那天晚上和@FeignClient注解的深度交流
废话篇
那晚,我和@FeignClient注解的深度交流了一次,爽!
主要还是在技术群里看到有同学在问相关问题,比如: contextId是干嘛的?name相同的多个Client会报错?
然后觉得有必要写篇文章聊聊@FeignClient的使用,百忙之中抽时间,写篇文章不容易啊,记得点赞。
正式篇
Feign基本介绍
首先来个基本的普及,怕有些同学还没接触过Spring Cloud。Feign是Netflix开源的一个REST客户端,通过定义接口,使用注解的方式描述接口的信息,就可以发起接口调用。
GitHub地址:https://github.com/OpenFeign/feign
下面是GitHub主页上给的一个最基本的使用示列,示列中采用Feign调用GitHub的接口。
interface GitHub {
@RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
List<Contributor> contributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo);
@RequestLine("POST /repos/{owner}/{repo}/issues")
void createIssue(Issue issue, @Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo);
}
public static class Contributor {
String login;
int contributions;
}
public static class Issue {
String title;
String body;
List<String> assignees;
int milestone;
List<String> labels;
}
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String... args) {
GitHub github = Feign.builder()
.decoder(new GsonDecoder())
.target(GitHub.class, "https://api.github.com");
// Fetch and print a list of the contributors to this library.
List<Contributor> contributors = github.contributors("OpenFeign", "feign");
for (Contributor contributor : contributors) {
System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")");
}
}
}
Spring Cloud OpenFeign介绍
Spring Cloud OpenFeign是Spring Cloud团队将原生的Feign结合到Spring Cloud中的产物。从上面原生Feign的使用示列来看,用的注解都是Feign中自带的,但我们在开发中基本上都是基于Spring MVC的注解,不是很方便调用。所以Spring Cloud OpenFeign扩展了对Spring MVC注解的支持,同时还整合了Ribbon和Eureka来提供均衡负载的HTTP客户端实现。
GitHub地址:https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign
官方提供的使用示列:
@FeignClient("stores")
public interface StoreClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/stores")
List<Store> getStores();
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = "/stores/{storeId}", consumes = "application/json")
Store update(@PathVariable("storeId") Long storeId, Store store);
}
FeignClient注解的使用介绍
value, name
value和name的作用一样,如果没有配置url那么配置的值将作为服务名称,用于服务发现。反之只是一个名称。
serviceId
serviceId已经废弃了,直接使用name即可。
contextId
比如我们有个user服务,但user服务中有很多个接口,我们不想将所有的调用接口都定义在一个类中,比如:
Client 1
@FeignClient(name = "optimization-user")
public interface UserRemoteClient {
@GetMapping("/user/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id") int id);
}
Client 2
@FeignClient(name = "optimization-user")
public interface UserRemoteClient2 {
@GetMapping("/user2/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id") int id);
}
这种情况下启动就会报错了,因为Bean的名称冲突了,具体错误如下:
Description:
The bean 'optimization-user.FeignClientSpecification', defined in null, could not be registered. A bean with that name has already been defined in null and overriding is disabled.
Action:
Consider renaming one of the beans or enabling overriding by setting spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
解决方案可以增加下面的配置,作用是允许出现beanName一样的BeanDefinition。
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
另一种解决方案就是为每个Client手动指定不同的contextId,这样就不会冲突了。
上面给出了Bean名称冲突后的解决方案,下面来分析下contextId在Feign Client的作用,在注册Feign Client Configuration的时候需要一个名称,名称是通过getClientName方法获取的:
String name = getClientName(attributes);
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
private String getClientName(Map<String, Object> client) {
if (client == null) {
return null;
}
String value = (String) client.get("contextId");
if (!StringUtils.hasText(value)) {
value = (String) client.get("value");
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(value)) {
value = (String) client.get("name");
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(value)) {
value = (String) client.get("serviceId");
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(value)) {
return value;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Either 'name' or 'value' must be provided in @"
+ FeignClient.class.getSimpleName());
}
可以看到如果配置了contextId就会用contextId,如果没有配置就会去value然后是name最后是serviceId。默认都没有配置,当出现一个服务有多个Feign Client的时候就会报错了。
其次的作用是在注册FeignClient中,contextId会作为Client 别名的一部分,如果配置了qualifier优先用qualifier作为别名。
private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName();
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
validate(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("url", getUrl(attributes));
definition.addPropertyValue("path", getPath(attributes));
String name = getName(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("name", name);
String contextId = getContextId(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("contextId", contextId);
definition.addPropertyValue("type", className);
definition.addPropertyValue("decode404", attributes.get("decode404"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallback", attributes.get("fallback"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallbackFactory", attributes.get("fallbackFactory"));
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
// 拼接别名
String alias = contextId + "FeignClient";
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
boolean primary = (Boolean) attributes.get("primary"); // has a default, won't be
// null
beanDefinition.setPrimary(primary);
// 配置了qualifier优先用qualifier
String qualifier = getQualifier(attributes);
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
alias = qualifier;
}
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className,
new String[] { alias });
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry);
}
url
url用于配置指定服务的地址,相当于直接请求这个服务,不经过Ribbon的服务选择。像调试等场景可以使用。
使用示列
@FeignClient(name = "optimization-user", url = "http://localhost:8085")
public interface UserRemoteClient {
@GetMapping("/user/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id") int id);
}
decode404
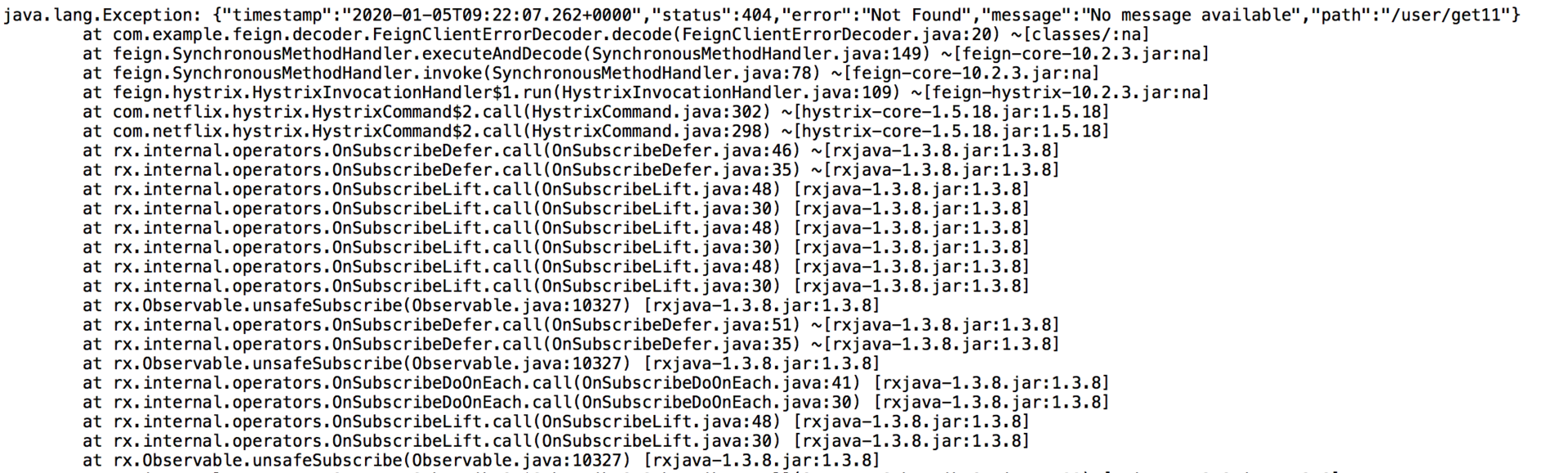
当调用请求发生404错误时,decode404的值为true,那么会执行decoder解码,否则抛出异常。
解码也就是会返回固定的数据格式给你:
{"timestamp":"2020-01-05T09:18:13.154+0000","status":404,"error":"Not Found","message":"No message available","path":"/user/get11"}
抛异常的话就是异常信息了,如果配置了fallback那么就会执行回退逻辑:
configuration
configuration是配置Feign配置类,在配置类中可以自定义Feign的Encoder、Decoder、LogLevel、Contract等。
configuration定义
public class FeignConfiguration {
@Bean
public Logger.Level getLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
@Bean
public BasicAuthRequestInterceptor basicAuthRequestInterceptor() {
return new BasicAuthRequestInterceptor("user", "password");
}
@Bean
public CustomRequestInterceptor customRequestInterceptor() {
return new CustomRequestInterceptor();
}
// Contract,feignDecoder,feignEncoder.....
}
使用示列
@FeignClient(value = "optimization-user", configuration = FeignConfiguration.class)
public interface UserRemoteClient {
@GetMapping("/user/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id")int id);
}
fallback
定义容错的处理类,也就是回退逻辑,fallback的类必须实现Feign Client的接口,无法知道熔断的异常信息。
fallback定义
@Component
public class UserRemoteClientFallback implements UserRemoteClient {
@Override
public User getUser(int id) {
return new User(0, "默认fallback");
}
}
使用示列
@FeignClient(value = "optimization-user", fallback = UserRemoteClientFallback.class)
public interface UserRemoteClient {
@GetMapping("/user/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id")int id);
}
fallbackFactory
也是容错的处理,可以知道熔断的异常信息。
fallbackFactory定义
@Component
public class UserRemoteClientFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<UserRemoteClient> {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserRemoteClientFallbackFactory.class);
@Override
public UserRemoteClient create(Throwable cause) {
return new UserRemoteClient() {
@Override
public User getUser(int id) {
logger.error("UserRemoteClient.getUser异常", cause);
return new User(0, "默认");
}
};
}
}
使用示列
@FeignClient(value = "optimization-user", fallbackFactory = UserRemoteClientFallbackFactory.class)
public interface UserRemoteClient {
@GetMapping("/user/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id")int id);
}
path
path定义当前FeignClient访问接口时的统一前缀,比如接口地址是/user/get, 如果你定义了前缀是user, 那么具体方法上的路径就只需要写/get 即可。
使用示列
@FeignClient(name = "optimization-user", path="user")
public interface UserRemoteClient {
@GetMapping("/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id") int id);
}
primary
primary对应的是@Primary注解,默认为true,官方这样设置也是有原因的。当我们的Feign实现了fallback后,也就意味着Feign Client有多个相同的Bean在Spring容器中,当我们在使用@Autowired进行注入的时候,不知道注入哪个,所以我们需要设置一个优先级高的,@Primary注解就是干这件事情的。
qualifier
qualifier对应的是@Qualifier注解,使用场景跟上面的primary关系很淡,一般场景直接@Autowired直接注入就可以了。
如果我们的Feign Client有fallback实现,默认@FeignClient注解的primary=true, 意味着我们使用@Autowired注入是没有问题的,会优先注入你的Feign Client。
如果你鬼斧神差的把primary设置成false了,直接用@Autowired注入的地方就会报错,不知道要注入哪个对象。
解决方案很明显,你可以将primary设置成true即可,如果由于某些特殊原因,你必须得去掉primary=true的设置,这种情况下我们怎么进行注入,我们可以配置一个qualifier,然后使用@Qualifier注解进行注入,示列如下:
Feign Client定义
@FeignClient(name = "optimization-user", path="user", qualifier="userRemoteClient")
public interface UserRemoteClient {
@GetMapping("/get")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id") int id);
}
Feign Client注入
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userRemoteClient")
private UserRemoteClient userRemoteClient;
那天晚上和@FeignClient注解的深度交流的更多相关文章
- FeignClient注解及参数
一.FeignClient注解 FeignClient注解被@Target(ElementType.TYPE)修饰,表示FeignClient注解的作用目标在接口上 1 2 3 4 5 @FeignC ...
- SpringCloud 服务间互相调用 @FeignClient注解
SpringCloud搭建各种微服务之后,服务间通常存在相互调用的需求,SpringCloud提供了@FeignClient 注解非常优雅的解决了这个问题 首先,保证几个服务都在一个Eureka中注册 ...
- @FeignClient注解详解
Spring Cloud 是目前最火的微服务框架,Feign 作为基础组件之一,在 Spring Cloud 体系中发挥了重要的作用. 一.FeignClient注解 FeignClient注解被@T ...
- FeignClient注解属性configuration不生效问题排查思路
FeignClient注解属性configuration不生效问题排查思路 问题背景 我们知道,"如果需要自定义单个Feign配置,Feign的@Configuration 注解的类不能与@ ...
- SpringCloud使用Feign调用服务时,@FeignClient注解无法使用
关于解决这个问题的理论根源传送门:https://blog.csdn.net/alinyua/article/details/80070890我在这里只提供解决方案 0. 结论和解决方案 Spring ...
- SpringCloud(三)- OpenFeign简介及@FeignClient等注解的使用
唯能极于情,故能极于剑 有问题或错误请及时联系小编或关注小编公众号 "CodeCow",小编一定及时回复和改正,期待和大家一起学习交流 此文由四部分组成(OpenFeign简介.@ ...
- SpringCloud @FeignClient的类注解@ReqestMapping无效报错:No message available","path":"/xxxx
最近在使用Feign组合微服务的时候发现在@FeignClient接口类上使用@ReqestMapping无效. 像下面的这个代码: @FeignClient("xxx") @Re ...
- spring cloud: Hystrix(六):feign的注解@FeignClient:fallbackFactory(类似于断容器)与fallback方法
fallbackFactory(类似于断容器)与fallback方法 feign的注解@FeignClient:fallbackFactory与fallback方法不能同时使用,这个两个方法其实都类似 ...
- SpringCloud(四)- Hystris简介及@EnableCircuitBreaker 和 @HystrixCommand 注解的使用
唯能极于情,故能极于剑有问题或错误请及时联系小编或关注小编公众号 “CodeCow”,小编一定及时回复和改正,期待和大家一起学习交流 此文由四部分组成(Hystris简介.@EnableCircuit ...
随机推荐
- 【codeforces 798D】Mike and distribution
[题目链接]:http://codeforces.com/contest/798/problem/D [题意] 让你选一个下标集合 p1,p2,p3..pk 使得2*(a[p1]+a[p2]+..+a ...
- laravel5.6 QQ 第三方登录
https://socialiteproviders.github.io/providers/qq.html 1. Installation // This assumes that you have ...
- 洛谷 1372 又是毕业季I
题目背景 “叮铃铃铃”,随着高考最后一科结考铃声的敲响,三年青春时光顿时凝固于此刻.毕业的欣喜怎敌那离别的不舍,憧憬着未来仍毋忘逝去的歌.1000多个日夜的欢笑和泪水,全凝聚在毕业晚会上,相信,这一定 ...
- 20190527-JavaScriptの打怪升级旅行 { 语句 [ 声明 ,变量 ] }
写在前面的乱七八糟:时间总是轻易地溜走,不留一丝念想,近一个月,倒是过得有点丧,从今天开始起,已经开始接触后台了,而JavaScript也只是大致有了个分类框架,那些细枝末节还有的补,任重道远,天将降 ...
- java的System.currentTimeMillis()如何转换成C#的DateTime.Now.Ticks?
考虑到我们是东八时区的话,应做如下转换: long milli = System.currentTimeMillis() + 8*3600*1000; long ticks = (milli*1000 ...
- SuperSocket 扩展你的 Logger
SuperSocket 允许你自定义你的 Logger. 例如,你如果想要把你的业务操作日志保存到一个独立的地方,你仅需要在log4net配置文件中添加一个新的 logger 并为这个 logger ...
- 利用arguments求任意数量数字的和/最大值/最小值
文章地址 https://www.cnblogs.com/sandraryan/ arguments是函数内的临时数据,用完销毁,有类似于数组的操作,但不是数组. 举个栗子1:利用arguments求 ...
- Python--day63--图书管理系统表结构设计
pycharm中运行manage.py的工具: 1,将变更翻译成SQL语句,去数据库中执行(ORM操作过数据库后都要执行这两条命令) 2,ForeignKey会自动在属性后面加_id 3,ORM封装p ...
- H3C OSPF协议工作过程概述
- [Atom 编辑器 ] Packages
Atom包 https://atom.io/packages 常用包整理: atom-chinese-menu 中文插件 atom-ternjs 对 es5,es6的语法支持 ato ...
