CF Round #427 (Div. 2) C. Star sky [dp]
2 seconds
256 megabytes
The Cartesian coordinate system is set in the sky. There you can see n stars, the i-th has coordinates (xi, yi), a maximum brightness c, equal for all stars, and an initial brightness si (0 ≤ si ≤ c).
Over time the stars twinkle. At moment 0 the i-th star has brightness si. Let at moment t some star has brightness x. Then at moment (t + 1) this star will have brightness x + 1, if x + 1 ≤ c, and 0, otherwise.
You want to look at the sky q times. In the i-th time you will look at the moment ti and you will see a rectangle with sides parallel to the coordinate axes, the lower left corner has coordinates (x1i, y1i) and the upper right — (x2i, y2i). For each view, you want to know the total brightness of the stars lying in the viewed rectangle.
A star lies in a rectangle if it lies on its border or lies strictly inside it.
The first line contains three integers n, q, c (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 105, 1 ≤ c ≤ 10) — the number of the stars, the number of the views and the maximum brightness of the stars.
The next n lines contain the stars description. The i-th from these lines contains three integers xi, yi, si(1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 100, 0 ≤ si ≤ c ≤ 10) — the coordinates of i-th star and its initial brightness.
The next q lines contain the views description. The i-th from these lines contains five integers ti, x1i, y1i, x2i, y2i (0 ≤ ti ≤ 109, 1 ≤ x1i < x2i ≤ 100, 1 ≤ y1i < y2i ≤ 100) — the moment of the i-th view and the coordinates of the viewed rectangle.
For each view print the total brightness of the viewed stars.
2 3 3
1 1 1
3 2 0
2 1 1 2 2
0 2 1 4 5
5 1 1 5 5
3
0
3
3 4 5
1 1 2
2 3 0
3 3 1
0 1 1 100 100
1 2 2 4 4
2 2 1 4 7
1 50 50 51 51
3
3
5
0
Let's consider the first example.
At the first view, you can see only the first star. At moment 2 its brightness is 3, so the answer is 3.
At the second view, you can see only the second star. At moment 0 its brightness is 0, so the answer is 0.
At the third view, you can see both stars. At moment 5 brightness of the first is 2, and brightness of the second is 1, so the answer is 3.
我们可以得到状态cnt[t][x][y]表示在t时刻区间[1,x],[1,y]构成的矩形内星星的总亮度。
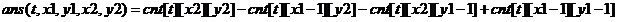
那么状态怎么转移呢?
我们还可以知道,第i颗星星在t时刻的亮度为。
由简单的二维dp就可以写出
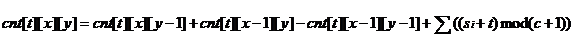
t很大???模c+1就好啦?
这样子就通过这道题啦。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define dbg(x) cout<<#x<<" = "<<x<<endl; int read(){
bool flag=;
int re=;
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='-'&&(ch<''||ch>''));
ch=='-'?flag=:re=ch-'';
while((ch=getchar())>=''&&ch<='') re=re*+ch-'';
return flag?-re:re;
} const int maxn=,maxsize=,maxc=;
const int X=,Y=; int n,m,head[maxsize][maxsize],nxt[maxn],s[maxn];
int dp[maxc][maxsize][maxsize],c; int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&c); c++;
for(int i=,x,y;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&s[i]);
nxt[i]=head[x][y];
head[x][y]=i;
}
for(int i=,pos;i<c;i++)
for(int x=;x<=X;x++)
for(int y=;y<=Y;y++){
pos=;
for(int j=head[x][y];j;j=nxt[j])
pos+=(s[j]+i)%c;
dp[i][x][y]=dp[i][x-][y]+dp[i][x][y-]-dp[i][x-][y-]+pos;
// printf("dp[%d][%d][%d] = %d\n",i,x,y,dp[i][x][y]);
}
for(int i=,t,x1,y1,x2,y2;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&t,&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2); t%=c;
printf("%d\n",dp[t][x2][y2]-dp[t][x1-][y2]-dp[t][x2][y1-]+dp[t][x1-][y1-]);
// printf("%d %d %d %d\n",dp[t][x2][y2],dp[t][x1-1][y2],dp[t][x2][y1-1],dp[t][x1-1][y1-1]);
}
return ;
}
CF Round #427 (Div. 2) C. Star sky [dp]的更多相关文章
- 动态规划:Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2) C Star sky
C. Star sky time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outp ...
- Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2) [ C. Star sky ] [ D. Palindromic characteristics ] [ E. The penguin's game ]
本来准备好好打一场的,然而无奈腹痛只能带星号参加 (我才不是怕被打爆呢!) PROBLEM C - Star sky 题 OvO http://codeforces.com/contest/835/p ...
- CodeForces 835C - Star sky | Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2)
s <= c是最骚的,数组在那一维开了10,第八组样例直接爆了- - /* CodeForces 835C - Star sky [ 前缀和,容斥 ] | Codeforces Round #4 ...
- CF Round #551 (Div. 2) D
CF Round #551 (Div. 2) D 链接 https://codeforces.com/contest/1153/problem/D 思路 不考虑赋值和贪心,考虑排名. 设\(dp_i\ ...
- CF Round #510 (Div. 2)
前言:没想到那么快就打了第二场,题目难度比CF Round #509 (Div. 2)这场要难些,不过我依旧菜,这场更是被\(D\)题卡了,最后\(C\)题都来不及敲了..最后才\(A\)了\(3\) ...
- 竞赛题解 - CF Round #524 Div.2
CF Round #524 Div.2 - 竞赛题解 不容易CF有一场下午的比赛,开心的和一个神犇一起报了名 被虐爆--前两题水过去,第三题卡了好久,第四题毫无头绪QwQ Codeforces 传送门 ...
- CF Round #600 (Div 2) 解题报告(A~E)
CF Round #600 (Div 2) 解题报告(A~E) A:Single Push 采用差分的思想,让\(b-a=c\),然后观察\(c\)序列是不是一个满足要求的序列 #include< ...
- CodeForces 835D - Palindromic characteristics | Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2)
证明在Tutorial的评论版里 /* CodeForces 835D - Palindromic characteristics [ 分析,DP ] | Codeforces Round #427 ...
- cf Round#273 Div.2
题目链接,点击一下 Round#273 Div.2 ================== problem A Initial Bet ================== 很简单,打了两三场的cf第一 ...
随机推荐
- Elastic Search 小调研
一.概况: Elastic Search 是一个基于Apache Lucene™工具包的开源搜索引擎.无论在开源还是专有领域,Lucene 可以被认为是迄今为止最先进.性能最好的.功能最全的搜索引擎库 ...
- usleep - 睡眠若干微秒
总览 (SYNOPSIS) usleep [number] 描述 (DESCRIPTION) usleep 睡眠 指定的 微秒数. 缺省值 是 1. 选项 (OPTIONS) --usage 显示 简 ...
- cpu相关信息查看
查看CPU型号:grep "model name" /proc/cpuinfo | uniqdmidecode -s processor-version | uniq 查看物理CP ...
- Mariadb 10.2.8版本GTID主从环境搭建以及切换
1.首先搭建主从 主环境:192.168.1.117 从环境:192.168.1.123 a.首先以二进制包的形式安装好MariaDB (忽略不计) b.配置环境的变量 通配 [mysqld] bin ...
- BCZM : 1.16
24点游戏 解法一:穷举法 解法二:分治法
- VC++6.0环境中输出特殊字符
该方法最靠谱:https://blog.csdn.net/xiaofeilong321/article/details/8713002 输出特殊字符需使用扩展的ASCII码. 修改控制台显示设置: ( ...
- OpenSceneGraph | OSG如何存储带纹理osgb格式可以节省空间
在使用OSG(OpenSceneGraph)存储带纹理osgb格式的过程中,大家会遇到这样一种情况:存储后的osgb文件所占用的大小远大于原始文件的大小,几倍至几十倍.这是为何呢?原因是OSG默认 ...
- 2018-2019-2-20175323 java实验三敏捷开发与XP实践
代码规范 安装alibaba插件 首先使用code栏里面的reformat code使代码的格式更加规范 再用编码规约扫描,alibaba把问题分为block/critical/major三个等级,出 ...
- hdu多校第八场 1009 (hdu6665) Calabash and Landlord 计算几何/dfs
题意: 给定两个矩形,输出这两个矩形把平面分成了多少块. 题解: 本来是道计算几何的大讨论,被我生生写成了bfs. 离散化边,注意不重合的边中间要空出来一格,四周也要空出来一圈,然后暴力bfs计算一共 ...
- Spring AOP之xml 配置实现
首先这个配置模式估计现在已经不用了,因为我在我们公司的项目里面并没有看到这么配置AOP相关的东西.不过,这个就和学习spring的控制反转(IOC)和依赖注入(DI)一样,刚刚开始的时候,都是从简单的 ...
