { tag[x] ^= 1 ; swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; }
inline void pushup(int x) { mn[x] = max(val[x] , max(mn[ls(x)] , mn[rs(x)])) ; }
inline void pushdown(int x) { if(tag[x]) { tag[x] = 0 ; if(ls(x)) pushr(ls(x)) ; if(rs(x)) pushr(rs(x)) ; }}
inline void rotate(int x) { int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] , k = getr(x) ;
if(!isroot(y)) ch[z][getr(y)] = x ;
fa[x] = z ; fa[y] = x ; fa[ch[x][k ^ 1]] = y ; ch[y][k] = ch[x][k ^ 1] ; ch[x][k ^ 1] = y ;
pushup(y) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushdown(x) ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int y = fa[x] ;
if(! isroot(y)) rotate(getr(x) ^ getr(y) ? x : y) ;
rotate(x) ;
} pushup(x) ;
}
inline void access(int x) { for( int tp = 0 ; x ; rs(x) = tp , tp = x , x = fa[tp]) splay(x) ; }
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; pushr(x) ; }
inline void split(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; }
inline int findroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; while(ls(x)) x = ls(x) ; splay(x) ; return x ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; if(findroot(y) != x) fa[x] = y ; }
inline void cut(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ; if(ls(y) == x) ls(y) = fa[x] = 0 , pushup(y) ;}
inline pair < int , int > query(int x , int y) { split(x , y) ; return mn[y] ; }
} lct ;
inline int find(int x) { return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]) ;}
signed main() {
n = read() ; m = read() ; q = read() ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
int u = read() , v = read() , w = read() ;
if(u > v) swap(u , v) ;
e[i] = {u , v , w} ;
p[e[i].u][e[i].v] = e[i].w ;
}
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= q ; i ++) {
qs[i].op = read() ;
qs[i].x = read() ;
qs[i].y = read() ;
if(qs[i].x > qs[i].y) swap(qs[i].x , qs[i].y) ;
if(qs[i].op == 2) {
qs[i].w = p[qs[i].x][qs[i].y] ;
p[qs[i].x].erase(qs[i].y) ;
}
}
sort(e + 1 , e + m + 1) ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) f[i] = i ;
id = n ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
int u = e[i].u , v = e[i].v ;
if(! p[u].count(v)) continue ;
u = find(u) , v = find(v) ;
if(u ^ v) {
f[v] = u ;
++ id ;
lct.val[id] = lct.mn[id] = make_pair(e[i].w , id) ;
lct.link(id , l[id] = e[i].u) ;
lct.link(id , r[id] = e[i].v) ;
}
}
static int st[100005] , top = 0 ;
for(register int i = q ; i ; -- i) {
if(qs[i].op == 1) st[++ top] = (qs[i].x ^ qs[i].y) ? lct.query(qs[i].x , qs[i].y).first : 0 ;
else {
int x = qs[i].x , y = qs[i].y ;
pair < int , int > d = lct.query(x , y) ;
if(d.fi <= qs[i].w) continue ;
int t = d.se ;
lct.cut(l[t] , t) ;
lct.cut(r[t] , t) ;
++ id ;
lct.val[id] = lct.mn[id] = make_pair(qs[i].w , id) ;
lct.link(l[id] = x , id) ;
lct.link(r[id] = y , id) ;
}
}
while(top) printf("%d\n" , st[top --]) ;
return 0 ;
}
大概题意就是合并两个连通块 查询连通块内点到其他点的最大距离 对于这道题更简单 因为每次只有一个点和一个连通块合并 所以直接求两次距离即可 每个点的权值设为1 split后上面那个点的sum-1即为距离
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmax(T & x , T y) {
return x < y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmin(T & x , T y) {
return x > y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cabs(T & x) {
return x > 0 ? 1 : (x = - x) , 0 ;
}
inline int QP(int x , int y , int Mod) {
int ans = 1 ;
for( ; y ; y >>= 1 , x = (x * x) % Mod)
if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % Mod ;
return ans ;
}
int q , m = 0 ;
const int N = 1000000 + 5 ;
int val[N] ;
class LCT {
public :
int ch[N][2] ; int fa[N] ; int size[N] ; int rev[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline void pushup(int rt) { size[rt] = size[ls(rt)] + size[rs(rt)] + 1 ; }
inline void pushr(int rt) { rev[rt] ^= 1 ;swap(ls(rt) , rs(rt)) ; }
inline void pushdown(int rt) {
if(! rev[rt]) return ;
rev[rt] ^= 1 ;
if(ls(rt)) pushr(ls(rt)) ;
if(rs(rt)) pushr(rs(rt)) ;
}
inline bool getr(int x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline void rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] , rs = getr(x) , grs = getr(y) ;
int son = ch[x][rs ^ 1] ;
if(! isroot(y)) ch[z][grs] = x ;
ch[y][rs] = son ; ch[x][rs ^ 1] = y ;
fa[x] = z ; fa[y] = x ;
if(son) fa[son] = y ; pushup(y) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushdown(x) ; }
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
if(! isroot(fa[x])) rotate(getr(fa[x]) ^ getr(x) ? x : fa[x]) ;
rotate(x) ;
} pushup(x) ;
}
inline void access(int x) { for(register int tp = 0 ; x ; tp = x , x = fa[tp]) splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , pushup(x) ; }
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; splay(x) ; pushr(x) ; }
inline void split(int x , int y) { makeroot(y) ; access(x) ; splay(x) ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { if(! x || ! y || x == y) return ; split(x , y) ; fa[y] = x ; }
inline void cut(int x , int y) { if(! x || ! y || x == y) return ; split(x , y) ; if(size[x] <= 2) ls(x) = fa[y] = 0 ;}
} lct ;
struct node{
int u , v , w ;
} e[N] ;
int f[N] ;
inline int find(int x) { return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]) ;}
inline int query(int x , int y) { lct.split(x , y) ; return lct.size[x] - 1 ;}
inline void Merge(int x , int y) {
lct.link(x , y) ; f[x] = y = find(y) ;
register int a = x , b = e[y].u , c = e[y].v , maxn = e[y].w , tmp ;
tmp = query(a , b) ;
if(cmax(maxn , tmp)) e[y].u = a , e[y].v = b ;
tmp = query(a , c) ;
if(cmax(maxn , tmp)) e[y].u = a , e[y].v = c ;
tmp = query(b , c) ;
if(cmax(maxn , tmp)) e[y].u = b , e[y].v = c ;
e[y].w = maxn ;
}
inline int getopt() { register char c = getchar() ;
while(c != 'Q' && c != 'B') c = getchar() ;
return c == 'B' ;
}
signed main() {
q = read() ;
while(q --) {
int opt = getopt() ;
if(opt == 1) {
int x = ++ m ;
int y = read() ;
e[x].u = e[x].v = x , f[x] = x ;
if(~ y) Merge(x , y) ;
}
else {
int x = read() , y = find(x) ;
printf("%lld\n" , max(query(x , e[y].u) , query(x , e[y].v))) ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
LCT维护树的重心
首都
具体找法:类似树上二分,我们需要不断逼近树的重心的位置。记下lsum表示当前链中搜索区间左端点以左的子树大小,rsum表示右端点以右的。x的整个子树就表示了当前搜索区间,在中序遍历中x把搜索区间分成了左右两块(在Splay中对应x的左子树和右子树)。
如果x左子树的s加上lsum和x右子树的s加上rsum都不超过新树总大小的一半,那么x当然就是重心啦!当然,如果总大小是奇数,重心只会有一个,那就找到了。否则,因为必须编号最小,所以还要继续找下去。
当我们没有确定答案时,还要继续找下去,那么就要跳儿子了。x把整个链分成了左右两个部分,而重心显然会在大小更大的一部分中,这个也应该好证明。如果x左子树的s加上lsum小于x右子树的s加上rsum,那就跳右儿子继续找。这时候当前搜索区间减小了,搜索区间以外的部分增大了,lsum应该加上sz[x]+1。反之亦然。如果跳进了空儿子,那肯定所有情况都考虑完了,直接结束查找。
当然,重心找到了就还是要伸展一下,保证复杂度。
这一部分套用Splay的复杂度,是均摊\(O(\log N)\)的,总复杂度也就降到了\(O(N\log N)\)。
findroot实在很慢,于是可以写个并查集来维护每个点所在树的重心。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
int n , m ;
const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;
const int INF = INT_MAX ;
int fa[N] , ch[N][2] , sz[N] , sum[N] , r[N] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline bool getr(int x) { return rs(fa[x]) == x ; }
inline void pushup(int x) {
sum[x] = sum[ls(x)] + sum[rs(x)] + sz[x] + 1 ;
}
inline void pushdown(int x) {
if(! r[x]) return ;
r[x] = 0 ; r[ls(x)] ^= 1 ; r[rs(x)] ^= 1 ;
swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] , k = getr(x) , w = ch[x][k ^ 1] ;
if(! isroot(y)) { ch[z][getr(y)] = x ; }
fa[fa[fa[ch[ch[x][k ^ 1] = y][k] = w] = y] = x] = z ; pushup(y) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) {
if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; pushdown(x) ;
}
inline void splay(int x) {
pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int y = fa[x] ;
if(! isroot(y)) { rotate((getr(x) ^ getr(y)) ? x : y) ; }
rotate(x) ;
}
pushup(x) ;
}
inline void access(int x) {
for( int tp = 0 ; x ; x = fa[tp = x]) {
splay(x) ;
sz[x] += sum[rs(x)] ;
sz[x] -= sum[rs(x) = tp] ;
pushup(x) ;
}
}
inline void makeroot(int x) {
access(x) ; splay(x) ; r[x] ^= 1 ;
}
inline void split(int x , int y) {
makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; splay(y) ;
}
inline void link(int x , int y){
split(x , y) ; sz[fa[x] = y] += sum[x] ; pushup(y) ;
}
int f[N] ;
inline int find(int x) { return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]) ; }
inline int upd(int x) {
int l , r , j = sum[x] & 1 , Sum = sum[x] >> 1 ; int lsum = 0 , rsum = 0 ;
int newp = INF , nowl = 0 , nowr = 0 ;
while(x) {
pushdown(x) ;
nowl = sum[l = ls(x)] + lsum ;
nowr = sum[r = rs(x)] + rsum ;
if(nowl <= Sum && nowr <= Sum) {
if(j) { newp = x ; break ; }
else if(newp > x) { newp = x ; }
}
if(nowl < nowr) { lsum += sum[l] + sz[x] + 1 ; x = r ; }
else { rsum += sum[r] + sz[x] + 1 ; x = l ; }
}
splay(newp) ;
return newp ;
}
int ans = 0 ;
signed main() {
#ifdef _WIN64
freopen("0.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
#endif
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false) ;
cin.tie(nullptr) ;
cout.tie(nullptr) ;
cin >> n >> m ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) { sum[i] = 1 ; f[i] = i ; ans ^= i ; }
while(m --) {
register char ch ; cin >> ch ;
if(ch == 'A') {
int x , y ; cin >> x >> y ;
link(x , y) ;
split(x = find(x) , y = find(y)) ;
int z = upd(y) ;
ans ^= x ^ y ^ z ;
f[x] = f[y] = f[z] = z ;
}
if(ch == 'Q') {
int x ; cin >> x ;
cout << find(x) << '\n' ;
}
if(ch == 'X') {
cin >> ch >> ch ;
cout << ans << '\n' ;
}
}
}
最小差值生成树
给定一个标号为从 \(1\) 到 \(n\) 的、有 \(m\) 条边的无向图,求边权最大值与最小值的差值最小的生成树
要保证边权差最小,不妨假设当前边权为\(k\),则此时我们需要最小边权最大。
所以可以按照边权排序。
类似于求最小生成树的方法,我们每次加边后都需要判一下连通性,如果联通就减去边权中最小值。
至于如何求出所有边权中的最小值,因为已经排序,所以有下标小的点其点权一定小。
所以我们可以用 \(flg\) 数组来标记那些点已经被标记,然后类似与队列的一个一个弹??
当然,需要统计答案的时候,还要判断\(id_{num}\)
num(合并次数)(当前联通块数量是否为1)是否为\(n-1\)
区别与最小生成树的模板,因为我们有编号小的点且为边的点其越小,所以我们可以这样写\(pushup\)
inline void pushup(int x) { id[x] = x ;
if(id[ls(x)] > n && (id[x] <= n || id[x] > id[ls(x)]))id[x] = id[ls(x)] ;
if(id[rs(x)] > n && (id[x] <= n || id[x] > id[rs(x)])) id[x] = id[rs(x)] ;
}
// Isaunoya
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std ;
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
inline int read() {
register int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
register char c = getchar() ;
for( ; ! isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1 ;
for( ; isdigit(c) ; c = getchar()) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15) ;
return x * f ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmax(T & x , T y) {
return x < y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
template < typename T > inline bool cmin(T & x , T y) {
return x > y ? (x = y) , 1 : 0 ;
}
inline int QP(int x , int y , int Mod){ int ans = 1 ;
for( ; y ; y >>= 1 , x = (x * x) % Mod)
if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % Mod ;
return ans ;
}
int n , m ;
const int N = 4e5 + 10 ;
const int M = 4e5 + 10 ;
struct node { int u , v , w ; } e[M << 1] ;
inline bool cmp(node x , node y) {
return x.w < y.w ;
}
bool flg[M] ;
class LCT {
public :
int fa[M] , id[M] ;
bool rev[M] ;
int ch[M][2] ;
#define ls(x) ch[x][0]
#define rs(x) ch[x][1]
inline bool isroot(int x) { return ls(fa[x]) != x && rs(fa[x]) != x ; }
inline void pushup(int x) { id[x] = x ;
if(id[ls(x)] > n && (id[x] <= n || id[x] > id[ls(x)]))id[x] = id[ls(x)] ;
if(id[rs(x)] > n && (id[x] <= n || id[x] > id[rs(x)])) id[x] = id[rs(x)] ;
}
inline void rever(int x) { if(! rev[x]) return ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; rev[ls(x)] ^= 1 ; rev[rs(x)] ^= 1 ; swap(ls(x) , rs(x)) ; }
inline void rotate(int x) { int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ;
int qwq = rs(y) == x ; fa[x] = z ;
if(! isroot(y)) ch[z][rs(z) == y] = x ;
fa[ch[x][qwq ^ 1]] = y ; ch[y][qwq] = ch[x][qwq ^ 1] ;
fa[y] = x ; ch[x][qwq ^ 1] = y ;
pushup(y) , pushup(x) ;
}
inline void pushall(int x) { if(! isroot(x)) pushall(fa[x]) ; rever(x) ; }
inline void Splay(int x) { pushall(x) ;
while(! isroot(x)) {
int y = fa[x] , z = fa[y] ;
if(! isroot(y)) rotate((rs(z) == y) ^ (rs(y) == x) ? x : y) ;
rotate(x) ;
}
}
inline void access(int x) {for(int tp = 0 ; x ; tp = x , x = fa[tp]) Splay(x) , rs(x) = tp , pushup(x) ;}
inline void makeroot(int x) { access(x) ; Splay(x) ; rev[x] ^= 1 ; rever(x) ; }
inline int findroot(int x) {access(x) ; Splay(x) ; rever(x) ;
while(ls(x)) rever(x = ls(x)) ;
return x ;
}
inline void split(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; access(y) ; Splay(y) ; }
inline bool chk(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; return findroot(y) != x ; }
inline void link(int x , int y) { makeroot(x) ; fa[x] = y ; }
} lct ;
int st[M << 2] ;
int book[N << 1] ;
signed main() {
n = read() ; m = read() ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) { int u = read() , v = read() , w = read() ;
e[i] = {u , v , w} ;
} sort(e + 1 , e + m + 1 , cmp) ;
int idx = n , idnum = 0 ;
int ll = 1 ; int ans = INT_MAX ;
for(register int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++) {
++ idx ;
int x , y ;
x = e[i].u , y = e[i].v ;
if(x == y) { flg[i] = 1 ; continue ; }
if(lct.chk(x , y)) lct.link(x , idx) , lct.link(idx , y) , idnum ++ ;
else {
lct.split(x , y) ;
int now = lct.id[y] ;
flg[now - n] = 1 ; lct.Splay(now) ;
lct.fa[lct.ls(now)] = lct.fa[lct.rs(now)] = 0 ;
lct.link(x , idx) , lct.link(idx , y) ;
} while(flg[ll] && ll <= i) ++ ll ;
if(idnum >= n - 1) ans = min(ans , e[i].w - e[ll].w) ;
} printf("%lld\n" , ans) ;
return 0 ;
}
还有两题
- CF1137F Matches Are Not a Child's Play
- CF1172E Nauuo and ODT
先咕着 到时候补…
LCT[Link-Cut-Tree学习笔记]的更多相关文章
- Link Cut Tree学习笔记
从这里开始 动态树问题和Link Cut Tree 一些定义 access操作 换根操作 link和cut操作 时间复杂度证明 Link Cut Tree维护链上信息 Link Cut Tree维护子 ...
- LCT(link cut tree) 动态树
模板参考:https://blog.csdn.net/saramanda/article/details/55253627 综合各位大大博客后整理的模板: #include<iostream&g ...
- 【学习笔记】LCT link cut tree
大概就是供自己复习的吧 1. 细节讲解 安利两篇blog: Menci 非常好的讲解与题单 2.模板 把 $ rev $ 和 $ pushdown $ 的位置记清 #define lc son[x][ ...
- 学习笔记:Link Cut Tree
模板题 原理 类似树链剖分对重儿子/长儿子剖分,Link Cut Tree 也做的是类似的链剖分. 每个节点选出 \(0 / 1\) 个儿子作为实儿子,剩下是虚儿子.对应的边是实边/虚边,虚实时可以进 ...
- LCT总结——概念篇+洛谷P3690[模板]Link Cut Tree(动态树)(LCT,Splay)
为了优化体验(其实是强迫症),蒟蒻把总结拆成了两篇,方便不同学习阶段的Dalao们切换. LCT总结--应用篇戳这里 概念.性质简述 首先介绍一下链剖分的概念(感谢laofu的讲课) 链剖分,是指一类 ...
- 洛谷P3690 [模板] Link Cut Tree [LCT]
题目传送门 Link Cut Tree 题目背景 动态树 题目描述 给定n个点以及每个点的权值,要你处理接下来的m个操作.操作有4种.操作从0到3编号.点从1到n编号. 0:后接两个整数(x,y),代 ...
- LuoguP3690 【模板】Link Cut Tree (动态树) LCT模板
P3690 [模板]Link Cut Tree (动态树) 题目背景 动态树 题目描述 给定n个点以及每个点的权值,要你处理接下来的m个操作.操作有4种.操作从0到3编号.点从1到n编号. 0:后接两 ...
- $LCT$维护子树信息学习笔记
\(LCT\)维护子树信息学习笔记 昨天\(FDF\)好题分享投了 \([ZJOI2018]\)历史 这题. 然后我顺势学学这个姿势. 结果调了一年...于是写个笔记记录一下. 基本原理 比较显然地, ...
- link cut tree 入门
鉴于最近写bzoj还有51nod都出现写不动的现象,决定学习一波厉害的算法/数据结构. link cut tree:研究popoqqq那个神ppt. bzoj1036:维护access操作就可以了. ...
- P3690 【模板】Link Cut Tree (动态树)
P3690 [模板]Link Cut Tree (动态树) 认父不认子的lct 注意:不 要 把 $fa[x]$和$nrt(x)$ 混 在 一 起 ! #include<cstdio> v ...
随机推荐
- js关于时间(date)的比较
之前在工作上遇到一个问题:使用一些时间插件,如果有俩个时间,要判断结束时间和开始时间的大小?后来就查找了一些资料,这边整理出俩个比较简便的方法. 在这我拿 laydate.js 这个插件来举例: 首先 ...
- 每日一练_PAT_B_真题
A+B和C (15) 时间限制 1000 ms 内存限制 32768 KB 代码长度限制 100 KB 判断程序 Standard (来自 小小) 题目描述 给定区间[-2的31次方, 2的31次方] ...
- [JavaScript]AO对象
1, 形式参数 2, 局部变量 3, 函数声明表达式
- HDU_1455_dfs
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1455 int dfs(int all,int sum,int now),all代表剩余总长,sum,代表每段长, ...
- 对权值线段树剪枝的误解--以HDU6703为例
引子 对hdu6703,首先将问题转化为"询问一个排列中大于等于k的值里,下标超过r的最小权值是多少" 我们采用官方题解中的做法:权值线段树+剪枝 对(a[i],i)建线段树,查询 ...
- 1276:【例9.20】P2758 编辑距离
题目传送门[(https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2758)] 题目描述 设A和B是两个字符串.我们要用最少的字符操作次数,将字符串A转换为字符串B.这里所说的字符操作 ...
- 大神是如何学习 Go 语言之 Channel 实现原理精要
转自: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ElzD2dXWeldYkJmVVY6Djw 作者Draveness Go 语言中的管道 Channel 是一个非常有趣的数据结构,作为语 ...
- make: *** No targets specified and no makefile found. Stop.错误
# make make: *** No targets specified and no makefile found. Stop. # yum install gcc gcc-c++ gcc-g77 ...
- Node.js的__dirname,__filename,process.cwd(),./的一些坑
参考博客:https://github.com/jawil/blog/issues/18
- 利用VS Code在Azure上构建部署静态页面
0x00 前言 前一段时间,我找到了Jendrik Illner的个人网站.除了那里的精彩文章,网站的主题也吸引了我的注意力,而且我发现该网站的主题采用了Hugo的Academic主题. 然后,我认为 ...
