python数据结构:pandas(2)数据操作
一、Pandas的数据操作
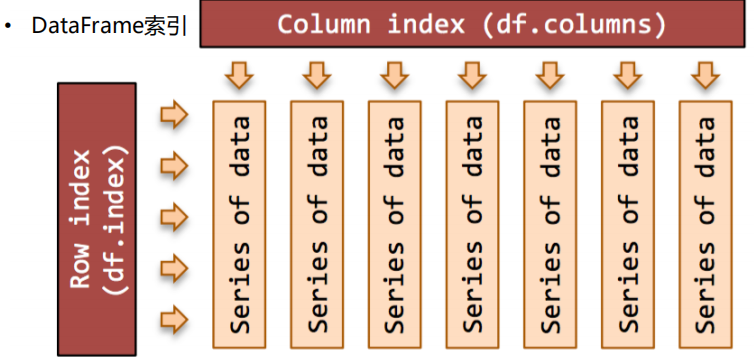
0.DataFrame的数据结构
1.Series索引操作
(0)Series
class Series(base.IndexOpsMixin, generic.NDFrame):
"""
One-dimensional ndarray with axis labels (including time series). #带轴标签的一维ndarray(包括时间序列)。 Labels need not be unique but must be a hashable type. The object #标签不一定是唯一的,但必须是可清洗的类型
supports both integer- and label-based indexing and provides a host of
methods for performing operations involving the index. Statistical
methods from ndarray have been overridden to automatically exclude
missing data (currently represented as NaN). Operations between Series (+, -, /, *, **) align values based on their
associated index values-- they need not be the same length. The result
index will be the sorted union of the two indexes. Parameters
----------
data : array-like, dict, or scalar value
Contains data stored in Series .. versionchanged :: 0.23.
If data is a dict, argument order is maintained for Python 3.6
and later. index : array-like or Index (1d)
Values must be hashable and have the same length as `data`.
Non-unique index values are allowed. Will default to
RangeIndex (, , , ..., n) if not provided. If both a dict and index
sequence are used, the index will override the keys found in the
dict.
dtype : numpy.dtype or None
If None, dtype will be inferred
copy : boolean, default False
Copy input data
"""
(1)Series索引,ser_obj['label'],ser_obj[pos],通过字符串的标签或者索引位置进行索引
import pandas as pd
ser_obj = pd.Series(range(,),index=['a','b','c','d','e']) #将索引设置为['a','b','c','d','e']
print(ser_obj) # 进行行索引
print(ser_obj['a']) #这里索引的是标签本身
print(ser_obj[]) #注意这里索引的是标签的位置
返回值都是5
(2)切片索引
#切片索引
print(ser_obj[:]) #按照索引位置进行切片操作的时候,是不包含最后一个元素的返回第2个索引以及第3个索引 c 7; d 8
print(ser_obj['b':'d']) #按照索引名切片操作的时候,最后一个元素是包含在其中的,返回的是b 6,c 7,d 8
(3)不连续的索引,ser_obj[['label1','label3','label3']] 或者ser_obj[[pos1,pos2,pos3]],注意ser_obj[]中放的的是一个list列表,列表中放的是lab或者position,第一个[]表示需要对列表进行索引
print(ser_obj[[,,]])
a 5
c 7
e 9
dtype: int64
print(ser_obj[['a','e']])
a 5
e 9
dtype: int64
(4)布尔索引
#布尔索引
ser_bool = ser_obj> #判断值是否大于7
print(ser_bool) #打印出判断的结果
a False
b False
c False
d True
e True
dtype: bool
print(ser_obj[ser_bool]) #找出ser_obj>7的情况并打印
d 8
e 9
dtype: int64
print(ser_obj[ser_obj>]) #找出ser_obj大于7的情况
d 8
e 9
dtype: int64
2.DataFrame索引,分为行索引和列索引,DataFrame是优先访问列索引的,如果访问不连续的列索引,那就将索引写进列表中,然后将列表进行索引操作。
class DataFrame(NDFrame):
""" Two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data #两维的大小可变的,可能异构的表格数据标记轴(行和列)的结构
structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). Arithmetic operations #算术运算:在行标签和列标签上对齐。 可以被认为是一个像字典一样,Series对象的容器。 主要的pandas数据结构。
align on both row and column labels. Can be thought of as a dict-like
container for Series objects. The primary pandas data structure.
Parameters
----------
data : numpy ndarray (structured or homogeneous), dict, or DataFrame
Dict can contain Series, arrays, constants, or list-like objects
.. versionchanged :: 0.23.
If data is a dict, argument order is maintained for Python 3.6
and later.
index : Index or array-like
Index to use for resulting frame. Will default to RangeIndex if
no indexing information part of input data and no index provided
columns : Index or array-like
Column labels to use for resulting frame. Will default to
RangeIndex (, , , ..., n) if no column labels are provided
dtype : dtype, default None
Data type to force. Only a single dtype is allowed. If None, infer
copy : boolean, default False
Copy data from inputs. Only affects DataFrame / 2d ndarray input
Examples
--------
Constructing DataFrame from a dictionary.
>>> d = {'col1': [, ], 'col2': [, ]}
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
>>> df
col1 col2
Notice that the inferred dtype is int64.
>>> df.dtypes
col1 int64
col2 int64
dtype: object
To enforce a single dtype:
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data=d, dtype=np.int8)
>>> df.dtypes
col1 int8
col2 int8
dtype: object
Constructing DataFrame from numpy ndarray:
>>> df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(low=, high=, size=(, )),
... columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
>>> df2
a b c d e
See also
--------
DataFrame.from_records : constructor from tuples, also record arrays
DataFrame.from_dict : from dicts of Series, arrays, or dicts
DataFrame.from_items : from sequence of (key, value) pairs
pandas.read_csv, pandas.read_table, pandas.read_clipboard
"""
df_obj =pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(,),columns=['a','b','c','d']) #生成一个5行4列的随机矩阵
print(df_obj)
a b c d
0 0.996924 0.681100 0.866762 0.379989
1 0.351276 0.661369 0.679242 0.099117
2 0.668854 0.023886 0.074815 0.745030
3 0.527927 0.200501 0.439957 0.486921
4 0.011786 0.303719 0.521673 0.821344
(1)列索引:df_obj['label']
#创建DataFrame的数据结构
import numpy as np
df_obj =pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(,),columns=['a','b','c','d']) #生成一个5行4列的随机矩阵
print(df_obj) #列索引
print('列索引')
print(df_obj['a']) #打印出a这一列的数据
print(type(ser_obj['a'])) #这个地方返回的数据类型是Series数据类型
print(ser_obj[[]]) #返回的是a
print(type(ser_obj[[]])) #返回class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
(2)不连续索引df_obj[['label1','label2']]
#不连续的索引
print('不连续索引')
print(df_obj[['a','c']]) #打印出a列和c列的数据
a c
0 0.706947 0.668036
1 0.248566 0.602534
2 0.659694 0.816147
3 0.659362 0.271291
4 0.951508 0.435010
3.Pandas的索引可以归纳为3种
(1):loc,标签索引,使用的是索引的名称,就是标签,标签索引是包含末尾位置的
# 标签索引loc
#Series
print(ser_obj['b':'d']) #使用标签索引是包含最后一个元素的
print(ser_obj.loc['b':'d']) #标签索引是包含最后一个元素的
#上面两个最后输出的都是:
b 6
c 7
d 8
dtype: int6
#DataFrame
print(df_obj['b']) #打印出b这一列所有的值
0 0.007736
1 0.099958
2 0.974213
3 0.289881
4 0.106485
Name: b, dtype: float64
print(df_obj.loc[0:2,'b']) #z注意这里是loc标签索引是包含最后一个元素的,输出的是0,1,2这3个
0 0.007736
1 0.099958
2 0.974213
Name: b, dtype: float64
(2)iloc,位置索引,按照标签的位置进行索引
(3)ix ,标签于位置的混合索引,如果标签和位置是一样的,就先按照标签尝试操作,然后按照位置尝试操作(这个目前的版本中已经过期了)
注意:DataFramen索引的时候,可以将其看做ndarray的操作
标签的切片索引是包含末尾位置的
4.运算与对齐
(0)np.ones()函数
def ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C'):
"""
返回一个给定类型和大小的新的数组,其中填充值为1
Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with ones. Parameters
----------
大小:整数值或者整数序列值
shape : int or sequence of ints
新数组的大小,例如(2,3)或者2
Shape of the new array, e.g., ``(, )`` or ````.
dtype : data-type, optional
数据类型:可选,一个数组期望的数据类型
The desired data-type for the array, e.g., `numpy.int8`. Default is
`numpy.float64`.
order : {'C', 'F'}, optional, default: C
Whether to store multi-dimensional data in row-major
(C-style) or column-major (Fortran-style) order in
memory. Returns
-------
out : ndarray
Array of ones with the given shape, dtype, and order. See Also
--------
ones_like : Return an array of ones with shape and type of input.
empty : Return a new uninitialized array.
zeros : Return a new array setting values to zero.
full : Return a new array of given shape filled with value. Examples
--------
>>> np.ones()
array([ ., ., ., ., .]) >>> np.ones((,), dtype=int)
array([, , , , ]) >>> np.ones((, ))
array([[ .],
[ .]]) >>> s = (,)
>>> np.ones(s)
array([[ ., .],
[ ., .]]) """
a = empty(shape, dtype, order)
multiarray.copyto(a, , casting='unsafe')
return a
(1)按照索引对齐运算,没对齐的位置NaN
Series按照行索引对齐
s1 = pd.Series(range(,),index=range())
s2 = pd.Series(range(,),index=range())
print('s1=\n',s1)
print('s2=\n',s2) #按索引对齐运算,没有对齐的位置补空,如下s1的索引是0-,而s2的索引是0-,
#最后计算的时候将0-4的数据进行相加,剩下的5-9的数据直接补空就可以
print(s1+s2)
DataFrame按照行、列索引对齐
(2)填充未对齐的数据进行运算
使用add,sub,div,mul
同时通过fill_value指定填充值
充未对齐的数据进行运算
# print(s1)
# print(s2) #将s2中未对齐的数据填充为-,然后再进行匀速那
print('s1+s2',s1.add(s2,fill_value=-))
#对未对齐的数据进行运算
print('df1+df2=\n',df1+df2)
#加法运算,未对齐的值填充-1
print(df1.add(df2,fill_value=-1))
# 减法运算,未对齐的值填充2.0
print(df1.sub(df2,fill_value=2))
(3)填充NaN
fillna
#填充NaN
s3 =s1 + s2
print(s3)
#将填充的NaN值填充为-1
s3_filled =s3.fillna(-1)
print(s3_filled)
#加法运算,未对齐的部分填充NaN
df3 =df1+df2
print('df3=\n',df3)
#加法运算,未对齐的部分填充NaN
df3 =df1+df2
print('df3=\n',df3) df3.fillna(100,inplace=True)
print(df3)
5.函数应用
(1)可直接使用Numpy的ufunc函数,如abs等
#numpy的ufunc函数,创建一个5行4列的随机数矩阵
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(,))
print(df)
#
# print('绝对值为:',np.abs(df))
(2)通过apply应用到行或者列上
注意指定轴的方向,默认axis=0,axis=0表示在列的方向上
#使用apply方法应用行或者列数据,这里注意x= 是用在列的方向上,x=1是在行的方向上
f = lambda x:x.max() print('在axis=0即列的方向上:',df.apply(f,axis=))
print('在axis=1即行的方向上:',df.apply(f,axis=)) #指定轴的方向,x=1表示在行的方向上
print(df.apply(lambda x:x.max(),axis=))
(3)通过applymap将函数应用到每个数据上
# 使用applymap应用到每个数据上面
f2 = lambda x:'%2f' %x
print(df.applymap(f2))
6.排序
(1)sort_index,索引排序
对 DataFrame操作的时候注意轴的方向
#索引排序
s4.sort_index(ascending=False) #按照索引降序排列 df4 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(,),
index=np.random.randint(,size=), #行索引,3行
columns=np.random.randint(,size=) #列索引,4个数
)
print(df4) # 对索引进行排序
print(df4.sort_index(axis=))
(2)按值排序
sort_values(by='label')
python数据结构:pandas(2)数据操作的更多相关文章
- Python数据结构之序列及其操作
数据结构是计算机存储,组织数据的方式.数据结构是指相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合. 在Python中,最基本的数据结构为序列(sequence).序列中的每个元素都有编号:从0开始递增 ...
- Python利用pandas处理数据后画图
pandas要处理的数据是一个数据表格.代码: 1 import pandas as pd 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ...
- python之MySQL学习——数据操作
1.增 import pymysql as ps # 打开数据库连接 db = ps.connect(host=', database='test', charset='utf8') # 创建一个游标 ...
- python 利用pandas导入数据
- 用Python的pandas框架操作Excel文件中的数据教程
用Python的pandas框架操作Excel文件中的数据教程 本文的目的,是向您展示如何使用pandas 来执行一些常见的Excel任务.有些例子比较琐碎,但我觉得展示这些简单的东西与那些你可以在其 ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析(12) pandas基础: 数据合并
pandas 提供了三种主要方法可以对数据进行合并: pandas.merge()方法:数据库风格的合并: pandas.concat()方法:轴向连接,即沿着一条轴将多个对象堆叠到一起: 实例方法c ...
- python 抓取金融数据,pandas进行数据分析并可视化系列 (一)
终于盼来了不是前言部分的前言,相当于杂谈,算得上闲扯,我觉得很多东西都是在闲扯中感悟的,比如需求这东西,一个人只有跟自己沟通好了,总结出某些东西了,才能更好的和别人去聊,去说. 今天这篇写的是明白需求 ...
- python 金融网贷数据,pandas进行数据分析并可视化系列 (词频统计,基本操作)
需求: 某某金融大亨想涉足金融网贷,想给网贷平台取一个名字,那么取什么名字,名字里面包含哪些关键字,在行业内的曝光率会相比较高一些呢? 可以理解为: 你负责某某网贷平台的网络推广工作,如何进一步优化各 ...
- Python利用pandas处理Excel数据的应用
Python利用pandas处理Excel数据的应用 最近迷上了高效处理数据的pandas,其实这个是用来做数据分析的,如果你是做大数据分析和测试的,那么这个是非常的有用的!!但是其实我们平时在做 ...
随机推荐
- 网络相关辅助类NetUtils
package yqw.java.util; import java.net.NetworkInterface;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util. ...
- Springboot(八):emoji表情保存到mysql出错的解决办法
emoji表情保存到mysql出错的解决办法 今天,在前端的说明信息中输入emoji表情的时候,插入数据库会报错 百度了一下,是因为mysql数据库的字符编码集不正确,utf8无法存入表情字符,只能将 ...
- hibernate中的@GeneratedValue与@GenericGenerator
1.GeneratedValue与GenericGenerator的区别 @GeneratorValue注解----JPA通用策略生成器 @GenericGenerator注解----自定义主键生成策 ...
- JAVA周二学习总结
第一周我感觉我学到了不少东西,其中有上学期C语言学的不好的原因,因为不想再挂科就有认真的在听. 学到的东西有JAVA的基本书写模式自己懂了,还在课堂上弄会了交换数据的方法,还有运算的算法,另外还有数据 ...
- 后盾网lavarel视频项目---lavarel中间件(使用中间件拦截没登录的用户)
后盾网lavarel视频项目---lavarel中间件(使用中间件拦截没登录的用户) 一.总结 一句话总结: 1.中间件中验证用户是否登录:if(!Auth::guard('admin')->c ...
- ERROR:imshow、Mat、waitkey找不到标识符(opencv)
可以发现imshow.Mat.waitkey这三个都是opencv相关的. 在添加了相关库文件后还是有问题. #include "stdafx.h" #include <st ...
- vim系统剪切板
原文地址 1.vim常用复制粘贴命令 Vim的复制粘贴命令无疑是y (yank),p(paster),加上yy,P PS: vim有个很有意思的约定(我觉得是一种约定),就是某个命令的大小写都是实现某 ...
- Git-Runoob:Git 工作流程
ylbtech-Git-Runoob:Git 工作流程 1.返回顶部 1. Git 工作流程 本章节我们将为大家介绍 Git 的工作流程. 一般工作流程如下: 克隆 Git 资源作为工作目录. 在克隆 ...
- leetcode434 字符串中的单词树(python)
统计字符串中的单词个数,这里的单词指的是连续的不是空格的字符. 请注意,你可以假定字符串里不包括任何不可打印的字符. 示例: 输入: "Hello, my name is John" ...
- Monkey测试:日志信息分析
在跑monkey时,我们需要将日志输出到文件,然后对日志信息进行分析. 一.输出日志到文件 在monkey命令后加>文件地址 如:adb shell monkey 1000>E:/text ...
